Control mechanism of tectonic action on continuous accumulation and coupling of conventional-unconventional oil and gas reservoirs: a case study of Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 为探索川东南平桥地区构造作用对常规和非常规气藏成藏过程的动态控制作用及差异,基于地震、地质和包裹体等资料,根据断层相关褶皱理论,系统剖析了该区构造特征及演化过程、常规气藏和非常规气藏动态成藏过程及构造对两者影响的差异性,建立了典型常规—非常规油气连续聚集耦合成藏模式。平桥地区位于川东南SE-NW前展式递进变形带中,受多套滑脱层和江南—雪峰造山带联合控制,发育断展构造和背冲构造。平桥背斜构造形成于燕山期。中燕山期,受江南—雪峰构造体系前展式扩展影响,研究区发生NE向强烈断褶作用。晚燕山期—喜马拉雅期川中隆起阻挡和青藏高原隆升使平桥背斜不断抬升;寒武系筇竹寺组和奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组烃源岩在早燕山期及以前主要经历了长期的埋藏生烃,中燕山期构造变形扩展至研究区,常规气藏储层(洗象池群)、盖层、油气圈闭及运移均受到影响,气藏保存条件较差。非常规气层被改造成为背斜构造,页岩气向背斜核部聚集,整体保存条件较好。晚燕山期—喜马拉雅期,地层隆升泄压,两类气藏保存条件继续变差。因此,构造作用对常规气藏和非常规气藏成藏控制差异体现在控制方式和改造时间上:中燕山期侧向供烃是常规气藏成藏的关键;晚白垩世构造活动改造和晚燕山期—喜马拉雅期构造抬升影响了页岩气的保存。Abstract: This study explored the dynamic control and differences of tectonic action on the formation of conventional and unconventional gas reservoirs in Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin. Based on seismic, geolo-gical, inclusion, and other relevant data, together with fault-related fold theory, this study systematically analyzed thestructural characteristics and evolution processes of the area, as well as the dynamic accumulation processes of conventional and unconventional gas reservoirs and the differences in structural impacts on both. A coupled accumulation model of typical conventional and unconventional oil and gas continuous aggregation was established. The Pingqiao area, located in the SE-NW foreland progressive deformation zone of southeastern Sichuan, is controlled by multiple detachment layers and the Jiangnan-Xuefeng orogenic belt, developing fault extension structures and back-thrust structures. The Pingqiao anticline structure was formed during the Yanshanian period. During the middle Yanshanian period, influenced by the foreland expansion of the Jiangnan-Xuefeng tectonic system, the study area experienced intense NE-directed fault-folding. From the late Yanshanian to the Himalayan period, the uplift of central Sichuan and the rise of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau caused the Pingqiao anticline to continuously uplift. The Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation and Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Silurian Longmaxi Formation source rocks mainly experienced long-term burial and hydrocarbon generation in the early Yanshanian period and before. In the middle Yanshanian period, tectonic deformation extended to the study area, affecting the conventional gas reservoir (Xixiangchi Group), cap rocks, hydrocarbon traps, and migration, resulting in poor preservation conditions of gas reservoirs. Unconventional gas layers were transformed into anticline structures, with shale gas accumulating towards the core of the anticline, resulting in better overall preservation conditions. From the late Yanshanian to the Himalayan period, strata uplift and depressurization continued to deteriorate the preservation conditions of both types of gas reservoirs. Therefore, this study suggests that the difference in tectonic control on conventional and unconventional gas reservoirs is reflected in the control methods and transformation timing: the lateral hydrocarbon supply during the middle Yanshanian period is the key for conventional gas reservoir formation; tectonic activity in the Late Cretaceous and tectonic uplift from the late Yanshanian to the Himalayan period affect the preservation of shale gas.
-
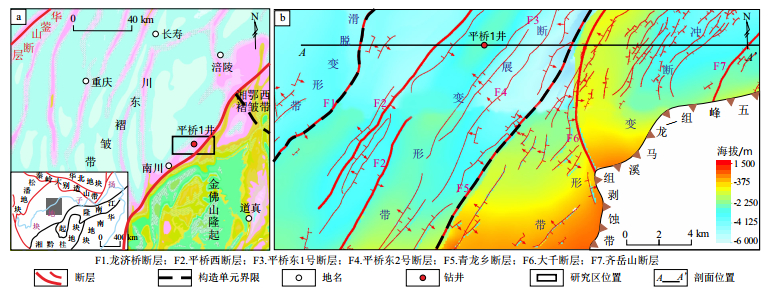
图 1 川东南平桥地区区域地质概况(a)和五峰组底界构造(b)
a图据参考文献[13]修改。
Figure 1. Regional geological overview of Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin (a) and bottom boundary structure of Wufeng Formation (b)
图 2 川东南平桥地区综合柱状图
据参考文献[18]修改。
Figure 2. Comprehensive bar chart of Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
图 3 川东南南川地区E-W向地质剖面
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 3. E-W geological profile of Nanchuan area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
图 4 川东南平桥地区构造演化
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 4. Structural evolution of Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
图 6 川东南平桥1井筇竹寺组和五峰组—龙马溪组埋藏、生烃及热史曲线
据参考文献[27]修改。
Figure 6. Burial, hydrocarbon generation, and thermal history curves of Qiongzhusi Formation and Wufeng - Longmaxi formations of well Pingqiao 1 in southeastern Sichuan Basin
表 1 川东南平桥地区龙马溪组与洗象池群样品气体组分
Table 1. Gas composition of samples from Longmaxi and Xixiangchi formations of Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
序号 层位 气体组分/% 甲烷 乙烷 丙烷 二氧化碳 硫化氢 氮气 氢气 氦气 1 龙马溪组 99.04 0.46 0.01 0.3 0 0.11 0.03 0.05 2 龙马溪组 98.58 0.45 0.01 0.33 0 0.56 0.02 0.05 3 洗象池群 95.65 0.33 0.01 2.48 0.48 0.89 0.11 0.05 4 洗象池群 95.46 0.33 0.01 1.86 0.49 1.77 0.03 0.05 -
[1] 冯冲, 郭彤楼, 邹华耀, 等. 川东北地区飞仙关组—长兴组天然气富集机制[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(4): 907-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201304019.htmFENG Chong, GUO Tonglou, ZOU Huayao, et al. Enriched mechanism of natural gas in the Feixianguan-Changxing formations in the northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(4): 907-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201304019.htm [2] 郭旭升. 南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律: 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htmGUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichment for marine shale gas in southern China: understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htm [3] 张海涛, 张颖, 何希鹏, 等. 渝东南武隆地区构造作用对页岩气形成与保存的影响[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(5): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201805006.htmZHANG Haitao, ZHANG Ying. HE Xipeng, et al. The effect of tectonism on shale gas formation and preservation in Wulong area, southeastern Chongqing[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(5): 47-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201805006.htm [4] 凡元芳. 鄂西渝东区关键构造期构造作用与海相油气成藏作用响应关系研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2016.FAN Yuanfang. Interrelationship between tectonism and hydrocarbon accumulation in marine strata at critical tectonic moment in west Hubei-east Chongqing, South China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2016. [5] 付晓飞, 吕丁友, 黄江波, 等. 断裂—盖层耦合封闭机理及断层圈闭油气聚集模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(3): 21-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202203003.htmFU Xiaofei, LYU Dingyou, HUANG Jiangbo, et al. Fault-caprock coupling sealing mechanism and fault trap hydrocarbon accumulation model[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(3): 21-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202203003.htm [6] 刘冉, 霍飞, 王鑫, 等. 普光气田下三叠统飞仙关组碳酸盐岩储层特征及主控因素分析[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(6): 34-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201706005.htmLIU Ran, HUO Fei, WANG Xin, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation carbonate reservoir in Puguang Gas Field[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(6): 34-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201706005.htm [7] 赵正望. 川东南地区构造特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2005.ZHAO Zhengwang. The regional tectonic characteristic of southeast Sichuan Basin and its control to oil and gas reservoir[D]. Bejing: China University of Geosciences, 2005. [8] 汪凯明. 川东南盆缘复杂构造区深层页岩气富集特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(2): 334-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202302012.htmWANG Kaiming. Enrichment characteristics of deep shale gas in tectonically complex regions of the southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(2): 334-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202302012.htm [9] 何希鹏, 齐艳平, 何贵松, 等. 渝东南构造复杂区常压页岩气富集高产主控因素再认识[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(5): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905004.htmHE Xipeng, QI Yanping, HE Guisong, et al. Further understanding of main controlling factors of normal pressure shale gas enrichment and high yield in the area with complex structure of the southeast area of Chongqing[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(5): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905004.htm [10] 郭旭升, 腾格尔, 魏祥峰, 等. 四川盆地深层海相页岩气赋存机理与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202204001.htmGUO Xusheng, TENGER B, WEI Xiangfeng, et al. Occurrence mechanism and exploration potential of deep marine shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202204001.htm [11] 郭彤楼, 刘若冰. 复杂构造区高演化程度海相页岩气勘探突破的启示: 以四川盆地东部盆缘JY1井为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4): 643-651. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304000.htmGUO Tonglou, LIU Ruobing. Implications from marine shale gas exploration breakthrough in complicated structural area at high thermal stage: taking Longmaxi Formation in well JY1 as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 643-651. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304000.htm [12] 邹玉涛, 段金宝, 赵艳军, 等. 川东高陡断褶带构造特征及其演化[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(11): 2046-2052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201511016.htmZOU Yutao, DUAN Jinbao, ZHAO Yanjun, et al. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of the high and steep fault folding belt in east Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(11): 2046-2052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201511016.htm [13] 汤济广, 汪凯明, 秦德超, 等. 川东南南川地区构造变形与页岩气富集[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 11-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105003.htmTANG Jiguang, WANG Kaiming, QIN Dechao, et al. Tectonic deformation and its constraints to shale gas accumulation in Nanchuan area, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 11-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202105003.htm [14] 陈曼霏, 何生, 易积正, 等. 涪陵页岩气田平桥区块页岩气储层有机质孔发育特征[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(4): 423-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201904004.htmCHEN Manfei, HE Sheng, YI Jizheng, et al. Development characteristics of organic pore in shale gas reservoir of Wufeng Formation member 1 of Longmaxi Formation in Pingqiao block, Fuling shale gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(4): 423-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201904004.htm [15] 郭旭升. 四川盆地涪陵平桥页岩气田五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901001.htmGUO Xusheng. Controlling factors on shale gas accumulations of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Pingqiao Shale Gas Field in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201901001.htm [16] SUN Ziming. Superimposed hydrocarbon accumulation through multi-source and multi-stage evolution in the Cambrian Xixiangchi Group of eastern Sichuan Basin: a case study of the Pingqiao gas-bearing anticline[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2023, 4(1): 131-142. doi: 10.1016/j.engeos.2022.09.001 [17] 魏国齐, 王志宏, 李剑, 等. 四川盆地震旦系、寒武系烃源岩特征、资源潜力与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701001.htmWEI Guoqi, WANG Zhihong, LI Jian, et al. Characteristics of source rocks, resource potential and exploration direction of Sinian and Cambrian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701001.htm [18] 孙自明, 孙炜, 林娟华, 等. 四川盆地东部中上寒武统洗象池群油气成藏条件与主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(6): 933-940. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106933SUN Ziming, SUN Wei, LIN Juanhua, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and main controlling factors of the Middle-Upper Cambrian Xixiangchi group in the eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(6): 933-940. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106933 [19] 庹秀松, 陈孔全, 罗顺社, 等. 四川盆地东南缘齐岳山断裂构造特征与页岩气保存条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 1017-1027.TUO Xiusong, CHEN Kongquan, LUO Shunshe, et al. Structural characteristics of Qiyueshan fault and shale gas preservation at the southeastern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1017-1027. [20] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等. 湘鄂西—川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形: 来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2010, 35(2): 161-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201002000.htmMEI Lianfu, LU Zhaoqian, TANG Jiguang, et al. Mesozoic intra-continental progressive deformation in western Hunan-Hubei-eastern Sichuan Provinces of China: evidence from apatite fission track and balanced cross-section[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2010, 35(2): 161-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201002000.htm [21] 覃作鹏, 刘树根, 邓宾, 等. 川东南构造带中新生代多期构造特征及演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(6): 703-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201306010.htmQIN Zuopeng, LIU Shugen, DENG Bin, et al. Multiphase structural features and evolution of southeast Sichuan tectonic belt in China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(6): 703-711. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201306010.htm [22] 张旭亮. 鄂西—渝东地区构造演化及成因机制[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.ZHANG Xuliang. Tectonic evolution and genetic mechanism of western Hubei and eastern Chongqing area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019. [23] 孙自明, 刘光祥, 卞昌蓉, 等. 四川盆地东部寒武系油气跨层成藏及天然气勘探意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 504-516. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303504SUN Ziming, LIU Guangxiang, BIAN Changrong, et al. Cross-formational hydrocarbon accumulation of Cambrian sequences and its significance for natural gas exploration in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 504-516. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303504 [24] 郭卫星, 熊亮, 魏力民. 川东南构造变形特征及其对页岩气保存的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2016, 44(6): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201606004.htmGUO Weixing, XIONG Liang, WEI Limin. Structure deformation of southeast Sichuan and its influences on preservation of shale gas[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2016, 44(6): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201606004.htm [25] 姜磊. 强改造作用下川南下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019.JIANG Lei. Research on the preservation conditions of Lower Paleozoic shale gas in southern Sichuan under strong transformation[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019. [26] 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 包书景, 等. 我国南方海相页岩气富集高产主控因素及前景预测[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707002.htmZHAI Gangyi, WANG Yufang, BAO Shujing, et al. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity of marine shale gas and prospect forecast in southern China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707002.htm [27] 高键, 李慧莉, 何治亮, 等. 川东南平桥地区寒武系洗象池群多元复合成藏过程及其勘探启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 263-276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306019.htmGAO Jian, LI Huili, HE Zhiliang, et al. Multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation in Cambrian Xixiangchi Group, Pingqiao area, southeastern Sichuan and its implications for hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 263-276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306019.htm [28] 李英强, 高键, 李双建, 等. 四川盆地中—上寒武统洗象池群油气成藏模式与勘探前景[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(3): 29-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202203004.htmLI Yingqiang, GAO Jian, LI Shuangjian, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation model and exploration prospect of the Xixiangchi Group of Middle-Upper Cambrian in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(3): 29-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202203004.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号