Geochemical evidence of paleo-depositional environment of Triassic Adula Formation source rocks of eastern Qiangtang Basin
-
摘要: 上三叠统阿堵拉组泥岩是羌塘盆地重要烃源岩系之一,目前对其古沉积环境的认识存在较大争议。通过对羌塘盆地东部雀莫错地区鄂尔托陇巴剖面阿堵拉组开展岩石学、有机地球化学和元素地球化学分析等系统研究,探讨阿堵拉组烃源岩古沉积环境及其对烃源岩发育的影响。阿堵拉组泥岩总有机碳(TOC)含量为0.27%~3.46%,平均为1.60%,总体为好烃源岩,局部发育优质烃源岩;阿堵拉组下段陆棚相泥岩形成于海平面上升时期,水体较深且贫氧,古气候为半干燥—半湿润气候,化学风化程度中等,陆源输入较低,水体盐度较高;上段泥岩沉积期处于盆地萎缩消亡阶段,沉积环境逐渐由陆棚相转变为三角洲相,水体较浅且富氧,经历了干燥—半干燥—半湿润的古气候变化,陆源输入相应增多,为咸水—半咸水环境,受到淡水输入的影响。阿堵拉组的源岩为长英质火山岩,源区构造背景以大陆岛弧为主,可能来自早—中三叠世金沙江缝合带岛弧源区。阿堵拉组下段陆棚相泥岩TOC含量与氧化还原条件指标具有较好的正相关性,表明烃源岩发育主要受到海平面上升时贫氧水体控制;上段陆棚—三角洲相泥岩TOC含量与古环境参数无明显相关性,TOC含量大于2%的泥岩沉积期具有较高陆源输入和相对湿润的古气候,综合分析认为烃源岩发育受到古气候、陆源输入等多种因素综合影响。Abstract: The mudstone within the Upper Triassic Adula Formation constitutes a crucial hydrocarbon source rock reservoir in the Qiangtang Basin, yet there is considerable debate regarding its paleo-depositional environment. Through systematic studies, including petrology, organic geochemistry, and elemental geochemistry analyses of the Adula Formation at the Eertuolongba section in the Quemocuo area of the eastern Qiangtang Basin, this study investigated the paleo-depositional environment of the Adula Formation source rocks and its impact on hydrocarbonsource rock development. The total organic carbon (TOC) content of the Adula Formation mudstone ranges from 0.27% to 3.46%, with an average of 1.60%, indicating overall favorable source rocks with locally deve-loped high-quality source rocks. The shelf facies mudstone in the lower section of the Adula Formation was formed during a phase of sea-level rise, characterized by deeper, oxygen-poor water, a semi-arid to semi-humid paleoclimate, moderate chemical weathering, minimal terrigenous input, and higher salinity. The deposition of the upper section occurred during a phase of basin contraction and demise, suggesting a transition from shelf facies to delta facies. This period was marked by relatively shallower, oxygen-rich water and a shift from arid to semi-arid to semi-humid paleoclimate, with increased terrigenous input and a saline to semi-saline water environment influenced by freshwater input. The source rocks of the Adula Formation are felsic volcanic rocks, primarily from a continental island arc tectonic setting, likely sourced from the island arc source domain in the Jinsha River suture zone during the Early to Middle Triassic. In the lower section of the Adula Formation, the TOC content of shelf facies mudstone shows a robust positive correlation with redox condition indicators, suggesting that source rock development was mainly controlled by oxygen-poor water conditions during sea-level rise period. In contrast, no significant correlation was observed between TOC content and paleo-environmental parameters in the upper shelf delta facies mudstones. Mudstones with TOC content greater than 2% were likely deposited during periods of high terrigenous input and relatively humid paleoclimate, indicating that source rock development was influenced by multiple factors such as paleoclimate and terrigenous input.
-
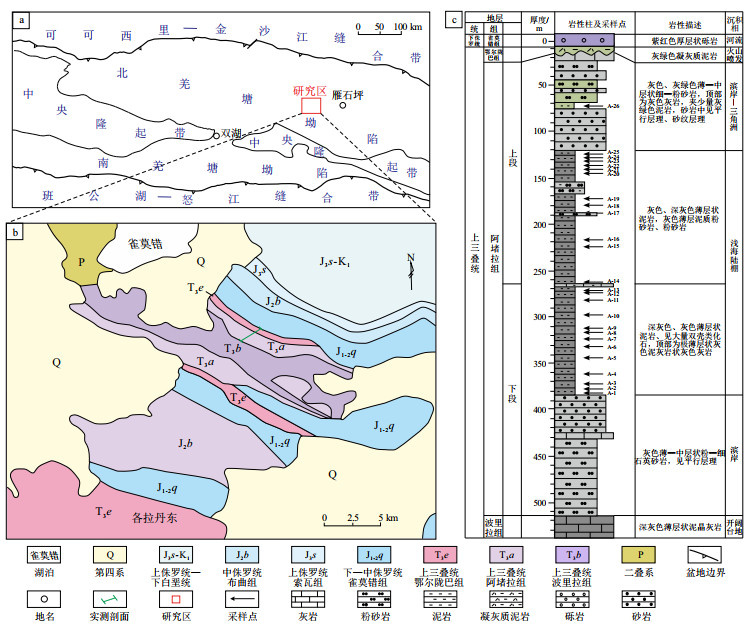
图 1 羌塘盆地构造单元(a),研究区地表地层分布(b)及鄂尔托陇巴剖面地层柱状图(c)
图b修改自参考文献[23]。
Figure 1. Tectonic units of Qiangtang Basin (a), surface stratigraphic distribution in study area (b) and lithology column of Eertuolongba section (c)
图 2 羌塘盆地东部鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组岩性特征
a.波里拉组深灰色泥晶灰岩;b.阿堵拉组深灰色薄片状泥岩;c.阿堵拉组灰色薄板状粉砂岩;d.样品A-26,含灰粉砂质泥岩,128.04 m;e.样品A-25,含灰粉砂质泥岩,130.55 m;f.样品A-15,含灰残余生屑泥岩,263.31 m;g.样品A-9,泥岩,312.66 m;h.样品A-6, 泥岩,331.61 m; i.样品A-1,残余生屑泥岩,383.25 m。
Figure 2. Lithologic characteristics of Triassic Adula Formation in Eertuolongba section of eastern Qiangtang Basin
图 3 羌塘盆地东部鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组泥岩PAAS标准化稀土元素配分模式
PAAS标准值参考MCLENNAN[36]。
Figure 3. Post Australia Archean Shale-normalized REE distribution patterns of mudstone in Triassic Adula Formation of Eertuolongba section in eastern Qiangtang Basin
图 5 羌塘盆地东部鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组泥岩MoEF-UEF交会图
底图据参考文献[42]。
Figure 5. Crossplot of MoEF vs. UEF of Triassic Adula Formation mudstone in Eertuolongba section of eastern Qiangtang Basin
图 7 羌塘盆地东部鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组泥岩Ti/Zr-La/Sc(a)和Th-Co-Sc(b)图解
底图据参考文献[44]。
Figure 7. Diagrams of Ti/Zr vs. La/Sc (a) and Th-Co-Sc (b) for mudstone in Triassic Adula Formation in Eertuolongba section of eastern Qiangtang Basin
表 1 北羌塘坳陷东部鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组泥岩主量和微量元素含量
Table 1. Contents of major and trace elements in mudstones of Triassic Adula Formation of Eertuolongba section in eastern area of North Qiangtang Depression
样号 ω(TOC)/% ω(TS)/% 主量元素含量/% 微量元素含量/(μg/g) Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO MnO Na2O TiO2 Ba Co Cr Cu Ni Sr V Mo Zr Th U Ga Rb Sc A-28 1.13 0.11 15.73 0.49 4.30 3.61 1.15 0.03 1.01 0.72 648.70 7.82 66.98 31.62 20.55 104.52 93.84 1.40 242.98 22.21 3.40 26.03 172.81 10.89 A-27 1.79 0.14 17.10 5.07 5.17 3.40 1.46 0.07 0.91 0.59 245.72 10.00 58.67 33.80 27.22 143.95 97.43 2.77 189.65 24.44 3.56 21.83 174.46 13.34 A-26 2.21 0.17 16.64 6.61 5.47 3.23 1.56 0.08 0.90 0.55 989.91 10.58 56.26 44.85 36.42 208.01 138.15 7.25 179.58 24.73 4.17 28.60 182.07 13.52 A-25 1.84 0.18 16.67 4.45 4.69 3.17 1.40 0.05 1.16 0.58 260.68 12.21 63.38 41.29 33.74 137.46 93.24 3.15 204.46 24.90 3.95 21.25 165.76 13.65 A-24 3.23 0.15 16.41 6.44 4.31 3.30 1.41 0.05 0.82 0.50 273.98 5.70 57.73 57.69 21.58 177.92 83.77 2.59 169.94 24.35 3.57 21.52 178.49 13.06 A-23 2.60 0.17 17.76 3.63 4.11 3.66 1.29 0.04 0.79 0.53 379.01 10.37 53.48 50.54 28.18 160.12 91.32 3.40 187.66 25.30 4.34 24.93 171.60 13.01 A-22 2.45 0.17 16.40 6.14 5.01 3.23 1.38 0.05 0.96 0.50 251.22 8.38 48.63 44.53 24.87 188.75 70.17 2.55 168.84 26.71 3.72 21.07 170.59 13.37 A-21 2.24 0.17 10.09 26.33 3.03 2.02 0.91 0.12 0.54 0.31 264.50 5.92 32.34 42.30 21.13 322.75 51.99 1.48 100.70 14.06 2.35 14.01 114.75 9.18 A-20 1.93 0.13 16.21 8.57 4.15 3.12 1.30 0.06 1.03 0.45 246.95 8.84 66.79 39.31 21.43 223.23 85.37 1.08 153.59 26.58 3.31 20.82 179.73 13.76 A-19 2.34 0.32 14.79 12.14 4.05 2.74 1.40 0.05 0.89 0.38 268.78 5.56 61.37 38.28 20.35 341.48 74.83 2.02 126.07 22.72 3.18 19.05 161.75 12.63 A-18 0.96 0.14 8.90 21.74 3.20 1.68 0.96 0.09 1.06 0.30 827.77 5.30 29.24 24.09 15.04 325.88 40.19 0.80 114.90 16.08 2.57 19.71 98.75 9.29 A-17 1.18 0.14 11.94 18.47 3.65 2.14 1.13 0.10 0.74 0.34 234.24 4.68 35.20 33.38 17.64 302.68 47.50 1.08 118.69 18.74 2.81 16.43 126.75 10.81 A-16 1.65 0.19 16.02 11.90 4.80 3.12 1.37 0.09 0.58 0.44 271.70 8.59 63.33 43.17 32.01 285.83 118.20 6.27 135.23 22.03 3.61 21.09 191.91 14.58 A-15 1.13 0.16 14.95 15.43 4.29 2.86 1.44 0.10 0.64 0.39 632.74 13.42 35.54 37.96 26.21 401.63 61.01 2.03 132.22 18.67 3.28 23.44 173.61 13.63 A-14 0.36 0.19 19.58 3.55 6.37 3.57 1.94 0.03 0.53 0.57 257.91 20.38 56.32 28.83 34.01 174.32 103.55 0.50 177.83 22.62 3.42 26.34 174.69 16.26 A-13 1.19 0.23 12.20 20.62 4.02 2.14 1.36 0.10 0.64 0.33 771.08 5.28 34.19 33.01 19.58 452.89 50.64 1.43 110.09 16.69 3.15 22.15 131.93 11.54 A-12 1.05 0.13 9.56 24.22 3.70 1.89 1.23 0.10 0.63 0.30 1062.15 6.74 29.49 26.22 20.70 463.65 46.07 1.56 100.84 14.58 2.90 23.07 116.13 10.28 A-11 0.84 0.25 18.68 4.19 6.24 3.46 1.63 0.12 0.66 0.62 475.50 16.66 73.16 32.81 38.10 182.75 129.24 2.20 179.99 22.86 3.74 26.16 187.39 16.07 A-10 1.73 0.21 17.24 6.96 5.54 3.29 1.53 0.10 0.70 0.48 785.69 12.83 78.17 44.66 46.42 255.22 180.20 5.73 149.57 22.97 4.35 28.32 194.66 13.86 A-09 1.08 0.11 19.71 3.04 5.72 3.93 1.64 0.08 0.57 0.57 234.20 19.36 64.47 34.91 40.43 154.85 138.38 3.70 174.76 25.16 3.99 25.81 197.09 15.73 A-08 1.64 0.19 17.10 9.46 5.83 3.37 1.63 0.15 0.56 0.48 509.65 15.08 64.58 41.39 50.02 315.36 176.75 10.30 145.27 22.85 4.54 24.35 210.27 13.93 A-07 1.56 0.11 13.87 18.63 5.41 2.68 1.43 0.25 0.36 0.35 598.01 8.49 58.85 38.54 35.48 985.29 179.12 9.15 111.92 18.05 4.60 21.81 170.21 11.88 A-06 0.96 0.11 18.05 9.55 5.84 3.61 1.71 0.14 0.43 0.48 183.99 16.99 59.48 36.49 40.15 287.95 136.19 4.17 147.76 23.46 4.29 22.90 227.05 15.71 A-06 1.41 0.19 15.46 14.08 6.04 2.94 1.63 0.19 0.42 0.42 575.02 10.46 56.16 46.82 37.85 452.39 149.34 7.14 124.41 20.03 4.22 23.67 178.71 12.69 A-04 1.45 0.09 18.84 6.49 7.31 3.81 1.73 0.41 0.43 0.48 448.81 35.42 56.12 65.63 94.07 248.68 150.11 8.08 160.44 24.67 4.24 26.67 213.20 16.72 A-03 1.62 0.12 14.60 16.59 5.29 2.91 1.44 0.14 0.45 0.37 711.24 7.56 50.60 39.52 30.45 653.30 146.26 4.49 119.74 20.48 4.12 23.75 172.69 11.80 A-02 1.78 0.17 16.16 13.78 5.70 3.39 1.61 0.16 0.37 0.39 2530.29 13.14 59.69 50.12 50.05 446.09 191.78 6.00 124.61 20.89 5.24 44.66 214.16 14.33 A-01 1.17 0.19 13.38 19.01 5.22 2.71 1.56 0.20 0.39 0.36 1302.36 10.67 38.57 37.12 28.55 578.31 67.20 2.47 107.34 17.00 3.79 28.13 158.81 11.23 表 2 北羌塘坳陷东部地区鄂尔托陇巴剖面三叠系阿堵拉组泥岩稀土元素含量
Table 2. Contents of rare earth elements in mudstones of Triassic Adula Formation of Eertuolongba section in eastern area of North Qiangtang Depression
样号 稀土元素含量/(μg/g) ∑REE/(μg/g) LREE/HREE PAAS标准化 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu δCe δEu (La/Yb)N A-28 36.25 71.44 8.32 29.42 5.25 1.09 5.62 0.82 4.90 1.00 3.25 0.48 3.29 0.50 171.63 7.64 0.95 0.94 0.81 A-27 36.34 72.69 8.45 31.38 6.20 1.11 6.40 0.94 5.27 1.06 3.24 0.47 3.21 0.48 177.24 7.41 0.96 0.83 0.83 A-26 35.85 73.23 8.56 32.46 6.59 1.38 6.83 1.01 5.71 1.13 3.39 0.48 3.27 0.50 180.39 7.08 0.96 0.97 0.81 A-25 37.24 76.86 8.94 33.34 6.74 1.16 6.93 1.02 5.86 1.16 3.56 0.51 3.43 0.52 187.29 7.14 0.97 0.80 0.80 A-24 32.09 64.21 7.72 28.65 5.76 1.04 6.13 0.92 5.29 1.05 3.23 0.46 3.06 0.46 160.07 6.77 0.94 0.83 0.77 A-23 36.08 72.95 8.35 30.48 5.82 1.04 6.22 0.92 5.44 1.09 3.41 0.51 3.44 0.52 176.27 7.17 0.97 0.81 0.77 A-22 34.08 69.81 8.52 32.35 6.93 1.20 7.15 1.07 6.01 1.15 3.44 0.48 3.32 0.49 176.00 6.62 0.95 0.81 0.76 A-21 30.24 60.75 6.98 26.60 5.65 1.27 6.03 0.85 4.69 0.91 2.63 0.37 2.42 0.35 149.76 7.20 0.96 1.02 0.92 A-20 34.73 71.67 8.24 30.79 6.02 1.07 6.33 0.92 5.17 1.02 3.12 0.44 2.99 0.44 172.96 7.46 0.98 0.82 0.86 A-19 28.47 57.47 7.09 27.11 5.60 0.94 5.86 0.88 4.98 0.98 2.98 0.42 2.87 0.42 146.07 6.53 0.93 0.77 0.73 A-18 29.47 59.19 6.95 26.88 5.57 1.13 5.67 0.83 4.53 0.90 2.68 0.37 2.45 0.37 146.98 7.26 0.95 0.94 0.89 A-17 29.06 56.66 7.08 27.45 5.77 1.05 6.16 0.91 5.07 0.97 2.87 0.38 2.59 0.39 146.42 6.57 0.91 0.83 0.83 A-16 30.25 61.39 7.55 28.32 6.09 1.09 6.54 0.97 5.46 1.07 3.17 0.45 3.04 0.46 155.84 6.37 0.94 0.81 0.73 A-15 29.82 57.41 6.78 25.10 5.33 1.06 5.84 0.87 5.09 1.03 3.18 0.46 3.07 0.45 145.48 6.28 0.93 0.89 0.72 A-14 38.83 79.37 9.12 33.40 6.04 1.08 6.28 0.91 5.20 1.06 3.25 0.47 3.19 0.48 188.69 8.05 0.97 0.83 0.90 A-13 28.10 52.67 6.48 24.91 5.20 1.14 5.80 0.86 4.84 0.95 2.83 0.39 2.63 0.38 137.19 6.34 0.90 0.98 0.79 A-12 26.94 50.49 6.28 24.09 5.14 1.18 5.64 0.82 4.60 0.90 2.66 0.37 2.43 0.34 131.87 6.42 0.90 1.03 0.82 A-11 38.71 79.63 9.01 33.47 6.37 1.28 6.89 0.99 5.59 1.11 3.35 0.48 3.26 0.50 190.64 7.60 0.98 0.91 0.88 A-10 30.60 61.21 7.16 26.29 5.30 1.12 5.73 0.84 4.80 0.97 2.95 0.43 2.95 0.43 150.78 6.90 0.95 0.96 0.77 A-09 30.03 62.33 6.78 24.49 4.98 0.92 5.39 0.83 4.89 0.98 3.11 0.46 3.16 0.47 148.81 6.71 1.01 0.83 0.70 A-08 31.75 64.84 7.52 27.86 5.72 1.14 6.18 0.88 5.01 0.99 3.00 0.43 2.88 0.44 158.64 7.01 0.97 0.91 0.81 A-07 27.47 55.78 6.99 27.81 6.33 1.68 6.71 0.93 4.91 0.95 2.82 0.39 2.62 0.38 145.78 6.39 0.93 1.21 0.78 A-06 33.82 71.17 8.12 30.32 6.26 1.13 6.48 0.94 5.26 1.03 3.16 0.45 3.03 0.45 171.64 7.25 0.99 0.83 0.82 A-06 31.49 63.88 7.46 27.99 5.96 1.19 6.31 0.93 5.24 1.05 3.11 0.44 2.95 0.42 158.41 6.75 0.96 0.92 0.79 A-04 36.35 89.66 8.83 33.20 7.06 1.30 7.62 1.12 6.31 1.23 3.79 0.53 3.63 0.55 201.18 7.12 1.15 0.84 0.74 A-03 28.42 56.80 6.65 24.40 4.95 1.07 5.38 0.79 4.52 0.89 2.72 0.38 2.64 0.39 140.00 6.91 0.95 0.98 0.80 A-02 27.54 57.85 6.81 25.36 5.53 1.53 5.78 0.84 4.73 0.92 2.78 0.39 2.69 0.40 143.18 6.72 0.97 1.27 0.76 A-01 27.52 57.37 6.87 25.81 5.57 1.32 5.81 0.83 4.58 0.89 2.61 0.37 2.42 0.36 142.34 6.96 0.96 1.09 0.84 注: PAAS标准值据MCLENNAN[36], ∑REE=La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu+Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu, LREE/HREE= (La+Ce+Pr+Nd+Sm+Eu)/(Gd+Tb+Dy+Ho+Er+Tm+Yb+Lu), δCe=CeN/(LaN×PrN)1/2, δEu = EuN/(SmN×GdN)1/2, 下标N表示计算使用PAAS标准化。 -
[1] 王成善, 伊海生, 李勇, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地地质演化与油气远景评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.WANG Chengshan, YI Haisheng, LI Yong, et al. The geological evolution and prospective oil and gas assessment of the Qiangtang Basin in northern Tibetan Plateau[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2001. [2] 王剑, 付修根. 论羌塘盆地沉积演化[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(2): 237-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201802004.htmWANG Jian, FU Xiugen. Sedimentary evolution of the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(2): 237-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201802004.htm [3] 谭富文, 王剑, 王小龙, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地: 中国油气资源战略选区的首选目标[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2002, 22(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2002.01.003TAN Fuwen, WANG Jian, WANG Xiaolong, et al. The Qiangtang Basin in Xizang as the target area for the oil and gas resources in China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2002, 22(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2002.01.003 [4] 王剑, 付修根, 沈利军, 等. 论羌塘盆地油气勘探前景[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htmWANG Jian, FU Xiugen, SHEN Lijun, et al. Prospect of the potential of oil and gas resources in Qiangtang Basin, Xizang (Tibet)[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htm [5] 丁文龙, 李超, 苏爱国, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地中生界海相烃源岩综合地球化学剖面研究及有利生烃区预测[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3): 878-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103025.htmDING Wenlong, LI Chao, SU Aiguo, et al. Study on the comprehensive geochemical cross section of Mesozoic marine source rocks and prediction of favorable hydrocarbon generation area in Qiangtang Basin, Tibeta[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(3): 878-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103025.htm [6] 李高杰, 夏国清, 伊海生, 等. 西藏南羌塘坳陷泥质烃源岩评价及有利生烃区预测[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1241-1260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005016.htmLI Gaojie, XIA Guoqing, YI Haisheng, et al. Characteristics of the Mesozoic marine argillaceous source rocks and prediction of favorable hydrocarbon generation area in South Qiangtang Depression, Xizang (Tibet)[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1241-1260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005016.htm [7] 刘中戎, 杨平, 张国常, 等. 北羌塘坳陷上三叠统沉积模式及对油气勘探的启示[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2022, 42(03): 465-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202203011.htmLIU Zhongrong, YANG Ping, ZHANG Guochang, et al. Sedimentary model and its implications for oil and gas exploration of Upper Triassic in Northern Qiangtang Depression[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2022, 42(3): 465-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202203011.htm [8] 伍新和, 张丽, 王成善, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地中生界海相烃源岩特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(3): 348-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.03.010WU Xinhe, ZHANG Li, WANG Chengshan, et al. Characteristics of the Mesozoic marine source rocks in the Qiangtang Basin, Tibet[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(3): 348-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.03.010 [9] 陈文彬, 付修根, 谭富文, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地上三叠统典型剖面烃源岩地球化学特征研究[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4): 1151-1160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.028CHEN Wenbin, FU Xiugen, TAN Fuwen, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Upper Triassic source rocks from typical sections in Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(4): 1151-1160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.028 [10] 占王忠, 谭富文. 羌塘盆地晚三叠世岩相古地理特征与烃源岩[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(4): 876-885.ZHAN Wangzhong, TAN Fuwen. Lithofacies palaeogeography and source rock of the Late Triassic in the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(4): 876-885. [11] 宋春彦, 王剑, 付修根, 等. 羌塘盆地东部上三叠统巴贡组烃源岩特征及意义[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2018, 42(5): 104-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.05.011SONG Chunyan, WANG Jian, FU Xiugen, et al. Geochemical characteristics and the significance of the Upper Triassic hydrocarbon source rocks of the Bagong Formation in the eastern Qiangtang Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2018, 42(5): 104-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2018.05.011 [12] PENG Jinning, LIU Xu, ZHUANG Xinbing, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of source rocks in the Qiangtang Basin: new discoveries from the Upper Triassic Xiaochaka Formation in the Woruoshan Mountain[J]. Unconventional Resources, 2023, 3: 103-110. doi: 10.1016/j.uncres.2022.12.001 [13] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 边立曾, 等. 中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(三)南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的沉积相及发育的控制因素[J]. 海相油气地质, 2009, 14(2): 1-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2009.02.001LIANG Digang, GUO Tonglou, BIAN Lizeng, et al. Some progresses on studies of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in marine sedimentary regions, southern China (part 3): controlling factors on the sedimentary facies and development of Palaeozoic marine source rocks[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2009, 14(2): 1-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2009.02.001 [14] 韩杨, 蒋文龙, 杨海波, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中段侏罗系烃源岩热演化史及其对天然气成藏的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(5): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202205005.htmHAN Yang, JIANG Wenlong, YANG Haibo, et al. Thermal evolution and natural gas accumulation of Jurassic source rocks in middle of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(5): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202205005.htm [15] 许露露, 温雅茹, 周向辉, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜南缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组一段古沉积环境演化特征: 以秭地1井为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 456-465. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203456?viewType=HTMLXU Lulu, WEN Yaru, ZHOU Xianghui, et al. Paleo-environment of the first member of Niutitang Formation on the southern margin of Huangling anticline, western Hubei province: a case study of well ZD-1[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(3): 456-465. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203456?viewType=HTML [16] 徐海, 周向辉, 林俊峰, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区秭地1井陡山沱组古沉积环境演化特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(6): 72-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.06.010XU Hai, ZHOU Xianghui, LIN Junfeng, et al. Characteristics of paleo-sedimentary environment evolution of Doushantuo Formation in well Zidi 1 of Yichang area in west Hubei of China[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(6): 72-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.06.010 [17] 占王忠, 彭清华, 陈文彬. 羌塘盆地冬曲地区上三叠统巴贡组古网迹的发现及古环境意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(2/3): 208-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2019Z1003.htmZHAN Wangzhong, PENG Qinghua, CHEN Wenbin. The discovery of paleodictyon in Upper Triassic Bagong Formation in Dongqu area of Qiangtang Basin and its palaeoenvironment significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2019, 38(2/3): 208-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2019Z1003.htm [18] 王忠伟, 肖杨, 占王忠, 等. 羌塘盆地东部上三叠统巴贡组泥岩特征及油气地质意义[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2022, 46(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2022.02.001WANG Zhongwei, XIAO Yang, ZHAN Wangzhong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Upper Triassic Bagong Formation mudstones in eastern Qiangtang Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2022, 46(2): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2022.02.001 [19] YU Fei, FU Xiugen, XU Guang, et al. Geochemical, palynological and organic matter characteristics of the Upper Triassic Bagong Formation from the north Qiangtang Basin, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 515: 23-33. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.12.002 [20] 程建, 郑伦举. 川南地区金页1井早寒武世烃源岩沉积地球化学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 800-810. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004014.htmCHENG Jian, ZHENG Lunju. Sedimentary geochemical characteristics of the Early Cambrian source rocks in well Jinye 1 in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 800-810. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004014.htm [21] 王亚如, 张昌民, 冀冬升, 等. 齐古断褶带头屯河组—清水河组地球化学特征及古环境[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5): 563-571. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202205008.htmWANG Yaru, ZHANG Changmin, JI Dongsheng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironment of Toutunhe Formation-Qingshuihe Formation in Qigu fault-fold belt[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(5): 563-571. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202205008.htm [22] 李浩, 徐怀民, 王千军, 等. 准东地区平地泉组微量元素地球化学特征及油气地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 277-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202302023.htmLI Hao, XU Huaimin, WANG Qianjun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and petroleum geological significance of trace elements of Pingdiquan Formation in eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 277-285. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202302023.htm [23] 马骥. 北天山依林黑比尔根断裂带充填物地球化学特征及构造指示意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(5): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202305006.htmMA Ji. Geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of fillings of Yilin Heibiergen Fault Zone in Northern Tianshan Mountain[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(5): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202305006.htm [24] 杨日红, 李才, 杨德明, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地中生代构造岩相演化及油气远景[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 2000(3): 237-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2000.03.007YANG Rihong, LI Cai, YANG Deming, et al. Mesozoic tectonic-petrographic evolution and oil-gas perspective in Qiangtang Basin, Tibet[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Techno-logy, 2000(3): 237-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2000.03.007 [25] 李勇, 王成善, 伊海生, 等. 青藏高原中侏罗世—早白垩世羌塘复合型前陆盆地充填模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(1): 20-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101003.htmLI Yong, WANG Chengshan, YI Haisheng, et al. Fill models of in the Qiangtang composite foreland basin in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(1): 20-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200101003.htm [26] 黄继钧, 伊海生, 林金辉. 羌塘盆地构造特征及油气远景初步分析[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200401000.htmHUANG Jijun, YI Haisheng, LIN Jinhui. Structural features of the Qiangtang Basin and preliminary analysis on oil-gas potentials[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200401000.htm [27] 谭富文, 王剑, 付修根, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地基底变质岩的锆石SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(1): 139-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200901012.htmTAN Fuwen, WANG Jian, FU Xiugen, et al. U-Pb zircon SHRIMP age of metamorphic rocks from the basement of the Qiangtang Basin, northern Tibet, and its geological significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(1): 139-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200901012.htm [28] 刘若涵, 何碧竹, 郑孟林, 等. 羌塘盆地东部晚三叠世—侏罗纪构造—沉积演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(6): 1857-1874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201906014.htmLIU Ruohan, HE Bizhu, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Tectonic-sedimentary evolution during Late Triassic-Jurassic period in the eastern part of the Qiangtang Basin, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(6): 1857-1874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201906014.htm [29] 曾胜强, 王剑, 陈文彬, 等. 羌塘盆地东部晚三叠世—早中侏罗世沉积环境转变研究: 来自地质浅钻岩芯的证据[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(5): 1231-1244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202105006.htmZENG Shengqiang, WANG Jian, CHEN Wenbin, et al. Late Triassic to Early-Middle Jurassic depositional environment transformation process study in the eastern Qiangtang Basin: evidence from the record by the core samples[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(5): 1231-1244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202105006.htm [30] 王剑, 付修根, 谭富文, 等. 羌塘中生代(T3-K1)盆地演化新模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(5): 884-893. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005007.htmWANG Jian, FU Xiugen, TAN Fuwen, et al. A new sedimentary model for the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(5): 884-893. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005007.htm [31] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 沉积岩中总有机碳的测定: GB/T 19145-2003[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2003.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Determination of total organic carbon in sedimentary rock: GB/T 19145-2003[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2003. [32] 国家能源局. 岩石薄片鉴定: SY/T 5368-2016[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2016.National Energy Administration. Identification for thin section of rocks: SY/T 5368-2016[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2016. [33] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第30部分: 44个元素量测定: GB/T 14506.30-2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Methods for chemical analysis of silicate rocks Part 30: determination of 44 elements: GB/T 14506.30-2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011. [34] 国家能源局. 烃源岩地球化学评价方法: SY/T 5735-2019[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2019.National Energy Administration. Geochemical method for source rock evaluation: SY/T 5735-2019[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2019. [35] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985: 312. [36] MCLENNAN S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mine-ralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200. [37] 冯连君, 储雪蕾, 张启锐, 等. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)及其在新元古代碎屑岩中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(4): 539-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200304027.htmFENG Lianjun, CHU Xuelei, ZHANG Qirui, et al. CIA (Chemical Index of Alteration) and its applications in the Neoproterozoic clastic rocks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(4): 539-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200304027.htm [38] 李清山, 郭少斌, 侯泽生, 等. 柴达木盆地上新世狮子沟期古气候演化与层序地层[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 28-36. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001028?viewType=HTMLLI Qingshan, GUO Shaobin, HOU Zesheng, et al. Palaeoclimate evolution and sequence stratigraphy during Pliocene Shizigou stage, Qaidam Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 28-36. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001028?viewType=HTML [39] 李振明, 熊伟, 王斌, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区二叠系风城组细粒沉积特征与演化模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 693-704. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304693?viewType=HTMLLI Zhenming, XIONG Wei, WANG Bin, et al. Fine-grained sedimentary characteristics and evolution model of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 693-704. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304693?viewType=HTML [40] WEI Wei, ALGEO T J. Elemental proxies for paleosalinity analysis of ancient shales and mudrocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2020, 287: 341-366. [41] JONES B, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstone[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129. [42] TRIBOVILLARD N, ALGEO T J, BAUDIN F, et al. Analysis of marine environmental conditions based on molybdenum-uranium covariation: applications to Mesozoic paleoceanography[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 324-325: 46-58. [43] 黄梓桑, 王兴志, 杨西燕, 等. 沉积环境对页岩中有机质富集的约束: 以蜀南地区五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(3): 631-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103010.htmHUANG Zisang, WANG Xingzhi, YANG Xiyan, et al. Constraints of sedimentary environment on organic matter accumulation in shale: a case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(3): 631-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103010.htm [44] BHATIA M R, CROOK K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2): 181-193. [45] WRONKIEWICZ D J, CONDIE K C. Geochemistry of Archean shales from the Witwatersrand Supergroup, South Africa: source-area weathering and provenance[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9): 2401-2416. [46] 王忠伟, 占王忠, 高远, 等. 羌塘盆地北缘上三叠统藏夏河组沉积物源及构造背景分析[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1199-1215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005013.htmWANG Zhongwei, ZHAN Wangzhong, GAO Yuan, et al. Provenance and tectonic setting analysis of the Upper Triassic Zangxiahe Formation sandstone in the northern Qiangtang Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1199-1216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005013.htm [47] 朱同兴, 冯心涛, 王晓飞, 等. 青藏高原晚三叠世构造—古地理综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(3): 59-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202003007.htmZHU Tongxing, FENG Xintao, WANG Xiaofei, et al. Summary of the Late Triassic tectonic paleogeography in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(3): 59-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202003007.htm [48] 宋春彦, 王剑, 付修根, 等. 羌塘盆地藏夏河组砂岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2013, 38(3): 508-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201303010.htmSONG Chunyan, WANG Jian, FU Xiugen, et al. Geochemical characteristics and signatures of the sandstones from Zangxiahe Formation in Qiangtang Basin[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2013, 38(3): 508-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201303010.htm [49] 熊伟, 王越, 熊峥嵘, 等. 准噶尔盆地石北凹陷岛弧环境下火山—沉积建造特征及源储发育模式: 以石炭系姜巴斯套组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656?viewType=HTMLXIONG Wei, WANG Yue, XIONG Zhengrong, et al. Characteristics of volcanic-sedimentary formations and developmental patterns of source and reservoir rocks in an island arc environment of Shibei Sag, Junggar Basin: taking the Carboniferous Jiangbasitao Formation as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656?viewType=HTML [50] 李志扬. 陆棚海泥岩的岩相特征及沉积过程: 以晚白垩世北美西部内陆海道为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1): 168-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101012.htmLI Zhiyang. Facies characteristics and depositional processes of shelf mudstones: examples from the Late Cretaceous western interior seaway of North America[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1): 168-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101012.htm -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号