Microscopic characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoirs in the Shigang Oilfield of the Subei Basin and strategies for enhancing oil recovery
-
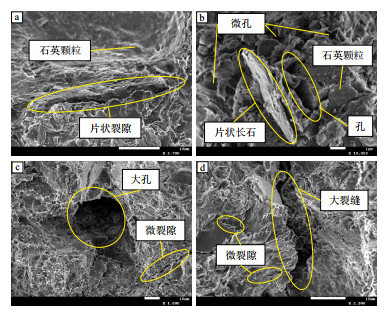
摘要: 苏北盆地石港油田属低孔、特低渗砂岩油藏,油井自然产能低,采用水力压裂后注水开发可提高产油能力,但油田开发中呈现低采油速度、低采出程度和开发效果差的特点,开发矛盾加剧。因此,需明确低效开发原因,探究提高采收率对策,为提高石港油田开发效果提供理论依据。通过全岩矿物成分分析、气测岩心孔渗参数、岩心敏感性评价等方法,从岩石矿物组成、孔喉结构和岩石敏感性等方面分析了其储层的微观特性;通过油藏数值模拟以及室内岩心实验研究了压裂水驱后剩余油的分布特征;通过核磁共振在线驱替实验探究了提高采收率的对策。结果显示,储层岩心呈现出典型的低孔、特低渗特征,且在开发过程中具有一定的速度敏感性和水敏感性。压裂水驱后,岩心中剩余油主要分布在0.01~1 μm中小孔径的孔道中,使用表面活性剂驱及二次水驱将岩心中剩余油采收率提高了14.81%。储层渗透率特低、微孔隙和微裂缝发育、速敏、水敏等是其低效开发的主要原因。注水开发会导致岩石矿物膨胀、运移,增大流动阻力,所以区块经压裂水驱仅明显提高主流线上剩余油的采出程度,整体动用程度不高,剩余油仍有较多富集。建议采用化学驱及多轮次驱替以增强中小孔道中原油动用程度,进一步提升油田开发效果。Abstract: The Shigang Oilfield in the Subei Basin is characterized by low-porosity and ultra-low permeability sandstone reservoirs. The natural productivity of the oil wells is low, but hydraulic fracturing followed by water injection can improve oil production capacity. However, during the development of the oilfield, problems such as low oil recovery rates, low recovery factors, and poor development effectiveness have become apparent, exacerbating development challenges. Therefore, it is necessary to identify the reasons for inefficient development and explore strategies to enhance recovery, providing a theoretical basis for improving the development effectiveness of the Shigang Oilfield. Using methods such as whole-rock mineral composition analysis, gas-measured core porosity and permeability parameters, and core sensitivity evaluation, the micro characteristics of the reservoir were analyzed in terms of rock mineral composition, pore-throat structure, and rock sensitivity. Numerical reservoir simulations and laboratory core experiments were conducted to study the distribution characteristics of residual oil after fracturing water flooding. Strategies to enhance oil recovery were investigated through nuclear magnetic resonance online displacement experiments. The results showed that the reservoir cores exhibited typical low-porosity and ultra-low permeability characteristics, with certain velocity sensitivity and water sensitivity during development. After fracturing water flooding, residual oil in the cores was mainly distributed in pore channels with diameters ranging from 0.01 to 1 μm. The use of surfactant flooding and secondary water flooding increased the recovery rate of residual oil in the cores by 14.81%. The main reasons for inefficient development included ultra-low reservoir permeability, the development of micro pores and micro fractures, and sensitivity to velocity and water. Water injection development could cause rock mineral swelling and migration, increasing flow resistance. Therefore, after fracturing water flooding, only the recovery of residual oil along the main flow paths was significantly improved, with the overall utilization degree remaining low, and a considerable amount of residual oil still concentrated in the reservoir. It is recommended to use chemical flooding and multiple rounds of displacement to enhance the utilization of oil in medium and small pore channels, further improving the development effectiveness of the oilfield.
-
表 1 苏北盆地石港油田石5井浅灰色粉砂岩岩心矿物成分
Table 1. Rock mineral composition of shallow gray siltstone cores in well Shi 5, Shigang Oilfield, Subei Basin
单位: % 岩心编号 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 铁白云石 黏土 石盐 石5-1 37.9 5.8 22.2 6.8 3.7 16.3 6.9 0.4 石5-2 31.7 4.4 25.8 5.9 5.2 12.8 14.3 0.0 石5-3 42.8 5.7 22.1 7.1 7.5 8.0 6.8 0.0 石5-4 39.1 5.9 18.8 6.6 3.9 18.1 7.3 0.3 石5-5 40.2 3.8 19.6 5.4 2.3 22.4 6.1 0.2 表 2 苏北盆地石港油田石4井浅灰色粉砂岩岩心孔隙度和渗透率
Table 2. Core porosity and permeability results of shallow gray siltstone cores of well Shi 4, Shigang Oilfield, Subei Basin
岩心编号 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 石4-1 7.51 0.110 石4-2 11.57 0.257 石4-3 9.42 0.165 石4-4 13.59 2.540 石4-5 14.83 4.566 表 3 苏北盆地石港油田石5断块油藏数值模拟参数
Table 3. Reservoir numerical simulation parameters of block Shi 5, Shigang Oilfield, Subei Basin
数值模拟参数 参数值 原始地层压力/MPa 22.6 饱和压力/MPa 2.9 平均渗透率/10-3 μm2 4.2 平均孔隙度/% 13.4 地下原油黏度/(mPa·s) 7 地面原油密度/(g/cm3) 0.877 原油体积系数 1.05 原始溶解油气比/(m3/t) 1.13 原油压缩系数/(1/MPa) 4.8×10-4 岩石压缩系数/(1/MPa) 5.6×10-4 地层水压缩系数/(1/MPa) 4.2×10-4 表 4 驱替实验不同阶段采收率情况
Table 4. Recovery rates at different stages of displacement experiment
驱替阶段 采收率/% 小孔(<0.1 μm) 中孔(0.1~10 μm) 大孔(>10 μm) 综合 水驱 8.91 4.88 13.04 6.77 表面活性剂驱 15.50 19.67 16.50 18.12 二次水驱 19.86 22.73 19.43 21.58 -
[1] 王哲, 曹广胜, 白玉杰, 等. 低渗透油藏提高采收率技术现状及展望[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202301001.htmWANG Zhe, CAO Guangsheng, BAI Yujie, et al. Development status and prospect of EOR technology in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoir, 2023, 30(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202301001.htm [2] 宋良业. XL区块低渗透油藏水驱油实验研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2021.SONG Liangye. Experimental study on water flooding in low permeability reservoirs in XL block[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2021. [3] 张阳, 芦凤明, 李际, 等. 中低渗储层物性特征对水驱油效率的定量影响[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(1): 94-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202101019.htmZHANG Yang, LU Fengming, LI Ji, et al. Quantitative effect of physical characteristics of medium and low permeability reservoirs on water flooding efficiency[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(1): 94-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202101019.htm [4] 吕前军. 非均质地层化学驱剩余油分布规律研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018.LV Qianjun. Distribution of residual oil after chemical flooding in heterogeneous formation[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2018. [5] 王欣然, 蔡晖, 张国浩, 等. 层内非均质性下聚合物驱对油田开发影响[J]. 天然气与石油, 2021, 39(3): 56-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYS202103009.htmWANG Xinran, CAI Hui, ZHANG Guohao, et al. Effect of polymer flooding on oil field development under intra-layer heterogeneity[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2021, 39(3): 56-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRYS202103009.htm [6] 阳晓燕. 非均质油藏水驱开发效果研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(2): 152-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902028.htmYANG Xiaoyan. Waterflood development effect study of heterogeneous reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(2): 152-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902028.htm [7] 李桂平, 赵志强, 梁飞, 等. 提高低渗透油藏开发效果研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2012, 32(2): 118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201202104.htmLI Guiping, ZHAO Zhiqiang, LIANG Fei, et al. Research on improving the development effect of low permeability reservoir[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2012, 32(2): 118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201202104.htm [8] 孟小芳, 姜杰, 任继波, 等. 低渗油藏提高采收率研究与应用[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2021, 41(7): 103-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ202107048.htmMENG Xiaofang, JIANG Jie, REN Jibo, et al. Research and application of enhanced oil recovery in low permeability reservoir[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2021, 41(7): 103-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ202107048.htm [9] 袁铨. 低渗油藏注水开发水窜机理及控制方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.YUAN Quan. The study on mechanism and control methodologies of water breakthrough for waterflood development in the low-permeability reservoir[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018. [10] 高雪梅. 低渗透油藏压裂开发水窜机理及改善方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2014.GAO Xuemei. Study on the mechanism and improving method of water channeling in hydraulic fractured low permeability reservoirs[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2014. [11] 张丛迪. 涠洲低渗油藏注水影响因素分析及增注措施研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2021.ZHANG Congdi. Analysis of influencing factors of water injection and study on increasing injection measures in Weizhou low permeability reservoir[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2021. [12] 王成俊, 洪玲, 高瑞民, 等. 低渗透油藏提高采收率技术现状与挑战[J]. 非常规油气, 2018, 5(3): 102-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ201803019.htmWANG Chengjun, HONG Ling, Gao Ruimin, et al. Status-quo and challenges of enhanced oil recovery in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2018, 5(3): 102-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ201803019.htm [13] 祝仰文, 孟红丽, 马宝东, 等. 低渗透油藏表面活性剂降压增注效果影响因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(1): 74-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201601011.htmZHU Yangwen, MENG Hongli, MA Baodong, et al. Factors effecting decompression and augmented injection by surfactant in low permeability reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(1): 74-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201601011.htm [14] 王成俊. 特低渗油藏表面活性剂驱适应性评价及应用基础研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2018.WANG Chengjun. Applied basic research and adaptability evaluation of surfactant flooding in ultra-low permeability reserviors[D]. Xi'an: Shanxi University of Science & Technology, 2018. [15] 邓永刚. 低渗透油田驱油剂的开发与应用[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2016.DENG Yonggang. Research and application of low damaged fracturing fluid system in Chanqing Oil and Gas Field [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2016. [16] 杨景斌, 侯吉瑞, 屈鸣, 等. 2-D智能纳米黑卡在低渗透油藏中的驱油性能评价[J]. 油田化学, 2020, 37(2): 305-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202002021.htmYANG Jingbin, HOU Jirui, QU Ming, et al. Evaluation of oil displacement performance of two-dimensional smart black nano-card in low permeability reservoir[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2020, 37(2): 305-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202002021.htm [17] 尚丹森, 侯吉瑞, 程婷婷. SiO2纳米流体在低渗透油藏中的驱油性能和注入参数优化[J]. 油田化学, 2021, 38(1): 137-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202101025.htmSHANG Dansen, HOU Jirui, CHENG Tingting. Flooding performance and optimization of injection parameters of SiO2 nanofluid in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2021, 38(1): 137-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202101025.htm [18] 国家能源局. 沉积岩中黏土矿物和常见非黏土矿物X射线衍射分析方法: SY/T 5163-2018[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018.National Energy Administration. Analysis method for clay minerals and ordinary non-clay minerals in sedimentary rocks by the X-ray diffraction: SY/T 5163-2018[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2018. [19] 国家能源局. 油气储层评价方法: SY/T 6285-2011[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.National Energy Administration. Evaluating methods of oil and gas reservoirs: SY/T 6285-2011[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011. [20] GAO Hui, CAO Jie, WANG Chen, et al. Comprehensive characterization of pore and throat system for tight sandstone reservoirs and associated permeability determination method using SEM, rate-controlled mercury and high pressure mercury[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174: 514-524. [21] 国家能源局. 储层敏感性流动实验评价方法: SY/T 5358-2010[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.National Energy Administration. Formation damage evaluation by flow test: SY/T 5358-2010[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [22] 赵明伟, 刘时春, 李阳, 等. 核磁共振T2谱与成像技术检测岩心中原油分布特征的综合性实验设计[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2021, 38(11): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJL202111013.htmZHAO Mingwei, LIU Shichun, LI Yang, et al. Comprehensive experimental design of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) T2 spectroscopy and imaging technology for detecting distribution characteristics of crude oil in core[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2021, 38(11): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJL202111013.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号