Influence of sedimentary microfacies on the rock mechanics of ultra-deep reservoirs and its application: a case study of the Cretaceous formation in the BZ gas field of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin
-
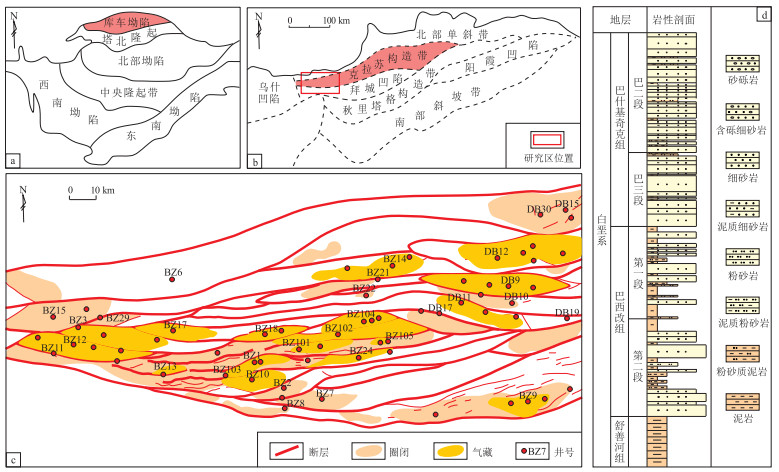
摘要: 为了优选塔里木盆地库车坳陷白垩系超深致密砂岩储层单井天然裂缝发育的甜点层段,利用露头、岩石薄片、成像测井等资料系统分析了BZ气田不同沉积微相的储层岩石力学性质差异,并结合相关露头中不同沉积微相的几何参数模型,提出了一种优化储层岩石力学参数模型的方法,提高了井筒周围(<200 m)天然裂缝预测精度。研究结果表明:(1) BZ气田白垩系巴什基奇克组三段不同沉积微相、相同微相不同位置的储层中,岩石组构和岩石组合(包括碎屑含量、杂基含量、粒度分选、砂地比和砂泥岩组合等)具有差异,从而影响了储层的泊松比和杨氏模量,不同微相储层具有不同的岩石力学参数。(2)不同沉积微相砂体的裂缝发育程度有所差异,扇三角洲前缘水下分支河道砂岩的裂缝最发育,比扇三角洲前缘支流间湾微相及扇三角洲平原分支河道微相更容易形成裂缝。(3)进一步根据露头中沉积微相几何参数,建立不同微相的三维模型,即可建立和优化井筒周围的沉积微相模型及岩石力学参数模型,并应用到井筒周围的裂缝预测中。Abstract: To optimize the identification of sweet spots with natural fracture development in ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs of Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin, this study systematically analyzed the differences in rock mechanical properties across various sedimentary microfacies in the BZ gas field. Utilizing data from outcrops, rock slices, imaging logging, and other sources, a method for optimizing the rock mechanics parameter model of reservoirs was proposed, which enhanced the prediction accuracy of natural fractures within 200 m around the wellbore. Key findings of the research include: (1) In the third member of the Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in the BZ gas field, different sedimentary microfacies and the same microfacies at different positions had differences in rock composition and rock assemblages (including debris content, matrix content, grain size sorting, sand-to-mud ratio, and sand-mudstone combinations). These variations affected the reservoir's Poisson's ratio and Young's modulus, and different microfacies had different rock mechanical parameters. (2) The extent of fracture development differed across various sedimentary microfacies of sand bodies. Fractures were most developed in the underwater distributary channel sandstones at the fan delta front, making them more prone to fracturing compared to the interdistributary bay microfacies and distributary channel microfacies on the delta plain. (3) By further establishing three-dimensional models of different microfacies based on geometric parameters derived from outcrops, it would be feasible to optimize sedimentary microfacies models and rock mechanical parameter models around the wellbore, thereby facilitating more accurate fracture prediction.
-
图 3 塔里木盆地库车坳陷BZ气田白垩系巴什基奇克组砂岩微观特征
a.中细粒岩屑长石砂岩,分选较好,杂基较少,BZ3井,5 977.54 m;b.不等粒长石岩屑砂岩,分选差,杂基多,BZ6井,4 482.53 m;c.中粒岩屑长石砂岩,分选好,杂基少,BZ101井,6 917.81 m;d.不等粒岩屑长石砂岩,分选较差,杂基较少,BZ103井,7 217.21 m;e.紫红色细砂岩, 发育高角度缝, 半充填—未充填,缝长4 cm,缝宽0.1 mm,BZ101井,6 918.25 m;f.紫红色细砂岩,发育紫红色泥砾, BZ101, 6 917.99 m。
Figure 3. Micro-features of sandstones in Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in BZ gas field, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin
表 1 塔里木盆地库车坳陷BZ气田各井白垩系巴什基奇克组岩性、物性及岩石力学性质参数
Table 1. Lithology, physical properties, and rock mechanical property parameters of Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in various wells in BZ gas field, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin
相关参数 BZ3井 BZ6井 BZ101井 BZ103井 石英(相对含量)/% 50 40.5 52 35 长石(相对含量)/% 21.4 29.6 25 24.2 岩屑(相对含量)/% 28.6 29.5 23 40.6 杂基/% 3 13 4 15 粒径范围/mm 0.06~0.135 0.03~1.67 0.03~0.8 0.02~0.6 分选程度 中等—好 差—中等 较好 中等—好 孔隙度/% 5.85 0.03 0.6 渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 0.23 3.51 泊松比 0.23 0.27 0.23 0.29 杨氏模量/MPa 31 000 25 981 31 500 26 848 抗压强度/MPa 107 90.7 100.77 表 2 塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部索罕村露头单砂体规模参数统计
Table 2. Parameters of single sandbody scale of Suohan Village outcrop in northern Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin
沉积微相 宽度/m 厚度/m 宽度与厚度比 水下分流河道 18~39 1~3.6 7~70 水下分流河道中、边部 20~68 3.2~5.7 4~95 河口坝 26~48 0.5~2 24~52 远砂坝 24 0.6 40 -
[1] 杨海军, 李勇, 唐雁刚, 等. 塔里木盆地克拉苏盐下深层大气田的发现[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(1): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201901003.htmYANG Haijun, LI Yong, TANG Yan'gang, et al. Discovery of Kelasu subsalt deep large gas field, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(1): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201901003.htm [2] 张辉, 尹国庆, 王海应. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷天然裂缝地质力学响应对气井产能的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(3): 379-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201903010.htmZHANG Hui, YIN Guoqing, WANG Haiying. Effects of natural fractures geomechanical response on gas well productivity in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(3): 379-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201903010.htm [3] 梁顺军, 彭更新, 杨洪德, 等. 库车与川东高陡复杂构造地震勘探的可比性[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2005, 10(5): 20-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200505004.htmLIANG Shunjun, PENG Gengxin, YANG Hongde, et al. Comparison of seismic exploration for steep-dipping complex structure in Kuqa area with eastern Sichuan area[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2005, 10(5): 20-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200505004.htm [4] 王珂, 张荣虎, 曾庆鲁, 等. 库车坳陷博孜—大北地区下白垩统深层—超深层储层特征及成因机制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(2): 311-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202202010.htmWANG Ke, ZHANG Ronghu, ZENG Qinglu, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of Lower Cretaceous deep and ultra-deep reservoir in Bozi-Dabei area, Kuqa Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(2): 311-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202202010.htm [5] 施辉, 罗晓容, 王宗秀, 等. 库车坳陷克深地区超深层致密砂岩储层裂缝非均一性发育机理[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(S1): 109-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2020S1044.htmSHI Hui, LUO Xiaorong, WANG Zongxiu, et al. The heterogeneous forming mechanism of structural fractures in the deep-buried tight sandstones of Keshen area, Kuqa Depression[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(S1): 109-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2020S1044.htm [6] 张荣虎, 王珂, 王俊鹏, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深构造带克深8区块裂缝性低孔砂岩储层地质模型[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(9): 1264-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201809005.htmZHANG Ronghu, WANG Ke, WANG Junpeng, et al. Reservoir geological model of fracture low porosity sandstone of Keshen 8 wellblock in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(9): 1264-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201809005.htm [7] 付小涛, 王益民, 邵剑波, 等. 超深层裂缝性致密砂岩储层砂体、裂缝发育特征及对产能的影响: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷KS2气田为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 326-337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102003.htmFU Xiaotao, WANG Yimin, SHAO Jianbo, et al. Characteristics and effect on productivity of the sandstone and fractures in ultra-deep and fractured tight sandstone gas reservoirs: a case study of KS2 Gasfield in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(2): 326-337. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202102003.htm [8] 杨海军, 张荣虎, 杨宪彰, 等. 超深层致密砂岩构造裂缝特征及其对储层的改造作用: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深气田白垩系为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(7): 942-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201807003.htmYANG Haijun, ZHANG Ronghu, YANG Xianzhang, et al. Characteristics and reservoir improvement effect of structural fracture in ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoir: a case study of Keshen Gasfield, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(7): 942-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201807003.htm [9] 史超群, 王佐涛, 朱文慧, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷克拉苏构造带大北地区超深储层裂缝特征及其对储层控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(12): 1687-1699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202012004.htmSHI Chaoqun, WANG Zuotao, ZHU Wenhui, et al. Fracture characteristic and its impact on reservoir quality of ultra-deep reservoir in Dabei region, Kelasu tectonic belt, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(12): 1687-1699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202012004.htm [10] 袁龙, 信毅, 吴思仪, 等. 深层白垩系致密砂岩裂缝定性识别、参数建模与控制因素分析: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深地区白垩系巴什基奇克组储层为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2021, 45(1): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202101003.htmYUAN Long, XIN Yi, WU Siyi, et al. Research on qualitative identification, parameter modeling and control factors of cracks in deep Cretaceous tight sandstone: taking the Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation reservoir in Keshen area, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2021, 45(1): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY202101003.htm [11] 王珂, 张荣虎, 王俊鹏, 等. 超深层致密砂岩储层构造裂缝分布特征及其成因: 以塔里木盆地库车前陆冲断带克深气田为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(2): 338-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202102008.htmWANG Ke, ZHANG Ronghu, WANG Junpeng, et al. Distribution and origin of tectonic fractures in ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of Keshen gas field, Kuqa foreland thrust belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(2): 338-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202102008.htm [12] 江同文, 张辉, 徐珂, 等. 克深气田储层地质力学特征及其对开发的影响[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY202004001.htmJIANG Tongwen, ZHANG Hui, XU Ke, et al. Reservoir geomechanical characteristics and the influence on development in Keshen gas field[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(4): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY202004001.htm [13] JOHRI M, ZOBACK M D, HENNINGS P. A scaling law to characterize fault-damage zones at reservoir depths[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(10): 2057-2079. doi: 10.1306/05061413173 [14] GENSTERBLUM Y, GHANIZADEH A, CUSS R J, et al. Gas transport and storage capacity in shale gas reservoirs-A review. Part A: Transport processes[J]. Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, 2015, 12: 87-122. doi: 10.1016/j.juogr.2015.08.001 [15] ZOBACK M D. Reservoir geomechanics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. [16] ITO T, ZOBACK M D, PESKA P. Utilization of mud weights in excess of the least principal stress to stabilize wellbores: theory and practical examples[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2001, 16(4): 221-229. [17] ZOBACK M D, BARTON C A, BRUDY M, et al. Determination of stress orientation and magnitude in deep wells[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7/8): 1049-1076. [18] KOHLI A, ZOBACK M. Stratigraphically controlled stress variations at the hydraulic fracture test site-1 in the midland basin, TX[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(24): 8328. doi: 10.3390/en14248328 [19] COLMENARES L B, ZOBACK M D. Hydraulic fracturing and wellbore completion of coalbed methane wells in the Powder River Basin, Wyoming: implications for water and gas production[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(1): 51-67. doi: 10.1306/07180605154 [20] 张辉, 杨海军, 尹国庆, 等. 地质工程一体化关键技术在克拉苏构造带高效开发中的应用实践[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(2): 120-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202002012.htmZHANG Hui, YANG Haijun, YIN Guoqing, et al. Application practice of key technologies of geology-engineering integration in efficient development in Kelasu structural belt[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(2): 120-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202002012.htm [21] 徐珂, 田军, 杨海军, 等. 深层致密砂岩储层现今地应力场预测及应用: 以塔里木盆地克拉苏构造带克深10气藏为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(4): 708-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202004009.htmXU Ke, TIAN Jun, YANG Haijun, et al. Prediction of current in-situ stress filed and its application of deeply buried tight sandstone reservoir: a case study of Keshen 10 gas reservoir in Kelasu structural belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(4): 708-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202004009.htm [22] 江同文, 张辉, 徐珂, 等. 超深层裂缝型储层最佳井眼轨迹量化优选技术与实践: 以克拉苏构造带博孜A气藏为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(4): 149-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202104012.htmJIANG Tongwen, ZHANG Hui, XU Ke, et al. Technology and practice of quantitative optimization of borehole trajectory in ultra- deep fractured reservoir: a case study of Bozi A gas reservoir in Kelasu structural belt, Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(4): 149-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202104012.htm [23] 杨海军, 张辉, 尹国庆, 等. 基于地质力学的地质工程一体化助推缝洞型碳酸盐岩高效勘探: 以塔里木盆地塔北隆起南缘跃满西区块为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(2): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201802004.htmYANG Haijun, ZHANG Hui, YIN Guoqing, et al. Geomechanics- based geology-engineering integration boosting high-efficiency exploration of fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs: a case study on West Yueman block, northern Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(2): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201802004.htm [24] 张杨, 王振兰, 范文同, 等. 基于裂缝精细评价和力学活动性分析的储层改造方案优选及其在博孜区块的应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(6): 47-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201706006.htmZHANG Yang, WANG Zhenlan, FAN Wentong, et al. Optimization of reservoir stimulation scheme based on fine fracture evaluation and mechanical activity analysis and its application in Bozi block[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(6): 47-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201706006.htm [25] 田军, 杨海军, 吴超, 等. 博孜9井的发现与塔里木盆地超深层天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 11-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001004.htmTIAN Jun, YANG Haijun, WU Chao, et al. Discovery of well Bozi 9 and ultra-deep natural gas exploration potential in the Kelasu tectonic zone of the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 11-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001004.htm [26] 徐珂, 杨海军, 张辉, 等. 克拉苏构造带博孜1气藏现今地应力场和高效开发[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 726-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106013.htmXU Ke, YANG Haijun, ZHANG Hui, et al. Current in-situ stress field and efficient development of Bozi-1 gas reservoir in Kelasu structural belt[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 726-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106013.htm [27] 徐珂, 张辉, 鞠玮, 等. 库车坳陷博孜X区块超深储层有效裂缝分布规律及对天然气产能的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2489-2505. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307005.htmXU Ke, ZHANG Hui, JU Wei, et al. Effective fracture distribution and its influence on natural gas productivity of ultra-deep reservoir in Bozi-X block of Kuqa Depression[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2489-2505. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307005.htm [28] 徐珂, 田军, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷超深层现今地应力对储层品质的影响及实践应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(1): 13-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202201002.htmXU Ke, TIAN Jun, YANG Haijun, et al. Effects and practical applications of present-day in-situ stress on reservoir quality in ultra-deep layers of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(1): 13-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202201002.htm [29] 郎晓玲, 郭召杰. 基于DFN离散裂缝网络模型的裂缝性储层建模方法[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(6): 964-972. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201306004.htmLANG Xiaoling, GUO Zhaojie. Fractured reservoir modeling method based on discrete fracture network model[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(6): 964-972. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201306004.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号