Micromechanical characteristics and controlling mechanism of deep shale: a case study of well JYA in Pingqiao block, Fuling area
-
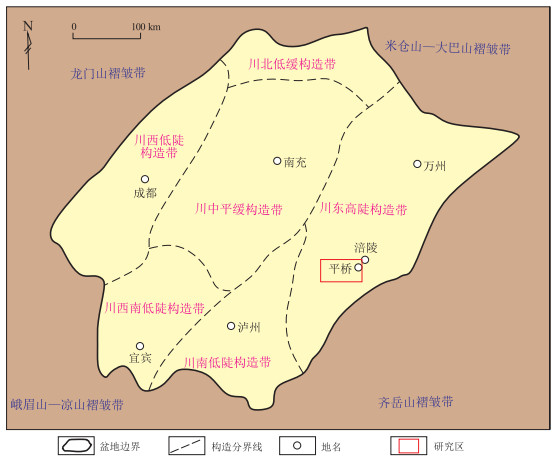
摘要: 四川盆地涪陵地区深层页岩气具有构造复杂、地应力高、地应力差大、地层温度高、致密化程度高、低孔低渗、孔渗变化规律复杂等地质特征,不同井之间产量差异大,原因之一是对于深层页岩气储层的地质力学特征和控制机理认识不足,适合压裂的甜点区间识别不准确。因此,对涪陵地区五峰组—龙马溪组海相页岩进行研究,围绕深层页岩气储层的微观地质力学特征与控制机理这一关键科学问题,通过微观岩石力学实验、数字光斑实验、X射线衍射、总有机碳含量、SEM扫描电镜等5个系列实验设计,结合数字图像处理技术,精细刻画了龙马溪组页岩在加载条件下的应力场和位移场变化及微观裂纹扩展过程,分析了龙马溪组页岩的变形与破裂特征。实验测得深层页岩总有机碳含量约为4.2%,石英含量为55.4%,黏土矿物含量为26.9%,明确了深层页岩的微观损伤变化的5个过程,即压密、弹性、裂纹均匀扩展、裂纹扩展破坏及脆性破坏。在石英等脆性矿物及有机质等软组分的控制作用下,深层页岩微观破裂具有多种裂缝扩展模式。同时,计算了深层页岩样品的断裂韧性指数,其中Ⅰ型断裂韧性指数为18.279 $\mathrm{MPa} \cdot \sqrt{\mathrm{m}}$, Ⅱ型断裂韧性指数为1.243 $\mathrm{MPa} \cdot \sqrt{\mathrm{m}}$。实验得到的断裂韧性指数可应用于评价深层页岩的脆性,也可为深层页岩的压裂改造提供指导。Abstract: The deep shale gas in the Fuling area is characterized by complex structures, high crustal stress, significant stress differences, high formation temperatures, high compaction levels, low porosity, low permeability, and complex porosity-permeability variation patterns. One reason for the significant production differences between wells is the insufficient understanding of the geomechanical features and controlling mechanisms of deep shale gas reservoirs, and the inaccurate identification of sweet spots for hydraulic fracturing. This study focuses on the marine shale of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the Fuling area, investigating the micromechanical characteristics and controlling mechanisms of deep shale gas reservoirs through five series of experiments: micro rock mechanics experiments, digital speckle experiments, X-ray diffraction, total organic carbon content measurement, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Coupled with digital image processing technology, the changes in stress field and displacement field, and microcrack propagation processes in the Longmaxi shale under loading conditions were meticulously depicted. The deformation and fracture characteristics of the Longmaxi shale were analyzed. Experimental results indicated that the total organic carbon content in the deep shale is approximately 4.2%, with quartz content at 55.4% and clay mineral at 26.9%. The study identified five stages of microdamage evolution in deep shale: compaction, elasticity, uniform crack propagation, crack propagation failure, and brittle failure. Under the influence of brittle minerals such as quartz, and soft components such as organic matter, the microcracks in deep shale exhibit various propagation modes, including transgranular, intergranular, and laminated layer cracks. Additionally, the fracture toughness indices of the deep shale samples were calculated, with Mode Ⅰ index being 8.279 $\mathrm{MPa} \cdot \sqrt{\mathrm{m}}$ and Mode Ⅱ index being 1.243 $\mathrm{MPa} \cdot \sqrt{\mathrm{m}}$. These experimentally obtained fracture toughness indices can be applied to evaluate the brittleness of deep shale, providing guidance for deep shale fracturing modification.
-
Key words:
- micromechanical characteristics /
- brittleness characteristics /
- fracturing /
- deep shale /
- Fuling area
-
表 1 四川盆地涪陵地区深层页岩微观力学参数
Table 1. Micromechanical parameters of deep shale in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin
样品编号 长/mm 宽/mm 高/mm 受力面积/mm2 峰值载荷/N 单轴抗压强度/MPa 绝对位移/mm 1 12.37 3.20 3.63 11.62 1 340 115.32 0.15 2 12.19 3.63 3.52 12.78 1 850 144.78 0.20 3 12.25 3.59 3.53 12.67 500 0.09 4 12.18 3.65 3.39 12.37 1 000 0.07 表 2 四川盆地涪陵地区深层页岩微观裂纹参数
Table 2. Microcrack parameters of deep shale in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin
裂纹序号 裂纹面积/μm2 裂纹长度/μm 裂纹宽度/μm 裂纹周长/μm 方位角/(°) 1 27 555.00 1 763.31 56.82 3 672.25 6.74 2 8 379.00 732.75 38.72 1 757.58 1.81 3 11 982.00 980.00 11.12 2 285.61 2.75 4 7 888.00 694.66 10.78 1 676.18 63.18 5 3 536.00 400.87 7.44 1 078.27 7.02 6 1 003.00 129.45 7.52 366.75 7.85 表 3 四川盆地涪陵地区深层页岩断裂韧性参数
Table 3. Fracture toughness parameters of deep shale in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin
序号 峰值载荷/N 抗拉强度/MPa 断裂韧性/($\mathrm{MPa} \cdot \sqrt{\mathrm{m}}$) KIC0 KⅡC0 KC0 1 1 220 11.65 27.52 1.53 14.53 2 1 200 11.45 26.57 1.50 14.04 3 1 100 10.50 22.10 1.37 11.74 -
[1] 邹才能, 赵群, 王红岩, 等. 中国海相页岩气主要特征及勘探开发主体理论与技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202208001.htmZOU Caineng, ZHAO Qun, WANG Hongyan, et al. The main characteristics of marine shale gas and the theory & technology of exploration and development in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202208001.htm [2] 李雨桐, 杨西燕, 范存辉. 富有机质页岩天然裂缝表征研究进展[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2023, 37(1): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN202301006.htmLI Yutong, YANG Xiyan, FAN Cunhui. Progress in characterization of natural fractures in organic-rich shale[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2023, 37(1): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN202301006.htm [3] 时贤, 程远方, 蒋恕, 等. 页岩微观结构及岩石力学特征实验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(S2): 3439-3445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2014S2008.htmSHI Xian, CHENG Yuanfang, JIANG Shu, et al. Experimental study of microstructure and rock properties of shale samples[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(S2): 3439-3445. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2014S2008.htm [4] 王超, 张柏桥, 舒志国, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区五峰组—龙马溪组海相页岩岩相类型及储层特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(3): 485-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201803007.htmWANG Chao, ZHANG Boqiao, SHU Zhiguo, et al. Lithofacies types and reservoir characteristics of marine shales of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Fuling area, the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(3): 485-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201803007.htm [5] 贾锁刚, 万有余, 王倩, 等. 页岩各向异性力学特性微观测试方法研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2021, 27(1): 10-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202101003.htmJIA Suogang, WAN Youyu, WANG Qian, et al. Research on the micro-scale method for testing the mechanical anisotropy of shale[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 27(1): 10-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202101003.htm [6] 陈天宇, 李荣艳, 周密, 等. 牛蹄塘组与龙马溪组页岩细观结构特征研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(6): 163-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201906032.htmCHEN Tianyu, LI Rongyan, ZHOU Mi, et al. Study on microstructure characteristics of the Niutitang Formation shale and the Longmaxi Formation shale[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2019, 28(6): 163-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201906032.htm [7] 钟建华, 刘圣鑫, 马寅生, 等. 页岩宏观破裂模式与微观破裂机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(2): 242-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201502017.htmZHONG Jianhua, LIU Shengxin, MA Yinsheng, et al. Macro-fracture mode and micro-fracture mechanism of shale[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(2): 242-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201502017.htm [8] 崔振东, 刘大安, 李晓, 等. 页岩微纳观断裂的原位观测[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2017, 13(1): 117-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201701017.htmCUI Zhendong, LIU Da'an, LI Xiao, et al. In-situ observation on the micro-nano cracks of shale[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(1): 117-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE201701017.htm [9] LEI Bo, LI Hongtao, ZUO Jianping, et al. Meso-fracture mechanism of Longmaxi shale with different crack-depth ratios: experimental and numerical investigations[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 257: 108025. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.108025 [10] 彭女佳, 何生, 郝芳, 等. 川东南彭水地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构及差异性[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1134-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707009.htmPENG Nüjia, HE Sheng, HAO Fang, et al. The pore structure and difference between Wufeng and Longmaxi shales in Pengshui area, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1134-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707009.htm [11] 王超勇, 鲍园, 琚宜文. 利用FE-SEM、HIP、N2吸附实验表征生物气化煤系有机岩储层微观孔隙结构演化[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1): 251-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202001020.htmWANG Chaoyong, BAO Yuan, JU Yiwen. Micropore structure evolution of organic matters in coal measures due to bioconversion using FE-SEM, HIP and N2, adsorption experiments[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(1): 251-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202001020.htm [12] 王玉龙. 页岩各向异性的微观实验测定与表征方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.WANG Yulong. Research on micro-experimental measurement and characterization method of shale anisotropy[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2021. [13] LI Shengtao, CHEN Xudong, GUO Shengshan. Evaluation of fracture process zone in the flexural response of different concrete materials using DIC method[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 24(8): 2435-2448. doi: 10.1007/s12205-020-0255-3 [14] 大久保诚介, 汤杨, 许江, 等. 3D-DIC系统在岩石力学试验中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(8): 3263-3273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201908044.htmSEISUKE O, TANG Yang, XU Jiang, et al. Application of 3D-DIC system in rock mechanic test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(8): 3263-3273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201908044.htm [15] 杜梦萍, 潘鹏志, 纪维伟, 等. 炭质页岩巴西劈裂载荷下破坏过程的时空特征研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(12): 3437-3446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201612012.htmDU Mengping, PAN Pengzhi, JI Weiwei, et al. Time-space laws of failure process of carbonaceous shale in Brazilian split test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(12): 3437-3446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201612012.htm [16] 刘子, 王树太. 巴西劈裂实验的龙马溪页岩研究[C]//北京力学会第二十七届学术年会论文集. 北京: 北京力学会, 2021.LIU Zi, WANG Shutai. The Longmaxi shale study of the Brazi-lian Splitting experiment[C]//Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference of Beijing Force Society. Beijing: Beijing Socitey of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021. [17] 马少鹏. 基于数字图像相关的岩石结构损伤破坏分析[C]//中国科协第235次青年科学家论坛——极端复杂测试环境下实验力学的挑战与应对. 北京: [s. n. ], 2011.MA Shaopeng. Damage and failure analysis of rock structures based on digital images[C]//The 235th Young Scientist Forum of the China Association for Science and Technology—Challenges and responses to experimental mechanics in extremely complex test Environments. Beijing: [s. n. ], 2011. [18] 张皓, 亢一澜, 宋海鹏, 等. 压头作用下岩石变形及破坏机理实验研究[C]//第十三届全国实验力学学术会议. 昆明: 中国力学学会实验力学专业委员会, 2012.ZHANG Hao, KANG Yilan, SONG Haipeng, et al. Experimental study on deformation and failure mechanism of rock under indenter action[C]// 13th National Conference on Experimental Mechanics. Kunming: Experimental Mechanics Professional Committee of the Chinese Society of Mechanics, 2012. [19] 马少鹏, 曹彦彦, 王显, 等. 数字图像相关方法在岩石受力失稳过程研究中的发展[C]//第五届二十一世纪的实验力学学科发展——海峡两岸实验力学研讨会. 昆明: 中国力学学会, 2012.MA Shaopeng, CAO Yanyan, WANG Xian, et al. The development of digital image correlation methods in the study of rock instability[C]// The 5th Development of Experimental Mechanics in the 21st Century—Cross-Strait Experimental Mechanics Seminar. Kunming: The Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2012. [20] 折海成, 刘思其, 胡再强. 基于SEM数字图像的岩石结构特征分析方法[J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(11): 167-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202211039.htmZHE Haicheng, LIU Siqi, HU Zaiqiang. An analysis method of rock structure characteristics based on SEM digital images[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40(11): 167-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202211039.htm [21] 范宜仁, 李格贤, 冀昆, 等. 基于数字岩心技术的页岩储层可压裂性定量评价[J]. 测井技术, 2017, 41(6): 685-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS201706012.htmFAN Yiren, LI Gexian, JI Kun, et al. Fracability quantitative interpretation of shale reservoir based on digital core technology[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2017, 41(6): 685-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS201706012.htm [22] 刘磊, 姚军, 孙海, 等. 考虑微裂缝的数字岩心多点统计学构建方法[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(30): 3146-3157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201830010.htmLIU Lei, YAO Jun, SUN Hai, et al. Reconstruction of digital rock considering micro-fracture based on multi-point statistics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(30): 3146-3157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201830010.htm [23] 刘慧, 杨更社, 任建喜. 基于数字图像处理的冻融页岩温度场的数值分析方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(8): 1678-1683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200708024.htmLIU Hui, YANG Gengshe, REN Jianxi. Numerical analysis method for temperature field of freezing-thawing shale based on digital image processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Enginee-ring, 2007, 26(8): 1678-1683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200708024.htm [24] 宋怀雷, 邬忠虎, 李利平, 等. 基于数字图像的微观尺度下方解石脉对页岩各向异性的影响[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 91-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDGY202105010.htmSONG Huailei, WU Zhonghu, LI Liping, et al. Influence of calcite veins on shale anisotropy at the microscopic scale based on digital images[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Science), 2021, 51(5): 91-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDGY202105010.htm [25] 王佳部. 基于数字图像技术的陆相页岩微观结构特征研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2020.WANG Jiabu. Microstructure characteristics of continental shale of research based on digital image technology[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2020. [26] 楼一珊, 陈勉, 史明义, 等. 岩石Ⅰ、Ⅱ型断裂韧性的测试及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(4): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200704018.htmLOU Yishan, CHEN Mian, SHI Mingyi, et al. Measurement of type-Ⅰ and type-Ⅱ fracture toughness for rocks and its influence factors analysis[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2007, 31(4): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200704018.htm [27] 纪国法, 李奎东, 张公社, 等. 页岩Ⅰ型断裂韧性的分形计算方法与应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(5): 1925-1931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201905035.htmJI Guofa, LI Kuidong, ZHANG Gongshe, et al. Fractal calculation method of model Ⅰ fracture toughness of shale rock and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(5): 1925-1931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201905035.htm [28] 张保平, 田国荣, 申卫兵, 等. 不同应力条件下岩石断裂韧性的研究[C]//第六次全国岩石力学与工程学术大会. 武汉: 中国科学技术出版社, 2000.ZHANG Baoping, TIAN Guorong, SHEN Weibing, et al. The study of fracture toughness under different stress conditions[C]//Proceedings of the Sixth National Conference on Rock Mechanics and Engineering. Wuhan: Science and Technology of China Press, 2000. [29] 张旭东, 金衍, 陈勉. 利用测井资料预测深部地层岩石断裂韧性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2001, 20(4): 454-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200104010.htmZHANG Xudong, JIN Yan, CHEN Mian. Determination of fracture toughness for deep well rock with geophysical logging data[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2001, 20(4): 454-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200104010.htm [30] 姚飞. 水力裂缝延伸过程中的岩石断裂韧性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(14): 2346-2350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200414007.htmYAO Fei. Fracture toughness in hydraulic fracture propagation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(14): 2346-2350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200414007.htm [31] 唐颖, 邢云, 李乐忠, 等. 页岩储层可压裂性影响因素及评价方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 356-363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205036.htmTANG Ying, XING Yun, LI Lezhong, et al. Influence factors and evaluation methods of the gas shale fracability[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 356-363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205036.htm -





 下载:
下载:















 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号