Disturbance characteristics of in-situ stress field within ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs in thrust-nappe structures: a case study from Cretaceous reservoirs in Bozi-Dabei area, Tarim Basin
-
摘要: 塔里木盆地库车坳陷博孜—大北地区白垩系致密砂岩储层在由北向南的逆冲推覆下,发育了一系列大规模的北倾断层和叠瓦状堆叠的褶皱构造。复杂的构造形貌致使该区地应力复杂多变,储层改造效果差异明显。因此,亟需厘清研究区内复杂构造对地应力的扰动特征。结合多种方法对单井现今地应力的精确解释,分别分析断裂、褶皱和断褶复合构造对地应力的扰动效果,明确了相关扰动机理,并绘制了研究区地应力扰动特征分区图。基于扰动特征,绘制了不同构造的地应力扰动特征模式图,并提出井位、井轨迹建议。断裂对地应力有卸载作用,断裂附近水平主应力梯度出现不同程度的降低,其中最大水平主应力梯度降低约0.3 MPa/hm;近EW走向的断裂使得近SN向的区域应力方向发生顺时针偏转,偏转角度最大达60°;不同规模断裂的扰动范围为断距的60%。当地层曲率超过0.4 km-1时,褶皱对地应力存在扰动,褶皱地层上部张性扰动区地应力较区域应力减小,下部挤压扰动区地应力增加;张性扰动区最大水平主应力梯度最大约降低0.3 MPa/hm,地应力方向逆时针偏转,偏转角度最大达70°;褶皱变形曲率越大,张性扰动区厚度越大,扰动越明显。断褶复合构造下,断裂扰动区和褶皱张性扰动区叠加会使得地应力进一步减小,地应力方向在两者扰动效果抵消后较区域应力偏转较小或不偏转。综合考虑储层改造难易程度和致密气富集特征,应优先于断褶复合构造带断裂和褶皱张性扰动叠合区部署钻井,建议钻深不超过褶皱中性面,水平井轨迹沿EW向设计。Abstract: A series of large-scale north-dipping faults and imbricate folding structures have developed in the Cretaceous ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs in Bozi-Dabei area of Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin under the north-to-south thrust-nappe movement in this area. This complex structural morphology results in highly variable in-situ stress fields, leading to significant differences in reservoir modification effectiveness. Therefore, it is urgent to clarify the disturbance characteristics of the in-situ stress caused by the complex structures in the study area. In this study, multiple methods were combined for the accurate interpretation of the current in-situ stress of a single well. The disturbance effects of faults, folds, and fault-fold composite structures on the in-situ stress were analyzed separately. The relevant disturbance mechanisms were identified, and a zoning map of the disturbance characte-ristics of the in-situ stress for the study area was presented. Based on these disturbance characteristics, models of in-situ stress disturbance for different structures, as well as recommendations for well deployment and trajectory, were proposed. Faults exhibit an unloading effect on the in-situ stress, leading to varying degrees of reduction in the horizontal principal stress gradient near the faults, with the maximum reduced by about 0.3 MPa/hm. Near EW-oriented faults, the regional stress direction near SN exhibits a clockwise deflection, with the maximum deflection angle reaching 60°. The disturbance range of faults with different scales is approximately 60% of the fault throw. A disturbance of the in-situ stress appears when the strata curvature exceeds 0.4 km-1. The in-situ stress is lower than the regional stress in the upper tensile disturbance zone of the folded strata, while it increases in the lower compressive disturbance zone. In the tensile disturbance zone, the maximum decrease in the horizontal principal stress gradient is approximately 0.3 MPa/hm, with the stress direction deflecting counterclockwise, reaching a maximum deflection angle of 70°. The greater the fold deformation curvature, the thicker the tensile disturbance zone, and the more significant the disturbance. Under fault-fold composite structures, the superposition of fault disturbance zones and fold tensile disturbance zones further reduces the magnitude of the in-situ stress. After offsetting the disturbance effects of both, the in-situ stress direction deviates less or does not deviate at all from the regional stress. Considering the difficulty of reservoir modification and the characteristics of tight gas enrichment, drilling should be prioritized in the overlapping areas of faults and fold tensile disturbance zones within the fault-fold composite structure zone. It is recommended that the drilling depth should not exceed the neutral plane of the folds, and the horizontal well trajectory should be designed along the EW direction.
-
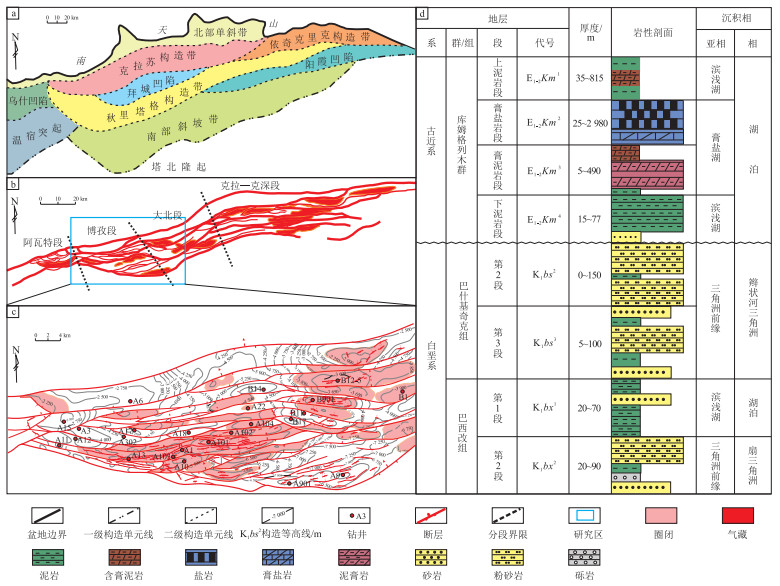
图 1 塔里木盆地博孜—大北地区构造地理位置及岩性柱状图
据参考文献[18]修改。
Figure 1. Structural location and lithology column of Bozi-Dabei area in Tarim Basin
图 2 塔里木盆地博孜—大北地区A6-A13井地震剖面
据参考文献[3]修改。
Figure 2. Seismic profile of wells A6 to A13 in Bozi-Dabei area, Tarim Basin
图 3 水力压裂曲线关键节点示意图(a)和B12-5井水力压裂曲线(b)
a图据参考文献[24]。
Figure 3. Key points on hydraulic fracturing curves (a) and a case of well B12-5 (b)
图 5 井壁崩落法的应力多边形二次约束示意图(a)及B901井应用实例(b、c)
a图据参考文献[27],NF、RF、SS分别表示正断层、逆断层和走滑断层;Sv为垂向应力。
Figure 5. Stress polygon quadratic constraint of wellbore collapse method (a) and a case of well B901 (b、c)
图 7 诱导缝、井壁崩落原理以及A3井成像测井响应
a图据参考文献[32]。
Figure 7. Principles of induced fractures and wellbore collapse and their imagining logging responses in well A3
-
[1] 郭宏辉, 冯建伟, 赵力彬. 塔里木盆地博孜—大北地区被动走滑构造特征及其对裂缝发育的控制作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 962-975. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202304010.htmGUO Honghui, FENG Jianwei, ZHAO Libin. Characteristics of passive strike-slip structure and its control effect on fracture development in Bozi-Dabei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 962-975. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202304010.htm [2] 杨学文, 王清华, 李勇, 等. 库车前陆冲断带博孜—大北万亿方大气区的形成机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(6): 175-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202206012.htmYANG Xuewen, WANG Qinghua, LI Yong, et al. Formation mechanism of the Bozi-Dabei trillion cubic natural gas field, Kuqa foreland thrust belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(6): 175-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202206012.htm [3] 王志民, 王翠丽, 徐珂, 等. 超深层致密砂岩构造裂缝发育特征及控制因素: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷博孜—大北地区下白垩统储集层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(9): 1535-1551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202309005.htmWANG Zhimin, WANG Cuili, XU Ke, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of tectonic fractures of ultra-deep tight sandstone: case study of the Lower Cretaceous reservoir in Bozi-Dabei area, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(9): 1535-1551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202309005.htm [4] GHOLAMI R, RASOULI V, AADNOY B, et al. Application of in situ stress estimation methods in wellbore stability analysis under isotropic and anisotropic conditions[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2015, 12(4): 657-673. doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/12/4/657 [5] WASANTHA P L P, KONIETZKY H, XU C. Effect of in-situ stress contrast on fracture containment during single- and multi-stage hydraulic fracturing[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2019, 205: 175-189. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.11.016 [6] 王生奥, 韩复兴, 孙章庆, 等. 地应力测量及其对油气运移和断层封堵性影响的发展现状与趋势[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(2): 675-688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202102026.htmWANG Sheng'ao, HAN Fuxing, SUN Zhangqing, et al. Present situation and the development trend of in-situ stress measurement and its effect on hydrocarbon migration and fault block[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(2): 675-688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202102026.htm [7] 印兴耀, 马妮, 马正乾, 等. 地应力预测技术的研究现状与进展[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(4): 488-504. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201804002.htmYIN Xingyao, MA Ni, MA Zhengqian, et al. Review of in-situ stress prediction technology[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(4): 488-504. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201804002.htm [8] BAI Xin, ZHANG Dongming, WANG Hao, et al. A novel in situ stress measurement method based on acoustic emission Kaiser effect: a theoretical and experimental study[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2018, 5(10): 181263. doi: 10.1098/rsos.181263 [9] HAN Yannong, FENG Yongcun, LI Xiaorong, et al. Evaluation of in-situ stress orientation: a laboratory approach combining paleo magnetic test and acoustic anisotropy test[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107870. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107870 [10] LIU Jingshou, DING Wenlong, YANG Haimeng, et al. 3D geomechanical modeling and numerical simulation of in-situ stress fields in shale reservoirs: a case study of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in the Cen'gong block, South China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 712-713: 663-683. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.06.030 [11] LI Ze, LI Gao, YU Hao, et al. Fracability evaluation based on the three-dimensional geological numerical simulation of in situ stress: case study of the Longmaxi Formation in the Weirong shale gas field, southwestern China[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 2022, 54(6): 1069-1096. doi: 10.1007/s11004-022-10001-5 [12] LIU Jingshou, YANG Haimeng, WU Xiaofei, et al. The in situ stress field and microscale controlling factors in the Ordos Basin, central China[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 135: 104482. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104482 [13] 段淑倩, 孙远达, 熊杰程, 等. 高地应力判据及其影响因素研究综述[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2023, 19(3): 1038-1050. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202303034.htmDUAN Shuqian, SUN Yuanda, XIONG Jiecheng, et al. A review of research on the criteria of high geostress and its influencing factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(3): 1038-1050. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE202303034.htm [14] 徐珂, 戴俊生, 商琳, 等. 南堡凹陷现今地应力特征及影响因素[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(3): 570-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201903011.htmXU Ke, DAI Junsheng, SHANG Lin, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of in-situ stress of Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(3): 570-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201903011.htm [15] SUN Shuai, HOU Guiting, ZHENG Chunfang. Fracture zones constrained by neutral surfaces in a fault-related fold: insights from the Kelasu tectonic zone, Kuqa Depression[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2017, 104: 112-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2017.10.005 [16] 翁剑桥, 曾联波, 吕文雅, 等. 断层附近地应力扰动带宽度及其影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(1): 39-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202001005.htmWENG Jianqiao, ZENG Lianbo, LYU Wenya, et al. Width of stress disturbed zone near fault and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(1): 39-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202001005.htm [17] ZHANG Ronghu, WANG Ke, ZENG Qinglu, et al. Effectiveness and petroleum geological significance of tectonic fractures in the ultra-deep zone of the Kuqa foreland thrust belt: a case study of the Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in the Keshen gas field[J]. Petroleum Science, 2021, 18(3): 728-741. [18] 杨海军, 孙雄伟, 潘杨勇, 等. 塔里木盆地克拉苏构造带西部构造变形规律与油气勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001007.htmYANG Haijun, SUN Xiongwei, PAN Yangyong, et al. Structural deformation laws and oil & gas exploration direction in the western Kelasu tectonic zone of the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001007.htm [19] 王珂, 张荣虎, 曾庆鲁, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷秋里塔格构造带箱形褶皱形成机制及油气勘探意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(9): 1384-1396.WANG Ke, ZHANG Ronghu, ZENG Qinglu, et al. Formation mechanism of the box fold and its significance in the Qiulitage structural belt of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(9): 1384-1396. [20] 卞青, 陈琰, 张国卿, 等. 柴达木盆地膏盐层岩石物理特征及其对构造变形的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(2): 197-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202002007.htmBIAN Qing, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Guoqing, et al. Petrophysical characteristics of the gypsum-salt layer in Qaidam Basin and its influences on tectonic deformation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(2): 197-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202002007.htm [21] 段云江, 黄少英, 罗彩明, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷盐构造变形平衡恢复及相关问题讨论[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(5): 780-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202305003.htmDUAN Yunjiang, HUANG Shaoying, LUO Caiming, et al. Discussion on balance restoration of salt structure deformation and related problems in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(5): 780-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202305003.htm [22] 罗晓容, 杨海军, 王震亮, 等. 深层—超深层碎屑岩储层非均质性特征与油气成藏模式[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(9): 2802-2819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202309002.htmLUO Xiaorong, YANG Haijun, WANG Zhenliang, et al. Heterogeneity characteristics of clastic reservoirs and hydrocarbon accumulation mode in deep-ultradeep basins[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(9): 2802-2819. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202309002.htm [23] 刘宏坤, 艾勇, 王贵文, 等. 深层、超深层致密砂岩储层成岩相测井定量评价: 以库车坳陷博孜—大北地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 299-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202301025.htmLIU Hongkun, AI Yong, WANG Guiwen, et al. Quantitative well logging evaluation of diagenetic facies of deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of Bozi-Dabei area in Kuqa Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 299-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202301025.htm [24] 吴捷. 水力压裂法在地应力测量中的应用[J]. 广东化工, 2012, 39(13): 124-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG201213064.htmWU Jie. The application of hydraulic fracturing in the geostress survey[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2012, 39(13): 124-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG201213064.htm [25] 陈文婷, 郑质彬, 彭岩岩. 水力压裂法在地应力测量中的应用[J]. 煤炭技术, 2020, 39(2): 66-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS202002022.htmCHEN Wenting, ZHENG Zhibin, PENG Yanyan. Application of hydraulic fracturing method in in-situ stress measurement[J]. Coal Technology, 2020, 39(2): 66-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTJS202002022.htm [26] 刘畅, 赵亮, 吕冠颖, 等. 基于声发射法的地应力研究[J]. 采矿技术, 2021, 21(3): 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJCK202103016.htmLIU Chang, ZHAO Liang, LV Guanying, et al. In-situ stress research based on acoustic emission method[J]. Mining Technology, 2021, 21(3): 52-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJCK202103016.htm [27] 陈念, 王成虎, 陈平志, 等. 利用钻孔崩落数据再认识白鹤滩右岸地应力场特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 2021, 27(3): 430-440.CHEN Nian, WANG Chenghu, CHEN Pingzhi, et al. Re-analyzing the in-situ stress field in the right bank of the Baihetan hydroelectric power plant using the borehole breakout data[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2021, 27(3): 430-440. [28] 王璞, 王成虎, 杨汝华, 等. 基于应力多边形与震源机制解的深部岩体应力状态预测方法初探[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(11): 4486-4496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201911040.htmWANG Pu, WANG Chenghu, YANG Ruhua, et al. Preliminary investigation on the deep rock stresses prediction method based on stress polygon and focal mechanism solution[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(11): 4486-4496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201911040.htm [29] 唐志强, 李黔, 尹虎. 利用斜井井壁破坏信息计算最大水平地应力[J]. 断块油气田, 2017, 24(5): 709-713. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201705027.htmTANG Zhiqiang, LI Qian, YIN Hu, et al. Calculation of maximum horizontal stress using failure information of inclined wellbore[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2017, 24(5): 709-713. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201705027.htm [30] ZOBACK M D, BARTON C A, BRUDY M, et al. Determination of stress orientation and magnitude in deep wells[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7/8): 1049-1076. [31] 曹峰, 何建华, 王园园, 等. 合川地区须二段低各向异性储层现今地应力方向评价方法[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(7): 742-755. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ202207006.htmCAO Feng, HE Jianhua, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. Methods to evaluate present-day in-situ stress direction for low anisotropic reservoirs in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in Hechuan area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(7): 742-755. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ202207006.htm [32] 徐珂, 张辉, 刘新宇, 等. 库车坳陷深层裂缝性储层现今地应力特征及其对天然气勘探开发的指导意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(2): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202202004.htmXU Ke, ZHANG Hui, LIU Xinyu, et al. Current in-situ stress characteristics of deep fractured reservoirs in Kuqa Depression and its guiding significance to natural gas exploration and deve-lopment[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(2): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202202004.htm [33] 祁斌, 夏宏泉, 房国庆, 等. 基于偶极横波测井的地层各向异性研究[J]. 测井技术, 2008, 32(5): 412-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200805008.htmQI Bin, XIA Hongquan, FANG Guoqing, et al. On stratum anisotropy based on DSI log information[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2008, 32(5): 412-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200805008.htm [34] 仵杰, 雪宇超, 路涛, 等. 各向异性地层中的偶极声波测井响应特性及反演[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 37(4): 76-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY202204011.htmWU Jie, XUE Yuchao, LU Tao, et al. Response characteristics and inversion of dipole acoustic logging in anisotropic formation[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science), 2022, 37(4): 76-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY202204011.htm [35] 李静, 刘晨, 刘惠民, 等. 复杂断层构造区地应力分布规律及其影响因素[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(1): 123-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202101013.htmLI Jing, LIU Chen, LIU Huimin, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of in-situ stress in complex fault tectonic region[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(1): 123-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202101013.htm [36] 韩长城, 林承焰, 任丽华, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河10区奥陶系断裂特征及对岩溶储层的控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(5): 790-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605005.htmHAN Changcheng, LIN Chengyan, REN Lihua, et al. Characte-ristics of Ordovician fault in the block 10 of Tahe Oilfield, Tarim Basin and its controlling effect on karst reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(5): 790-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605005.htm [37] 邓虎成, 周文, 姜昊罡, 等. 构造变形对现今地应力方向的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2009, 31(4): 57-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZC200904017.htmDENG Hucheng, ZHOU Wen, JIANG Haogang, et al. Effect of tectonic deformation on current geo-stress orientation[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 31(4): 57-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZC200904017.htm [38] 刘洪涛, 刘举, 刘会锋, 等. 塔里木盆地超深层油气藏试油与储层改造技术进展及发展方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(11): 76-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202011014.htmLIU Hongtao, LIU Ju, LIU Huifeng, et al. Progress and development direction of production test and reservoir stimulation technologies for ultra-deep oil and gas reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(11): 76-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202011014.htm [39] 费世祥, 崔越华, 夏守春, 等. 致密砂岩气藏水平井整体开发关键地质技术: 以苏里格气田苏东南区为例[C]//中国石油学会天然气专业委员会. 2018年全国天然气学术年会论文集(03非常规气藏). 福州: 中国石油学会天然气专业委员会, 2018: 17.FEI Shixiang, CUI Yuehua, XIA Shouchun, et al. Key geological technology for integrated development of horizontal well in tight sandstone gas reservoir: a case study from the Sulige gas field in southeast Jiangsu[C]//Presented at Natural Gas Committee of China Petroleum Society. Fuzhou: Natural Gas Professional Committee of China Petroleum Society, 2018: 17. [40] 陈守田, 吴玉金, 付喜春, 等. 肇源地区薄砂体精细刻画及水平井轨迹设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 598-607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002024.htmCHEN Shoutian, WU Yujin, FU Xichun, et al. Fine portray of thin sand-bodies and trajectory design of horizontal well in Zhaoyuan area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(2): 598-607. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002024.htm -





 下载:
下载:



















 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号