Study on development mechanism and variability of strike-slip fault-controlled reservoirs regulated by multi-stage structural stress: a case study of the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin
-
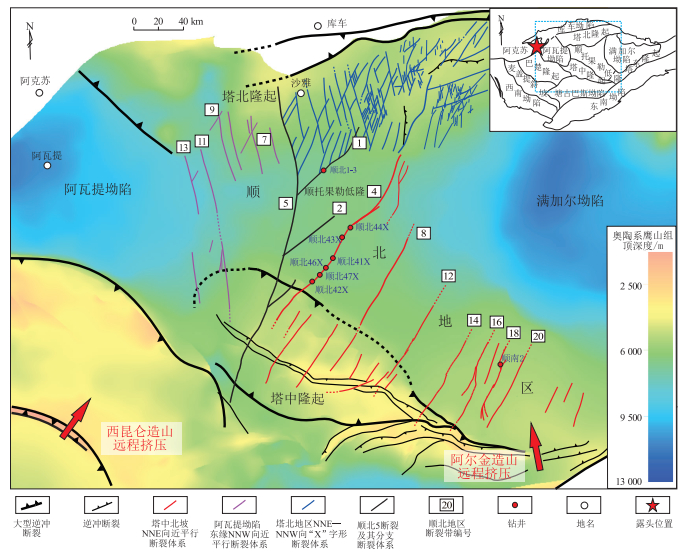
摘要: 塔里木盆地顺北油气田发育典型走滑断控缝洞型储层。区别于受原始沉积相带控制的基质孔洞、受岩溶改造的洞穴等储集类型,走滑断控缝洞型储层的形成主要受断裂活动期构造应力导致的破裂作用控制。为研究走滑断裂多期活动背景下构造应力控制的断控储层发育机理与分布规律,综合应用野外、岩心、测录井、地震及钻井动态等资料,开展不同走滑断裂、同一走滑断裂沿走向不同部位、垂向不同层系断控储层发育特征表征,并结合应力场数值模拟手段开展多期构造应力恢复,预测断控储层发育的主要时期与分布规律。结果表明,走滑断裂活动期不同分段内部应力状态差异显著,其中拉分段内部以张应力为主,主要派生张性裂缝;压隆段内部以挤压应力为主,派生裂缝类型多样。顺北地区勘探目的层奥陶系一间房组顶面断控裂缝主要在加里东中期Ⅲ幕及加里东晚期—海西早期发育,海西中—晚期及之后裂缝基本不发育,且滑移距大的顺北18号断裂带较顺北1号断裂带派生裂缝开度、密度更高。走滑断控储层具有“簇状”结构特征,断裂活动期不同分段内部应力状态控制储层结构差异,拉分段“空腔”多,以“双簇”结构为主,核带规模大,压隆段核带结构多,以“多簇”结构为主,分割性强;走滑断裂活动期应力强度控制储集空间类型与规模,小型断裂储集空间以裂缝为主,大型断裂带发育核带结构,断控储层规模与断裂活动强度呈正相关关系;断控裂缝发育主要受断裂早期活动控制,晚期由于地层埋深增大,岩石不易破裂,新派生裂缝发育较少。Abstract: The Shunbei oil-and-gas field in the Tarim Basin features a typical strike-slip fault-controlled fractured-vuggy reservoir. The formation of these reservoirs is primarily influenced by fracturing related to structural stress during periods of fault activity. This contrasts with reservoir types such as matrix vugs controlled by original sedimentary facies and caves modified by karst. To study the development mechanism and distribution patterns of strike-slip fault-controlled reservoirs under the influence of multi-stage structural stress, comprehensive analysis of field observations, core samples, well logging data, seismic surveys, and drilling dynamic data was conducted to characterize the development characteristics of fault-controlled reservoirs. This included different strike-slip faults, different parts along a single strike-slip fault, and different stratigraphic levels vertically. Combined with stress field numerical modeling, multi-stage structural stress recovery was carried out to predict the main development periods and distribution patterns of fault-controlled reservoirs. Significant variations in internal stress states were observed across different segments during periods of strike-slip fault activity. Tensile stress predominated in pull-apart segments, resulting in predominantly tensile fractures, whereas compressional stress state in push-up segments led to a variety of fracture types. The fault-controlled fractures in the top of the Yijianfang Formation in the Shunbei area were mainly developed during episode Ⅲ of the Middle Caledonian period and the Late Caledonian-Early Hercynian period. Few fractures were developed during the Middle to Late Hercynian period and thereafter. Compared to the Shunbei No.1 fault, the Shunbei No.18 fault exhibited higher fracture opening degree and density with a large displacement. Strike-slip fault-controlled reservoirs exhibit a cluster-like structure. Structural differences of the reservoirs are influenced by internal stress states in different segments during fault activity. Pull-apart segments typically feature a large fault core-damage zone with more cavities and 'double-cluster' structures, whereas push-up segments display more diverse fault core-damage zones with greater separability and 'multi-cluster' structures. The stress intensity during the strike-slip fault activity controls the types and scale of reservoir spaces, with smaller fault zones dominated by fractures and larger fault zones developing extensive fault core-damage zone architectures. The scale of fault-controlled reservoirs is positively correlated with fault activity intensity. Early fault activity promotes significant fracture development, while later stages, characterized by increased burial depths, result in few newly derived fractures due to reduced rock susceptibility to fracturing.
-
表 1 塔里木盆地顺北地区4号断裂带不同分段内部核带统计
Table 1. Statistical summary of internal core zones in different segments of Shunbei No.4 fault zone, Tarim Basin
分段类型 单断面控制的角砾带个数/个 单断面控制的裂缝带个数/个 角砾带总宽度/
m裂缝带总宽度/
m核带总数量/
个核带总宽度/
m压隆段 3.00 4.25 33.97 45.83 7.25 79.80 拉分段 1.29 3.25 8.97 29.41 4.54 38.35 平移段 1.75 2.38 10.62 14.98 4.13 25.60 表 2 塔里木盆地顺北地区1号、18号断裂带典型拉分段裂缝发育程度对比
Table 2. Comparison of fracture development degree of typical pull-apart segments in Shunbei No.1 and No.18 fault zones, Tarim Basin
井名 断裂带 滑移距/m 裂缝数量/条 裂缝开度/mm 裂缝长度/cm 裂缝密度/(条/m) 顺北1-3井 顺北1号带 350 31 0.1~1.2 1~14 2.8 顺南2井 顺北18号带 1 760 109 0.1~30 1~90 3.83 -
[1] CAINE J S, EVANS J P, FORSTER C B. Fault zone architecture and permeability structure[J]. Geology, 1996, 24(11): 1025-1028. [2] WOODCOCK N H, DICKSON J A D, TARASEWICZ J P T. Transient permeability and reseal hardening in fault zones: evidence from dilation breccia textures[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2007, 270(1): 43-53. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2007.270.01.03 [3] 贾茹, 付晓飞, 孟令东, 等. 断裂及其伴生微构造对不同类型储层的改造机理[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(3): 286-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201703005.htmJIA Ru, FU Xiaofei, MENG Lingdong, et al. Transformation mechanism of fault and its associated microstructures for different kinds of reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(3): 286-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201703005.htm [4] 张煜, 李海英, 陈修平, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区超深断控缝洞型油气藏地质-工程一体化实践与成效[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1466-1480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206015.htmZHANG Yu, LI Haiying, CHEN Xiuping, et al. Practice and effect of geology-engineering integration in the development of ultra-deep fault-controlled fractured-vuggy oil/gas reservoirs, Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1466-1480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206015.htm [5] 郝绵柱, 姜振学, 聂舟, 等. 深层页岩储层孔隙连通性发育特征及其控制因素: 以川南地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htmHAO Mianzhu, JIANG Zhenxue, NIE Zhou, et al. Development characteristics of pore connectivity in deep shale reservoirs and its controlling factors: a case study of Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htm [6] 汪如军, 冯建伟, 李世银, 等. 塔北-塔中隆起奥陶系富油气三角带断裂特征及控藏分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(2): 26-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202302004.htmWANG Rujun, FENG Jianwei, LI Shiyin, et al. Analysis on fault characteristics and reservoir control of Ordovician hydrocarbon-rich triangle zone in Tabei-Tazhong Uplift[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(2): 26-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202302004.htm [7] 张钰祥, 杨胜来, 李强, 等. 应力对超深层碳酸盐岩气藏孔喉结构的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(1): 49-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202301004.htmZHANG Yuxiang, YANG Shenglai, LI Qiang, et al. Effects of stress on pore and throat structures of ultra-deep carbonate gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(1): 49-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202301004.htm [8] 徐珂, 张辉, 刘新宇, 等. 库车坳陷深层裂缝性储层现今地应力特征及其对天然气勘探开发的指导意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(2): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202202004.htmXU Ke, ZHANG Hui, LIU Xinyu, et al. Current in-situ stress characteristics of deep fractured reservoirs in Kuqa Depression and its guiding significance to natural gas exploration and deve-lopment[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(2): 34-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202202004.htm [9] 宋刚, 李海英, 叶宁, 等. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒低隆起顺北4号走滑断裂带成岩流体类型及活动特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 603-612. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204603SONG Gang, LI Haiying, YE Ning, et al. Types and features of diagenetic fluids in Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone in Shun-tuoguole Low Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(4): 603-612. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204603 [10] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 李慧莉, 等. 深层-超深层碳酸盐岩储层发育机理新认识与特深层油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306001.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, LI Huili, et al. New insights into the formation mechanism of deep-ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs and the direction of oil and gas exploration in extra-deep strata[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306001.htm [11] BILLI A, SALVINI F, STORTI F. The damage zone-fault core transition in carbonate rocks: implications for fault growth, structure and permeability[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25(11): 1779-1794. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00037-3 [12] 吴智平, 陈伟, 薛雁, 等. 断裂带的结构特征及其对油气的输导和封堵性[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(4): 570-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201004012.htmWU Zhiping, CHEN Wei, XUE Yan, et al. Structural characte-ristics of faulting zone and its ability in transporting and sealing oil and gas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(4): 570-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201004012.htm [13] 李映涛, 邓尚, 张继标, 等. 深层致密碳酸盐岩走滑断裂带核带结构与断控储集体簇状发育模式: 以塔里木盆地顺北4号断裂带为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 80-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306007.htmLI Yingtao, DENG Shang, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Fault zone architecture of strike-slip faults in deep, tight carbonates and development of reservoir clusters under fault control: a case study in Shunbei, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 80-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306007.htm [14] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, YUN Lu, et al. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htm [15] 云露, 邓尚. 塔里木盆地深层走滑断裂差异变形与控储控藏特征: 以顺北油气田为例[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(6): 770-787. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202206003.htmYUN Lu, DENG Shang. Structural styles of deep strike-slip faults in Tarim Basin and the characteristics of their control on reservoir formation and hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Shunbei oil and gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 770-787. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202206003.htm [16] XU Zhiqin, HE Bizhu, ZHANG Chuanlin, et al. Tectonic framework and crustal evolution of the Precambrian basement of the Tarim block in NW China: new geochronological evidence from deep drilling samples[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 235: 150-162. [17] 贾承造, 马德波, 袁敬一, 等. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造特征、形成演化与成因机制[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(8): 81-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108012.htmJIA Chengzao, MA Debo, YUAN Jingyi, et al. Structural characteristics, formation & evolution and genetic mechanisms of strike-slip faults in the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(8): 81-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202108012.htm [18] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htmDENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm [19] DENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Structural characte-rization of intracratonic strike-slip faults in the central Tarim Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(1): 109-137. [20] 邓尚, 刘雨晴, 刘军, 等. 克拉通盆地内部走滑断裂发育、演化特征及其石油地质意义: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(6): 1111-1126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202106003.htmDENG Shang, LIU Yuqing, LIU Jun, et al. Structural styles and evolution models of intracratonic strike-slip faults and the implications for reservoir exploration and appraisal: a case study of the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallo-genia, 2021, 45(6): 1111-1126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202106003.htm [21] 刘雨晴, 邓尚, 张继标, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区走滑断裂体系差异发育特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 95-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306008.htmLIU Yuqing, DENG Shang, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the strike-slip fault networks in the Shunbei area and the surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 95-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202306008.htm [22] QIU Huabiao, DENG Shang, CAO Zicheng, et al. The evolution of the complex anticlinal belt with crosscutting strike-slip faults in the central Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Tectonics, 2019, 38(6): 2087-2113. [23] AYDIN A. Fractures, faults, and hydrocarbon entrapment, migration and flow[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2000, 17(7): 797-814. [24] AYDIN A, NUR A. The types and role of stepovers in strike-slip tectonics[M]//BIDDLE K T, CHRISTIE-BLICK N. Strike-slip deformation, basin formation, and sedimentation. Tulsa: Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, 1985: 35-44. [25] LIN Wei, CHU Yang, JI Wenbin, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints for a Middle Paleozoic continental arc on the northern margin of the Tarim block: implications for the Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the South Chinese Tianshan[J]. Lithosphere, 2013, 5(4): 355-381. [26] WANG Xinshui, KLEMD R, GAO Jun, et al. Final assembly of the southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt as constrained by the evolution of the South Tianshan Orogen: links with Gondwana and Pangea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(9): 7361-7388. [27] 李映涛, 汝智星, 邓尚, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩储层天然裂缝实验评价及油气意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 422-433. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303422LI Yingtao, RU Zhixing, DENG Shang, et al. Experimental evaluation and hydrocarbon significance of natural fractures in Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate reservoir, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 422-433. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303422 [28] 吕海涛, 韩俊, 张继标, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区超深碳酸盐岩断溶体发育特征与形成机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(1): 14-22. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101014LÜ Haitao, HAN Jun, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of ultra-deep carbonate fault-dissolution body in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(1): 14-22. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101014 [29] 刘敬寿, 丁文龙, 肖子亢, 等. 储层裂缝综合表征与预测研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(6): 2283-2300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201906019.htmLIU Jingshou, DING Wenlong, XIAO Zikang, et al. Advances in comprehensive characterization and prediction of reservoir fractures[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(6): 2283-2300. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201906019.htm [30] 张继标, 刘士林, 戴俊生, 等. 塔里木盆地玉北地区奥陶系储层构造裂缝定量预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(2): 177-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201902003.htmZHANG Jibiao, LIU Shilin, DAI Junsheng, et al. The quantitative prediction of structural fractures in Ordovician reservoir in Yu-Bei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(2): 177-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201902003.htm [31] 张继标, 张仲培, 汪必峰, 等. 塔里木盆地顺南地区走滑断裂派生裂缝发育规律及预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 955-963. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805011.htmZHANG Jibiao, ZHANG Zhongpei, WANG Bifeng, et al. Development pattern and prediction of induced fractures from strike-slip faults in Shunnan area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 955-963. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805011.htm [32] 季宗镇, 戴俊生, 汪必峰. 地应力与构造裂缝参数间的定量关系[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201001013.htmJI Zongzhen, DAI Junsheng, WANG Bifeng. Quantitative relationship between crustal stress and parameters of tectonic fracture[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(1): 68-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201001013.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号