Characteristics and main controlling factors of structural fracture development in deep buried hill reservoirs of basement metamorphic rocks: a case study of B block, Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要: 构造裂缝是改善基底变质岩潜山储层物性、提高油气产能的关键因素,但对于基底变质岩潜山储层构造裂缝的发育特征及主控因素的多尺度综合研究较少。以渤海湾盆地渤中B区块为例,综合利用薄片、岩心和成像测井资料,系统总结了基底变质岩潜山储层构造裂缝的特征,明确了主控因素,揭示了构造裂缝有效性影响因素和发育模式。研究区构造裂缝主要发育剪性裂缝,张性缝次之,斜交缝和直立缝较发育;裂缝整体充填程度高,主要充填物为泥质,其次为碳酸盐类;识别出近EW向、NE—SW向、NW—SE向和NNW—SSE向四组构造裂缝,其中近EW向裂缝较为发育,说明印支早期的强挤压作用环境是裂缝大规模发育的关键时期。研究区构造裂缝主要受岩石力学性质、构造作用、风化作用、储层物性和岩性控制。构造裂缝有效性主要受控于最大水平主应力方向与构造裂缝走向的夹角、构造运动、裂缝充填以及溶蚀作用等因素。纵向上基底变质岩深部潜山的构造裂缝随着深度增加所受风化作用减弱,在内幕带中沿断层局部发育溶蚀孔隙;不同岩石力学性质的岩石发育裂缝程度不同,脆性指数较大的岩石裂缝发育程度较高。横向上背斜核部的构造裂缝线密度大于翼部,当储层孔隙度和渗透率处于合适范围时有利于构造裂缝发育。Abstract: Structural fractures are pivotal in enhancing the physical properties of buried hill reservoirs within basement metamorphic rocks, thereby increasing oil and gas productivity. However, there is limited comprehensive, multi-scale investigations into the development characteristics and main controlling factors of such fractures. Taking B block in the Bohai Bay Basin as a case study, this research systematically synthesized thin-section, core, and imaging logging data to delineate the characteristics of structural fractures in buried hill reservoirs within basement metamorphic rocks. This study identified the principal controlling factors and revealed the influencing factors and development patterns of these fractures. The study area mainly developed shear fractures, followed by tensile fractures, with lesser occurrences of oblique and vertical fractures. The fractures exhibited a high overall filling degree, primarily filled with mud followed by carbonate. Four groups of structural fractures in near-EW, NE-SW, NW-SE and NNW-SSE directions were identified. Among them, the near-EW fractures were more developed, indicating that the strong compressive environment during the early stage of Indosinian was crucial for widespread fracture development. The development of structural fractures in the study area was mainly controlled by rock mechanics properties, tectonic activity, weathering processes, reservoir physical properties, and lithology. The effectiveness of structural fractures was mainly controlled by factors including the angle between the maximum horizontal principal stress direction and the orientation of structural fractures, tectonic movement, fracture filling and dissolution. Vertically, the influence of weathering decreased with depth in buried hill reservoirs, with local development of dissolution pores along faults in the internal zones. Rocks with different mechanical properties showed different degrees of fracture development. Rocks with higher brittleness index exhibited higher degree of fracture development. Laterally, the line density of structural fractures in the core of the anticlines was greater than that in the flanks, providing favorable conditions for the development of structural fractures when reservoir porosity and permeability were within suitable ranges.
-
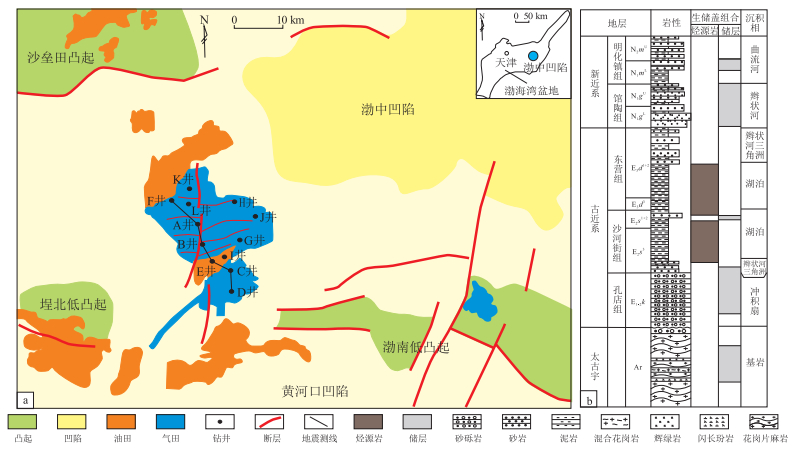
图 1 渤海湾盆地渤中B区块区域位置(a)及地层岩性柱状图(b)
据参考文献[12]修改。
Figure 1. Regional location map (a) and stratigraphic lithology column (b) in B block, Bohai Bay Basin
图 3 渤海湾盆地渤中B区块太古宇变质岩潜山储层岩心构造裂缝发育类型及特征
a.构造剪裂缝,E井,4 363.24~4 364.0 m;b.构造张裂缝,E井,4 365.45~4 366.18 m;c.矿物溶蚀,E井,4 361.55~4 362.39 m;d.多期裂缝,E井,4 368.46~4 369.16 m。
Figure 3. Types and characteristics of structural fractures in cores from buried hill reservoirs in Archean metamorphic rocks, B block, Bohai Bay Basin
图 4 渤海湾盆地渤中B区块太古宇变质岩潜山储层成像测井构造裂缝发育类型及特征
a.高导缝成像测井图像,L井,4 449.4~4 452.6 m;b.高阻缝成像测井图像,L井,4 543.6~4 546.9 m;c.溶蚀改造缝成像测井图像,L井,4 469.4~4 472.4 m;d.构造裂缝走向玫瑰花图;e.构造裂缝倾角统计图。
Figure 4. Types and characteristics of structural fractures development shown by imaging logs of buried hill reservoirs in Archean metamorphic rocks, B block, Bohai Bay Basin
图 6 渤海湾盆地渤中B区块太古宇变质岩潜山储层成像测井构造裂缝参数与构造作用的关系
a.4期构造运动应力场及裂缝走向模式(据参考文献[24]修改);b.构造裂缝线密度与距断层距离的关系;c.背斜不同部位与构造裂缝线密度的关系;d.各井区构造裂缝线密度与距深大断裂的关系;e.主要深大断裂分布及各井区裂缝走向玫瑰花图(据参考文献[12]修改)。
Figure 6. Relationship between structural fracture parameters in imaging logs and tectonism of buried hill reservoirs in Archean metamorphic rocks, B block, Bohai Bay Basin
图 11 渤海湾盆地渤中B区块太古宇变质岩潜山储层构造裂缝发育模式
剖面位置见图 1地震测线。
Figure 11. Structural fracture development pattern of buried hill reservoirs in Archean metamorphic rocks, B block, Bohai Bay Basin
-
[1] 薛永安, 李慧勇. 渤海海域深层太古界变质岩潜山大型凝析气田的发现及其地质意义[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(3): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803001.htmXUE Yong'an, LI Huiyong. Large condensate gas field in deep Archean metamorphic buried hill in Bohai Sea: discovery and geological significance[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(3): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803001.htm [2] 魏刚, 刘小刚, 陶林, 等. 锦州25-1区块探井钻井实践与认识[J]. 海洋石油, 2009, 29(3): 71-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY200903013.htmWEI Gang, LIU Xiaolin, TAO Lin, et al. Drilling practice and cognition of exploration wells in JZ 25-1 block[J]. Offshore Oil, 2009, 29(3): 71-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY200903013.htm [3] 郭子南. 兴隆台潜山基岩油藏储层分类评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(2): 64-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202202009.htmGUO Zinan. Classification and evaluation of bedrock reservoirs in Xinglongtai Buried Hill[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(2): 64-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202202009.htm [4] 袁静. 埕北30潜山带太古界储层特征及其影响因素[J]. 石油学报, 2004, 25(1): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200401009.htmYUAN Jing. Characters and influence factors on Archeozoic reservoir in the Chengbei 30 buried hills[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(1): 48-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200401009.htm [5] 范廷恩, 牛涛, 范洪军, 等. 渤中19-6凝析气田太古界潜山储层地质模式及开发策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(3): 85-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202103009.htmFAN Tingen, NIU Tao, FAN Hongjun, et al. Geological model and development strategy of Archean buried hill reservoir in BZ19-6 condensate field[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(3): 85-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202103009.htm [6] 许鹏, 牛成民, 李慧勇, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷西南部变质岩潜山裂缝型储层特征及主控因素[J]. 矿产勘查, 2022, 13(4): 418-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202204005.htmXU Peng, NIU Chengmin, LI Huiyong, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of natural gas fracture-related reservoir in Archen metamorphic rocks in southwest Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2022, 13(4): 418-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202204005.htm [7] 侯明才, 曹海洋, 李慧勇, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6构造带深层潜山储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(1): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901005.htmHOU Mingcai, CAO Haiyang, LI Huiyong, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of deep buried-hill reservoirs in the BZ19-6 structural belt, Bohai Sea area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(1): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901005.htm [8] 周心怀, 王清斌, 冯冲, 等. 渤海海域大型太古界潜山储层形成条件及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(5): 1534-1548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202205002.htmZHOU Xinhuai, WANG Qingbin, FENG Chong, et al. Formation conditions and geological significance of large Archean buried hill reservoirs in Bohai Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(5): 1534-1548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202205002.htm [9] XU Changgui, YU Haibo, WANG Jun, et al. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 27-40. [10] 范廷恩, 牛涛, 范洪军, 等. 渤中19-6凝析气田太古宇潜山储层发育主控因素及地质模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4): 170-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202104013.htmFAN Ting'en, NIU Tao, FAN Hongjun, et al. Archaeozoic buried-hill reservoir of Bozhong 19-6 condensate field: main controlling factors and development model[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 170-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202104013.htm [11] 漆家福, 于福生, 陆克政, 等. 渤海湾地区的中生代盆地构造概论[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(S1): 199-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY2003S1027.htmQI Jiafu, YU Fusheng, LU Kezheng, et al. Conspectus on Mesozoic basins in Bohai Bay province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(S1): 199-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY2003S1027.htm [12] WANG Wei, YI Jian, SHAN Xuanlong, et al. Characteristics of fractures development and its controlling factors within the buried hill reservoirs from the Archaean metamorphic basement in the Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2022, 10: 935508. [13] 徐长贵, 于海波, 王军, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6大型凝析气田形成条件与成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 25-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901003.htmXU Changgui, YU Haibo, WANG Jun, et al. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 25-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901003.htm [14] 宋国民. 渤中凹陷19-6构造区太古界潜山变质岩裂缝型储层特征与控制因素分析[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2021.SONG Guomin. Characteristics and control factors of Archean buried-hill metamorphic fractured reservoirs in the BZ19-6 structural region, Bozhong Sag[D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2021. [15] 胡志伟, 吕丁友, 王德英, 等. 渤海海域前新生代关键构造期变形特征与潜山油气成藏意义[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(1): 50-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202301005.htmHU Zhiwei, LYU Dingyou, WANG Deying, et al. Deformation characteristics of critical tectonic periods during pre-Cenozoic and significance of buried hill hydrocarbon accumulation in the Bohai Sea area[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(1): 50-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202301005.htm [16] 吕丁友, 杨海风, 于海波, 等. 渤海海域印支期逆冲推覆体系的分带性及其动力学成因机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(3): 720-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202303015.htmLYU Dingyou, YANG Haifeng, YU Haibo, et al. Zonation and dynamic genetic mechanism of the Indosinian thrust nappe system in Bohai Sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(3): 720-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202303015.htm [17] 李伟, 吴智平, 赵文栋. 渤海湾盆地区燕山期构造特征与盆地转型[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(6): 2068-2077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201006028.htmLI Wei, WU Zhiping, ZHAO Wendong. Structural characteristics and basin transformation in the Bohai Bay Basin in the Yanshan era[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(6): 2068-2077. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201006028.htm [18] WANG Guangzeng, LI Sanzhong, WU Zhiping, et al. Early Paleogene strike-slip transition of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone across the southeast Bohai Bay Basin: constraints from fault characteristics in its adjacent basins[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(2): 835-849. [19] 高松洋. 成像测井资料在裂缝识别中的应用[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2007.GAO Songyang. Application of imaging logging data in identification of fracture[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2007. [20] 曹东升, 曾联波, 黄诚, 等. 多尺度岩石力学层对断层和裂缝发育的控制作用[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2535-2556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307008.htmCAO Dongsheng, ZENG Lianbo, HUANG Cheng, et al. Control of multi-scale mechanical stratigraphy on development of faults and fractures[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2535-2556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307008.htm [21] 周欣, 巴晶, 符力耘, 等. 页岩脆性评价岩石物理模型及地震预测[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(5): 1736-1744. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202005013.htmZHOU Xin, BA Jing, FU Liyun, et al. Rock physics model for shale brittleness evaluation and seismic prediction[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(5): 1736-1744. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202005013.htm [22] 巩磊, 姚嘉琪, 高帅, 等. 岩石力学层对构造裂缝间距的控制作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(6): 965-973. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201806002.htmGONG Lei, YAO Jiaqi, GAO Shuai, et al. Controls of rock mechanical stratigraphy on tectonic fracture spacing[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(6): 965-973. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201806002.htm [23] GROSS M R, FISCHER M P, ENGELDER T, et al. Factors controlling joint spacing in interbedded sedimentary rocks: integrating numerical models with field observations from the Monterey Formation, USA[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1995, 92(1): 215-233. [24] AGOSTA F, WILSON C, AYDIN A. The role of mechanical stratigraphy on normal fault growth across a Cretaceous carbonate multi-layer, central Texas (USA)[J]. Italian Journal of Geosciences, 2015, 134(3): 423-441. [25] CORRADETTI A, TAVANI S, PARENTE M, et al. Distribution and arrest of vertical through-going joints in a seismic-scale carbonate platform exposure (Sorrento Peninsula, Italy): insights from integrating field survey and digital outcrop model[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2018, 108: 121-136. [26] 廖新武, 谢润成, 周文, 等. 古地貌对渤海湾盆地B区块太古宇暴露型潜山变质岩风化带储层裂缝发育的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(2): 406-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202302012.htmLIAO Xinwu, XIE Runcheng, ZHOU Wen, et al. The effects of paleogeomorphology on the development of fractures in reservoirs of weathering metamorphic zone in an exposed Archean burial hill, block B, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(2): 406-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202302012.htm [27] 牛成民, 王飞龙, 何将启, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6潜山气藏成藏要素匹配及成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 259-267. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102259NIU Chengmin, WANG Feilong, HE Jiangqi, et al. Accumulation factor matching and model of Bozhong 19-6 buried hill gas reservoir, Bohai Sea area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 259-267. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102259 [28] 万远飞, 秦启荣, 范宇, 等. 长宁背斜龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及期次解析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 59-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101008.htmWAN Yuanfei, QIN Qirong, FAN Yu, et al. Development characteristics of shale fractures in Longmaxi Formation of Changning anticline and the stage analysis[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(1): 59-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101008.htm [29] 刘春, 张荣虎, 张惠良, 等. 塔里木盆地库车前陆冲断带不同构造样式裂缝发育规律: 证据来自野外构造裂缝露头观测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(1): 52-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701006.htmLIU Chun, ZHANG Ronghu, ZHANG Huiliang, et al, Fracture development of different structural styles in Kuqa foreland thrust belt: from outcrop observation of structural fracture[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(1): 52-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701006.htm [30] 时培兵. 渤海湾盆地上太古界潜山储层裂缝特征[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2017.SHI Peibing. The characteristics of Archeozoic buried hill reservoir fractures in the area of Bohai Bay Basin[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2017. [31] 李睿琦, 吕文雅, 王浩南, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷克拉苏构造带克深地区典型断背斜天然裂缝分布特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(2): 271-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202302007.htmLI Ruiqi, LÜ Wenya, WANG Haonan, et al. Distribution characteristics of natural fractures of the typical fault anticlines in Keshen area of Kelasu structural belt, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(2): 271-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202302007.htm [32] 郑华, 康凯, 刘卫林, 等. 渤海深层变质岩潜山油藏裂缝主控因素及预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(3): 29-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202203003.htmZHENG Hua, KANG Kai, LIU Weilin, et al. Main controlling factors and prediction of fractures in deep metamorphic buried hill reservoirs in Bohai Sea[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(3): 29-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202203003.htm [33] 周波, 贾承造, 顾家裕, 等. 塔中台地边缘上奥陶统灰岩段裂缝对储层发育的控制作用: 以塔中Ⅰ号断裂坡折带为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(2): 198-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200802006.htmZHOU Bo, JIA Chengzao, GU Jiayu, et al. Controlling effect of the fractures in Upper Ordovician fractures upon reservoir formation at the platform edge of Tazhong oilfield, the Tarim Basin: an example from the Tazhong-Ⅰ slope break zone[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(2): 198-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200802006.htm [34] 王杰, 胡晨光, 潘勇利, 等. 吉华1地区潜山变质岩储层裂缝发育特征及综合评价[J]. 地质科学, 2022, 57(2): 463-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202202009.htmWANG Jie, HU Chenguang, PAN Yongli, et al. Fracture deve-lopment characteristics and comprehensive evaluation of buried hill metamorphic reservoir in Jihua 1 area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2022, 57(2): 463-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202202009.htm [35] 李战奎, 尚锁贵, 郭明宇, 等. 变质岩潜山储层分带特征及在地质作业中的应用: 以渤中凹陷及周缘潜山为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(5): 61-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202305006.htmLI Zhankui, SHANG Shuogui, GUO Mingyu, et al. Zoning characte-ristics of metamorphic rock buried hill reservoirs and application in geological operations: a case study of Bozhong Sag and surrounding buried hills[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(5): 61-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202305006.htm [36] 胡冬亮, 吴时国, 蒲玉国, 等. 东营凹陷纯化油田西部侵入岩裂缝系统研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2008, 15(2): 67-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200802023.htmHU Dongliang, WU Shiguo, PU Yuguo, et al. Fracture system of irruptive rocks in the west of Chunhua Oilfield, Dongying Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2008, 15(2): 67-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200802023.htm [37] 黄玉越, 王贵文, 宋连腾, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩储集层裂缝测井识别与有效性分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(3): 540-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202203010.htmHUANG Yuyue, WANG Guiwen, SONG Lianteng, et al. Fracture logging identification and effectiveness analysis of shale reservoir of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2022, 24(3): 540-555. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202203010.htm [38] 冯振伟, 梁积伟, 章佩锋, 等. 塔河南部一间房组构造裂缝有效性分析[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 950-959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB202205014.htmFENG Zhenwei, LIANG Jiwei, ZHANG Peifeng, et al. Analysis of structural fracture effectiveness of Yijianfang Formation in the southern of Tahe area[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2022, 42(5): 950-959. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKXB202205014.htm [39] 徐长贵, 杜晓峰, 刘晓健, 等. 渤海海域太古界深埋变质岩潜山优质储集层形成机制与油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2): 235-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002002.htmXU Changgui, DU Xiaofeng, LIU Xiaojian, et al. Formation mechanism of high-quality deep buried-hill reservoir of Archaean metamorphic rocks and its significance in petroleum exploration in Bohai Sea area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2): 235-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002002.htm [40] 邱登峰, 云金表, 刘全有, 等. 不同边界条件断层端部应力集中效应及对裂缝发育的启示[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1): 205-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901022.htmQIU Dengfeng, YUN Jinbiao, LIU Quanyou, et al. The stress concentration effect at fault end under various boundary conditions and its implications for fracture development[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 205-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901022.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号