Development characteristics and controlling factors of fractures in deep-buried tight oil reservoirs of the 3rd member of Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in southeast An'peng area, Nanxiang Basin
-
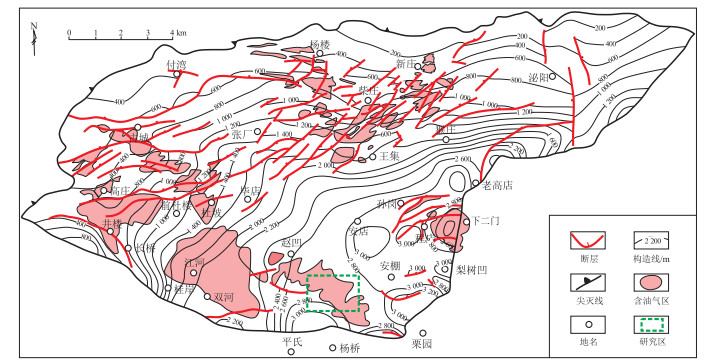
摘要: 为了探明深部致密油储层天然裂缝发育规律及其影响因素,以南襄盆地泌阳凹陷安棚东南区古近系核桃园组三段Ⅱ—Ⅵ油层组致密油藏为例,利用大量岩心、薄片、物性、成像及常规测井、注水压驱等资料,系统开展了致密油藏裂缝综合评价。该区目的层Ⅱ—Ⅵ油层组属扇三角洲前缘沉积,储层岩屑含量较高,为近源沉积;储层孔隙度与渗透率之间具有良好的正相关性。对于不同岩性砂岩储层,裂缝主要发育于细砂岩中,其次为粉砂岩,而含砾砂岩中裂缝通常不发育。目的层主要发育高角度缝及直立缝,其占比可达87.8%,低角度斜交缝和水平缝分别占比7.3%及4.9%。目的层致密储层裂缝发育主控因素主要包括岩性、沉积微相及局部构造,厚度较薄、粒度较细的单砂体或复合砂体部位裂缝通常较为发育。裂缝主要发育于前缘河道、河道侧翼、河口坝及其外缘远砂坝砂体部位,而席状砂及前缘三角洲微相中裂缝不发育。此外,裂缝还发育于构造转折端,且主要发育于正向构造的顶部及翼部。目的层裂缝主要沿着WE向、NE向分布,其次为NW向;裂缝主要形成于新近纪拗陷期(喜马拉雅晚期)。裂缝是导致致密油储层水窜的重要因素,因而要加强裂缝发育程度、扩展规模及方向的动、静态监测。Abstract: To elucidate the development patterns and influencing factors of natural fractures in deep-buried tight oil reservoirs, a comprehensive evaluation was conducted using a large amount of core samples, thin section, physical property data, imaging and conventional logging, water injection pressure testing and other data. The focus was on the tight oil reservoirs within the Ⅱ-Ⅵ oil layers of the third member of the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in the southeastern An'peng area of the Biyang Depression, Nanxiang Basin. These oil formations, deposited in fan-delta front environment, are characterized by a high content of rock debris, indicating proximal deposition. A strong positive correlation between reservoir porosity and permeability was observed. Among the various sandstone lithologies, fractures predominantly developed in fine sandstone, followed by siltstone, while gravelly sandstone generally lacked fractures. High-angle and vertical fractures were predominant, constituting 87.8% of the total, while low-angle oblique and horizontal fractures accounted for 7.3% and 4.9%, respectively. The main controlling factors for fracture development in these tight reservoirs included lithology, depositional microfacies, and local structures. Thin and fine-grained single or composite sand bodies typically had more deve-loped fractures, particularly in front channel, channel flank, mouth bar, and outer edge of distal bars. Conversely, fractures were less developed in sheet sands or delta front microfacies. Moreover, fractures primarily formed at structural inflection points, predominantly at the tops and wings of forward structures and were primarily oriented along the WE and NE directions, followed by the NW direction. These fractures predominantly formed during the Neogene depression period (late Himalayan). Fractures significantly influence water channeling in tight oil reservoirs, necessitating enhanced dynamic and static monitoring of the degree, extent, and orientation of fracture development.
-
Key words:
- fracture /
- tight oil /
- Hetaoyuan Formation /
- Paleogene /
- southeast An'peng area /
- Biyang Sag /
- Nanxiang Basin
-
图 6 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷安棚东南区核桃园组三段Ⅱ—Ⅵ油层组致密砂岩岩心裂缝照片
a.安2132井,细砂岩,2 786.8~2 787 m;b.安2132井,细砂岩,3 044.7~3 045 m;c.泌261井,中细砂岩,碳质纹层弱面发育2条水平缝,3 012.57~3 012.77 m;d.泌261井,含巨砾粗砂岩,3 309.38~3 309.68 m。
Figure 6. Photographs of tight sandstone core fractures in Ⅱ to Ⅵ oil formations in third member of Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation, southeast An'peng area, Biyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin
-
[1] 李智, 张志业, 李双建, 等. 南襄盆地地质结构与形成演化[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 116-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202202009.htmLI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, LI Shuangjian, et al. Geological architecture and tectonic evolution of Nanxiang Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 116-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202202009.htm [2] 袁玉哲, 罗家群, 朱颜, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(3): 364-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202103014.htmYUAN Yuzhe, LUO Jiaqun, ZHU Yan, et al. Petroleum exploration history and enlightenment of Biyang Sag and Nanyang Sag in Nanxiang Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(3): 364-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202103014.htm [3] 尹帅, 孙晓光, 邬忠虎, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北缘上古生界构造演化及裂缝耦合控气作用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3724-3737. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202209033.htmYIN Shuai, SUN Xiaoguang, WU Zhonghu, et al. Coupling control of tectonic evolution and fractures on the Upper Paleozoic gas reservoirs in the northeastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3724-3737. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD202209033.htm [4] 董艳蕾, 朱筱敏, 耿晓洁, 等. 泌阳凹陷东南部核桃园组近岸水下扇与扇三角洲沉积特征比较及控制因素分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(2): 271-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201502013.htmDONG Yanlei, ZHU Xiaomin, GENG Xiaojie, et al. Sedimentary characteristics comparison and controlling factors analyses of near-shore subaqueous fan and fan delta in the Hetaoyuan Formation of southeastern Biyang Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(2): 271-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201502013.htm [5] 章新文, 王优先, 王根林, 等. 河南省南襄盆地泌阳凹陷古近系核桃园组湖相页岩油储集层特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(1): 107-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201501012.htmZHANG Xinwen, WANG Youxian, WANG Genlin, et al. Reservoir characteristics of lacustrine shale oil of the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation in Biyang Sag of Nanxiang Basin, Henan Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(1): 107-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201501012.htm [6] 尹帅, 邬忠虎, 吴晓明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区洪德区块侏罗系延安组油藏富集规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(5): 1167-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205013.htmYIN Shuai, WU Zhonghu, WU Xiaoming, et al. Oil enrichment law of the Jurassic Yan'an Formation, Hongde block, Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(5): 1167-1179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205013.htm [7] 魏秀芹, 郭萌萌, 孙意博, 等. 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带栗园地区储层地质特征分析[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2015, 29(4): 31-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201504010.htmWEI Xiuqin, GUO Mengmeng, SUN Yibo, et al. Analysis of reservoir geological characteristics in Liyuan area of steep slope belt in southern Biyang depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2015, 29(4): 31-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201504010.htm [8] 龚银忠, 胡书奎, 沈祖吉, 等. 安棚深层系储层裂缝对开发的影响及对策[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2010, 24(5): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201005023.htmGONG Yinzhong, HU Shukui, SHEN Zuji, et al. The effect of Anpeng deep reservoir fracture to development and counter-measure[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2010, 24(5): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201005023.htm [9] 吕文雅, 曾联波, 周思宾, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部致密砂岩储层微观裂缝特征及控制因素: 以红河油田长8储层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(1): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202001004.htmLÜ Wenya, ZENG Lianbo, ZHOU Sibin, et al. Microfracture characteristics and its controlling factors in the tight oil sandstones in the southwest Ordos Basin: case study of the eighth member of the Yanchang Formation in Honghe Oilfield[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(1): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202001004.htm [10] 赵希, 张小莉, 杨振, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地樊学油区长8砂岩裂缝平面展布及控制因素[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(3): 667-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202103020.htmZHAO Xi, ZHANG Xiaoli, YANG Zhen, et al. The planar distribution and controlling factors of sandstone cracks in the Chang 8 reservoir, Fanxue oil district, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(3): 667-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT202103020.htm [11] 潇高健. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田长8段致密裂缝砂岩储层表征及"甜点油层"综合评价研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2022: 34-38.XIAO Gaojian. Characterization of tight fractured sandstone reservoir and comprehensive evaluation of "sweet spot reservoir" in Honghe Oilfield, Ordos Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2025: 34-38. [12] 尹帅, 丁文龙, 林利飞, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部志丹-吴起地区延长组裂缝特征及其控藏作用[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2614-2629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307013.htmYIN Shuai, DING Wenlong, LIN Lifei, et al. Characteristics and controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation of fractures in Yanchang Formation in Zhidan-Wuqi area, western Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2614-2629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307013.htm [13] 宿晓岑, 巩磊, 付晓飞, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三边地区延长组7段致密砂岩储层裂缝分布特征及有效性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2601-2613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307012.htmSU Xiaocen, GONG Lei, FU Xiaofei, et al. Fracture distribution characteristics and effectiveness evaluation of tight sandstone reservoir of Chang 7 member in Sanbian area, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2601-2613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307012.htm [14] 杨永利, 姜建伟, 卢小欧. 安棚油田深层系低渗透储层裂缝及其贡献[J]. 断块油气田, 2009, 16(5): 34-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200905013.htmYANG Yongli, JIANG Jianwei, LU Xiaoou. Deep low-permeability reservoir fractures and their contribution in Anpeng Oilfield[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2009, 16(5): 34-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200905013.htm [15] 李志明, 金芸芸, 李楚雄, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷渐新统核桃园组三Ⅲ亚段页岩油富集模式: 以中部深凹带YYY1井取心段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 952-962. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202305952LI Zhiming, JIN Yunyun, LI Chuxiong, et al. Discussion on shale oil enrichment pattern in the Ⅲ submember of the third member of Oligocene Hetaoyuan Formation, Biyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin: a case study of cored interval of well YYY1 in the central deep sag zone[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 952-962. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202305952 [16] 尹帅, 李爱荣, 陈梦娜, 等. 强变形区走滑断裂带伸展-聚敛应力效应构造解析及控气作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(11): 1568-1574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201811003.htmYIN Shuai, LI Airong, CHEN Mengna, et al. Stretch-convergence stress effect tectonic analysis and gas controlling of strike-slip fault zone in strong deformed zone[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(11): 1568-1574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201811003.htm [17] 刘敬寿, 丁文龙, 杨海盟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区天然裂缝与岩石力学层演化: 基于数值模拟的定量分析[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7): 2572-2588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307010.htmLIU Jingshou, DING Wenlong, YANG Haimeng, et al. Natural fractures and rock mechanical stratigraphy evaluation in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin: a quantitative analysis based on numerical simulation[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7): 2572-2588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202307010.htm [18] 李辉, 王峰, 王涛, 等. 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带砂砾岩体成藏模式分析[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 2006, 28(4): 239-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200604069.htmLI Hui, WANG Feng, WANG Tao, et al. Analysis on the model of sandstone and gravel rock formation in the steep slope zone in the south of Biyang Depression[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology (Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute), 2006, 28(4): 239-240. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX200604069.htm [19] 王国鹏, 郑浚茂, 樊中海, 等. 泌阳凹陷安棚鼻状构造的沉积成因及裂缝分布[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(2): 38-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200502007.htmWANG Guopeng, ZHENG Junmao, FAN Zhonghai, et al. Depositional genesis of Anpeng structural nose and fractures distributed in Anpeng deep zones[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(2): 38-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200502007.htm [20] 邱荣华, 付代国, 万力. 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带油气勘探实例分析[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(5): 605-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705012.htmQIU Ronghua, FU Daiguo, WAN Li. A case study of hydrocarbon exploration in the southern steep slope zone of the Biyang Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(5): 605-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200705012.htm [21] 周文, 闫长辉, 王洪辉, 等. 泌阳凹陷安棚油田核三段储层天然裂缝特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2003, 23(3): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200303012.htmZHOU Wen, YAN Changhui, WANG Honghui, et al. Study of characteristics of natural fracture in H3 reservoir of Miyang Sag, Anpeng oil field[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2003, 23(3): 57-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200303012.htm [22] 王子煜, 漆家福, 张永华. 泌阳凹陷新生代构造特征与形成机制及其与油气成藏的关系[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(3): 332-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200403005.htmWANG Ziyu, QI Jiafu, ZHANG Yonghua. Cenozoic structural characteristics and mechanism and their relationship with oil and gas reservoir in the Biyang Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(3): 332-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200403005.htm [23] 段心建, 冯士平, 陆建林, 等. 泌阳凹陷安棚深层储集层裂缝特征及勘探潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2002, 23(1): 30-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200201011.htmDUAN Xinjian, FENG Shiping, LU Jianlin, et al. The fracture characteristics and exploration potential of Anpeng deep reservoir in Miyang Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2002, 23(1): 30-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200201011.htm [24] 王振奇, 侯国伟, 张昌民, 等. 赵凹油田安棚区深层系低渗致密砂岩储层特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2001, 22(4): 372-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200104018.htmWANG Zhenqi, HOU Guowei, ZHANG Changmin, et al. Reservior characteristics of low permeable sandstones in deep level from Anpeng area, Zhaoao Oilfield[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2001, 22(4): 372-377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200104018.htm [25] 昝新. 泌阳凹陷南部陡坡带油气分布规律研究及勘探目标评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2008: 78-83.ZAN Xin. Oil and gas distribution and exploration target evaluation in the southern steep slope belt of Biyang Depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2008: 78-83. [26] 翁大丽, 赵跃华, 高孝田. 安棚深层系低渗透砂岩油藏裂缝研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 1999, 6(2): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ902.001.htmWONG Dali, ZHAO Yuehua, GAO Xiaotian. Study on fractures and fissures of low permeabilitysandstone reservoirs in Anpeng deep zone[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 1999, 6(2): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ902.001.htm -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号