Main controlling factors and exploration direction of gas reservoir in Jialingjiang Formation, Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 嘉陵江组是四川盆地天然气勘探的传统层系,近年来在川北、川西南等地区连续获得发现,但盆地内仍有大面积的勘探空白区,亟需深化对该层系天然气成藏规律的认识,明确成藏主控因素,进而指出未来的勘探方向。利用天然气地球化学等分析测试,结合构造恢复、盆地模拟等技术,以气源分析为基础,以典型气藏解剖为核心,结合对嘉陵江组成藏条件认识,通过对成藏过程的分析探讨了成藏主控因素,并建立了成藏模式。四川盆地嘉陵江组天然气主要来自下部的原油裂解气,嘉陵江组具有多套优质烃源岩供烃、发育多类型碳酸盐岩储层、通源断裂有效沟通气源的良好成藏条件,主生油期古构造、调整期构造及通源断裂、有利储层类型是嘉陵江组天然气成藏的主控因素;嘉陵江组具有“多源形成古油藏—古油藏裂解供气—通源断裂输导—晚期调整成藏”的成藏模式。基于此指出,分布于川西、川北等地区山前带,主生油期、气藏调整成藏期均处于相对高部位,发育通源断裂、保存条件较好的构造—岩性复合气藏是勘探的首选方向;分布于川东高陡构造带构造稳定区及向斜区的孔隙型岩性气藏是未来的主要勘探方向。Abstract: The Jialingjiang Formation is a traditional stratum for natural gas exploration in the Sichuan Basin, and in recent years it has been continuously discovered in northern and southwestern Sichuan, but there are still large areas of exploration blanks in the basin, which urgently needs to deepen the understanding of the natural gas accumulation law of this formation, clarify the main controlling factors of the accumulation, and then point out the exploration direction in the future. By using natural gas geochemistry and other analytical tests, combined with structural restoration, basin simulation and other technologies, based on gas source analysis, with typical gas reservoir anatomy as the core, combined with the understanding of the reservoir conditions of the Jialingjiang Formation, the main controlling factors of reservoir formation were discussed through the analysis of reservoir formation process, and the reservoir formation model was established. The results show that the natural gas of the Jialingjiang Formation is mainly cracked gas from crude oil in the lower part. The Jialingjiang Formation has good reservoir formation conditions such as multiple sets of high-quality source rocks supplying hydrocarbons, developing multiple types of carbonate reservoirs, and source-connected faults that effectively communicate gas sources. The paleostructures of the main oil generation period, the structures of the adjustment period, the source-connected faults, and the favorable reservoir types are the main controlling factors of the natural gas accumulation in the Jialingjiang Formation in the Sichuan Basin. The Jialingjiang Formation has an accumulation model of "multi-source charging to form ancient oil reservoirs, ancient oil reservoir cracking and supply gas, source-connected faults transport, and late adjustment accumulation". Based on this, it is proposed that the structural and litholo-gical composite gas reservoirs distributed in the piedmont belts of western and northern Sichuan, which are at relatively high positions during the main oil generation period and gas reservoir adjustment and accumulation period, have developed source-connecting faults, and have good preservation conditions, are the preferred exploration directions. The porous lithological gas reservoirs distributed in the structurally stable areas and syncline areas of the high and steep structural belts in eastern Sichuan are the main exploration directions in the future.
-
图 2 四川盆地嘉陵江组天然气成因类型与气源判识图
a.ln(C1/C2)与ln(C2/C3)相关图;b.碳同位素分布序列图;c.天然气成因类型划分(图版据文献[17]);d.天然气烃源分区
Figure 2. Genetic types and source identification of natural gas in Jialingjiang Formation, Sichuan Basin
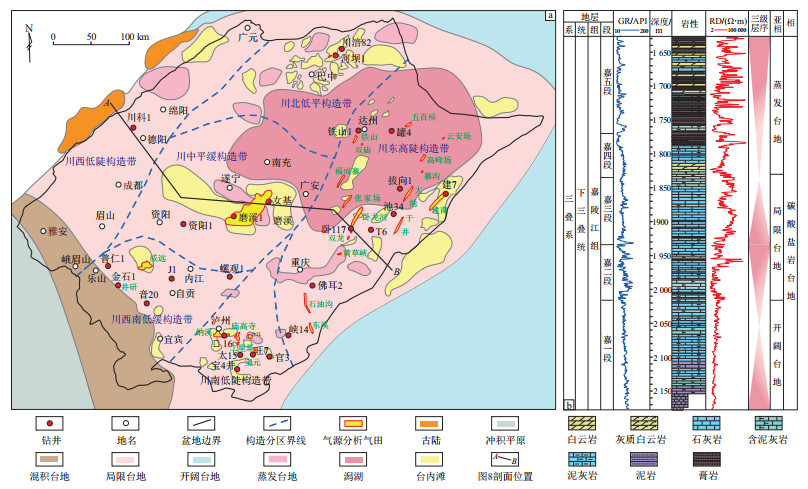
图 8 四川盆地嘉陵江组天然气成藏模式
剖面位置为图 1a中AB线。
图件据郭旭升等2023年“全国油气系统理论学术研讨会”报告修改。Figure 8. Accumulation pattern of natural gas of Jialingjiang Formation, Sichuan Basin
表 1 四川盆地嘉陵江组天然气组成对比
Table 1. Comparison of natural gas composition of Jialingjiang Formation, Sichuan Basin
地区 气田 烃类气体含量/% 干燥系数 非烃气体含量/% 组分碳同位素δ13C/‰ CH4 C2H6 C3H8 C4+ H2 N2 CO2 H2S CH4 C2H6 C3H8 川北 河坝场 97.379 0.212 0.019 0 0.998 0.010 2.700 0.719 0.742 -27.500 -26.400 -24.300 川东 大池干井 98.168 0.256 0.008 0.037 0.997 0.033 0.914 0.113 0.483 -30.528 -35.036 -34.000 川东 东溪 97.970 0.448 0.063 0.513 0.990 0 0.845 0.055 0.583 -30.430 -31.930 川东 福成寨 97.877 0.675 0.156 0.400 0.988 0.001 0.734 0.018 0.234 -33.485 -34.348 -28.854 川东 高峰场 96.978 0.245 0 0 0.997 0.004 0.524 0.412 1.817 -29.900 -34.200 -34.900 川东 黄草峡 98.015 0.684 0.132 0.218 0.989 0.155 0.611 0.096 0.265 -32.653 -36.051 -33.134 川东 建南 98.150 0.210 0.010 0.001 0.998 0 0.430 1.150 0.020 -32.400 -36.400 川东 石油沟 97.480 0.550 0.073 0.649 0.987 0.010 1.153 0.287 0.377 -31.460 -30.615 川东 双龙 98.488 0.476 0.089 0.036 0.994 0.011 0.585 0.068 0.217 -32.200 -30.700 -23.200 川东 双庙 97.970 0.350 0.010 0 0.996 0 1.500 0.120 0 -31.800 -31.700 川东 铁山 98.130 0.200 0.010 0.214 0.996 0 0.460 0 0.610 -31.670 -33.190 川东 卧龙河 94.558 1.002 0.399 0.213 0.985 0.161 0.811 0.396 3.576 -33.154 -29.326 -24.662 川东 五百梯 98.189 0.403 0.066 0.114 0.994 0 0.986 0 0.211 -32.400 -33.200 -27.700 川东 云安场 96.789 0.175 0 0 0.998 0.006 1.376 0.257 1.360 -28.400 -32.733 -30.700 川东 寨沟 95.828 0.313 0.017 0 0.997 0 0.654 0 3.162 -32.100 -32.100 -34.500 川东 张家场 98.738 0.358 0.038 0.219 0.994 0.017 0.545 0.160 0.096 -32.725 -34.680 -37.200 川南 二里场 96.340 0.660 0.135 0.010 0.992 0 2.550 0.080 0.035 -31.400 -33.550 -27.400 川南 合江 98.073 0.440 0.053 0 0.995 0 0.947 0.063 0.393 -29.833 -34.033 -29.500 川南 井研 93.770 2.460 0.763 0.830 0.959 0.020 1.607 0.493 0 川南 庙高寺 97.074 0.768 0.170 0.044 0.990 0 1.472 0.114 0.352 -31.300 -33.660 -29.825 川南 纳溪 93.743 2.533 0.903 0.623 0.958 0 1.203 0.110 0.010 -34.800 -32.767 -29.433 川南 威远 55.833 0.157 0 0.023 0.997 0 3.580 9.593 30.743 0 川中 磨溪 97.585 0.387 0.115 0 0.995 0.002 1.340 0.487 0.029 -33.400 -32.200 注:川北河坝场气田为自测数据,其他数据来自参考文献[4-5, 8, 12-16];表中数据均为平均值。 表 2 四川盆地北部主要烃源岩层热演化关键时期
Table 2. Critical moments of thermal evolution of major hydrocarbon rock layers, Sichuan Basin
烃源层 热演化关键时期/Ma Ro=0.5% Ro=1.2% Ro=2.0% Ro=3.0% 筇竹寺组 435 228 181 165 五峰组—龙马溪组 245 182 165 154 上二叠统 234 167 158 134 表 3 四川盆地嘉陵江组主要储层类型特征
Table 3. Characteristics of major reservoir types in Jialingjiang Formation, Sichuan Basin
储层类型 储层岩性 主要发育层段 沉积相带 储集空间类型 储层物性特征 储层厚度特征 典型代表气田 主要分布区域 孔隙型 粒屑白云岩、鲕粒灰岩、细晶白云岩 嘉二段 台内浅滩 晶间、晶内溶孔 孔隙度1%~8%,孔渗具有相关性 层状分布,但横向非均质性强 磨溪 川中地区 裂缝—孔隙复合型 细晶白云岩、鲕粒灰岩、生屑(砂屑) 灰岩及白云岩 嘉一、二、四、五段 云坪、台内浅滩 晶间溶孔及微裂缝 孔隙度1%~5%,渗透率受裂缝控制 层状分布,非均质性强,受断裂控制 井研、麻柳场、河坝场、宝元 川西南、川东南、川北等地区 裂缝型 砂屑灰岩、微粉晶白云岩 嘉二—五段 云坪、台内浅滩、灰坪等 裂缝、少量溶孔 孔隙度与渗透率相关性较差 受断裂控制明显 石油沟、卧龙河 川东、川南等构造较为复杂区域的背斜核部 表 4 四川盆地通南巴构造嘉陵江组二段主要钻井基本情况对比
Table 4. Comparison of basic conditions of major drilling wells in second member of Jialingjiang Formation in Tongnanba tectonic zone, Sichuan Basin
井号 钻探位置 嘉二段沉积环境 储层发育情况 通源断裂是否发育 解释结论 嘉二段测试情况 仁和1 仁和场构造 蒸发膏云坪 基本不发育储层 发育NW向通源断裂 干层 无 河坝1 河坝场构造 台内浅滩 发育裂缝—孔隙型储层 发育NW向通源断裂 气层 6.06×104 m3/d 母家1 母家梁构造 台内浅滩—膏云坪 孔隙—裂缝型储层,孔隙度0.58%~1.77% 发育NW向通源断裂 差气层 0.417 5×104 m3/d 马2 马路背构造 台内浅滩—膏云坪 储层较发育,孔隙度2%~8% 发育NWW向通源断裂 二类气层 微量气,高压水层 新黑池1 黑池梁高点 台内浅滩—膏云坪 发育砂屑白云岩储层 发育近EW向断裂 水层 微量气 -
[1] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293.ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. [2] 廖荣峰, 汤晶, 宋晓波, 等. 川西南下三叠统嘉陵江组四—五段孔隙型储层特征及勘探前景[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 60-70. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201060LIAO Rongfeng, TANG Jing, SONG Xiaobo, et al. Characteristics and exploration potential of porous reservoirs in 4th to 5th members of Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in southwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 60-70. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201060 [3] 刘善华, 金晓波, 胡永章, 等. 从川科1井看川西下三叠统勘探前景及目标[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2010, 33(4): 21-24.LIU Shanhua, JIN Xiaobo, HU Yongzhang, et al. Exploration prospect of Lower Triassic in western Sichuan Basin: an implication of Chuanke 1 well[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2010, 33(4): 21-24. [4] 左银辉, 文华国, 廖义沙, 等. 川东地区下三叠统嘉陵江组天然气特征及气源分析[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2021, 45(1): 62-72.ZUO Yinhui, WEN Huaguo, LIAO Yisha, et al. Natural gas characteristics and gas sources of the Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in the eastern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2021, 45(1): 62-72. [5] 庞崇友. 蜀南西部地区嘉陵江组天然气的运移与聚集条件研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油学院, 2005.PANG Chongyou. Study on migration and accumulation of natural gas in Jialingjiang Formation in western Shulan area[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2005. [6] 张本健, 裴森奇, 尹宏, 等. 川西南部嘉陵江组储层特征及主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(3): 80-83.ZHANG Benjian, PEI Senqi, YIN Hong, et al. Reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors of Jialingjiang Formation in southwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(3): 80-83. [7] 徐国盛, 何玉, 袁海锋, 等. 四川盆地嘉陵江组天然气藏的形成与演化研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(2): 171-178.XU Guosheng, HE Yu, YUAN Haifeng, et al. Study on the formation and evolution of gas accumulation in Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation of Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2011, 33(2): 171-178. [8] 孟昱璋. 四川盆地嘉陵江组岩相古地理与天然气成藏研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011.MENG Yuzhang. The lithofacies-paleogeographic and the natural gas accumulation of Jialingjiang Formation in Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2011. [9] 胡安平, 沈安江, 张杰, 等. 碳酸盐岩—膏盐岩高频沉积旋回组合生—储特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系马家沟组中—下组合为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4): 943-956.HU Anping, SHEN Anjiang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Source-reservoir characteristics of high-frequency cyclic carbonate-evaporite assemblages: a case study of the lower and middle assemblages in the Ordovician Majiagou Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 943-956. [10] 余海涛, 王兴志, 李斌, 等. 川东北地区嘉陵江组二段沉积相特征研究[J]. 海相油气地质, 2011, 16(3): 55-62.YU Haitao, WANG Xingzhi, LI Bin, et al. Sedimentation characteristics of Lower Triassic Jialingjiang 2nd member in northeast part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2011, 16(3): 55-62. [11] 吴可嘉. 川中磨溪地区下三叠统嘉陵江组储层研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2013.WU Kejia. The present study focuses on the reservoir of the Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in the Moxi area, located in central Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2013. [12] 龙胜祥, 郭彤楼, 刘彬, 等. 通江—南江—巴中构造河坝飞仙关组三段、嘉陵江组二段气藏形成特征研究[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(3): 338-345.LONG Shengxiang, GUO Tonglou, LIU Bin, et al. Gas-pool characteristics of the second section of the Jialingjiang Formation and the third section of the Feixianguan Formation in the Heba area of Tongjiang-Nanjiang-Bazhong structure belt, north Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(3): 338-345. [13] 黄士鹏, 廖凤蓉, 吴小奇, 等. 四川盆地含硫化氢气藏分布特征及硫化氢成因探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(5): 705-714.HUANG Shipeng, LIAO Fengrong, WU Xiaoqi, et al. Distribution characteristics of hydrogen sulphide-bearing gas pools and the genesis of hydrogen sulphide in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(5): 705-714. [14] 刘文汇, 腾格尔, 张中宁, 等. 四川盆地高硫天然气成藏机理的同位素研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2017, 47(2): 166-178.LIU Wenhui, TENGER, ZHANG Zhongning, et al. An isotope study of the accumulation mechanisms of high-sulfur gas from the Sichuan Basin, southwestern China[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2016, 59(11): 2142-2154. [15] NI Yunyan, LIAO Fengrong, DAI Jinxing, et al. Studies on gas origin and gas source correlation using stable carbon isotopes: a case study of the giant gas fields in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2014, 32(1): 41-74. [16] 戴金星. 天然气中烷烃气碳同位素研究的意义[J]. 天然气工业, 2011, 31(12): 1-6.DAI Jinxing. Significance of the study on carbon isotopes of alkane gases[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2011, 31(12): 1-6. [17] MILKOV A V. New approaches to distinguish shale-sourced and coal-sourced gases in petroleum systems[J]. Organic Geoche-mistry, 2021, 158: 104271. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2021.104271 [18] TANG Y, PERRY J K, JENDEN P D, et al. Mathematical modeling of stable carbon isotope ratios in natural gases[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(15): 2673-2687. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00377-X [19] LIU Quanyou, JIN Zhijun, LI Jian, et al. Origin of marine sour natural gas and gas-filling model for the Wolonghe gas field, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 58: 24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.07.007 [20] 李海平. 蜀南地区茅口组与嘉陵江组天然气成因与来源及运聚模式[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020.LI Haiping. Genetic, sources and transportation and accumulation patterns of natural gas in the Maokou and Jialingjiang Formations in southern Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2020. [21] 张涛. 川中磨溪—高石梯地区天然气成藏过程研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2017.ZHANG Tao. The research of accumulation process of the natural gas from Moxi-Gaoshiti area in the central of Sichuan Basin[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2017. [22] 李延钧, 梁艳, 雷卞军, 等. 川中—川南过渡带西部嘉二段天然气成因与来源[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(6): 820-823.LI Yanjun, LIANG Yan, LEI Bianjun, et al. Natural gas genesis for the section Ⅱ of west Jialingjiang Formation in middle Sichuan-south Sichuan transitional belt[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2006, 17(6): 820-823. [23] 董才源, 谢增业, 朱华, 等. 川中地区中二叠统气源新认识及成藏模式[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(4): 18-23.DONG Caiyuan, XIE Zengye, ZHU Hua, et al. New insight for gas source and gas accumulation modes of Middle Permian in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 32(4): 18-23. [24] 洪太元, 程喆, 许华明, 等. 四川盆地大中型气田形成的主控因素及勘探对策[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 406-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103406HONG Taiyuan, CHENG Zhe, XU Huaming, et al. Controlling factors and countermeasures for exploring large and medium-sized gas fields in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 406-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103406 [25] 杨雨, 罗冰, 张本健, 等. 四川盆地下寒武统筇竹寺组烃源岩有机质差异富集机制与天然气勘探领域[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(4): 611-619. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104611YANG Yu, LUO Bing, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Differential mechanisms of organic matter accumulation of source rocks in the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation and implications for gas exploration fields in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(4): 611-619. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104611 [26] 刘华. 四川盆地麻柳场气田嘉陵江组气藏描述[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2006.LIU Hua. Gas reservoir description of Jialingjiang Formation, Maliuchang Gas Field, Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2006. [27] 林雄. 四川盆地三叠系嘉陵江组沉积—成岩特征与孔隙演化关系研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011.LIN Xiong. Study on the relationship between reservoirs rocks characteristics and sedimentary-diagenesis evolution of Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2011. [28] 四川油气区石油地质志编写组. 中国石油地质志(卷十): 四川油气区[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1989.Editorial Committee of Petroleum Geology of Sichuan Oil and Gas Field. Petroleum geology of China(vol. 10): Sichuan oil and gas field[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1989. [29] 王国刚, 苏培东, 秦启荣. 罗家寨构造嘉陵江组嘉四2段底部裂缝预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(4): 82-86.WANG Guogang, SU Peidong, QIN Qirong. The crack prediction of T1j42 bottom of Luojiazhai structure[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(4): 82-86. [30] 乔占峰, 李国蓉, 李弢, 等. 泸州古隆起地区嘉陵江组层序特征及其对碳酸盐岩储层的控制[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(1): 92-99.QIAO Zhanfeng, LI Guorong, LI Tao, et al. Sequence-stratigraphic features and their controls on carbonate reservoirs for the Triassic Jialingjiang Formation of the Luzhou paleohigh in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(1): 92-99. [31] 李弢, 赵路子, 陆正元, 等. 川南地区嘉陵江组天然气气源研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(12): 9-11.LI Tao, ZHAO Luzi, LU Zhengyuan, et al. Research on the gas source of Jialingjiang Formation in south Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(12): 9-11. [32] 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 2011, 46(3): 589-606.HE Dengfa, LI Desheng, ZHANG Guowei, et al. Formation and evolution of multi-cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2011, 46(3): 589-606. [33] 谢增业, 田世澄, 魏国齐, 等. 川东北飞仙关组储层沥青与古油藏研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(3): 283-288.XIE Zengye, TIAN Shicheng, WEI Guoqi, et al. The study on bitumen and foregone pool of Feixianguan oolitic in northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(3): 283-288. [34] 郭彤楼. 川东北地区碳酸盐岩层系孔隙型与裂缝型气藏成藏差异性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(3): 311-317.GUO Tonglou. Differences in reservoir-forming between porous and fractured gas pools in carbonates, the northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(3): 311-317. [35] 胡安平, LI Maowen, 杨春, 等. 川东北高含硫化氢气藏中储层沥青的特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(2): 231-236.HU Anping, LI Maowen, YANG Chun, et al. Characteristics of reservoir bitumen in Puguang and Maoba gas fields with high H2S content in north-eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(2): 231-236. [36] 何治亮, 陆建林, 林娟华, 等. 中国海相盆地原型—改造分析与油气有序聚集模式[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(6): 60-72.HE Zhiliang, LU Jianlin, LIN Juanhua, et al. Marine basins in China: a prototype-reconstruction analyses and ordered hydrocarbon accumulation patterns[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(6): 60-72. [37] 陆正元, 赵路子, 李弢. 四川盆地南部嘉陵江组烃源研究[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 31(6): 720-722.LU Zhengyuan, ZHAO Luzi, LI Tao. Study on hydrocarbon sources of Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in south of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2004, 31(6): 720-722. [38] 赵永刚, 陈景山, 雷卞军, 等. 川中川南过渡带嘉二段成藏条件及主控因素[J]. 西南石油学院学报, 2006, 28(6): 9-12.ZHAO Yonggang, CHEN Jingshan, LEI Bianjun, et al. Jia-2 member gas reservoir forming conditions and the main controlling factors in the central-south Sichuan transitional zone[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2006, 28(6): 9-12. [39] 胡安平, 陈汉林, 杨树峰, 等. 卧龙河气田天然气成因及成藏主要控制因素[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(5): 643-649.HU Anping, CHEN Hanlin, YANG Shufeng, et al. Origin of natural gas and main controlling factors of reservoirs in Wolonghe gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(5): 643-649. [40] 陆正元, 栾海波, 吕宗刚, 等. 四川盆地南部嘉陵江组天然气远源成藏模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(6): 617-620.LU Zhengyuan, LUAN Haibo, LV Zonggang, et al. Study on the distal gas accumulation model of the Lower Triassic Jialingjiang Formation in the south of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2009, 36(6): 617-620. [41] 付广, 吕延防, 于丹. 中国大中型气田天然气聚集效率及其主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(6): 754-759.FU Guang, LV Yanfang, YU Dan. Gas accumulation efficiency and its main controlling factors in China's large and medium gas fields[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(6): 754-759. [42] 孙春燕, 胡明毅, 胡元伟. 鄂西—渝东地区嘉陵江组碳酸盐岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(29): 57-68.SUN Chunyan, HU Mingyi, HU Yuanwei. Characteristics and controlling factors of the carbonate reservoir of Jialingjiang Formation in western Hubei-eastern Chongqing area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(29): 57-68. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号