Sedimentary environment and oil-bearing characteristics of shale in Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin
-
摘要: 松辽盆地上白垩统青山口组页岩地层厚度大、分布广泛,有机质丰度高,蕴含了丰富的页岩油资源。对页岩地层形成时沉积环境的研究,以及对页岩油富集层段含油性特征的探索,可为页岩油富集层段与甜点的预测提供理论依据。结合前人的研究成果,通过对比松辽盆地中央坳陷区不同凹陷的2口典型井——古龙凹陷GY8HC井和三肇凹陷ZY1井部分样品的总有机碳(TOC)含量、热解数据、有机显微组分类型以及主、微量元素,深入研究了2个凹陷青山口组页岩的含油性差异与沉积环境特征,进而对含油性差异的影响因素进行了分析。研究区青山口组2口典型井的页岩含油性相关指标显示,ZY1井页岩TOC含量显著高于GY8HC井,但其游离烃含量与含油饱和度指数比GY8HC井低。页岩形成时的地球化学环境控制着有机质的富集。对比2口井样品的主、微量元素发现,ZY1井青山口组沉积时期气候更加湿润、水体还原性强,且其古生产力以及古水深要显著高于GY8HC井。这些条件都有利于有机质的保存,因而形成了ZY1井页岩更高的有机质丰度。GY8HC井有机质类型是以腐泥质为主的Ⅰ型干酪根,且处于成熟—高成熟阶段;而ZY1井有机质类型以Ⅱ1型干酪根为主,Ⅰ型含量较少,并处于低熟—成熟阶段,因此,GY8HC井页岩的生油潜力更好。Abstract: The Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Songliao Basin contains thick, widespread, and organic matter-rich shale layers, offering abundant shale oil resources. Studying the sedimentary environment during shale formation and exploring the oil-bearing characteristics of shale oil enrichment intervals provide a theoretical basis for the prediction of the intervals and sweet spots. Based on previous research, the study compared organic carbon content, pyrolysis data, types of organic macerals, and major and trace elements of samples from two typical wells of different sags, well GY8HC in the Gulong Sag and well ZY1 in the Sanzhao Sag, in the central depression zone of the Songliao Basin. The analysis delved into the differences in oil-bearing characteristics and sedimentary environment of the Qingshankou Formation shales in two different sags, further analyzing the factors influencing these differences. The oil-bearing indicators of shales from the two wells in the Qingshankou Formation of the Songliao Basin showed that the total organic carbon (TOC) content in well ZY1 was significantly higher than that in well GY8HC. However, the free hydrocarbon content (S1) and oil saturation index (OSI) in well ZY1 were lower than those in well GY8HC. The geochemical environment during shale formation controlled organic matter enrichment. Comparing major and trace elements in samples from both wells, it was found that the climate in well ZY1 was more humid during its sedimentary period, the water body had stronger reducing conditions, and its paleoproductivity and paleo-water depth were significantly higher than those in well GY8HC. These conditions were favorable for the preservation of organic matter, thereby forming a higher organic matter abundance in the shale of well ZY1. In addition, it was found that the organic matter type in well GY8HC is mainly Type Ⅰ, sapropelic kerogen, at a mature to highly mature stage, whereas well ZY1 contains mainly Type Ⅱ1 kerogen, with less Type Ⅰ, at a low to mature stage. Therefore, the shale in well GY8HC possesses better oil generation potential.
-
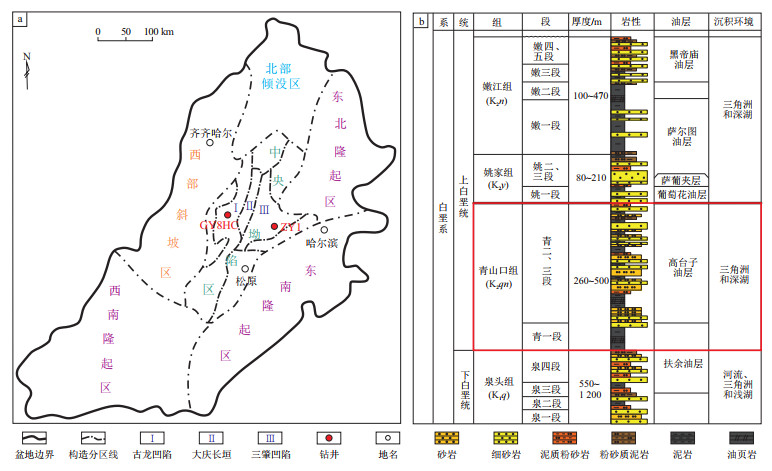
图 1 松辽盆地构造单元划分(a)及其地层综合柱状图(b)
据参考文献[13]修改。
Figure 1. Tectonic unit division of Songliao Basin (a) and comprehensive stratigraphic column (b)
图 7 松辽盆地白垩系青山口组页岩有机显微组分与古生物镜下照片
a.深灰色富有机质黏土质页岩,反射荧光(蓝光激发),沥青质体(B)中偶见小孢子体(MiS),2 525.6 m,GY8HC井;b.纹层状钙质页岩,反射荧光(蓝光激发),矿物沥青基质(MB)中见藻类体(Alg)富集分布,2 481.5 m,GY8HC井;c.油浸,反射单偏光下黏土矿物(Cl)基底中见沥青质体充填于岩石孔隙中,黄铁矿(Py)呈团粒状分布,2 021.1 m,ZY1井;d.深灰色页岩,反射荧光(蓝光激发),小孢子体大致平行层面分布,1 987.6 m,ZY1井;e.油浸,反射单偏光下黏土矿物基底中见镜质体(V)破碎呈条带状,碎屑惰质体(ID)零散分布,黄铁矿团粒易见,1 964.6 m,ZY1井;f.油浸,反射单偏光下黏土矿物基底中见丝质体(F)破碎呈不规则块状,沥青质体充填于裂隙中或吸附于黏土矿物中,黄铁矿团粒易见,2 026.1 m,ZY1井;g.生物介壳灰岩,椭圆形生物介壳杂乱分布,1 955.61 m,ZY1井;h.纹层状黏土质页岩,反射荧光(蓝光激发),矿物沥青基质中见藻类体富集呈层状分布,小孢子体呈蠕虫状,2 476 m,GY8HC井;i.黏土质页岩,反射荧光(蓝光激发),矿物沥青基质中见小孢子体呈蠕虫状大致平行层面分布,藻类体呈椭球状,2 384.17 m,GY8HC井。
Figure 7. Microscopic photographs of organic macerals and microfossils in shale of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin
表 1 松辽盆地2口井白垩系青山口组页岩含油性特征对比
Table 1. Comparison of oil-bearing characteristics of shale in Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation from two wells in Songliao Basin
井号 深度/m 层段 ω(TOC)/% S1/(mg/g) OSI/(mg/g) ZY1 2 020.1~2 050.1 Ⅰ $\frac{0.39 \sim 8.32}{3.72} $ $\frac{0.15 \sim 17.40}{8.01} $ $\frac{37.76 \sim 379.76}{208.78} $ 1 920.6~2 020.1 Ⅱ $\frac{0.47 \sim 4.96}{2.21} $ $\frac{0.26 \sim 9.53}{2.96} $ $\frac{35.94 \sim 555.99}{137.70} $ GY8HC 2 460.8~2 532.8 Ⅰ $\frac{0.55 \sim 3.74}{1.75} $ $\frac{0.31 \sim 12.18}{5.54} $ $\frac{56.86 \sim 482.09}{310.28} $ 2 340.8~2 460.8 Ⅱ $\frac{0.29 \sim 2.95}{1.36} $ $\frac{0.64 \sim 8.54}{4.17} $ $\frac{147.14 \sim 528.11}{302.75} $ 注:表中分式意义为$\frac{最小值 \sim 最大值}{平均值} $。 -
[1] 柳波, 吕延防, 冉清昌, 等. 松辽盆地北部青山口组页岩油形成地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(2): 280-285.LIU Bo, LÜ Yanfang, RAN Qingchang, et al. Geological conditions and exploration potential of shale oil in Qingshankou Formation, northern Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(2): 280-285. [2] 康淑娟, 仰云峰, 王华建, 等. 松辽盆地中央坳陷区三肇凹陷上白垩统青山口组一段页岩含油性特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(1): 89-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301089KANG Shujuan, YANG Yunfeng, WANG Huajian, et al. Oil - bearing capacity of shale in the first member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Sanzhao Sag, Central Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(1): 89-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301089 [3] 何文渊, 蒙启安, 张金友. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油富集主控因素及分类评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(5): 1-12.HE Wenyuan, MENG Qi'an, ZHANG Jinyou. Controlling factors and their classification-evaluation of Gulong shale oil enrichment in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. [4] 高波, 何文渊, 冯子辉, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩岩性、物性、含油性特征及控制因素[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2022, 41(3): 68-79.GAO Bo, HE Wenyuan, FENG Zihui, et al. Lithology, physical property, oil-bearing property and their controlling factors of Gulong shale in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(3): 68-79. [5] 卢双舫, 黄文彪, 陈方文, 等. 页岩油气资源分级评价标准探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2): 249-256.LU Shuangfang, HUANG Wenbiao, CHEN Fangwen, et al. Classification and evaluation criteria of shale oil and gas resources: discussion and application[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2): 249-256. [6] 侯启军, 冯子辉, 邹玉良. 松辽盆地齐家—古龙凹陷油气成藏期次研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2005, 27(4): 390-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200504390HOU Qijun, FENG Zihui, ZOU Yuliang. Study on the pool-forming periods of oil and gas in Qijia-Gulong Sag in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2005, 27(4): 390-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200504390 [7] 周卓明. 陆相泥页岩源—储协同演化特征分析: 以松辽盆地长岭断陷沙河子组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 243-251. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302243ZHOU Zhuoming. Co-evolution characteristics of organic matter and reservoir in continental shale: a case study of Shahezi Formation in Changling Faulted Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 243-251. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302243 [8] 柳波, 石佳欣, 付晓飞, 等. 陆相泥页岩层系岩相特征与页岩油富集条件: 以松辽盆地古龙凹陷白垩系青山口组一段富有机质泥页岩为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5): 828-838.LIU Bo, SHI Jiaxin, FU Xiaofei, et al. Petrological characteristics and shale oil enrichment of lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary system: a case study of organic-rich shale in first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 828-838. [9] 王岚, 曾雯婷, 夏晓敏, 等. 松辽盆地齐家—古龙凹陷青山口组黑色页岩岩相类型与沉积环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(8): 1125-1133.WANG Lan, ZENG Wenting, XIA Xiaomin, et al. Study on lithofacies types and sedimentary environment of black shale of Qingshankou Formation in Qijia-Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(8): 1125-1133. [10] 杨建国, 李士超, 姚玉来, 等. 松辽盆地北部上白垩统青山口组一段页岩油战略调查成果综述[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(3): 232-238.YANG Jianguo, LI Shichao, YAO Yulai, et al. Strategic survey results of shale oil in the first member of Qingshankou Formation, Upper Cretaceous in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(3): 232-238. [11] 孙龙德, 刘合, 何文渊, 等. 大庆古龙页岩油重大科学问题与研究路径探析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 453-463.SUN Longde, LIU He, HE Wenyuan, et al. An analysis of major scientific problems and research paths of Gulong shale oil in Daqing Oilfield, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 453-463. [12] ZHOU Yongsheng, LITTKE R. Numerical simulation of the thermal maturation, oil generation and migration in the Songliao Basin, Northeastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1999, 16(8): 771-792. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(99)00043-4 [13] FENG Zhiqiang, JIA Chengzao, XIE Xinong, et al. Tectonostratigraphic units and stratigraphic sequences of the nonmarine Songliao Basin, Northeast China[J]. Basin Research, 2010, 22(1): 79-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2009.00445.x [14] 付丽, 梁江平, 白雪峰, 等. 松辽盆地北部中浅层石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 23-32.FU Li, LIANG Jiangping, BAI Xuefeng, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential, and exploration direction of oil of middle-shallow layers in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 23-32. [15] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 沉积岩中总有机碳测定: GB/T 19145-2022[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022.State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration. Determination for total organic carbon in sedimentary rock: GB/T 19145-2022[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022. [16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 岩石热解分析: GB/T 18602—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Rock pyrolysis analysis: GB/T 18602-2012[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硅酸盐岩石化学分析方法第30部分: 44个元素量测定: GB/T 14506.30—2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Methods for chemical analysis of silicate rocks—Part 30: Determination of 44 elements: GB/T 14506.30-2010[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011. [18] 国家能源局. 透射光—荧光干酪根显微组分鉴定及类型划分方案: SY/T 5125-2014[S]. 北京: 中国石油天然气集团公司, 2014.National Energy Administration. Method of identification microscopically the macerals of kerogen and indivision the kerogen type by transmitted-light and fluorescence: SY/T 5125-2014[S]. Beijing: China National Petroleum Corporation, 2014. [19] HUNT J M. Distribution of hydrocarbons in sedimentary rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1961, 22(1): 37-49. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(61)90071-0 [20] 柳广弟. 石油地质学[M]. 5版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2018.LIU Guangdi. Petroleum geology[M]. 5th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2018. [21] LI Jinbu, JIANG Chunqing, WANG Min, et al. Adsorbed and free hydrocarbons in unconventional shale reservoir: a new insight from NMR T1-T2 maps[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 116: 104311. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104311 [22] 何文渊, 柳波, 张金友, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油地质特征及关键科学问题探索[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(1): 49-62.HE Wenyuan, LIU Bo, ZHANG Jinyou, et al. Geological characteristics and key scientific and technological problems of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(1): 49-62. [23] 焦方正, 邹才能, 杨智. 陆相源内石油聚集地质理论认识及勘探开发实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1067-1078.JIAO Fangzheng, ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi. Geological theory and exploration & development practice of hydrocarbon accumulation inside continental source kitchens[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1067-1078. [24] 朱国文, 王小军, 张金友, 等. 松辽盆地陆相页岩油富集条件及勘探开发有利区[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(1): 110-124.ZHU Guowen, WANG Xiaojun, ZHANG Jinyou, et al. Enrichment conditions and favorable zones for exploration and development of continental shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 110-124. [25] ZHANG Kun, LIU Rong, LIU Zhaojun, et al. Influence of volcanic and hydrothermal activity on organic matter enrichment in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, southern Ordos Basin, Central China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 112: 104059. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104059 [26] TRIBOVILLARD N, ALGEO T J, LYONS T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12-32. [27] MORFORD J L, EMERSON S. The geochemistry of redox sensitive trace metals in sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(11/12): 1735-1750. [28] CHEN Ruiqian, SHARMA S. Linking the Acadian Orogeny with organic-rich black shale deposition: evidence from the Marcellus shale[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 79: 149-158. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.11.005 [29] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford, England: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985. [30] 韦恒叶. 古海洋生产力与氧化还原指标: 元素地球化学综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(2): 76-88.WEI Hengye. Productivity and redox proxies of palaeo-oceans: an overview of elementary geochemistry[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2012, 32(2): 76-88. [31] 徐波, 刁慧, 王宁, 等. 东海盆地丽水凹陷古新统微量元素地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(12): 64-74.XU Bo, DIAO Hui, WANG Ning, et al. Geochemical characteristics and indicative significance of trace elements in the Paleocene in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(12): 64-74. [32] COUCH E L. Calculation of paleosalinities from boron and clay mineral data[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1971, 55(10): 1829-1837. [33] VAHRENKAMP V C, SWART P K. New distribution coefficient for the incorporation of strontium into dolomite and its implications for the formation of ancient dolomites[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(5): 387-391. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<0387:NDCFTI>2.3.CO;2 [34] JIA Jianliang, BECHTEL A, LIU Zhaojun et al. Oil shale formation in the Upper Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation of the Songliao Basin (NE China): implications from organic and inorganic geochemical analyses[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2013, 113: 11-26. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.03.004 [35] 白静, 徐兴友, 陈珊, 等. 松辽盆地长岭凹陷乾安地区青山口组一段沉积相特征与古环境恢复: 以吉页油1井为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 220-235.BAI Jing, XU Xingyou, CHEN Shan, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and paleo-environment restoration of the first member of Qingshankou Formation in Qian'an area, Changling Sag, Songliao Basin: a case study of Jiyeyou 1 well[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 220-235. [36] WIGNALL P B, TWITCHETT R J. Oceanic anoxia and the end Permian mass extinction[J]. Science, 1996, 272(5265): 1155-1158. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5265.1155 [37] WERNE J P, SAGEMAN B B, LYONS T W, et al. An integrated assessment of a "type euxinic" deposit: evidence for multiple controls on black shale deposition in the Middle Devonian Oatka Creek Formation[J]. American Journal of Science, 2002, 302(2): 110-143. doi: 10.2475/ajs.302.2.110 [38] JONES B, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129. [39] 吴智平, 周瑶琪. 一种计算沉积速率的新方法: 宇宙尘埃特征元素法[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 395-399.WU Zhiping, ZHOU Yaoqi. Using the characteristic elements from meteoritic must in strata to calculate sedimentation rate[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3): 395-399. [40] 申家年, 王庆红, 何江林, 等. 松辽盆地白垩纪湖泊水体温度与古气候温度估算[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(6): 946-952.SHEN Jianian, WANG Qinghong, HE Jianglin, et al. Estimation of the ancient lake temperature and paleo-climate of the Cretaceous period in the Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2008, 38(6): 946-952. [41] 贾云倩, 刘子平, 任晓海, 等. 有机质类型分异规律及其主控机制: 以威远志留系龙马溪组页岩储层为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(2): 341-352.JIA Yunqian, LIU Ziping, REN Xiaohai, et al. Organic matter type differentiation process and main control mechanism: case study of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale reservoir in Weiyuan area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(2): 341-352. [42] 焦淑静, 张慧, 薛东川, 等. 泥页岩有机显微组分的扫描电镜形貌特征及识别方法[J]. 电子显微学报, 2018, 37(2): 137-144.JIAO Shujing, ZHANG Hui, XUE Dongchuan, et al. Morphological structure and identify method of organic macerals of shale with SEM[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2018, 37(2): 137-144. [43] KHAN I, ZHONG Ningning, LUO Qingyong, et al. Maceral composition and origin of organic matter input in Neoproterozoic-Lower Cambrian organic-rich shales of Salt Range Formation, upper Indus Basin, Pakistan[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2020, 217: 103319. [44] BASKIN D K. 利用干酪根H/C比评价烃源岩热成熟度与生烃潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2002, 13(5/6): 41-49.BASKIN D K. Atomic H/C ratio of kerogen as an estimate of thermal maturity and organic matter conversion[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2002, 13(5/6): 41-49. [45] 李国雄, 刘成林, 王飞龙, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷东营组烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃模式[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(11): 1568-1584.LI Guoxiong, LIU Chenglin, WANG Feilong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon generation mode of source rocks of Dongying Formation in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(11): 1568-1584. [46] 张水昌, 张斌, 王晓梅, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油富集机制与常规—非常规油有序分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(5): 911-923.ZHANG Shuichang, ZHANG Bin, WANG Xiaomei, et al. Gulong shale oil enrichment mechanism and orderly distribution of conventional-unconventional oils in the Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(5): 911-923. -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号