Discussion on the uniformity of shale oil and gas in China
-
摘要: 页岩油气是我国重要的油气战略资源,具有赋存于页岩层系中、自生自储的特征。2012年我国涪陵页岩气获得突破,形成了海相页岩气“二元富集”理论,即深水陆棚优质泥页岩发育是页岩气“成烃控储”的基础,良好的保存条件是页岩气“成藏控产”的关键。近年来,页岩油高效勘探开发实践表明,我国陆相页岩油同样具有“二元富集”特征。通过解剖我国典型页岩油气藏特征,将页岩油气纳入同一套成烃、成储、成藏体系中,进一步深化页岩油气“二元富集”理论内涵,形成页岩油气富集统一性新认识,并对未来深化研究趋势进行展望。研究表明:①以半深水—深水陆棚相和半深湖—深湖相为主的沉积环境是页岩油气成烃控储的基础,不仅控制着页岩的有机质丰度与类型,也控制着优质储层和有利岩相组合的分布;②稳定的构造条件、有效的顶底板封盖和页岩自封闭性共同形成的以地层超压为依据的良好的保存条件是页岩油气成藏控产的关键,为页岩油气的富集与高产提供关键保障;③页岩油气形成与富集是一个统一的动态演化体系,以热演化为主线,有序形成页岩油、凝析油和页岩气;④今后研究中重点加强常非一体化的评价思路,深化常非油气资源的分配系数,从整体的角度思考油气的分配规律。相关研究成果对深化页岩油气富集理论和指导页岩油气勘探开发具有重要的科学与实践意义。Abstract: Shale oil and gas are important strategic resources in China's energy sector, existing in shale formations with self-generation and self-storage characteristics. In 2012, a significant breakthrough was achieved in Fuling, China, with the discovery of marine shale gas, which led to the formulation of the "two-factor enrichment" theory. This theory proposes that the development of high-quality mud shale in deep-water continental shelves is fundamental for hydrocarbon generation and controlled storage, while favorable preservation conditions are key to reservoir formation and controlled production. Recent efficient exploration and development practices in shale oil and gas have indicated that China's continental shale oil also exhibits "two-factor enrichment" characteristics. By analyzing the characteristics of typical shale oil and gas reservoirs in China, this study incorporates shale oil and gas into a unified system of hydrocarbon formation, storage, and accumulation, further deepening the theoretical connotation of the "two-factor enrichment" theory and forming a new understanding of the uniformity in shale oil and gas enrichment. Future research trends are also explored. Results show that: (1) Sedimentary environments dominated by semi-deep to deep-water continental shelves and semi-deep to deep lakes are the basis for hydrocarbon generation and controlled storage, controlling both the abundance and type of organic matter in shales as well as the distribution of high-quality reservoirs and favorable lithofacies combinations. (2) Stable tectonic conditions, effective top and bottom seals, and self-sealing properties of shale, in conjunction with overpressure, provide good preservation conditions that are crucial for reservoir formation and controlled production, providing key guarantees for the enrichment and high production of shale oil and gas. (3) The formation and enrichment of shale oil and gas are part of a unified dynamic evolutionary system, with thermal evolution as the main driver, following the sequential formation of shale oil, condensate oil, and shale gas. (4) Future study should focus on strengthening the integrated evaluation of conventional and non-conventional resources, deepening the understanding of distribution coefficients for conventional and non-conventional oil and gas, and considering the distribution patterns of oil and gas from a holistic perspective. The research results have important scientific and practical significance for deepening the theory of shale oil and gas enrichment and guiding their exploration and development.
-
图 2 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组生物硅格架原生孔内残余液态烃裂解形成的有机质孔
a.放大1 000倍,见生物硅格架;b.放大4 000倍,生物硅格架形态保留完好;c.放大8 000倍,生物硅格架进一步放大;d.放大12 000倍,生物硅格架发育非常丰富的原生粒间孔隙;e.放大50 000倍,生物硅格架原生孔全部充填有机质;f.放大100 000倍,滞留液态烃形成的有机质孔。
Figure 2. Organic matter pores formed by cracking of residual liquid hydrocarbons in primary pores of biogenic silica frameworks in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Sichuan Basin
图 3 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷沙三下亚段富有机质页岩沉积岩相空间分布模式示意[25]
Figure 3. Spatial distribution of organic-rich shale sedimentary facies in lower sub-member of the 3rd member of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
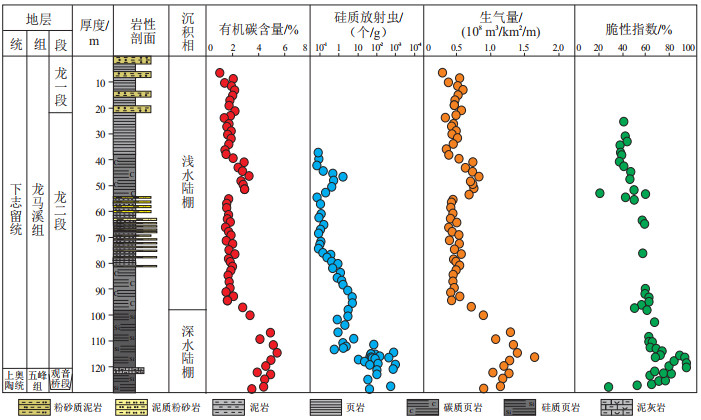
图 6 四川盆地典型井五峰组—龙马溪组页岩储层孔隙特征
a.焦页2井,2 575 m,有机质孔发育,孔隙保存良好;b.东页深1井,4 278 m,有机质孔发育,孔隙保存良好;c.民页1井,3 103 m,有机质孔不发育,孔隙保存较差;d.焦页2井页岩孔径分布图,孔隙以中孔为主;e. 东页深1井页岩孔径分布图,孔隙以中孔为主;f.民页1井页岩孔径分布图,孔隙以小孔为主。
Figure 6. Pore characteristics of shale reservoirs in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in typical wells of Sichuan Basin
图 8 我国不同盆地富有机质泥页岩不同热演化阶段孔隙发育特征
a-b.渤海湾盆地,沙三下亚段—沙四上亚段,利页1井,Ro为0.72%~0.85%;c.苏北盆地,阜二段,花页1井,Ro为0.85%~1.05%;d.四川盆地,东岳庙段,兴页1井,Ro为1.43%~1.62%;e.四川盆地,凉高山组,忠1井,Ro为1.28%~1.45%;f.四川盆地,凉高山组,兴页2井,Ro为1.25%~1.47%;g.四川盆地,五峰组—龙马溪组,东页深1井,Ro为2.59%~2.87%。
Figure 8. Pore development characteristics of organic-rich mud shales at different thermal evolution stages in various basins in China
表 1 中国陆相页岩油气藏特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters of continental shale oil and gas reservoirs in China
关键参数 典型地区及层位 济阳古近系沙河街组 长庆三叠系延长组 大庆白垩系青山口组 复兴侏罗系凉高山组 埋藏深度/m 3 000~4 200 1 500~2 900 2 000~2 700 2 000~3 000 成熟度Ro/% 0.7~1.0 0.75~1.2 1.2~1.7 1.2~1.7 原油密度/(g/cm3) 0.83~0.88 0.80~0.86 0.77~0.83 0.75~0.79 气油比/(m3/t) 60~1 200 60~120 50~2 000 1 303~2 124 压力系数 1.2~1.8 0.77~0.84 1.2~1.6 1.2~1.9 原油样品 



-
[1] 邹才能, 杨智, 王红岩, 等. "进源找油": 论四川盆地非常规陆相大型页岩油气田[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(7): 1551-1562.ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, WANG Hongyan, et al. "Exploring petroleum inside source kitchen": Jurassic unconventional continental giant shale oil & gas field in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(7): 1551-1562. [2] 黎茂稳, 马晓潇, 金之钧, 等. 中国海、陆相页岩层系岩相组合多样性与非常规油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 1-25.LI Maowen, MA Xiaoxiao, JIN Zhijun, et al. Diversity in the lithofacies assemblages of marine and lacustrine shale strata and significance for unconventional petroleum exploration in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 1-25. [3] 郭旭升, 马晓潇, 黎茂稳, 等. 陆相页岩油富集机理探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1333-1349.GUO Xusheng, MA Xiaoxiao, LI Maowen, et al. Mechanisms for lacustrine shale oil enrichment in Chinese sedimentary basins[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1333-1349. [4] 李志明, 刘雅慧, 何晋译, 等. 陆相页岩油"甜点"段评价关键参数界限探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1453-1467.LI Zhiming, LIU Yahui, HE Jinyi, et al. Limits of critical parameters for sweet spot interval evaluation of lacustrine shale oil[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1453-1467. [5] 赵文智, 胡素云, 侯连华, 等. 中国陆相页岩油类型、资源潜力及与致密油的边界[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(1): 1-10.ZHAO Wenzhi, HU Suyun, HOU Lianhua, et al. Types and resource potential of continental shale oil in China and its boundary with tight oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 1-10. [6] 金之钧, 朱如凯, 梁新平, 等. 当前陆相页岩油勘探开发值得关注的几个问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(6): 1276-1287.JIN Zhijun, ZHU Rukai, LIANG Xinping, et al. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6): 1276-1287. [7] 胡素云, 白斌, 陶士振, 等. 中国陆相中高成熟度页岩油非均质地质条件与差异富集特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(2): 224-237.HU Suyun, BAI Bin, TAO Shizhen, et al. Heterogeneous geolo-gical conditions and differential enrichment of medium and high maturity continental shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(2): 224-237. [8] 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26.ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, CUI Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. [9] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 董大忠, 等. 页岩油气科技进步、发展战略及政策建议[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(12): 1675-1686.ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, DONG Dazhong, et al. Scientific and technological progress, development strategy and policy suggestion regarding shale oil and gas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(12): 1675-1686. [10] 王继超, 崔鹏兴, 刘双双, 等. 页岩油储层微观孔隙结构特征及孔隙流体划分[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(4): 46-54.WANG Jichao, CUI Pengxing, LIU Shuangshuang, et al. Microscopic pore structure characteristics and pore fluid division of shale oil reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(4): 46-54. [11] 郭旭升. 南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律: 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218.GUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichiment for marine shale gas in southern China: understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. [12] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 641-653.ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 641-653. [13] KASTNER M. Authigenic silicates in deep-sea sediments; formation and diagenesis[M]//EMILIANI C. The oceanic lithosphere. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1981: 915-980. [14] 腾格尔, 申宝剑, 俞凌杰, 等. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气形成与聚集机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 69-78.BORJIGIN Tenger, SHEN Baojian, YU Lingjie, et al. Mechanisms of shale gas generation and accumulation in the Ordovician Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 69-78. [15] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 1984. [16] 李宇志, 周肖肖, 隋风贵, 等. 东营凹陷民丰地区沙四段下亚段烃源岩特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(3): 28-41.LI Yuzhi, ZHOU Xiaoxiao, SUI Fenggui, et al. Characteristics of source rock of Es4x in Minfeng area, Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(3): 28-41. [17] 郭彤楼, 张汉荣. 四川盆地焦石坝页岩气田形成与富集高产模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1): 28-36.GUO Tonglou, ZHANG Hanrong. Formation and enrichment mode of Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1): 28-36. [18] 何卫红, 张克信, 吴顺宝, 等. 二叠纪末扬子海盆及其周缘动物群的特征和古地理、古构造启示[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2015, 40(2): 275-289.HE Weihong, ZHANG Kexin, WU Shunbao, et al. End-Permian faunas from Yangtze Basin and its marginal region: implications for palaeogeographical and tectonic environments[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2015, 40(2): 275-289. [19] 胡东风, 魏志红, 王威, 等. 四川盆地东北部雷页1井上二叠统大隆组页岩气勘探突破及其启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(11): 28-39.HU Dongfeng, WEI Zhihong, WANG Wei, et al. Breakthrough of shale gas exploration in Dalong Formation of Upper Permian by well Leiye 1 in the northeastern Sichuan Basin and its implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(11): 28-39. [20] 卢龙飞, 秦建中, 申宝剑, 等. 中上扬子地区五峰组—龙马溪组硅质页岩的生物成因证据及其与页岩气富集的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(4): 226-236.LU Longfei, QIN Jianzhong, SHEN Baojian, et al. The origin of biogenic silica in siliceous shale from Wufeng-Longmaxi formation in the Middle and Upper Yangtze region and its relationship with shale gas enrichment[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(4): 226-236. [21] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 腾格尔, 等. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组深水陆棚相页岩生储机理探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(1): 193-201.GUO Xusheng, LI Yuping, BORJIGEN Tenger, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and storage mechanisms of deep-water shelf shales of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2020, 47(1): 193-201. [22] 王濡岳, 胡宗全, 龙胜祥, 等. 四川盆地上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩储层特征与演化机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2): 353-364.WANG Ruyue, HU Zongquan, LONG Shengxiang, et al. Reservoir characteristics and evolution mechanisms of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng-Lower Silurian Longmaxi shale, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 353-364. [23] 陈世悦, 张顺, 刘惠民, 等. 湖相深水细粒物质的混合沉积作用探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(2): 271-284.CHEN Shiyue, ZHANG Shun, LIU Huimin, et al. Discussion on mixing of fine-grained sediments in lacustrine deep water[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(2): 271-284. [24] 朱如凯, 张婧雅, 李梦莹, 等. 陆相页岩油富集基础研究进展与关键问题[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(9): 2874-2895.ZHU Rukai, ZHANG Jingya, LI Mengying, et al. Advances and key issues in the basic research of non-marine shale oil enrichment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(9): 2874-2895. [25] 刘惠民. 济阳坳陷古近系页岩油地质特殊性及勘探实践: 以沙河街组四段上亚段—沙河街组三段下亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(5): 581-594.LIU Huimin. Geological particularity and exploration practice of Paleogene shale oil in Jiyang Depression: a case study of the upper submember of member 4 to the lower submember of member 3 of Shahejie Formation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 581-594. [26] 王勇, 刘惠民, 宋国奇, 等. 湖相泥页岩中碳酸盐成因及页岩油气地质意义: 以东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段—沙河街组三段下亚段烃源岩为例[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(12): 1390-1400.WANG Yong, LIU Huimin, SONG Guoqi, et al. Carbonate genesis and geological significance of shale hydrocarbon in lacustrine facies mud shale: a case study of source rocks in the upper submember of member 4 and lower submember of member 3 of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(12): 1390-1400. [27] 刘惠民, 李军亮, 刘鹏, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系页岩油富集条件与勘探战略方向[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(12): 1717-1729.LIU Huimin, LI Junliang, LIU Peng, et al. Enrichment conditions and strategic exploration direction of Paleogene shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(12): 1717-1729. [28] 刘惠民, 张顺, 王学军, 等. 陆相断陷盆地页岩岩相组合类型及特征: 以济阳坳陷东营凹陷沙四上亚段页岩为例[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(1): 30-48.LIU Huimin, ZHANG Shun, WANG Xuejun, et al. Types and characteristics of shale lithofacies combinations in continental faulted basins: a case study from upper sub-member of Es4 in Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(1): 30-48. [29] 刘惠民, 包友书, 张守春, 等. 陆相富碳酸盐页岩结构特征与页岩油可动性: 以济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组页岩为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(6): 1150-1161.LIU Huimin, BAO Youshu, ZHANG Shouchun, et al. Structural characteristics of continental carbonate-rich shale and shale oil movability: a case study of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation shale in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(6): 1150-1161. [30] 刘惠民, 张顺, 包友书, 等. 东营凹陷页岩油储集地质特征与有效性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 512-523.LIU Huimin, ZHANG Shun, BAO Youshu, et al. Geological characteristics and effectiveness of the shale oil reservoir in Dongying Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 512-523. [31] 宋明水, 刘惠民, 王勇, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系页岩油富集规律认识与勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 225-235.SONG Mingshui, LIU Huimin, WANG Yong, et al. Enrichment rules and exploration practices of Paleogene shale oil in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 225-235. [32] 李志明, 孙中良, 黎茂稳, 等. 济阳坳陷第一轮页岩油探井"失利"原因剖析[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(1): 143-157.LI Zhiming, SUN Zhongliang, LI Maowen, et al. Cause analyses of "failure" for first round shale oil exploration wells in Jiyang Depression[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(1): 143-157. [33] 彭艳霞, 杜玉山, 蒋龙, 等. 济阳坳陷缓坡带页岩油储层微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(4): 535-544.PENG Yanxia, DU Yushan, JIANG Long, et al. Micropore structure and fractal characteristics of shale oil reservoir in gentle slope zone of Jiyang Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(4): 535-544. [34] 魏祥峰, 刘珠江, 王强, 等. 川东南丁山与焦石坝地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气富集条件差异分析与思考[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(8): 1041-1051.WEI Xiangfeng, LIU Zhujiang, WANG Qiang, et al. Analysis and thinking of the difference of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale gas enrichment conditions between Dingshan and Jiaoshiba areas in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(8): 1041-1051. [35] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 李国雄. 四川盆地普光大型气藏基本特征及成藏富集规律[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6): 858-865.MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, LI Guoxiong. Basic characteristics and concentration of the Puguang Gas Field in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(6): 858-865. [36] 刘昭茜, 梅廉夫, 郭彤楼, 等. 川东北地区海相碳酸盐岩油气成藏作用及其差异性: 以普光、毛坝气藏为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(5): 552-561.LIU Zhaoqian, MEI Lianfu, GUO Tonglou, et al. Characteristics and differences of hydrocarbon accumulations in marine carbonate rocks, northeast Sichuan Basin: a case study from Puguang and Maoba gas fields[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(5): 552-561. [37] 谢佳彤, 付小平, 秦启荣, 等. 丁山地区页岩储层裂缝分布预测及页岩气保存条件评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(1): 1-9.XIE Jiatong, FU XiaopinG, QIN Qirong, et al. Prediction of fracture distribution in shale reservoirs in the Dingshan area and evaluation of shale gas preservation conditions[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(1): 1-9. [38] 朱国文, 王小军, 张金友, 等. 松辽盆地陆相页岩油富集条件及勘探开发有利区[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(1): 110-124.ZHU Guowen, WANG Xiaojun, ZHANG Jinyou, et al. Enrichment conditions and favorable zones for exploration and development of continental shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 110-124. [39] 赵贤正, 蒲秀刚, 金凤鸣, 等. 黄骅坳陷页岩型页岩油富集规律及勘探有利区[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(1): 158-175.ZHAO Xianzheng, PU Xiugang, JIN Fengming, et al. Enrichment law and favorable exploration area of shale-type shale oil in Huanghua Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 158-175. [40] 云露, 何希鹏, 花彩霞, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷古近系陆相页岩油成藏地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(1): 176-187.YUN Lu, HE Xipeng, HUA Caixia, et al. Accumulation characteristics and resource potential of Paleogene continental shale oil in Qintong Sag of Subei Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 176-187. [41] 胡东风, 张汉荣, 倪楷, 等. 四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 17-23.HU Dongfeng, ZHANG Hanrong, NI Kai, et al. Main controlling factors for gas preservation conditions of marine shales in southeastern margins of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6): 17-23. [42] 张旭亮, 刘珠江, 陈超, 等. 高陡复杂构造带深层页岩气保存条件差异性分析: 以川东南綦江高陡复杂构造带为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(6): 1121-1131. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061121ZHANG Xuliang, LIU Zhujiang, CHEN Chao, et al. Differences in preservation conditions of deep shale gas in high-steep complex tectonic belt: taking Qijiang high-steep complex tectonic belt in southeast Sichuan as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(6): 1121-1131. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061121 [43] 杨勇. 济阳陆相断陷盆地页岩油富集高产规律[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(1): 1-20.YANG Yong. Enrichment and high production regularities of shale oil reservoirs in continental rift basin: a case study of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(1): 1-20. [44] 赵文智, 卞从胜, 李永新, 等. 陆相页岩油可动烃富集因素与古龙页岩油勘探潜力评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(3): 455-467.ZHAO Wenzhi, BIAN Congsheng, LI Yongxin, et al. Enrichment factors of movable hydrocarbons in lacustrine shale oil and exploration potential of shale oil in Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(3): 455-467. [45] 郭旭升, 腾格尔, 魏祥峰, 等. 四川盆地深层海相页岩气赋存机理与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 453-468.GUO Xusheng, BORJIGIN Tenger, WEI Xiangfeng, et al. Occurrence mechanism and exploration potential of deep marine shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. [46] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 俞凌杰, 等. 页岩自封闭性与页岩气保存的微观机理研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 821-831.GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, YU Lingjie, et al. Study on the micro mechanism of shale self-sealing and shale gas preservation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 821-831. [47] 万成祥. 海相页岩自封闭机理及控制因素: 以四川盆地龙马溪组为例[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023.WAN Chengxiang. Self-sealing mechanism and controlling factors of marine shale: a case study of Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. [48] YOUNG K F, FREDERIKSE H P R. Compilation of the static dielectric constant of inorganic solids[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1973, 2(2): 313-410. [49] LI Jing, LI Xiangfang, WU Keliu, et al. Water sorption and distribution characteristics in clay and shale: effect of surface force[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(11): 8863-8874. [50] 魏富彬, 刘珠江, 陈斐然, 等. 川东南五峰组—龙马溪组深层、超深层页岩储层特征及其页岩气勘探意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 751-760. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304751WEI Fubin, LIU Zhujiang, CHEN Feiran, et al. Characteristics of the deep and ultra-deep shale reservoirs of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and the significance of shale gas exploration[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 751-760. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304751 [51] 蒙启安, 林铁锋, 张金友, 等. 页岩油原位成藏过程及油藏特征: 以松辽盆地古龙页岩油为例[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2022, 41(3): 24-37.MENG Qi'an, LIN Tiefeng, ZHANG Jinyou, et al. In-situ accumulation process and reservoir characteristics of shale oil: a case study of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(3): 24-37. [52] 王勇, 刘惠民, 宋国奇, 等. 济阳坳陷页岩油富集要素与富集模式研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(2): 268-276.WANG Yong, LIU Huimin, SONG Guoqi, et al. Enrichment controls and models of shale oil in the Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(2): 268-276. [53] TANG Ling, WANG Pengfei, ZHAO Zhigang, et al. Overpressure origin and evolution during burial in the shale gas plays of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations of southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2024, 236: 212729. [54] 王勇. 岩性油藏成藏机理及运聚模式: 以牛庄洼陷为例[J]. 特种油气藏, 2012, 19(3): 18-21.WANG Yong. Formation mechanism and accumulation model of lithologic reservoirs: a case study with Niuzhuang Sub-Sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2012, 19(3): 18-21. [55] 马晓潇, 黎茂稳, 胡克珍, 等. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷古近系异常高压成因及其与陆相页岩油富集的关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(1): 145-156. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301145 MA Xiaoxiao, LI Maowen, HU Kezhen, et al. Abnormal pressure genesis and its relationship with continental shale oil accumulation in Paleogene, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(1): 145-156. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301145 [56] 李志明, 孙中良, 黎茂稳, 等. 陆相基质型页岩油甜点区成熟度界限探讨: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷沙三下—沙四上亚段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 767-775.LI Zhiming, SUN Zhongliang, LI Maowen, et al. Maturity limit of sweet spot area for continental matrix type shale oil: a case study of lower Es3 and upper Es4 sub-members in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 767-775. [57] 杨勇, 张世明, 吕琦, 等. 中国东部陆相断陷盆地中—低成熟度页岩油立体开发技术: 以济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(4): 672-682.YANG Yong, ZHANG Shiming, LÜ Qi, et al. Stereoscopic deve-lopment techniques for shale oil with low-medium maturity in continental faulted basins in eastern China: a case study of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(4): 672-682. [58] 唐令, 宋岩, 赵志刚, 等. 四川盆地上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩气藏超压成因及演化规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(10): 37-53.TANG Ling, SONG Yan, ZHAO Zhigang, et al. Origin and evolution of overpressure in shale gas reservoirs of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation–Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(10): 37-53. [59] 姜振学, 宋岩, 唐相路, 等. 中国南方海相页岩气差异富集的控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 617-628.JIANG Zhenxue, SONG Yan, TANG Xianglu, et al. Controlling factors of marine shale gas differential enrichment in southern China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 617-628. [60] KATZ B, LIN Fang. Lacustrine basin unconventional resource plays: key differences[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 56: 255-265. [61] JIAO Xin, LIU Yiqun, YANG Wan, et al. Mixed biogenic and hydrothermal quartz in Permian lacustrine shale of Santanghu Basin, NW China: implications for penecontemporaneous transformation of silica minerals[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 107(6): 1989-2009. [62] MASTALERZ M, SCHIMMELMANN A, DROBNIAK A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany shale across a maturation gradient: insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(10): 1621-1643. [63] APLIN A C, MACQUAKER J H S. Mudstone diversity: origin and implications for source, seal, and reservoir properties in petroleum systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(12): 2031-2059. [64] 李松, 马立元, 王濡岳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地石盒子组—山西组致密储层形成主控因素与发育模式: 以彬长地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 28-40.LI Song, MA Liyuan, WANG Ruyue, et al. Main controlling factors and development model of tight reservoirs in the Shihezi Formation-Shanxi Formation in the Ordos Basin: taking the Binchang area as an example[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 28-40. [65] GREENWOOD P F, BROCKS J J, GRICE K, et al. Organic geochemistry and mineralogy. I. Characterisation of organic matter associated with metal deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 50: 1-27. [66] ABARGHANI A, GENTZIS T, SHOKOUHIMEHR M, et al. Che-mical heterogeneity of organic matter at nanoscale by AFM-based IR spectroscopy[J]. Fuel, 2020, 261: 116454. [67] 赵文智, 卞从胜, 蒲秀刚, 等. 中国典型咸化湖盆页岩油富集与流动特征及在"甜点"评价中的意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(5): 25-37.ZHAO Wenzhi, BIAN Congsheng, PU Xiugang, et al. Enrichment and flow characteristics of shale oil in typical salinized lake basins in China and its significance for "sweet spot" evaluation[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(5): 25-37. [68] 王小军, 宋永, 郭旭光, 等. 陆相咸化湖盆细粒沉积岩分类及其石油地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(1): 303-317.WANG Xiaojun, SONG Yong, GUO Xuguang, et al. Classification of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in saline lacustrine basins and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(1): 303-317. [69] 付小平, 刘苗苗. 涪陵地区凉高山组富有机质泥岩微相特征及油气富集规律[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 230-237.FU Xiaoping, LIU Miaomiao. Microfacies characteristics of organic-rich mudstone and oil and gas enrichment law of Lianggaoshan Formation in Fuling area[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 230-237. [70] 李斌, 吉鑫, 彭军, 等. 川东南涪陵地区凉高山组湖相页岩生烃潜力评价[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 45(6): 43-56.LI Bin, JI Xin, PENG Jun, et al. Evaluation of hydrocarbon generation potential of lacustrine shale of Lianggaoshan Formation in Fuling area, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 45(6): 43-56. [71] 李进, 王学军, 王睿, 等. 普光地区千佛崖组半深湖相页岩含气性特征及影响因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 736-743.LI jin, WANG Xuejun, WANG Rui, et al. Gas-bearing characte-ristics and influencing factors of semi-deep lacustrine shale of Qianfoya Formation in Puguang Area[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 736-743. [72] 黄董, 曾德铭, 王兴志, 等. 川中地区侏罗系大安寨段沉积相及有利岩石组合分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(1): 65-73.HUANG Dong, ZENG Deming, WANG Xingzhi, et al. Sedimentary facies and favorable rock assemblages of Jurassic Da'anzhai member, central Sichuan[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(1): 65-73. [73] 李倩文, 刘忠宝, 陈斐然, 等. 四川盆地侏罗系页岩层系岩相类型及储集特征: 以元坝地区Y2井大安寨段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(5): 1127-1140.LI Qianwen, LIU Zhongbao, CHEN Feiran, et al. Lithofacies types and reservoir characteristics of Jurassic shale in the Sichuan Basin revealed by the Da'anzhai Member, well Y2, Yuanba area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(5): 1127-1140. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号