Glutenite reservoir characteristics and development model of Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
-
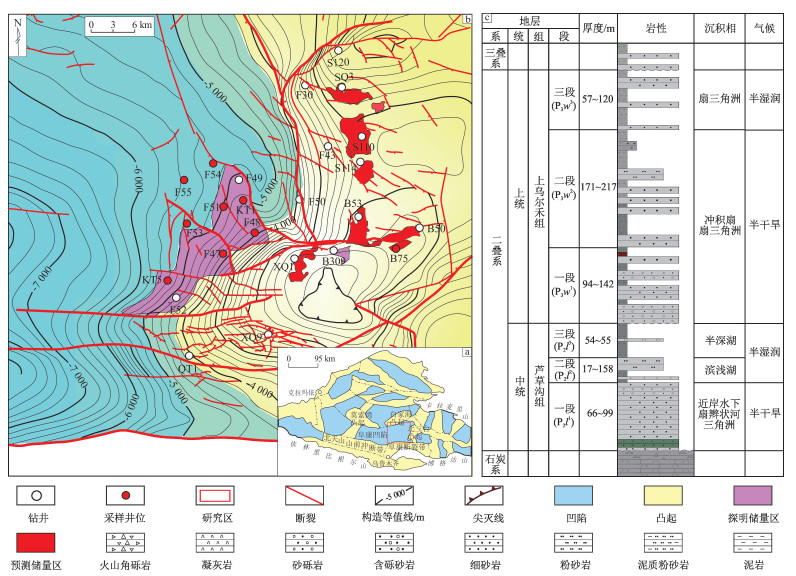
摘要: 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组砂砾岩具有较大的油气勘探潜力,目前存在的砂砾岩储层特征以及成储机制不清晰等问题,严重制约了对该类储层的勘探。利用显微薄片、扫描电镜、X射线衍射等对准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷上乌尔禾组砂砾岩储层特征、主控因素以及成储模式进行了系统研究。结果表明:上乌尔禾组砂砾岩具有“双填隙物”特征,砾石间主要被较粗的砂质组分填隙,胶结作用主要发生于砂质组分之间;砂砾岩孔隙度低,砾石中基本不发育孔隙,砂质填隙物中孔隙较发育,储集空间主要为晶间孔和次生溶孔;与储层形成有关的成岩演化现象主要发生在砾石之间的粗填隙物砂质组分中,主要为铝硅酸盐矿物的溶蚀作用,形成较多的溶蚀孔隙;河口坝、水下分流河道等高能沉积微相中储层更发育,储集空间主要与长石溶蚀有关,裂缝、不整合面是酸性流体运移的主要通道;早成岩期酸性流体主要为沿不整合面下渗的大气水,尤其是靠近北三台凸起的区域大气淡水溶蚀更为显著,中成岩期主要为有机酸溶蚀;砂砾岩中发育大气酸溶蚀型、有机酸溶蚀型和双源酸叠加溶蚀型等3类储层,不同类型储层分布决定了阜康凹陷上乌尔禾组砂砾岩油气藏的勘探方向,斜坡区、凹陷区的砂砾岩+断裂发育叠合区是阜康凹陷上乌尔禾组砂砾岩油气勘探的重点方向。Abstract: The glutenites in the Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation in the Fukang Sag of the Junggar Basin possess great potential for oil and gas exploration. However, uncertainties in the reservoir characteristics and formation mechanisms of these glutenites seriously restrict their effective exploration. The study provides a compre- hensive analysis on the characteristics, main controlling factors, and development models of glutenite reservoirs of the Upper Wuerhe Formation in the Fukang Sag of the Junggar Basin using microscopic thin sections, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results show that: (1) Two types of interstitial materials are observed in the glutenites of the Upper Wuerhe Formation, where the spaces between gravels are primarily interstitially filled with coarser sandy components, and the cementation mainly occurs between these sandy components. (2) The glutenites generally exhibit low porosity, with minimal pore development within gravels, while the pores in sandy interstitial materials are more developed. The reservoir space is mainly composed of intercrystalline and secondary dissolution pores. (3) Diagenetic processes related to reservoir formation mainly occur within the coarse sandy interstitial materials between gravels, mainly involving aluminosilicate dissolution, which results in abundant dissolution pores. (4) In high-energy sedimentary microfacies, such as estuary bars and underwater distributary channels, reservoirs are more favorably developed, where the reservoir space is mainly associated with feldspar dissolution. Fractures and unconformities are the main channels for acidic fluid migration. (5) During the eodiagenesis, acidic fluids, mainly atmospheric water, infiltrated along unconformities, with more significant dissolution near the Beisantai arch. During the middle diagenetic period, dissolution was mainly attributed to organic acid. (6) Three types of reservoirs are developed in the glutenites: atmospheric acid dissolution reservoirs, organic acid dissolution reservoirs, and dual-source acid superimposed dissolution reservoirs. The distribution of these reservoir types determines the exploration strategies for oil and gas reservoirs of glutenites of the Upper Wuerhe Formation in the Fukang Sag of the Junggar Basin. Glutenites in the slope and sag areas and zones of superimposed fault development are the key objectives for oil and gas exploration of glutenite reservoirs of the Upper Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag.
-
Key words:
- glutenite reservoir /
- reservoir development model /
- Upper Wuerhe Formation /
- Permian /
- Fukang Sag /
- Junggar Basin
-
图 3 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组成岩特征
a.砾石间自生高岭石,F47井,5 124.15 m,PPL(平面偏振光);b.粒间紧密充填高岭石,F48井,4 538.09 m,SEM(扫描电镜);c.砾岩中的裂缝与粒间溶蚀,F47井,5 130.17 m,PPL;d.砂质砾岩粒间胶结方解石,F48井,4 534.2 m,PPL;e.砂质砾岩粒间胶结方解石,F48井,4 534.2 m,XPL(正交偏光);f.粗砂质砾岩中沸石溶蚀残余(黄色箭头)及其外围方解石(红色箭头),F47井,5 111.2 m,PPL。
Figure 3. Diagenetic characteristics of Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
图 5 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组砂砾岩砾石间砂质组分储集空间类型
a.含砂细砾岩中的铸膜孔及充填高岭石,F47井,5 124.15 m,PPL;b.砾质粗砂岩中粒间浊沸石溶孔,F47井,5 111.20 m,PPL;c.砂质细砾岩砾石间砂质组分中的纳米级微孔,F53井,5 628.62 m,SEM(氩离子抛光);d.c图红框区域放大,长石的纳米级微孔十分发育。
Figure 5. Types of reservoir space within sandy components among gravels of glutenites of Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
图 9 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组砂砾岩溶蚀作用特征
a.砂质细—中砾岩粒间浊沸石溶孔,F50井,4 189.4 m,PPL;b:粒间浊沸石溶孔,孔隙壁发育绿泥石衬里,砂质细—中砾岩,F50井,4 189.4 m,PPL;c.含砂细砾岩中长石粒内溶孔,阜43井,3 135.41 m(单偏光);d.粗砂质砾岩中的沸石溶蚀(单偏光),阜47井,5 111.2 m(单偏光)。
Figure 9. Characteristics of dissolution processes of glutenites of Upper Permian Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组砂砾岩全岩XRD数据
Table 1. Whole-rock X-ray diffraction (XRD) data of glutenites of Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
井号 粒度/mm 深度/m 岩性 孔隙度/% 矿物组成/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 黄铁矿 石膏 硬石膏 菱铁矿 方沸石 浊沸石 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 F47 >2 5 112.00 含砾中—粗砂岩 6.79 56.2 3.9 18.2 0.8 0 0 0.8 0 0 6.4 0.4 0 13.3 F47 < 2 41.5 0.9 19.4 1.3 0 0 2.0 0 0 14.8 0.8 0 19.3 F47 >2 5 134.55 砂质中—细砾岩 6.89 54.8 6.4 26.4 0 0.8 0 0.7 0.5 0 2.3 0.3 0.7 7.1 F47 < 2 49.3 3.5 16.1 1.5 0.5 0 0 0 0 9.8 1.3 2.1 15.9 F48 >2 4 535.00 含砾细—中砂岩 4.95 49.9 0 31 3.7 0 0 0.3 0 0 0 1.1 0 14.0 F48 < 2 49.9 0 20.1 11.7 0 0 0.6 0 0.9 0 2.0 2.4 12.4 F48 >2 4 535.55 含砾中—粗砂岩 6.98 58.6 0 28.1 0.3 0 0 0.9 0 0 0 1.4 1.7 9.0 F48 < 2 49.2 0.7 29.3 1.2 0 1 0.8 0 0 0 0.4 2.0 15.4 F48 >2 4 443.18 含砾中—粗砂岩 2.97 59.3 0 18.4 3.7 0 0 0.9 0 0.6 2 2.6 0.5 12.0 F48 < 2 57.6 0 18.6 9.4 0 0 1.5 0 1.0 0 1.2 0.8 9.9 F50 >2 4 180.00 含砾中砂岩 6.34 51.2 0 27 0 0 1 1.6 0 0.5 0 4.5 0.2 14.0 F50 < 2 56.7 0 27.6 2.6 0 0 0.4 0 0 0 6.3 0.5 5.9 KT5 >2 5 972.84 含砾砂岩 4.16 60.0 0 25.2 0 0 0 0.9 0 1.0 0 4.7 0.6 7.6 KT5 < 2 52.6 0 28.4 1.0 0 0 1.0 0 0.1 0 5.6 1.0 10.3 KT5 >2 5 973.18 含砾细—中砂岩 2.65 50.0 0 32.6 1.0 0 0 0.9 0 0.6 0 2.5 1.4 11.0 KT5 < 2 58.1 0 31.9 0.9 0 0 0.7 0 0.7 0 1.9 1.0 4.8 表 2 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷上二叠统地层水离子类型及比值
Table 2. Types and ratios of formation water ions in Upper Permian of Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin
离子类型及比值 康探1井区 平均海水 平均河水 最大 最小 均值 Cl- / (mg/L) 19 959 13 453 16 310 18 980 3 Na++K+/ (mg/L) 3 820 3 742 3 781 10 940 6 Ca2+/ (mg/L) 4 593 4 652 4 623 400 15 Mg2+/ (mg/L) 0 0 0 1272 4 SO42-/ (mg/L) 93 78 86 2560 11 CO32-+ HCO3-/ (mg/L) 597 597 597 142 59 矿化度/ (g/L) 33.36 22.46 27.31 34.40 0.098 rNa+/rCl- 0.23 0.58 2.00 rSO42-×100/rCl- 0.53 13.49 366.67 r(CO32-+HCO3-)/rCl- 0.04 0.01 19.67 注:平均海水、平均河水数据分别引自参考文献[29]和[30];离子比值采用摩尔比。 -
[1] 唐勇, 郭文建, 王霞田, 等. 玛湖凹陷砾岩大油区勘探新突破及启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(2): 127-137.TANG Yong, GUO Wenjian, WANG Xiatian, et al. A new breakthrough in exploration of large conglomerate oil province in Mahu Sag and its implications[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(2): 127-137. [2] 杜金虎, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地上二叠统风险领域分析与沙湾凹陷战略发现[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(1): 24-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.004DU Jinhu, ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, et al. Prospects in Upper Permian and strategic discovery in Shawan Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(1): 24-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.004 [3] 何海清, 范土芝, 郭绪杰, 等. 中国石油"十三五"油气勘探重大成果与"十四五"发展战略[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1): 17-30.HE Haiqing, FAN Tuzhi, GUO Xujie, et al. Major achievements in oil and gas exploration of PetroChina during the 13th Five-Year Plan period and its development strategy for the 14th Five-Year Plan[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1): 17-30. [4] 何海清, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷康探1井重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.02.001HE Haiqing, ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, et al. A great discovery of well Kangtan 1 in the Fukang Sag in the Junggar Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.02.001 [5] 李庆昌, 薛连达, 裘亦楠. 裂缝性低渗透率储层的开发地质研究问题: 以克拉玛依油田八区乌尔禾组油层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1988(5): 46-52.LI Qingchang, XUE Lianda, QIU Yinan. Development of a fractured low permeability oil reservoir: the development of Urho reservoir in Ⅷ area in Kelamayi oil field[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1988(5): 46-52. [6] 于兴河, 李顺利, 谭程鹏, 等. 粗粒沉积及其储层表征的发展历程与热点问题探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2018, 20(5): 713-736.YU Xinghe, LI Shunli, TAN Chengpeng, et al. Coarse-grained deposits and their reservoir characterizations: a look back to see forward and hot issues[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2018, 20(5): 713-736. [7] 蔡毅. 中拐凸起南斜坡二叠系佳木河组砂砾岩储层特征分析[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.CAI Yi. The research onsandy conglomerate reservoir characte-ristics of Permian Jiamuhe Formation of the southern slope of Zhongguai Uplift[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2016. [8] 钱禹辰. 柴达木盆地昆北油田切12区下干柴沟组下段砂砾岩储层特征、分类及有效评价研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2015.QIAN Yuchen. Research of glutenite reservoir characters, classification and evaluation of Qie12 area in Kunbei oilfield of Lower Ganchaigou Formation in Qaidam Basin[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2015. [9] 吴海光, 康逊, 秦明阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷百口泉组砂砾岩非均质储层孔隙结构特征与成因[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3337-3353.WU Haiguang, KANG Xun, QIN Mingyang, et al. Pore structure characteristics and genesis of heterogeneous conglomerate reservoir of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3337-3353. [10] 陈思芮, 王卫学, 曲希玉, 等. 东营凹陷北带沙四上亚段砂砾岩储层物性主控因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(4): 1091-1106.CHEN Sirui, WANG Weixue, QU Xiyu, et al. Main controlling factors of physical properties of glutenite reservoirs of Es4s Member in north zone of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(4): 1091-1106. [11] 付瑜, 柳益群, 蒋宜勤, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘玛湖凹陷三叠系百口泉组砂砾岩储层孔隙结构及渗流特征[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(2): 223-234.FU Yu, LIU Yiqun, JIANG Yiqin, et al. Pore structures and seepag e characteristics of sand-conglomerate reservoirs of Baikouquan Formation in Triassic Mahu Sag, northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(2): 223-234. [12] 王玉祥. 砂砾岩致密储层填隙物特征及其对孔隙的影响[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报, 2017, 30(1): 75-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2017.01.015WANG Yuxiang. Characteristics of interstitial material in sandy conglomerate and its effects on reservoir porosity[J]. Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 2017, 30(1): 75-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-396X.2017.01.015 [13] 昝灵, 张枝焕, 王顺华, 等. 渤南洼陷北部陡坡带砂砾岩储层成岩作用研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(2): 299-306.ZAN Ling, ZHANG Zhihuan, WANG Shunhua, et al. Diagenesis of sandy conglomerate reservoir in northern steep slope of Bonan Subsag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(2): 299-306. [14] 雷海艳, 樊顺, 鲜本忠, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系下乌尔禾组沸石成因及溶蚀机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5): 102-112.LEI Haiyan, FAN Shun, XIAN Benzhong, et al. Genesis and corrosion mechanism of zeolite of Lower Urhe Formation of Permian in Mahu Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(5): 102-112. [15] 马永平, 张献文, 朱卡, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组扇三角洲沉积特征及控制因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(1): 57-70.MA Yongping, ZHANG Xianwen, ZHU Ka, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of fan-delta of the Upper Urho Formation of Permian in Mahu Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1): 57-70. [16] 侯云超, 樊太亮, 王宏语, 等. 银额盆地拐子湖凹陷深层优质储层特征及形成机理[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(4): 758-767.HOU Yunchao, FAN Tailiang, WANG Hongyu, et al. Characte-ristics and formation mechanism of a high-quality reservoir in the deep strata of the Guaizihu Depression, Yin-E Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(4): 758-767. [17] 朱筱敏, 张守鹏, 韩雪芳, 等. 济阳坳陷陡坡带沙河街组砂砾岩体储层质量差异性研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 1094-1104.ZHU Xiaomin, ZHANG Shoupeng, HAN Xuefang, et al. On the differences of reservoir quality of Shahejie Fm. in steep slope zones of Jiyang Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 1094-1104. [18] 王剑, 周路, 靳军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛南地区乌尔禾组砂砾岩优质储层特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(5): 34-44.WANG Jian, ZHOU Lu, JIN Jun, et al. Characteristics of high-quality glutenite reservoirs of Urho Formation in Manan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(5): 34-44. [19] 李佳思, 付磊, 张金龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌夏地区中上二叠统碎屑岩成岩作用及次生孔隙演化[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(6): 54-66.LI Jiasi, FU Lei, ZHANG Jinlong, et al. Diagenesis and secondary pore evolution of Middle and Upper Permian clastic rocks in Wu-Xia area, Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(6): 54-66. [20] 李嘉蕊, 杨智, 王兆云, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存定量表征及其主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681LI Jiarui, YANG Zhi, WANG Zhaoyun, et al. Quantitative characte-rization and main controlling factors of shale oil occurrence in Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 681-692. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304681 [21] 唐勇, 徐洋, 瞿建华, 等. 玛湖凹陷百口泉组扇三角洲群特征及分布[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2014, 35(6): 628-635.TANG Yong, XU Yang, QU Jianhua, et al. Fan-delta group characteristics and its distribution of the Triassic Baikouquan reservoirs in Mahu Sag of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2014, 35(6): 628-635. [22] 陈波, 王子天, 康莉, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛北地区三叠系百口泉组储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(1): 23-35.CHEN Bo, WANG Zitian, KANG Li, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Mabei region, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(1): 23-35. [23] 孟祥超, 蒋庆平, 李亚哲, 等. 同生逆断层控制的砂砾岩沉积模式及有利储集相带分布: 以玛湖凹陷南斜坡白25井区上乌尔禾组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1225-1240.MENG Xiangchao, JIANG Qingping, LI Yazhe, et al. Glutenite sedimentary pattern under the control of contemporaneous reverse thrust and favorable reservoir facies belt distribution: taking P3w, B25 block, Mahu Sag, as anexample[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 1225-1240. [24] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861.HE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. [25] 唐勇, 侯章帅, 王霞田, 等. 准噶尔盆地石炭纪—二叠纪地层对比框架新进展[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(2): 385-407.TANG Yong, HOU Zhangshuai, WANG Xiatian, et al. Progress of the Carboniferous and Permian stratigraphic framework and correlation of the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang, Northwest China[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(2): 385-407. [26] 王秋玉, 李树博, 闫文琦, 等. 深层特低孔—特低渗砂砾岩储层特征及主控因素: 以准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组为例[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2023, 47(2): 31-43.WANG Qiuyu, LI Shubo, YAN Wenqi, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of deep ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability glutenite reservoirs: a case study of the Upper Wuerhe Formation of Permian in Fukang Depression, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2023, 47(2): 31-43. [27] 庞德新. 砂砾岩储层成因差异及其对储集物性的控制效应: 以玛湖凹陷玛2井区下乌尔禾组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(5): 149-154.PANG Dexin. Sedimentary genesis of sand-conglomerate reservoir and its control effect on reservoir properties: a case study of the Lower Urho Formation in Ma 2 well block of Mahu Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(5): 149-154. [28] 国家石油和化学工业局. 岩石薄片鉴定: SY/T 5368-2000[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2000.State Bureau of Petroleum and Chemical Industries. Thin section examination of rock: SY/T 5368-2000[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2000. [29] 张德会, 赵仑山. 地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013.ZHANG Dehui, ZHAO Lunshan. Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2013. [30] 钱诗友, 曾溅辉. 东营凹陷沙河街组地层水化学特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4): 603-609.QIAN Shiyou, ZENG Jianhui. Chemical characteristics of Shahejie Formation formation water and their petroleum geological significance, Dongying Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(4): 603-609. [31] BARCLAY S A, WORDEN R H. Geochemical modelling of diagenetic reactions in a sub-arkosic sandstone[J]. Clay Minerals, 2000, 35(1): 57-67. [32] 应凤祥, 罗平, 何东博. 中国含油气盆地碎屑岩储集层成岩作用与成岩数值模拟[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.YING Fengxiang, LUO Ping, HE Dongbo. Diagenesis and diagenesis numerical simulation of clastic reservoir in petroliferous basins of China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004. [33] 曾溅辉, 朱志强, 吴琼, 等. 烃源岩的有机酸生成及其影响因素的模拟实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(6): 847-851.ZENG Jianhui, ZHU Zhiqiang, WU Qiong, et al. Experimental study on the generation of organic acids from source rocks and its effect factors[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(6): 847-851. [34] 吴胜和. 储层表征与建模[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.WU Shenghe. Reservoir characterization & modeling[M] Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [35] 蔡春芳. 塔里木盆地流体—岩石相互作用研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.CAI Chunfang. Approach to fluid-rock interaction in Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1997. [36] 张瑞. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷东部地区石炭系—二叠系油源对比与成藏模式[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2006.ZHANG Rui. Oil-source correlations and hydrocarbon accumulations of Carboniferous-Permian in eastern Fukang Depression, Junggar Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2016. [37] 王越, 熊伟, 于洪州, 等. 准噶尔盆地东部芦草沟组层序地层格架与沉积充填模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(4): 12-24.WANG Yue, XIONG Wei, YU Hongzhou, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary filling model of Lucaogou Formation in eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(4): 12-24. [38] 匡立春, 支东明, 王小军, 等. 准噶尔盆地上二叠统上乌尔禾组大面积岩性—地层油气藏形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(3): 325-340.KUANG Lichun, ZHI Dongming, WANG Xiaojun, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration directions of large-scale lithologic-stratigraphic oil and gas reservoirs in Upper Wuerhe Formation of Upper Permian in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(3): 325-340. [39] 刘超威, 尤新才, 李辉, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷芦草沟组烃源岩地球化学特征与生烃潜力研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 338-346. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302338LIU Chaowei, YOU Xincai, LI Hui, et al. Geochemical characte-ristics and hydrocarbon generation potential of Lucaogou Formation source rocks in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 338-346. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302338 -





 下载:
下载:












 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号