Current status and development trends of deep coalbed methane research in China
-
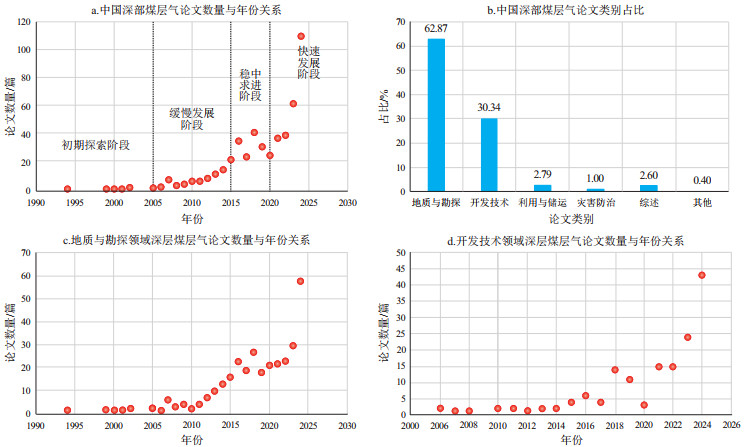
摘要: 深部煤层气的资源潜力巨大,是中国非常规天然气未来规模性增储上产的重要领域。为查明中国深部煤层气研究及勘探开发现状,基于中国知网和万方数据知识服务平台,系统检索并分类统计中国深部煤层气论文,以其为基础分析中国深部煤层气研究现状,探讨其发展趋势,可为发展深部煤层气适应性勘探开发技术提供借鉴。论文年代分布体现了中国深部煤层气研究和产业发展历程:初期探索阶段(1994—2005年)、缓慢发展阶段(2006—2015年)、稳中求进阶段(2016—2020年)和快速发展阶段(2021年以来)。地质—工程“双甜点”预测是深部煤层气开发地质领域的重点研究内容,在地质、工程参数量化表征的基础上,借助三维地质与地质力学建模,开展深部煤层气勘探开发地质—工程一体化研究是保障效益开发的关键路径。煤储层天然裂缝的产出状态及发育程度显著影响压裂改造效果,压裂前后缝网体系的连通性是决定深部煤层气开发效果的重要指标。深部煤层气开发技术及其适用性是未来需重点探讨的方向之一,深化理论认识、定量刻画地质—工程条件、全方位解析影响因素是决定中国深部煤层气进一步快速发展的基础和关键。鄂尔多斯盆地、准噶尔盆地、四川盆地、塔里木盆地等盆地内部深部—超深部煤层气将是研究和勘探开发重点。Abstract: Deep coalbed methane (CBM) possesses enormous resource potential and is essential for increasing unconventional natural gas reserves and production on a large scale in China. To understand the current status of CBM research and development in China, systematic retrieval and classification of deep CBM-related publications are conducted using the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database and Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform. Based on this analysis, the status of deep CBM research in China is reviewed, and its development trends are discussed, providing insights into adaptive exploration and development technologies for deep CBM. The results indicate that the temporal distribution of publications reflects the evolution of China's deep CBM research and industrial development, which can be divided into four stages: the initial exploration stage (1994 to 2005), the slow development stage (2006 to 2015), the steady progress stage (2016 to 2020), and the rapid development stage (since 2021). Geological and engineering "dual sweet spot" prediction is a key research focus for deep CBM research. Conducting geology and engineering integrated research for deep CBM exploration and development, based on the quantitative characterization of geological and engineering parameters and using three-dimensional geological and geomechanical modeling, is a critical pathway to ensuring profitable development. The production state and development degree of natural fractures in coal reservoirs significantly affect fracturing transformation. The connectivity of fracture networks before and after fracturing is an important indicator for determining the performance of deep CBM development. The development of deep CBM technologies and their applicability are the key areas to be explored in the future. Deepening theoretical understanding, quantitatively characterizing geological and engineering conditions, and comprehensively analyzing influencing factors are fundamental and crucial for the further rapid development of deep CBM in China. Deep and ultra-deep CBM in basins such as the Ordos, Junggar, Sichuan, and Tarim basins will be the research focus and the key exploration and development areas.
-
表 1 基于中国知网和万方数据知识服务平台的中国深部煤层气勘探开发区地质信息统计
Table 1. Geological information of deep coalbed methane exploration and development areas in China based on China National Knowledge Infrastructure and Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform
盆地/地区 深部煤层气主要勘探开发层位 煤层类型 埋深/m 煤层厚度/m 煤体结构 含气量/ (m3/t) 镜质体反射率/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/ 10-3 μm2 吐哈盆地 八道湾组、西山窑组 深层中阶煤 2 000~4 500 9.00~40.00,最大60.00 原生、碎裂 17.00~24.00 0.70~1.40 3.95~11.18 0.004~5.222 准噶尔盆地白家海地区 八道湾组、西山窑组 深层低阶煤 1 600~5500 2.00~20.00 原生、碎裂 8.28~26.18 0.47~1.05 8.80~11.90 0.018~1.253 新疆阜康西区 八道湾组、西山窑组 深层低阶煤 750~1 446 5.18~19.48 原生、碎裂 5.97~16.64 0.51~0.92 4.20~4.21 0.004~0.988 松辽盆地王府断陷 火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组 深层高阶煤 >2 000 1.00~12.00 原生 18.80~23.60 1.97~2.29 4.06~5.71 鄂尔多斯盆地大宁—吉县地区 本溪组、太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 2 000~2 400 1.50~9.80 原生 23.67~37.64 1.34~2.12 0.49~6.11 0.010~1.749 鄂尔多斯盆地延川南地区 山西组 深层高阶煤 800~1 600 2.80~6.90 原生、碎裂 8.00~20.00 2.02~3.08 3.00~6.20 0.013~0.990 鄂尔多斯盆地临汾地区 本溪组、太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 900~1 320 2.04~9.35 原生 7.00~21.00 1.69~2.30 约2.35 0.490~1.900 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区 本溪组、山西组 深层中、低阶煤 1 500~2 200 2.00~19.00 原生、碎裂 7.18~21.64 0.60~3.70 1.45~14.84 0.020~0.080 鄂尔多斯盆地神府地区 本溪组 深层高阶煤 1 800~2 100 1.80~18.70 原生、碎裂 0.80~34.00 0.67~1.50 1.70~5.10 0.010~0.360 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地地区 本溪组、太原组、山西组 深层中阶煤 2 500~2 900 3.00~10.00 原生、碎裂 14.00~33.00 1.50~1.70 4.00~7.00 0.010~0.100 沁水盆地柿庄北地区 太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 800~1 500 4.00~7.00 原生 3.11~21.51 2.29~2.54 4.20~7.40 0.010~0.460 济阳坳陷 太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 大于2 000,平均4 000 10.00~25.00 4.60~5.40 0.60~5.50 山西晋中地区 太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 1 600~2 200 1.50~18.00 碎裂 16.00~24.00 2.00~3.50 8.18~10.98 0.028~0.943 安徽两淮地区 太原组、山西组、下石盒子组、上石盒子组 深层低阶煤 1 000~1 500 1.03~8.26 碎裂 9.66~13.68 0.70~1.00 1.30~10.90 0.055~5.720 宁武盆地 太原组、山西组 深层高阶煤 1 200~2 700 10.00~13.70 原生、碎裂 4.06~20.00 1.03~1.81 0.71~8.26 河南焦作矿区 太原组、山西组、下石盒子组 深层高阶煤 800~2 000 3.81~7.20 碎裂、碎粒 0.00~36.00 江苏徐州地区 本溪组、太原组、山西组、下石盒子组 深层中阶煤 1 000~2 500 0.05~12.00 原生、碎裂、碎粒 1.22~53.32 0.70~0.97 5.67~10.89 四川盆地 龙潭组 深层高阶煤 2 000~4 500 1.50~4.50 原生 7.00~21.00 2.55~3.50 2.80~6.89 0.012~0.483 云南大河煤矿 龙潭组、长兴组 深层高阶煤 1 000~1 200 0.20~13.79 原生 7.23~10.60 1.01~1.24 约2.00 0.110~1.530 重庆南川地区 龙潭组 深层高阶煤 1 800~3 000 0.40~1.50 原生、碎裂 7.70~67.00 1.72~2.24 2.30~6.20 0.050~6.220 黔西、黔北地区 龙潭组 深层高阶煤 1 000~2 000 10.00~40.00 3.20~31.30 1.03~4.43 4.60~5.00 0.010~0.100 表 2 深部煤层气高效开发技术统计
Table 2. Statistics of efficient development technologies for deep coalbed methane
技术名称 代表性应用地区 参考文献 地质—工程开发甜点优选技术 大宁—吉县 [7] 地质—工程一体化导向技术 大宁—吉县 [7] 井网优化设计技术 大宁—吉县 [7] 大井丛井网设计技术 延川南 [25] 全生命周期不同生产阶段排采优化控制技术 大宁—吉县 [7] 基于解吸理论的智能化精细排采控制技术 延川南 [26] 适用于复杂地貌的地面集输以及气田数字化技术 延川南 [26] 水平井带压油管压裂技术 沁水盆地长治北 [27] 地面定向井+水力割缝卸压技术 [28] “充填预堵+大规模压裂+远端支撑”增产技术 沁水盆地郑庄北 [29] 遵循“四位一体”精准选段和“井间交错+ 段内差异化”设计原则的大规模体积压裂技术 大宁—吉县 [7] “密切割+大排量+组合支撑剂+前置酸+变黏滑溜水”的极限水平井分段压裂技术体系 临兴—神府 [12] “超大+超密+充分支撑体积缝网”极限体积压裂技术 大宁—吉县 [30] “前置酸+低伤害变黏压裂液体系+多粒径支撑剂立体支撑+ 等孔径限流射孔+电缆传输泵送可溶桥塞射孔联作+ 少段多簇密切割+投球暂堵+超大排量+超大砂量”的极限体积压裂技术 神府 [24] -
[1] 申建. 我国主要盆地深部煤层气资源量预测[R]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.SHEN Jian. Prediction of deep coalbed methane resources in major basins in China[R]. Xuzhou: China [2] 赵庆波. 煤层气富集规律研究及有利区块预测评价[R]. 廊坊: 中国石油勘探开发研究院, 2011.ZHAO Qingbo. Study on CBM enrichment law and prediction and evaluation of favorable blocks [R]. Langfang: Reasearch Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development, 2011. [3] 李松, 汤达祯, 许浩, 等. 深部煤层气储层地质研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(3): 10-16.LI Song, TANG Dazhen, XU Hao, et al. Progress in geological researches on the deep coalbed methane reservoirs[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(3): 10-16. [4] 李辛子, 王运海, 姜昭琛, 等. 深部煤层气勘探开发进展与研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(1): 24-31.LI Xinzi, WANG Yunhai, JIANG Zhaochen, et al. Progress and study on exploration and production for deep coalbed methane[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(1): 24-31. [5] 江同文, 熊先钺, 金亦秋. 深部煤层气地质特征与开发对策[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1918-1930.JIANG Tongwen, XIONG Xianyue, JIN Yiqiu. Geological characteristics and development countermeasures of deep coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1918-1930. [6] 秦勇. 中国深部煤层气地质研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1791-1811.QIN Yong. Progress on geological research of deep coalbed methane in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1791-1811. [7] 徐凤银, 聂志宏, 孙伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气高效开发理论技术体系[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(1): 528-544.XU Fengyin, NIE Zhihong, SUN Wei, et al. Theoretical and technological system for highly efficient development of deep coalbed methane in the eastern edge of Erdos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(1): 528-544. [8] 李勇, 徐凤银, 唐书恒, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地煤层(岩)气勘探开发进展及发展方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(10): 63-79.LI Yong, XU Fengyin, TANG Shuheng, et al. Progress and development direction of coalbed methane (coal-rock gas) exploration and development in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(10): 63-79. [9] 秦勇, 申建, 史锐. 中国煤系气大产业建设战略价值与战略选择[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(1): 371-387.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian, SHI Rui. Strategic value and choice on construction of large CMG industry in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 371-387. [10] 秦勇. 从CNKI论文看中国煤层气产业发展[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(12): 26-29.QIN Yong. Having a view on Chinese coalbed methane industry development from CNKI publications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(12): 26-29. [11] 徐凤银, 王成旺, 熊先钺, 等. 深部(层)煤层气成藏模式与关键技术对策: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(4): 30-42.XU Fengyin, WANG Chengwang, XIONG Xianyue, et al. Deep (layer) coalbed methane reservoir forming modes and key technical countermeasures: taking the eastern margin of Ordos Basin as an example[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(4): 30-42. [12] 刘建忠, 朱光辉, 刘彦成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气勘探突破及未来面临的挑战与对策: 以临兴—神府区块为例[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1827-1839.LIU Jianzhong, ZHU Guanghui, LIU Yancheng, et al. Breakthrough, future challenges and countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin: a case study of Linxing-Shenfu block[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1827-1839. [13] 姚红生, 陈贞龙, 何希鹏, 等. 深部煤层气"有效支撑"理念及创新实践: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延川南煤层气田为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(6): 97-106.YAO Hongsheng, CHEN Zhenlong, HE Xipeng, et al. "Effective support" concept and innovative practice of deep CBM in South Yanchuan Gas Field of the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(6): 97-106. [14] 陈河青, 杨兆彪, 李道清, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地白家海凸起深部煤层气孔渗系统特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(6): 33-43.CHEN Heqing, YANG Zhaobiao, LI Daoqing, et al. Characteristics of the pore and seepage system of deep coalbed methane in the Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(6): 33-43. [15] 兰浩, 杨兆彪, 仇鹏, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地白家海凸起深部煤层气勘探开发进展及启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(2): 13-22.LAN Hao, YANG Zhaobiao, CHOU Peng, et al. Exploration and exploitation of deep coalbed methane in the Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin: progress and its implications[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(2): 13-22. [16] 孙斌, 杨敏芳, 杨青, 等. 准噶尔盆地深部煤层气赋存状态分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(S1): 195-202.SUN Bin, YANG Minfang, YANG Qing, et al. Analysis on occurrence state of deep coalbed methane in Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(S1): 195-202. [17] 明盈, 孙豪飞, 汤达祯, 等. 四川盆地上二叠统龙潭组深—超深部煤层气资源开发潜力[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(2): 102-112.MING Ying, SUN Haofei, TANG Dazhen, et al. Potential for the production of deep to ultradeep coalbed methane resources in the Upper Permian Longtan Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(2): 102-112. [18] 沈霞, 公海涛, 邵明礼, 等. 松辽盆地南部王府断陷深部煤层气地质特征及有利区评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(2): 113-121.SHEN Xia, GONG Haitao, SHAO Mingli, et al. Geological characteristics and favorable area evaluation of deep coalbed methane in Wangfu Fault Depression, southern Songliao Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(2): 113-121. [19] 杨兆彪, 高为, 秦勇, 等. 贵州深部煤层气地质特征及其资源潜力[J]. 煤炭学报, 2024, 49(S1): 348-361.YANG Zhaobiao, GAO Wei, QIN Yong, et al. Geological characteristics and resource potential of deep coalbed methane in Guizhou[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2024, 49(S1): 348-361. [20] LI Song, TANG Dazhen, PAN Zhejun, et al. Geological conditions of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China: implications for coalbed methane development[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 53: 394-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2018.03.016 [21] LI Song, QIN Yong, TANG Dazhen, et al. A comprehensive review of deep coalbed methane and recent developments in China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2023, 279: 104369. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2023.104369 [22] 桑树勋, 韩思杰, 周效志, 等. 华东地区深部煤层气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2023, 13(4): 403-415.SANG Shuxun, HAN Sijie, ZHOU Xiaozhi, et al. Deep coalbed methane resource and its exploration and development prospect in East China[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2023, 13(4): 403-415. [23] 郭伟. 延川南煤层气田基本特征与成藏关键因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(3): 341-346. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503341GUO Wei. Basic characteristics and key factors of gas accumulation in Yanchuannan coalbed gas field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(3): 341-346. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503341 [24] 李斌, 杨帆, 张红杰, 等. 神府区块深部煤层气高效开发技术研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(8): 57-68.LI Bin, YANG Fan, ZHANG Hongjie, et al. Technology for efficient production of deep coalbed methane in the Shenfu block[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(8): 57-68. [25] 吴聿元, 陈贞龙. 延川南深部煤层气勘探开发面临的挑战和对策[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(4): 1-11.WU Yuyuan, CHEN Zhenlong. Challenges and countermeasures for exploration and development of deep CBM of South Yanchuan[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(4): 1-11. [26] 陈贞龙, 郭涛, 李鑫, 等. 延川南煤层气田深部煤层气成藏规律与开发技术[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(9): 112-118.CHEN Zhenlong, GUO Tao, LI Xin, et al. Enrichment law and development technology of deep coalbed methane in South Yanchuan Coalbed Methane Field[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(9): 112-118. [27] 申鹏磊, 吕帅锋, 李贵山, 等. 深部煤层气水平井水力压裂技术: 以沁水盆地长治北地区为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(8): 2488-2500.SHEN Penglei, LV Shuaifeng, LI Guishan, et al. Hydraulic fracturing technology for deep coalbed methane horizontal wells: a case study in north Changzhi area of Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(8): 2488-2500. [28] 卢义玉, 李瑞, 鲜学福, 等. 地面定向井+水力割缝卸压方法高效开发深部煤层气探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(3): 876-884.LU Yiyu, LI Rui, XIAN Xuefu, et al. Discussion on the efficient exploitation method of deep coalbed methane with pressure relief by ground directional well+hydraulic slotting[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(3): 876-884. [29] 张聪, 李梦溪, 胡秋嘉, 等. 沁水盆地南部中深部煤层气储层特征及开发技术对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(2): 122-133.ZHANG Cong, LI Mengxi, HU Qiujia, et al. Moderately deep coalbed methane reservoirs in the southern Qinshui Basin: characteristics and technical strategies for exploitation[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(2): 122-133. [30] 马新华. 非常规天然气"极限动用"开发理论与实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(2): 326-336.MA Xinhua. "Extreme utilization" development theory of unconventional natural gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(2): 326-336. [31] 李曙光, 王成旺, 王红娜, 等. 大宁—吉县区块深层煤层气成藏特征及有利区评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(9): 59-67.LI Shuguang, WANG Chengwang, WANG Hongna, et al. Reservoir forming characteristics and favorable area evaluation of deep coalbed methane in Daning-Jixian block[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(9): 59-67. [32] 傅雪海, 秦勇. 多相介质煤层气储层渗透率预测理论与方法[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 2003: 172.FU Xuehai, QIN Yong. Theories and techniques of permeability prediction of multiphase medium coalbed-methane reservoirs[M]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology Press, 2003: 172. [33] 金毅, 祝一搏, 吴影, 等. 煤储层粗糙割理中煤层气运移机理数值分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(9): 1826-1834.JIN Yi, ZHU Yibo, WU Ying, et al. Numerical investigation of migration mechanism for coal-bed methane flow through cleats with rough surfaces in coal reservoir[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(9): 1826-1834. [34] HERIAWAN M N, KOIKE K. Coal quality related to microfractures identified by CT image analysis[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 140: 97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2015.02.001 [35] 秦勇, 申建. 论深部煤层气基本地质问题[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(1): 125-136.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian. On the fundamental issues of deep coalbed methane geology[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 125-136. [36] 康永尚, 皇甫玉慧, 张兵, 等. 含煤盆地深层"超饱和"煤层气形成条件[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1426-1438.KANG Yongshang, HUANGFU Yuhui, ZHANG Bing, et al. Formation conditions for deep oversaturated coalbed methane in coal-bearing basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1426-1438. [37] 李小刚, 杨兆中, 梁知, 等. 深埋煤层气藏水力压裂增产技术探讨[J]. 天然气与石油, 2011, 29(6): 46-48.LI Xiaogang, YANG Zhaozhong, LIANG Zhi, et al. Discussion on hydraulic fracturing for deep buried CBM[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2011, 29(6): 46-48. [38] SONG Hongqing, DU Shuyi, YANG Jiaosheng, et al. Evaluation of hydraulic fracturing effect on coalbed methane reservoir based on deep learning method considering physical constraints[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 212: 110360. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110360 [39] MOORE T A. Coalbed methane: a review[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 101: 36-81. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.05.011 -





 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号