Combined characterization of pore structurein deep medium-rank coal using mercury intrusion and liquid nitrogen adsorption methods and its pore fractal characteristics
-
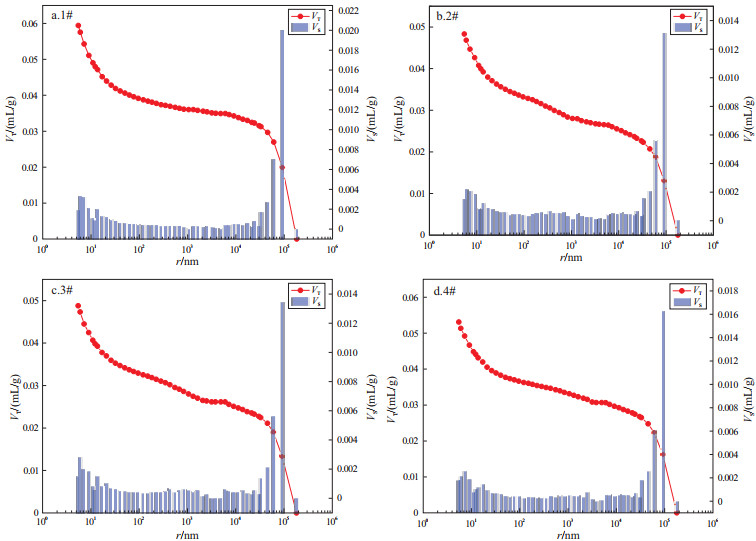
摘要: 为研究深部中阶煤的孔隙结构特征与孔隙分形规律,利用压汞法和液氮吸附法对沈阳红阳三矿、开滦林西矿、淮南新集二矿和平顶山平煤六矿等典型深部开采矿区的主采煤层煤样进行了孔径、孔容、比表面积等参数测试,基于Menger海绵模型和FHH模型进行了孔隙分形规律的研究。结果表明:①基于压汞法的孔隙结构参数测试中平均孔径31.10~34.70 nm,总孔容0.048 3 ~0.059 4 mL/g,总比表面积5.590 9 ~7.652 8 m2/g,得出典型深部开采矿区的主采煤层孔隙发育比较接近;孔容分布以大孔孔容占主导,微孔与过渡孔孔容比重相当,中孔的孔容分布相对较小,表明大孔孔隙连通性较好,中孔较为闭塞;比表面积分布以微孔为主,占比达70%以上,而中孔和大孔的比重甚微,可见微孔吸附能力最强,不利于深部煤层瓦斯治理;Menger海绵模型分形维数介于2.6~3之间,表明孔隙形状很不规则,孔隙较为复杂,整体上孔隙表面较为粗糙。②基于液氮吸附法测试的有效孔径范围为3~177 nm,总孔容与比表面积不同的矿区差异明显,孔容分布以过渡孔和中孔为主,微孔分布较低,大孔为0,表明利用液氮吸附法对于中孔、过渡孔有很好的表征,而难以表征大孔结构,且微孔的孔隙连通性较差;比表面积分布中主要为过渡孔、微孔和中孔,大孔为0,其中以过渡孔为主,且其吸附能力也较强;FHH模型分形维数介于2.0~2.7,结构较为简单规则。③讨论了深部中阶煤孔隙结构差异性,其中压汞法和液氮法的孔隙结构参数(比表面积、孔容)随埋深的增加均呈非线性的凹曲线变化;Menger海绵模型与FHH模型分形维数则随埋深的增加呈凸曲线的变化趋势。Abstract: To study the pore structure and fractal characteristics of deep medium-rank coal, combined characterization using mercury intrusion and liquid nitrogen adsorption methods was conducted on coal samples from the main coal seams in typical deep mining areas, including Shenyang Hongyang Third Mine, Kailuan Linxi Mine, Huainan Xinji Second Mine, and Pingdingshan Pingmei Sixth Mine. Parameters such as pore size, pore volume, and specific surface area were obtained, and the pore fractal characteristics were studied based on the Menger sponge model and the FHH model. The results showed that: (1) Among the pore structure parameters tested with mercury intrusion method, the average pore size ranged from 31.10 to 34.70 nm, pore volume from 0.048 3 to 0.059 4 mL/g, and specific surface area from 5.590 9 to 7.652 8 m2/g. The pore development in the main coal seams of typical deep mining areas was relatively similar. The pore volume distribution was dominated by macropores, with micropores and transition pores contributing roughly equally, and mesopores having a relatively small distribution. This indicated that macropores had better connectivity and mesopores were more closed. Micropores accounted for more than 70% of the total specific surface area, while the proportions of mesopores and macropores were minimal, indicating that micropores had the strongest adsorption capacity, which was negatively affected gas management in deep coal seams. The fractal dimensions based on the Menger sponge model ranged from 2.6 to 3.0, indicating irregular pore shapes, complex pore structures, and generally rough pore surfaces. (2) The effective pore size tested using liquid nitrogen adsorption method ranged from 3 to 177 nm with significant differences in total pore volume and specific surface area among the mining areas. Pore volume distribution was dominated by transition pores and mesopores, with a lower distribution of micropores and no macropores. This indicated that liquid nitrogen adsorption was effective for characterizing mesopores and transition pores but struggled to characterize macropore structures. Moreover, the connectivity of micropores was relatively poor. The specific surface area was mainly composed of transition pores, micropores, and mesopores, with no macropores. Among them, transition pores were mostly dominant and had relatively strong adsorption capacity. The fractal dimensions based on the FHH model ranged from 2.0 to 2.7, indicating a relatively simple and regular structure. (3) The differences in pore structures of deep medium-rank coal were discussed. The pore structure parameters (specific surface area and pore volume) determined by mercury intrusion and liquid nitrogen adsorption methods showed a non-linear concave curve variation with increasing burial depth. The fractal dimensions derived from the Menger sponge model and the FHH model showed a convex curve trend with increasing burial depth.
-
表 1 典型矿区深部主采煤层基础参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of deep main coal seams in typical mining areas
试样编号 试样来源 采样煤层 埋深/m 工业分析指标/% 煤种 Mad Aad Vad FCad 1# 红阳三矿 7#煤 1 100 0.73 11.40 11.93 75.94 瘦煤 2# 林西矿 12煤 950 0.90 11.17 18.85 69.08 焦煤 3# 新集二矿 9煤 800 2.22 26.04 28.81 42.93 气煤 4# 平煤六矿 戊8煤 940 1.70 13.74 29.27 55.29 1/3焦煤 注:Mad.空气干燥基水分;Aad.空气干燥基灰分;Vad.空气干燥基挥发分;FCad.空气干燥基固定碳。 表 2 典型矿区深部主采煤层孔径参数(压汞法)
Table 2. Pore size parameters of deep main coal seams in typical mining areas (mercury intrusion method)
试样编号 样品质量/g 孔隙度/% VT/(mL/g) ST/(m2/g) 体积中值孔径/nm 面积中值孔径/nm 平均孔径/nm 1# 1.196 3 7.720 4 0.059 4 7.652 8 44 676.40 7.700 31.10 2# 1.162 6 6.360 6 0.048 3 5.590 9 16 958.10 8.000 34.60 3# 1.148 8 6.588 8 0.048 8 5.980 5 13 595.50 7.600 32.60 4# 1.140 0 7.014 1 0.053 1 6.126 3 32 597.70 8.000 34.70 表 3 典型矿区深部主采煤层孔容分布计算表(压汞法)
Table 3. Calculation of pore volume distribution in deep main coal seams of typical mining areas (mercury intrusion method)
试样编号 总孔容(VT)/(mL/g) 分阶段孔容(VS)/(mL/g) 分阶段孔容占比/% V1 V2 V3 V4 V1/VT V2/VT V3/VT V4/VT 1# 0.059 4 0.010 4 0.010 3 0.002 7 0.036 0 17.51 17.31 4.57 60.61 2# 0.048 3 0.007 5 0.007 9 0.004 8 0.028 0 15.61 16.45 9.93 58.00 3# 0.048 8 0.008 1 0.008 1 0.004 5 0.028 1 16.67 16.66 9.23 57.44 4# 0.053 1 0.008 2 0.008 6 0.003 1 0.033 2 15.52 16.15 5.86 62.47 注:表中V1、V2、V3、V4分别指微孔(r<10 nm)、过渡孔(10≤r<100 nm)、中孔(100≤r<1 000 nm)、大孔(>1 000 nm)的孔容。 表 4 典型矿区深部主采煤层比表面积分布计算表(压汞法)
Table 4. Calculation of specific surface area distribution in deep main coal seams of typical mining areas (mercury intrusion method)
试样编号 总比表面积(ST)/(m2/g) 分阶段比表面积(SS)/(m2/g) 分阶段比表面积占比/% S1 S2 S3 S4 S1/ST S2/ST S3/ST S4/ST 1# 7.652 8 5.671 1 1.936 3 0.041 0 0.004 4 74.10 25.30 0.54 0.06 2# 5.590 9 4.079 1 1.444 4 0.062 0 0.005 4 72.96 25.83 1.11 0.10 3# 5.980 5 4.441 7 1.476 8 0.055 0 0.007 0 74.27 24.69 0.92 0.12 4# 6.126 3 4.471 9 1.607 4 0.039 2 0.007 8 73.00 26.24 0.64 0.12 注:表中S1、S2、S3、S4分别指微孔、过渡孔、中孔和大孔的比表面积。 表 5 典型矿区深部主采煤层海绵模型分形维数计算表
Table 5. Calculation of fractal dimensions of Sponge model for deep main coal seams in typical mining areas
试样编号 拟合方程 拟合度(R2) 方程斜率(K) 分形维数(DS) 1# y=-1.356 5x-2.042 5 0.945 8 -1.356 5 2.643 5 2# y=-1.060 9x-2.415 6 0.949 3 -1.060 9 2.939 1 3# y=-1.128 2x-2.295 1 0.964 7 -1.128 2 2.871 8 4# y=-1.214 7x-2.152 9 0.968 4 -1.214 7 2.735 3 表 6 典型矿区深部主采煤层孔容分布计算表(液氮法)
Table 6. Calculation of pore volume distribution in deep main coal seams of typical mining areas (liquid nitrogen method)
试样编号 样品质量/g 总孔容(VT)/(mL/mg) 分阶段孔容(VS)/(mL/mg) 分阶段孔容占比/% V1 V2 V3 V4 V1/VT V2/VT V3/VT V4/VT 1# 2.794 1 1.801 3 0.003 6 0.754 1 1.043 6 0 0.20 41.86 57.94 0 2# 3.310 5 3.838 8 0.088 7 1.689 9 2.060 2 0 2.31 44.02 53.67 0 3# 2.679 4 8.199 1 1.131 2 3.753 9 3.314 0 0 13.80 45.78 40.42 0 4# 3.338 1 3.117 0 0.110 8 1.308 8 1.697 4 0 3.55 41.99 54.46 0 表 7 典型矿区深部主采煤层比表面积分布计算表(液氮法)
Table 7. Calculation of specific surface area distribution in deep main coal seams of typical mining areas (liquid nitrogen adsorption method)
试样编号 样品质量/g 总比表面积(ST)/(m2/g) 分阶段比表面积(SS)/(m2/g) 分阶段比表面积占比/% S1 S2 S3 S4 S1/ST S2/ST S3/ST S4/ST 1# 2.794 1 0.117 7 0.001 5 0.092 6 0.023 6 0 1.27 78.67 20.05 0 2# 3.310 5 0.324 5 0.048 1 0.221 5 0.054 9 0 14.82 68.26 16.92 0 3# 2.679 4 1.561 4 0.882 2 0.590 5 0.088 8 0 56.49 37.82 5.69 0 4# 3.338 1 0.283 5 0.056 5 0.182 9 0.044 2 0 19.93 64.51 15.56 0 表 8 典型矿区深部主采煤层FHH模型分形维数计算表
Table 8. Calculation of fractal dimensions of FHH model for deep main coal seams in typical mining areas
试样编号 拟合方程 拟合度(R2) 方程斜率(K) 分形维数(DF) 1# y=-0.939 5x-4.298 6 0.986 9 -0.939 5 2.060 5 2# y=-0.558 9x-1.869 1 0.980 5 -0.558 9 2.441 1 3# y=-0.376 2x-0.055 0 0.999 7 -0.376 2 2.623 8 4# y=-0.635 2x-2.313 5 0.999 1 -0.635 2 2.364 8 -
[1] YAO Yanbin, LIU Dameng, CAI Yidong, et al. Advanced characterization of pores and fractures in coals by nuclear magnetic resonance and X-ray computed tomography[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2010, 53(6): 854-862. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-0057-4 [2] LI Qi, WU Yong, QIAO Lei. Comprehensive characterization and metamorphic control analysis of full apertures in different coal ranks within deep coal seams[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(18): 8566. doi: 10.3390/app14188566 [3] YAO Yanbin, LIU Dameng, CHE Yao, et al. Non-destructive characterization of coal samples from China using microfocus X-ray computed tomography[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2009, 80(2): 113-123. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2009.08.001 [4] LI Qi, QIN Yujin, REN Shaokui. Structural characterization analysis and macromolecular model construction of coal from Qinggangping coal mine[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 14365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-40753-x [5] 秦雷, 王平, 翟成, 等. 基于氮气吸附法和压汞法低温液氮冻结煤体分形特征研究[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2023, 40(1): 184-193.QIN Lei, WANG Ping, ZHAI Cheng, et al. Research on fractal characteristics of coal freezing with low temperature liquid nitrogen using nitrogen adsorption method and mercury intrusion method[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2023, 40(1): 184-193. [6] 楚亚培, 张东明, 王满, 等. 基于核磁共振技术和压汞法的液氮冻融煤体孔隙结构损伤演化规律试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(9): 1820-1831.CHU Yapei, ZHANG Dongming, WANG Man, et al. Experiment study on influence of liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw on pore structure of coal based on nuclear magnetic resonance technology and mercury intrusion methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(9): 1820-1831. [7] 申艳军, 王旭, 赵春虎, 等. 榆神府矿区富油煤多尺度孔隙结构特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(3): 33-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.03.005SHEN Yanjun, WANG Xu, ZHAO Chunhu, et al. Experimental study on multi-scale pore structure characteristics of tar-rich coal in Yushenfu mining area[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3): 33-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2021.03.005 [8] 杨明, 柳磊, 刘佳佳, 等. 中阶煤孔隙结构的氮吸附—压汞—核磁共振联合表征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(5): 67-74.YANG Ming, LIU Lei, LIU Jiajia, et al. Study on joint characterization of pore structure of middle-rank coal by nitrogen adsorption-mercury intrusion-NMR[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 67-74. [9] 聂百胜, 马延崑, 何学秋, 等. 煤与瓦斯突出微观机理探索研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(2): 207-220.NIE Baisheng, MA Yankun, HE Xueqiu, et al. Micro-scale mechanism of coal and gas outburst: a preliminary study[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(2): 207-220. [10] 孙家广, 赵贤正, 桑树勋, 等. 基于光学显微观测的煤层裂隙发育特征、成因及其意义: 以沁水盆地南部3#煤层为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(6): 738-744.SUN Jiaguang, ZHAO Xianzheng, SANG Shuxun, et al. Development characteristics, origins and significance of coal seam fractures under optical microscope: taking coal seam 3# in southern Qinshui Basin as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(6): 738-744. [11] 张宁远, 姚素平. 脆性变形序列构造煤纳米孔隙和粗糙度的原子力显微镜研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(5): 32-42.ZHANG Ningyuan, YAO Suping. Nanopore structure and surface roughness in brittle tectonically deformed coals explored by atomic force microscopy[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(5): 32-42. [12] PAN Jienan, WANG Kai, HOU Quanlin, et al. Micro-pores and fractures of coals analysed by field emission scanning electron microscopy and fractal theory[J]. Fuel, 2016, 164: 277-285. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.10.011 [13] 赵迪斐, 郭英海, 毛潇潇, 等. 基于压汞、氮气吸附与FE-SEM的无烟煤微纳米孔特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(6): 1517-1526.ZHAO Difei, GUO Yinghai, MAO Xiaoxiao, et al. Characteristics of macro-nanopores in anthracite coal based on mercury injection, nitrogen adsorption and FE-SEM[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(6): 1517-1526. [14] 杨青, 李剑, 田文广, 等. 海拉尔盆地褐煤全孔径结构特征及影响因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(11): 1603-1614.YANG Qing, LI Jian, TIAN Wenguang, et al. Characteristics on pore structures on full scale of lignite and main controlling factors in Hailar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(11): 1603-1614. [15] 张文政, 王经玺. 基于显微CT的不同煤种微观孔隙结构综合表征[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(S2): 85-92.ZHANG Wenzheng, WANG Jingxi. Characterization of microscopic pore structure of different coal types based on micro CT[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(S2): 85-92. [16] 杨明, 柳磊, 张学博, 等. 不同阶煤孔隙结构与流体特性的核磁共振试验研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(1): 81-88.YANG Ming, LIU Lei, ZHANG Xuebo, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance experimental study on pore structure and fluid characteristics of coal at different ranks[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(1): 81-88. [17] 翟成, 孙勇, 范宜仁, 等. 低场核磁共振技术在煤孔隙结构精准表征中的应用与展望[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(2): 828-848.ZHAI Cheng, SUN Yong, FAN Yiren, et al. Application and prospect of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance technology in accurate characterization of coal pore structure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(2): 828-848. [18] 孙英峰, 赵毅鑫, 王欣, 等. 基于同步辐射装置定量表征煤孔隙结构非均质性和各向异性[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6): 1128-1137.SUN Yingfeng, ZHAO Yixin, WANG Xin, et al. Synchrotron radiation facility-based quantitative evaluation of pore structure heterogeneity and anisotropy in coal[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1128-1137. [19] 蒋静宇, 程远平, 张硕. 低阶煤孔隙结构定量表征及瓦斯吸附放散特性[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(10): 3221-3233.JIANG Jingyu, CHENG Yuanping, ZHANG Shuo. Quantitative characterization of pore structure and gas adsorption and diffusion properties of low-rank coal[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(10): 3221-3233. [20] 张驰, 关平, 张济华, 等. 分形理论表征非常规油气储层孔隙结构特征研究进展[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 59(5): 897-908.ZHANG Chi, GUAN Ping, ZHANG Jihua, et al. A review of the progress on fractal theory to characterize the pore structure of unconventional oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2023, 59(5): 897-908. [21] MANDELBROT B. How long is the coast of Britain?Statistical self-similarity and fractional dimension[J]. Science, 1967, 156(3775): 636-638. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3775.636 [22] MANDELBROT B B. On the geometry of homogeneous turbulence, with stress on the fractal dimension of the iso-surfaces of scalars[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1975, 72(3): 401-416. doi: 10.1017/S0022112075003047 [23] 陈向军, 赵伞, 司朝霞, 等. 不同变质程度煤孔隙结构分形特征对瓦斯吸附性影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(2): 118-124.CHEN Xiangjun, ZHAO San, SI Zhaoxia, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore structure of coal with different metamorphic degrees and its effect on gas adsorption characteristics[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(2): 118-124. [24] 王秀娟, 要惠芳, 李伟, 等. 基于热力学模型的煤孔隙结构分形表征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2014, 42(6): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.06.004WANG Xiujuan, YAO Huifang, LI Wei, et al. Fractal characterization of pore structure in coals based on thermodynamics model[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2014, 42(6): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.06.004 [25] 杨师宇, 姚艳斌, 魏韧, 等. 乌鲁木齐河东矿区煤储层渗流孔孔隙分形特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(8): 175-183.YANG Shiyu, YAO Yanbin, WEI Ren, et al. Study on fractal characteristics of seepage pores of coal reservoirs in Hedong mining area of Urumqi[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(8): 175-183. [26] 刘怀谦, 王磊, 谢广祥, 等. 煤体孔隙结构综合表征及全孔径分形特征[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2022, 39(3): 458-469.LIU Huaiqian, WANG Lei, XIE Guangxiang, et al. Comprehensive characterization and full pore size fractal characteristics of coal pore structure[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2022, 39(3): 458-469. [27] KROHN C E. Fractal measurements of sandstones, shales, and carbonates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1988, 93(B4): 3297-3305. doi: 10.1029/JB093iB04p03297 [28] 李俊键, 刘洋, 高亚军, 等. 微观孔喉结构非均质性对剩余油分布形态的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6): 1043-1052.LI Junjian, LIU Yang, GAO Yajun, et al. Effects of microscopic pore structure heterogeneity on the distribution and morphology of remaining oil[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6): 1043-1052. [29] 贺伟, 钟孚勋, 贺承祖, 等. 储层岩石孔隙的分形结构研究和应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2000, 20(2): 67-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2000.02.019HE Wei, ZHONG Fuxun, HE Chengzu, et al. Fractal texture research on the pores in reservoir rocks and its application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2000, 20(2): 67-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2000.02.019 [30] 薛海腾, 李希建, 陈刘瑜, 等. 黔西突出煤的微观孔隙分形特征及其对渗透率的影响[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(3): 118-122.XUE Haiteng, LI Xijian, CHEN Liuyu, et al. Micro-pore fractal characteristics of outburst coal in western Guizhou and its influence on permeability[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(3): 118-122. [31] PFEIFER P, WU Y J, COLE M W, et al. Multilayer adsorption on a fractally rough surface[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1989, 62(17): 1997-2000. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.1997 [32] 周三栋, 刘大锰, 蔡益栋, 等. 低阶煤吸附孔特征及分形表征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 373-383.ZHOU Sandong, LIU Dameng, CAI Yidong, et al. Characterization and fractal nature of adsorption pores in low rank coal[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 373-383. [33] HU Song, SUN Xuexin, XIANG Junzheng, et al. Correlation characteristics and simulations of the fractal structure of coal char[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2004, 9(3): 291-303. doi: 10.1016/S1007-5704(02)00135-1 [34] HU Song, LI Min, JUN Xiang, et al. Fractal characteristic of three Chinese coals[J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(10): 1307-1313. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2003.12.011 [35] 熊益华, 周尚文, 焦鹏飞, 等. 基于低温CO2吸附的煤和页岩微孔结构分形分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(7): 1028-1040.XIONG Yihua, ZHOU Shangwen, JIAO Pengfei, et al. Fractal analysis of micropore structures in coal and shale based on low-temperature CO2 adsorption[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(7): 1028-1040. [36] 郝晋伟, 李阳. 构造煤孔隙结构多尺度分形表征及影响因素研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(8): 164-174.HAO Jinwei, LI Yang. Research on multi-scale fractal characteristics of pore structure in tectonic coal and analysis of its influence factors[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(8): 164-174. [37] 于不凡. 煤矿瓦斯灾害防治及利用技术手册[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2005.YU Bufan. Technical manual for prevention and utilization of coal mine gas disasters[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Publishing House, 2005. [38] YU Song, JIANG Bo, PEI Shao, et al. Matrix compression and multifractal characterization for tectonically deformed coals by Hg porosimetry[J]. Fuel, 2018, 211: 661-675. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.09.070 [39] WASHBURN E W. The dynamics of capillary flow[J]. Physical Review, 1921, 17(3): 273-283. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.17.273 [40] LEON C A L. New perspectives in mercury porosimetry[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 1998, 76: 341-372. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Carlos_Leon_Y_Leon3/publication/232359690_New_Perspectives_in_Mercury_Porosimetry/links/548ed75c0cf225bf66a725cf.pdf [41] FALLICO C, TARQUIS A M, DE BARTOLO S, et al. Scaling analysis of water retention curves for unsaturated sandy loam soils by using fractal geometry[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 61(3): 425-436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01239.x [42] HODOT B B. Outburst of coal and coalbed gas[M]. Beijing: China Industry Press, 1966: 310-318. [43] OUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739-1758. doi: 10.1351/pac199466081739 [44] PFEIFER P, AVNIR D. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three. I. Fractal theory of heterogeneous surfaces[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1983, 79(7): 3558-3565. doi: 10.1063/1.446210 [45] AVNIR D, JARONIEC M. An isotherm equation for adsorption on fractal surfaces of heterogeneous porous materials[J]. Langmuir, 1989, 5(6): 1431-1433. doi: 10.1021/la00090a032 [46] JARONIEC M. Evaluation of the fractal dimension from a single adsorption isotherm[J]. Langmuir, 1995, 11(6): 2316-2317. doi: 10.1021/la00006a076 [47] 谢和平. 分形—岩石力学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.XIE Heping. Introduction to fractal rock mechanics[M] Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [48] 陈静, 崔啸, 王磊, 等. 不同埋深煤体孔隙结构特征及瓦斯吸附特性研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2023, 43(3): 166-171.CHEN Jing, CUI Xiao, WANG Lei, et al. Study on pore structure characteristics and gas adsorption characteristics of coal body with different buried depths[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2023, 43(3): 166-171. [49] 冯翠荣, 马海军, 李彦朋. 呼和湖凹陷煤层气地质条件及资源潜力分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(26): 17-24.FENG Cuirong, MA Haijun, LI Yanpeng. Geological conditions and resource potential analysis of coalbed methane in the Huhehu Depression[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(26): 17-24. [50] 陆小霞, 黄文辉, 陈燕萍, 等. 沁水盆地南部深煤层孔隙结构特征[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2015, 39(3): 41-49.LU Xiaoxia, HUANG Wenhui, CHEN Yanping, et al. Pore structure of deep coal seam in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2015, 39(3): 41-49. [51] 刘长江, 张琨, 宋璠. CO2地质埋藏深度对高阶煤孔隙结构的影响[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(5): 32-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.005LIU Changjiang, ZHANG Kun, SONG Fan. Influences of burial depth on pore structure of high-rank coal during the CO2 storage process[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(5): 32-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.005 [52] 申建. 论深部煤层气成藏效应[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(9): 1599-1600.SHEN Jian. CBM-reservoiring effect in deep strata[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(9): 1599-1600. [53] 孟召平, 田永东, 李国富. 沁水盆地南部煤储层渗透性与地应力之间关系和控制机理[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(10): 1142-1148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.10.018MENG Zhaoping, TIAN Yongdong, LI Guofu. The relationship and control mechanism between permeability and geostress of coal reservoirs in the southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Progress in Natural Sciences, 2009, 19(10): 1142-1148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.10.018 -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号