Analysis of pressure-maintaining coring process in deep coal seams and gas content determination methods
-
摘要: 含气量是煤层气储量计算和勘探开发的重要参数。针对深煤层,由于提心时间长,损失气量计算失准,导致绳索取心含气量测试方法准确性降低。为了准确获取深煤层的真实含气量,确定气体的赋存状态,能够保留样品原位压力和原位含气量的保压取心技术被认为是最有效的方法。然而,由于非常规储层保压取心的特殊性(含吸附气),目前还没有统一的取心流程和标准的含气量测定方法。为此,通过分析保压取心各阶段的环境特点和含气量损失特征,针对深煤层存在吸附气和游离气的特点,提出了基于保压取心的吸附气和游离气的测定方法。分析表明,保压取心含气量计算具有“四阶段、两损失、两收集”的特点;合理设计保压取心降压集气阶段的压力点,能够有效区分吸附气和游离气。此外,分析保压取心和常规绳索取心的差异和联系,认为通过同井台保压取心含气量可校正绳索取心损失气量,进而建立基于绳索取心的深煤层含气量计算方法。保压取心技术的成功应用对深煤层勘探意义重大,建议在深煤层勘探区适当增加保压取心井测试,以明确储层的真实含气性。Abstract: Gas content is an important parameter for calculating coalbed methane (CBM) reserves and guiding their exploration and development. For deep coal seams, the prolonged coring duration and inaccuracies in lost gas volume calculations result in reduced accuracy in gas content measurement using conventional wireline coring methods. To accurately determine the actual gas content in deep coal seams and gas occurrence state, pressure-maintaining coring technology, which retains in-situ pressure and gas content in samples, is considered the most effective method. However, due to the unique characteristics of unconventional reservoirs, such as adsorption gas, there are currently no standardized coring processes or gas content determination methods. To address this issue, this paper analyzed the environmental conditions and gas loss characteristics during each stage of pressure-maintaining coring. Considering the presence of both adsorbed gas and free gas in deep coal seams, the study proposes a method for determining both components based on pressure-maintaining coring. The analysis shows that gas content calculations in pressure-maintaining coring have the characteristics of "four stages, two losses, and two collections". The reasonable design of pressure points during pressure-reducing and gas-collecting stages of pressure-maintaining coring can effectively distinguish adsorption gas from free gas. In addition, by analyzing the differences and connections between the two methods, the gas content measured using pressure-maintaining coring can be used to correct gas loss caused by using wireline coring at the same well platform. Based on this, a method for calculating gas content in deep coal seams based on wireline coring was established. The successful application of pressure-maintaining coring technology is significant for deep coal seam exploration. The study recommends appropriately increasing the number of pressure-maintaining coring test wells in deep coal seam exploration areas to precisely determine the actual gas content in reservoirs.
-
表 1 保压取心阶段划分
Table 1. Division of pressure coring stages
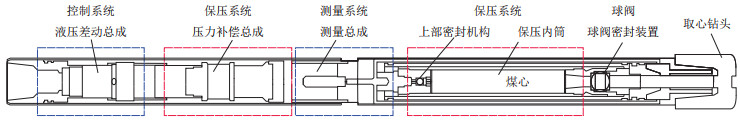
阶段 工具 环境条件 气体损失情况 重点测试数据 钻心阶段 保压取心工具 高温高压 基本无气体损失 岩心筒温压变化 提心阶段 保压取心工具 降温(高温—常温)高压 可能造成气体损失(保压率) 岩心筒温压变化 取心筒降压排气阶段 气液分离装置等 常温高压 可能造成气体损失(钻井泥浆喷射) 岩心筒温压变化、集气量、环境温压特点 岩心出筒阶段 记录设备等 常温常压 主要损失气阶段 岩心出筒时间以及岩心整理时间 解吸气和残余气测量阶段 解吸罐等 室温常压 基本无气体损失 装罐时间、岩心质量和长度等 表 2 保压取心和常规绳索取心测试方法结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of test results between pressure-maintaining coring and conventional wireline coring methods
矿区 井位 深度/m 取心类型 气类型 含气量/(m3/t) 昭通地区[17] Y151 1 699.50~1 726.68 常规取心 页岩气 0.72~2.13 1 727.07~1 764.96 保压取心 1.72~5.36 芦岭矿区[19] LLMBQX 673.6~675.9 常规取心 煤层气 8.70 676.8~678.1 保压取心 10.50~10.72 潘三矿区[19] PSK 739.9~740.7 常规取心 煤层气 5.92~6.04 736.4~738.9 保压取心 7.19~7.87 晋城矿区[20] SHX2-01 331.30~332.20 常规取心 煤层气 7.81~7.89 334.30~334.60 保压取心 8.93 SHX2-02 431.80~433.58 常规取心 煤层气 5.60~6.65 435.20~436.20 保压取心 7.25 SHX3-02 314.79~316.65 常规取心 煤层气 8.76~8.79 317.20~318.00 保压取心 9.89 晋城矿区[21] 常规取心 煤层气 18.07 保压取心 22.65 淮北矿区[21] 常规取心 煤层气 8.68 保压取心 11.76 大吉矿区[22] P19-Y1,P20-Y2,P22-Y1-Y2 >2 000 常规取心 煤层气 19.76~24.68 P20-Y2-Y5 >2 000 保压取心 煤层气 22.87~29.89 -
[1] 徐凤银, 侯伟, 熊先钺, 等. 中国煤层气产业现状与发展战略[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(4): 669-682.XU Fengyin, HOU Wei, XIONG Xianyue, et al. The status and development strategy of coalbed methane industry in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(4): 669-682. [2] 康永尚, 邓泽, 皇甫玉慧, 等. 中煤阶煤层气高饱和—超饱和带的成藏模式和勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(12): 1555-1566. doi: 10.7623/syxb202012009KANG Yongshang, DENG Ze, HUANGFU Yuhui, et al. Accumulation model and exploration direction of high- to over-saturation zone of the medium-rank coalbed methane[J]. Acta Petrolei sinica, 2020, 41(12): 1555-1566. doi: 10.7623/syxb202012009 [3] 周优, 张松航, 唐书恒, 等. 柿庄南区块3号煤层含气量三维建模[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(1): 96-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.013ZHOU You, ZHANG Songhang, TANG Shuheng, et al. Gas content modeling of No. 3 coal seam in district 3 of southern Shizhuang block[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(1): 96-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.01.013 [4] 徐凤银, 闫霞, 李曙光, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部(层)煤层气勘探开发理论技术难点与对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(1): 115-130.XU Fengyin, YAN Xia, LI Shuguang, et al. Theoretical and technological difficulties and countermeasures of deep CBM exploration and development in the eastern edge of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(1): 115-130. [5] 傅雪海, 张小东, 韦重韬. 煤层含气量的测试、模拟与预测研究进展[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(1): 13-31.FU Xuehai, ZHANG Xiaodong, WEI Chongtao. Review of research on testing, simulation and prediction of coalbed methane content[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(1): 13-31. [6] 吴双. 深部煤层气储层储渗机理及开发特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.WU Shuang. Storage-seepage mechanism and development features of deep coalbed methane reservoir[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018. [7] 范章群, 张群, 卢相臣, 等. 煤层气损失气含量及其影响因素分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2010, 38(3): 104-108.FAN Zhangqun, ZHANG Qun, LU Xiangchen, et al. Analysis on gas lost content of coal bed methane and influenced factors[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2010, 38(3): 104-108. [8] 张群, 范章群. 煤层气损失气含量模拟试验及结果分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2009, 34(12): 1649-1654. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.12.012ZHANG Qun, FAN Zhangqun. Simulation experiment and result analysis on lost gas content of coalbed methane[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(12): 1649-1654. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9993.2009.12.012 [9] 刘刚, 赵谦平, 高潮, 等. 提高页岩含气量测试中损失气量计算精度的解吸临界时间点法[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(2): 71-75.LIU Gang, ZHAO Qianping, GAO Chao, et al. A critical desorption time method to improve the calculation accuracy of gas loss in shale gas content testing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(2): 71-75. [10] 邓泽, 刘洪林, 康永尚. 煤层气含气量测试中损失气量的估算方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(3): 85-86. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.03.027DENG Ze, LIU Honglin, KANG Yongshang. Estimation methods of lost gas in coalbed gas content testing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(3): 85-86. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.03.027 [11] BJORUM M. A new coring technology to quantify hydrocarbon content and saturation[C]//Proceedings of the SPE Unconventional Resources Conference. Calgary: SPE, 2013: 1-4. [12] 陈雄, 胡杰. 不同取样方式对煤层瓦斯含量测定的研究分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2017, 43(2): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.02.004CHEN Xiong, HU Jie. The research on determination of coal seam gas content based on different sampling modes[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 43(2): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-425X.2017.02.004 [13] 杨昌光, 缑发现, 贾翠芝. 用风力排渣采样方法测定煤层瓦斯含量[J]. 煤矿安全, 2000, 31(2): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2000.02.005YANG Changguang, GOU Faxian, JIA Cuizhi. Determination of coal seam gas content by sampling method of wind slagging[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2000, 31(2): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-496X.2000.02.005 [14] 谢和平, 崔鹏飞, 尚德磊, 等. 深部煤层原位保压取心技术原理与瓦斯参数测定研究进展[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(8): 1-12.XIE Heping, CUI Pengfei, SHANG Delei, et al. Research advances on the in-situ pressure-preserved coring and gas parameter determination for deep coal seams[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(8): 1-12. [15] 俱养社, 马峰良, 华立. 钻孔瓦斯密闭保压取心器研制及应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(4): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.04.15JU Yangshe, MA Fengliang, HUA Li. Development and application of borehole gas airtight pressurized corer[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(4): 79-83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.04.15 [16] 王西贵, 邹德永, 杨立文, 等. 深层超深层煤层气保压取心工具设计[J]. 石油机械, 2020, 48(1): 40-45.WANG Xigui, ZOU Deyong, YANG Liwen, et al. Design of a pressure-preservation coring tool for deep and ultra-deep coalbed methane samples[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2020, 48(1): 40-45. [17] 周尚文, 张介辉, 邹辰, 等. 基于保压取心的页岩含气量测试新方法[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(4): 1637-1646.ZHOU Shangwen, ZHANG Jiehui, ZOU Chen, et al. A new method for testing shale gas content based on pressure-holding coring technology[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(4): 1637-1646. [18] 孙四清, 张群, 郑凯歌, 等. 地面井煤层气含量精准测试密闭取心技术及设备[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(7): 2523-2530.SUN Siqing, ZHANG Qun, ZHENG Kaige, et al. Technology and equipment of sealed coring for accurate determination of coalbed gas content in ground well[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(7): 2523-2530. [19] 任红, 裴学良, 吴仲华, 等. 天然气水合物保温保压取心工具研制及现场试验[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2018, 46(3): 44-48.REN Hong, PEI Xueliang, WU Zhonghua, et al. Development and field tests of pressure-temperature preservation coring tools for gas hydrate[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2018, 46(3): 44-48. [20] 龙威成, 孙四清. 煤层气含量测定用绳索密闭取心装置及技术研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(3): 133-139.LONG Weicheng, SUN Siqing. Research on wireline sealed coring equipment and technology for coalbed methane content determination[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(3): 133-139. [21] 景兴鹏. 煤层气含量密闭取心测定装置及测试技术[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2019, 39(4): 603-609.JING Xingpeng. Testing device of methane content sealed coring and measuring technology[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2019, 39(4): 603-609. [22] 聂志宏, 时小松, 孙伟, 等. 大宁—吉县区块深层煤层气生产特征与开发技术对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(3): 193-200.NIe Zhihong, SHI Xiaosong, SUN Wei, et al. Production characteristics of deep coalbed methane gas reservoirs in Daning-Jixian block and its development technology countermeasures[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 193-200. [23] 朱庆忠, 苏雪峰, 杨立文, 等. GW-CP194-80M型煤层气双保压取心工具研制及现场试验[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(5): 139-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.05.021ZHU Qingzhong, SU Xuefeng, YANG Liwen, et al. Development and field test of GW-CP194-80M CBM dual pressure coring tool[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(5): 139-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.05.021 [24] 杨立文, 苏洋, 罗军, 等. GW-CP194-80A型保压取心工具的研制[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(4): 91-96. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.04.011YANG Liwen, SU Yang, LUO Jun, et al. Development and application of GW-CP194-80A pressure-maintaining coring tool[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(4): 91-96. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.04.011 [25] LI Wenbiao, LI Xiao, ZHAO Shengxian, et al. Evaluation on carbon isotope fractionation and gas-in-place content based on pressure-holding coring technique[J]. Fuel, 2022, 315: 123243. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123243 [26] 李小洋, 张永勤, 王汉宝, 等. 煤层气调查评价钻探保压取心钻具设计与试制[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(4): 1045-1050.LI Xiaoyang, ZHANG Yongqin, WANG Hanbao, et al. Design and trial-manufacture of the pressure-holding core drilling tool for evaluation of coal-seam gas[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(4): 1045-1050. [27] 马力宁, 李江涛, 华锐湘, 等. 保压取心储层流体饱和度分析方法: 以柴达木盆地台南气田第四系生物成因气藏为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 76-80.MA Lining, LI Jiangtao, HUA Ruixiang, et al. An analysis method for reservoir fluid saturation by pressure coring: a case study from Quaternary biogenetic gas reservoirs in the Tainan Gas Field, Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(1): 76-80. [28] 杨立文, 孙文涛, 罗军, 等. GWY194-70BB型保温保压取心工具的研制和应用[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2014, 36(5): 58-61.YANG Liwen, SUN Wentao, LUO Jun, et al. Study and application of GWY194-70BB heat and pressure preservation coring tool[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2014, 36(5): 58-61. [29] 闫涛滔, 郭怡琳, 孟艳军, 等. 基于煤层气井生产数据的储层含气量校正新方法[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(5): 1360-1370.YAN Taotao, GUO Yilin, MENG Yanjun, et al. Coal reservoir gas content correction based on coalbed methane well production data[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(5): 1360-1370. [30] 王思远. 煤岩与页岩原位含气性评价与地质应用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2020.WANG Siyuan. Study on the method of gas-in-place content evaluation in coal and shale reservoirs and it's geological application[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2020. [31] 姚光华, 王晓泉, 杜宏宇, 等. USBM方法在页岩气含气量测试中的适应性[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(6): 802-806.YAO Guanghua, WANG Xiaoquan, DU Hongyu, et al. Applicability of USBM method in the test on shale gas content[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(6): 802-806. [32] 秦勇, 申建, 李小刚. 中国煤层气资源控制程度及可靠性分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(6): 19-32.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian, LI Xiaogang. Control degree and reliability of CBM resources in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(6): 19-32. [33] 秦勇, 申建. 论深部煤层气基本地质问题[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(1): 125-136.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian. On the fundamental issues of deep coalbed methane geology[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 125-136. [34] 李勇, 高爽, 吴鹏, 等. 深部煤层气游离气含量预测模型评价与校正: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层为例[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1892-1902.LI Yong, GAO Shuang, WU Peng, et al. Evaluation and correction of prediction model for free gas content in deep coalbed methane: a case study of deep coal seams in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1892-1902. [35] 徐旭辉, 周卓明, 宋振响, 等. 油气资源评价方法关键参数研究和资源分布特征: 以中国石化探区"十三五"资源评价为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 832-843. https://read.cnki.net/web/Journal/Article/SYSD202305002.htmlXU Xuhui, ZHOU Zhuoming, SONG Zhenxiang, et al. Methods and key parameters for oil and gas resource assessment and distribution characteristics of oil and gas resource: a case study of resource assessment of SINOPEC during the 13th Five-Year Plan period[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 832-843. https://read.cnki.net/web/Journal/Article/SYSD202305002.html [36] 程建, 周小进, 刘超英, 等. 中西部大盆地重点勘探领域战略选区研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 229-237. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302229CHENG Jian, ZHOU Xiaojin, LIU Chaoying, et al. Strategic area selection and key exploration fields in central and western large basins[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 229-237. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302229 -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号