Geological characteristics and development effect evaluation of coalbed methane reservoirs in Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
-
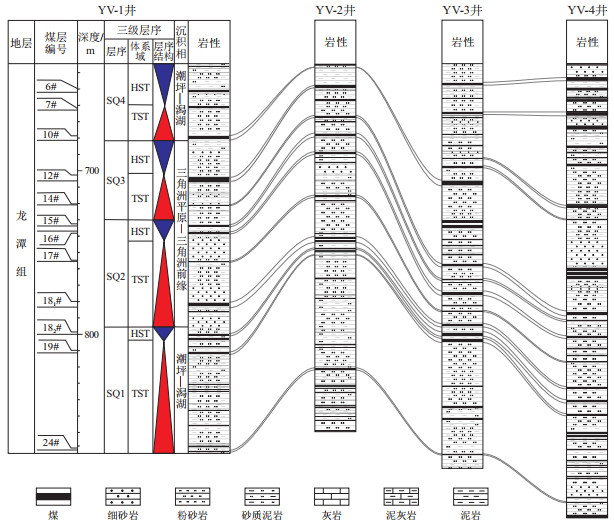
摘要: 贵州省上二叠统龙潭组煤层多,煤层气资源丰度高,具备煤层气开发的资源基础,但煤层渗透率较低,影响气、水产出,需探索适应贵州省低渗、多煤层条件下的煤层气开发关键技术。根据盘关向斜煤储层地质特征及煤层气井工程资料,从地质、压裂、排采指标3个维度开展研究分析,总结低渗、多煤层的煤层气开发技术。盘关向斜工程实践表明:①该向斜12#、18#煤层合层开发煤层气,渗透率、储层温度、破裂压力、每米煤层的加液量及加砂量、压降速率、提产速率对煤层气井产气的影响较大;②提高每米煤层的加液量及加砂量指标,能够显著提高压裂改造后的储层渗透率,YP-1井改造后渗透率达到64.158×10-3 μm2,提高1 304倍;③控制合适的压降速率、提产速率能够提高煤层气井的压裂液返排率及扩大压降漏斗半径,YP-1井排采210 d后压裂液累计返排率达到82.53%,产水半径达到压裂影响半径的91%,对扩大有效解吸半径及提高产气效果有利。针对盘关向斜低渗、多煤层的地质条件,建议采取“选层射孔、分段压裂、合层排采”的工艺技术进行煤层气开发,从而提高煤层气开发的地质及工程潜力。Abstract: The Upper Permian Longtan Formation in Guizhou Province contains multiple coal seams with abundant coalbed methane (CBM) resources, providing a solid base for CBM development. However, the low permeability of the coal seams hinders gas and water production, necessitating the development of key technologies for CBM development under conditions of low permeability and multiple coal seams in Guizhou. Based on the geological characteristics of coal reservoirs in the Panguan syncline and CBM well engineering data, the study analyzed geological, fracturing, and drainage and production parameters, and summarized development technologies for low-permeability and multi-seam CBM reservoirs. Engineering practices in Panguan syncline show that: (1) For commingled development of coal seams 12# and 18# in the syncline, factors such as permeability, reservoir temperature, fracture pressure, liquid and sand addition per meter of coal seam, pressure drop rate, and production enhancement rate significantly influence gas production of CBM wells. (2) Increasing the liquid and sand addition per meter of coal seam can significantly increase the reservoir permeability after fracturing. The permeability of well YP-1 after fracturing reached 64.158×10-3 μm2, 1 304 times higher than before. (3) Controlling pressure drop rate and production enhancement rate to appropriate levels can improve the fracturing fluid flowback rate and expand the pressure drop funnel radius of CBM wells. The cumulative fracturing fluid flowback rate of well YP-1 reached 82.53% after 210 days of drainage and production, with the water production radius reaching 91% of the fracturing influence radius. This helps to expand effective desorption radius and improve the effectiveness of gas production. For the Panguan syncline with low permeability and multiple coal seams, the study suggests adopting the technical approach of "selected layer perforation, segmented fracturing, and commingled drainage and production" to improve the geological and engineering potential of CBM development.
-
表 1 贵州省盘关向斜YV-1井含气性数据
Table 1. Gas content of well YV-1, Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
煤层号 煤层深度/m 兰氏体积/(m3/t) 兰氏压力/MPa 实测含气量/(m3/t) 含气饱和度/% 12# 723 22.90 1.85 15.52 88 18# 774 17.63 1.43 12.05 82 表 2 贵州省盘关向斜压力梯度
Table 2. Pressure gradient of Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
井号 煤层号 煤层深度/m 破裂压力/MPa 破裂压力梯度/(MPa/hm) 闭合压力/MPa 闭合压力梯度/(MPa/hm) YV-1井 12# 723 13.85 1.92 12.17 1.69 18# 774 14.17 1.83 12.18 1.57 YV-3井 12# 567 13.22 2.30 11.59 2.02 表 3 贵州省盘关向斜煤层气井射孔数据
Table 3. Perforation data of coalbed methane wells in Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
井号 压裂段 压裂煤层 煤层深度/m 煤层结构/m 射孔段/m 射孔厚度/m 孔密/(个/m) 相位/(°) 射孔数/个 射孔枪弹/mm 备注 YP-1井 第1段 18# 771.4 1(0.6)0.7 771.4~772.4 1.0 16 60 16 102/127 只射煤层夹矸避射 773.0~773.7 0.7 16 60 12 第2段 12# 719.7 3.6 719.7~722.7 3.0 16 60 48 注:煤层结构数据1(0.6)0.7表示煤(夹矸)煤的厚度。 表 4 贵州省盘关向斜煤层气井压裂规模
Table 4. Fracturing scale of coalbed methane wells in Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
井号 煤层编号 煤层深度/m 煤层厚度/m 压裂液量/m3 压裂砂量/m3 每米煤层液量/ m3 每米煤层砂量/m3 加液量与加砂量比值 YP-1井 18# 771.4 1.7 803 38.16 472.35 22.45 21.04 12# 719.7 3.6 1 257 64.37 349.17 17.88 19.53 综合 / 5.3 2 060 102.53 388.68 19.35 20.09 表 5 贵州省盘关向斜煤层气井压裂及测压降数据
Table 5. Fracturing and pressure drop data of coalbed methane wells in Panguan syncline, Guizhou Province
井号 压裂段 压裂煤层 煤层深度/m 煤层厚度/m 加液量/ m3 加砂量/ m3 停泵压力/ MPa 测压降时间/min 测压降后压力/MPa 压力降幅/ MPa 压力降幅与停泵压力比值/% YP-1井 第1段 18# 771.4 1.7 803 38.16 17.1 60 13.0 4.1 23.98 第2段第1次 12# 719.7 3.6 695 35.03 9.9 30 7.3 2.6 26.26 第2段第2次 12# 719.7 3.6 562 29.34 12.4 60 10.7 1.7 13.71 -
[1] 秦勇, 申建, 李小刚. 中国煤层气资源控制程度及可靠性分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(6): 19-32. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.002QIN Yong, SHEN Jian, LI Xiaogang. Control degree and reliability of CBM resources in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(6): 19-32. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.06.002 [2] 庚勐, 陈浩, 陈艳鹏, 等. 第4轮全国煤层气资源评价方法及结果[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(6): 64-68.GENG Meng, CHEN Hao, CHEN Yanpeng, et al. Methods and results of the fourth round national CBM resources evaluation[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(6): 64-68. [3] 毕彩芹. 中国煤层气资源量及分布[J]. 石油知识, 2018(2): 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4609.2018.02.005BI Caiqin. Coal bed methane resources and distribution in China[J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2018(2): 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4609.2018.02.005 [4] 秦勇, 申建, 沈玉林. 叠置含气系统共采兼容性: 煤系"三气"及深部煤层气开采中的共性地质问题[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(1): 14-23.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian, SHEN Yulin. Joint mining compatibility of superposed gas-bearing systems: a general geological problem for extraction of three natural gases and deep CBM in coal series[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(1): 14-23. [5] 徐凤银, 闫霞, 李曙光, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部(层)煤层气勘探开发理论技术难点与对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(1): 115-130.XU Fengyin, YAN Xia, LI Shuguang, et al. Theoretical and technological difficulties and countermeasures of deep CBM exploration and development in the eastern edge of Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(1): 115-130. [6] 高弟, 秦勇, 易同生. 论贵州煤层气地质特点与勘探开发战略[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2009, 21(3): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2009.03.006GAO Di, QIN Yong, YI Tongsheng. Geological condition, exploration and exploitation strategy of coal-bed methane resources in Guizhou, China[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2009, 21(3): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2009.03.006 [7] 易同生, 高为, 周培明. 贵州省煤层气资源特征及开发技术[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2018, 30(6): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.06.07YI Tongsheng, GAO Wei, ZHOU Peiming. CBM resource features and exploitation technology in Guizhou Province[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2018, 30(6): 35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2018.06.07 [8] 金军, 杨兆彪, 秦勇, 等. 贵州省煤层气开发进展、潜力及前景[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(11): 4113-4126.JIN Jun, YANG Zhaobiao, QIN Yong, et al. Progress, potential and prospects of CBM development in Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(11): 4113-4126. [9] 高玉巧, 郭涛, 何希鹏, 等. 贵州省织金地区煤层气多层合采层位优选[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 227-232. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102227GAO Yuqiao, GUO Tao, HE Xipeng, et al. Optimization of multi-layer commingled coalbed methane production in Zhijin area, Guizhou Province[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 227-232. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102227 [10] 郭晨, 夏玉成, 卢玲玲, 等. 黔西比德—三塘盆地多层叠置独立含煤层气系统发育规律与控制机理[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(4): 622-632.GUO Chen, XIA Yucheng, LU Lingling, et al. Development features and mechanism of multi-layer superimposed independent CBM systems in Bide-Santang Basin, western Guizhou, South China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(4): 622-632. [11] 杨恒, 龚文平, 郑伦举. 煤系烃源岩油气生成、排出与滞留特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 498-506. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103498YANG Heng, GONG Wenping, ZHENG Lunju. Characteristics of oil and gas generation, expelling and retention of coaly source rock[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 498-506. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103498 [12] 高为, 韩忠勤, 金军, 等. 六盘水煤田煤层气赋存特征及有利区评价[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(5): 81-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.013GAO Wei, HAN Zhongqin, JIN Jun, et al. Occurrence characteristics and assessment of favorable areas of coalbed methane exploration in Liupanshui coalfield[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(5): 81-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2018.05.013 [13] 李佳欣, 陈贞龙, 郭涛. 贵州织金地区煤层气合采开发实践与认识[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(9): 163-170.LI Jiaxin, CHEN Zhenlong, GUO Tao. Practice and understanding of coalbed methane co-production in Zhijin area, Guizhou[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(9): 163-170. [14] 陈捷, 胡海洋, 娄毅, 等. 贵州省低渗薄煤层水力增渗模拟及地面抽采试验: 以山脚树矿YP-7井为例[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(S2): 60-70. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1275CHEN Jie, HU Haiyang, LOU Yi, et al. Surface permeability improvement and gas control extraction test of low permeability thin coal seam in Guizhou Province: taking the YP-7 well of Shanjiaoshu Mine as an example[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(S2): 60-70. doi: 10.12438/cst.2023-1275 [15] 胡海洋, 赵凌云, 陈捷, 等. 基于煤储层可采性的多煤层合采开发层段优选: 以黔西地区发耳矿区为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(6): 775-779.HU Haiyang, ZHAO Lingyun, CHEN Jie, et al. Optimum selection of multi-seam development based on coal reservoir mineability: a case study of western Guizhou Fa'er ming area[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(6): 775-779. [16] 李全中, 胡海洋, 吉小峰. 厚煤层煤层气井水力压裂特点及效果评价[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2023, 50(1): 92-96.LI Quanzhong, HU Haiyang, JI Xiaofeng. Characteristics and effect evaluation of hydraulic fracturing of CBM well with thick coal seam[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2023, 50(1): 92-96. [17] 康永尚, 孙良忠, 张兵, 等. 中国煤储层渗透率主控因素和煤层气开发对策[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(5): 1401-1418.KANG Yongshang, SUN Liangzhong, ZHANG Bing, et al. The controlling factors of coalbed reservoir permeability and CBM development strategy in China[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(5): 1401-1418. [18] 孟召平, 禹艺娜, 李国富, 等. 沁水盆地煤储层地温场条件及其低地温异常区形成机理[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(1): 307-316.MENG Zhaoping, YU Yina, LI Guofu, et al. Geothermal field condition of coal reservoir and its genetic mechanism of low geothermal anomaly area in the Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(1): 307-316. [19] 孟召平, 卢易新. 高煤阶煤样水力压裂前后应力—渗透率试验研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(1): 353-360.MENG Zhaoping, LU Yixin. Experimental study on stress-permeability of high rank coal samples before and after hydraulic fracturing[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(1): 353-360. [20] 李全中, 倪小明, 胡海洋. 煤层气直井压裂规模对排采典型指标的影响[J]. 煤矿安全, 2021, 52(5): 182-187.LI Quanzhong, NI Xiaoming, HU Haiyang. Influence of fracturing scale of CBM vertical well on typical indexes of drainage and mining[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2021, 52(5): 182-187. [21] 张晓娜, 康永尚, 姜杉钰, 等. 沁水盆地柿庄区块3号煤层压裂曲线类型及其成因机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(S2): 441-451.ZHANG Xiaona, KANG Yongshang, JIANG Shanyu, et al. Fracturing curve types and their formation mechanism of coal seam 3 in Shizhuang block, Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(S2): 441-451. [22] 张争光. 滇东黔西煤层气井产能差异的控制因素[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2022.ZHANG Zhengguang. Controlling factors of productivity difference of coalbed methane wells in eastern Yunnan and western Guizhou[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2022. [23] 杨陆武, 崔玉环, 王国玲. 影响中国煤层气产业发展的技术和非技术要素分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(8): 2400-2411.YANG Luwu, CUI Yuhuan, WANG Guoling. Analysis of technical and regulational aspects affecting China CBM progresses[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(8): 2400-2411. [24] 杨焦生, 赵洋, 王玫珠, 等. 沁水盆地南部煤层气压裂、排采关键技术研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(1): 131-138.YANG Jiaosheng, ZHAO Yang, WANG Meizhu, et al. Study of key technologies on coalbed methane fracturing and drainage in the southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(1): 131-138. [25] 李全中, 申建, 胡海洋, 等. 煤层气井储层地质工程特征对产能的控制研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2023, 29(4): 644-656.LI Quanzhong, SHEN Jian, HU Haiyang, et al. Research on the control of CBM well reservoir geological engineering characteristics on productivity[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2023, 29(4): 644-656. [26] 胡海洋, 颜智华, 娄毅, 等. 贵州省煤层气井压裂改造对产气量的影响及开发建议: 以盘关向斜为例[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2024, 52(S1): 116-126. doi: 10.12438/cst.2024-0188HU Haiyang, YAN Zhihua, LOU Yi, et al. Influence of fracturing reconstruction of coalbed methane wells on gas production and development suggestions in Guizhou Province: taking Panguan syncline as an example[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2024, 52(S1): 116-126. doi: 10.12438/cst.2024-0188 -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号