Physical simulation of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in transport systems of allochthonous salt sheet development zone: a case study of Perdido Fold Belt in Burgos Basin, Gulf of Mexico
-
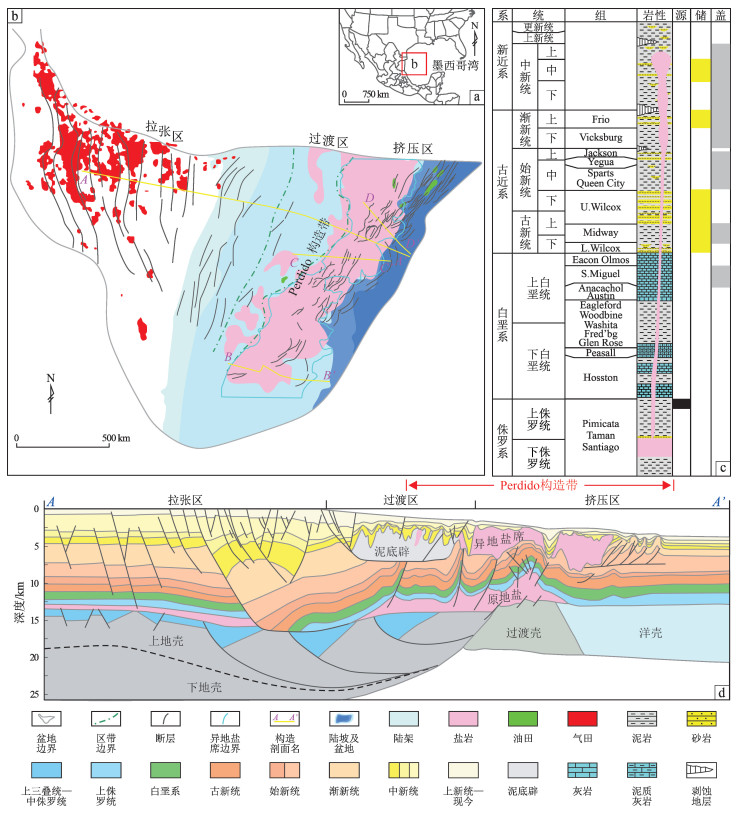
摘要: 博格斯盆地是墨西哥湾西部典型的含盐被动陆缘盆地,油气资源丰富,其Perdido构造带异地盐席发育区形成了由异地盐席底部构造、断层和古新统—始新统Wilcox组构成的油气输导体系。由于Perdido构造带水体较深且盐构造活动复杂,其异地盐席发育区的油气输导特征和输导效率不明。因此,定量评价Perdido构造带异地盐席发育区油气输导体系的输导效率、厘清不同类型输导体系输导效率的差异性及其影响因素对减少勘探风险尤为重要。基于地震、钻井和测井等资料,对Perdido构造带异地盐席发育区发育的下倾型、波浪型和上倾型三种形态的油气输导体系开展了油气运聚物理模拟实验。研究表明,与盐席底部砂泥岩相比,三种形态油气输导体系中Wilcox组均呈现更高的输导效率,是油气运移的优势通道。不同形态油气输导体系的输导效率在油气运移的不同时期存在差异,具体表现为始新世末期下倾型输导体系的输导效率最高;渐新世末期上倾型输导体系的输导效率最高。始新世末期和渐新世末期,研究区断层活动性强,促进油气输导。Perdido构造带异地盐席发育区的油气输导效率受输导体系的物性、油气运移距离和源储压差等因素的影响,其中,源储压差为主要控制因素,油气运移距离为次要控制因素,输导体系物性的影响相对较弱。
-
关键词:
- 输导效率 /
- 油气运聚物理模拟 /
- 盐构造 /
- Perdido构造带 /
- 博格斯盆地
Abstract: The Burgos Basin is a typical salt passive continental margin basin in the western Gulf of Mexico, rich in oil and gas resources. The allochthonous salt sheet development zone in the Perdido Fold Belt of the Burgos Basin has formed an oil and gas transport system comprising the underlying structures of allochthonous salt sheets, faults, and the Paleocene to Eocene Wilcox Formation. Due to the deep-water environment and complex salt tectonics, the hydrocarbon transport characteristics and efficiency in these allochthonous salt sheet development zones remain unclear. Therefore, to reduce exploration risks, it is important to quantitatively evaluate the transport efficiency of hydrocarbon transport systems in the allochthonous salt sheet development zone of the Perdido Fold Belt and to clarify transport efficiency differences among various types of transport systems and their influencing factors. Based on seismic, well drilling, and well logging data, the hydrocarbon migration and accumulation physical simulation experiments were carried out on three types of transport systems—downdip, wavy, and updip-developed in the allochthonous salt sheet zone of the Perdido Fold Belt. The results showed that compared to the sand and mudstone at the base of the salt sheets, the Wilcox Formation exhibited higher transport efficiency in all three transport systems, serving as the primary channel for hydrocarbon migration. The transport efficiency varied during different migration periods. Specifically, the downdip system demonstrated the highest transport efficiency at the end of the Eocene, and the updip system had the highest efficiency at the end of Oligocene. During these two periods, the study area experienced strong fault activities, facilitating hydrocarbon migration. The hydrocarbon transport efficiency in the allochthonous salt sheet development zone of the Perdido Fold Belt was affected by factors such as the physical properties of transport systems, hydrocarbon migration distance, and the pressure difference between source rock and reservoir. Among these, the pressure difference is the main controlling factor, followed by the migration distance, with the physical properties of transport systems having a relatively minor effect. -
图 2 博格斯盆地Perdido构造带异地盐席发育区典型剖面的断裂发育特征
a.异地盐席发育区南部剖面(测线BB’);b.异地盐席发育区中部剖面(测线CC’);c.异地盐席发育区北部剖面(测线DD’)。剖面位置见图 1b。
Figure 2. Fault development characteristics of typical profiles in allochthonous salt sheet development zone of Perdido Fold Belt, Burgos Basin
图 11 博格斯盆地Perdido构造带波浪型输导体系Wilcox组不同出口的充注压力、加权渗透率、运移距离比和输导效率随时间变化的关系
a、c、e.1出口;b、d、f. 2出口。
Figure 11. Temporal variations of charging pressure, weighted permeability, migration distance ratio, and transport efficiency at different outlets of Wilcox Formation in wave transport system of Perdido Fold Belt, Burgos Basin
表 1 博格斯盆地Perdido构造带油气运聚物理模拟实验所用砂粒直径和对应的换算渗透率
Table 1. Grain size diameters and corresponding converted permeability used in physical simulation experiments of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation for Perdido Fold Belt, Burgos Basin
石英砂直径/mm 换算渗透率/10-3 μm2 填砂序号 0.05~0.10 416.25 ① 0.10~0.15 1 156.25 ② 0.15~0.20 2 266.25 ③ 0.20~0.25 3 746.25 ④ 0.25~0.30 5 596.25 ⑤ 0.30~0.35 7 816.25 ⑥ 0.35~0.40 10 406.25 ⑦ 0.40~0.45 13 366.25 ⑧ 表 2 博格斯盆地Perdido构造带油气运聚物理模拟过程中的累积注油量、出油量和注油压力
Table 2. Cumulative injection volume, oil production, and injection pressure during physical simulation processes of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in Perdido Fold Belt, Burgos Basin
输导体系类型 时间/min 注油压力/MPa 累积注油量/mL 出油量/mL 出口1 出口2 出口3 出口4 下倾型 9 0.5 21.60 0 0 - - 14 0.5 32.47 0 0 - - 70 1.5 98.58 1 0 - - 121 3.0 292.60 143 0.1 - - 波浪型 15 2.5 34.47 0 0 0 0 34 2.5 110.72 3 0 0 0 73 5.0 281.01 96 1 0 0 271 7.5 1 378.73 706 315 0.5 0 340 10.0 1 752.80 838 418 5 0.5 上倾型 3 2.5 31.69 0 0 - - 7 2.5 50.19 0 0 - - 50 2.5 172.48 5 0 - - 120 5.0 441.53 213 1 - - -
[1] WALLER T D Ⅱ. Structural analysis of the Perdido Fold Belt: timing, evolution, and structural style[D]. College Station, Texas, USA: Texas A&M University, 2007. [2] WEIMER P, BOUROULLEC R, VAN DEN BERG A A, et al. Structural setting and evolution of the Mensa and Thunder Horse intraslope basins, northern deep-water Gulf of Mexico: a case study[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(7): 1145-1172. doi: 10.1306/09011609112 [3] WANG Chen, ZENG Jianhui, YU Yixin, et al. Origin, migration, and characterization of petroleum in the Perdido Fold Belt, Gulf of Mexico Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107843. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107843 [4] 梁建设, 黄兴文, 蔡文杰, 等. 墨西哥Burgos盆地Perdido构造带Wilcox组源—汇体系及勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1439-1450.LIANG Jianshe, HUANG Xingwen, CAI Wenjie, et al. Source-to-sink system and exploration prospects of the Wilcox Formation in Perdido Fold Belt, Burgos Basin, Mexico[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1439-1450. [5] 卢景美, 张金川, 严杰, 等. 墨西哥湾北部深水区Wilcox沉积特征及沉积模式研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(6): 1132-1139.LU Jingmei, ZHANG Jinchuan, YAN Jie, et al. Study on depositional characteristics and model of Wilcox in the deep waters of northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(6): 1132-1139. [6] 李爱山, 蔡文杰, 卢景美, 等. 墨西哥北部博格斯盆地石油地质条件与勘探潜力分析[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(7): 31-39.LI Aishan, CAI Wenjie, LU Jingmei, et al. Analysis on petroleum conditions and exploration potential in Burgos Basin, north of Mexico[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(7): 31-39. [7] 孔国英, 李爱山, 朱钇同, 等. 博格斯盆地深水挤压盐构造识别与圈闭落实关键技术及应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(8): 77-85.KONG Guoying, LI Aishan, ZHU Yitong, et al. Application of interpretation technology of salt-related trap in deepwater compression area offshore Burgos Basin, Mexico[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(8): 77-85. [8] 蔡文杰, 陈亮, 李爱山, 等. 含盐被动陆缘盆地油气输导体系与成藏模式研究: 以墨西哥湾南部Burgos和Sureste盆地为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(6): 34-43.CAI Wenjie, CHEN Liang, LI Aishan, et al. Study on hydrocarbon transport systems and accumulation models of salt-bearing passive continental margin basin: a case study of Burgos and Sureste basins in the southern Gulf of Mexico[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(6): 34-43. [9] 谷雨, 吴俊, 樊太亮, 吕峻岭. 塔北—塔中地区中—下寒武统岩性组合与变形特征及其对油气输导影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 313-331.GU Yu, WU Jun, FAN Tailiang, LÜ Junling. Lithological associations, deformation characteristics of the Lower-Middle Cambrian and their influence on oil and gas migration in the north-central Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 313-331. [10] 周波, 金之钧, 罗晓容, 等. 油气二次运移过程中的运移效率探讨[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(4): 522-526.ZHOU Bo, JIN Zhijun, LUO Xiaorong, et al. Discussion on the efficiency of secondary oil-gas migration[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(4): 522-526. [11] ZENG Jianhui, JIN Zhijun. Experimental investigation of episodic oil migration along fault systems[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 78-79: 493-498. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(03)00087-6 [12] 隆辉, 曾溅辉, 刘亚洲, 等. 可视化三维物理模拟实验技术在油气成藏研究中的应用: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区S53-2井为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(5): 1110-1122. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024051110LONG Hui, ZENG Jianhui, LIU Yazhou, et al. Application of visual 3D physical simulation experiment technology in oil and gas accumulation research: a case study of well S53-2 in Shunbei area of Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(5): 1110-1122. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024051110 [13] 李令喜, 刘爱永, 胡志成, 郭国强. 东濮凹陷濮卫地区油气输导特征及精细勘探方向[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(1): 96-99.LI Lingxi, LIU Aiyong, HU Zhicheng, GUO Guoqiang. Hydrocarbon transport features and fine exploration directions in Puwei region of Dongpu Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(1): 96-99. [14] 张伟, 蒋有录, 侯帅, 等. 垦东北地区古近系油气输导体系特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(6): 31-39.ZHANG Wei, JIANG Youlu, HAO Shuai, et al. Characteristics of the paleocene oil and gas transmission system in north Kengdong area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(6): 31-39. [15] 刘春, 陈世加, 赵继龙, 等. 库车前陆盆地南部斜坡带中—新生界油气运移输导体系与运聚模拟[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(10): 1450-1462.LIU Chun, CHEN Shijia, ZHA0 Jilong, et al. Hydrocarbon transportation system and accumulation simulation of Mesozoic-Cenozoic in south slope of Kuqa Foreland Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(10): 1450-1462. [16] 朱秀香, 曹自成, 隆辉, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区走滑断裂带压扭段和张扭段油气成藏实验模拟及成藏特征研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 289-304.ZHU Xiuxiang, CAO Zicheng, LONG Hui, et al. Experimental simulation and characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation in strike-slip fault zone in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 289-304. [17] 张少华, 杨明慧, 罗晓华. 断裂带油气幕式运移: 来自物理模拟实验的启示[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(5): 1183-1191.ZHANG Shaohua, YANG Minghui, LUO Xiaohua. Hydrocarbon episodic migration in fault zones: insights from physical simulation experiments[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(5): 1183-1191. [18] 尚晓庆, 刘洛夫, 高小跃, 等. 断裂—砂体复合输导体系输导效率的定量评价: 以库车前陆盆地北带白垩系为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2012, 34(3): 38-43.SHANG Xiaoqing, LIU Luofu, GAO Xiaoyue, et al. Quantitative evaluation of transporting efficiency of composite fault-sand body pathway system: by taking the Cretaceous in the north belt of Kuqa Foreland Basin for example[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2012, 34(3): 38-43. [19] BURRUS J, OSADETZ K, WOLF S, et al. A two-dimensional regional basin model of Williston Basin hydrocarbon systems 1[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(2): 265-290. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kirk_Osadetz/publication/302415097_A_two-dimensional_regional_basin_model_of_Williston_basin_hydrocarbon_system/links/573a006208ae9ace840dbfad.pdf [20] HINDLE A D. Petroleum migration pathways and charge concentration: a three-dimensional model[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(9): 1451-1481. [21] ENGLAND W A, MACKENZIE A S, MANN D M, et al. The movement and entrapment of petroleum fluids in the subsurface[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1987, 144(2): 327-347. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download;jsessionid=3BD6BD9F465225CCD9E208DD19E544E8?doi=10.1.1.453.5516&rep=rep1&type=pdf [22] CARRUTHERS D J. Modeling of secondary petroleum migration using invasion percolation techniques[M]//DVPPENBECKER S, MARZI R. Multidimensional basin modeling. [s. l. ]: AAPG/Datapages discovery series, 2003: 21-27. [23] 吉斐, 孙鑫鑫, 张琦. 新型产量递减方程的建立及渗流理论基础: 以吐哈油田非常规油藏为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(6): 696-702.JI Fei, SUN Xinxin, ZHANG Qi. Establishment of a new production decline equation and its theoretical basis: a case study of unconventional reservoirs in Tuha oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(6): 696-702. [24] 马立成, 江万, 施辉, 等. 柴达木盆地东部尕海南山地区新生代叠加褶皱与油气运移[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(05): 1209-1220.MA Licheng, JIANG Wan, SHI Hui. Relationship between Cenozoic superimposed folds and hydrocarbon migration in the Gahainanshan area, eastern Qaidam Basin, China[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(05): 1209-1220. [25] WANG Fuwei, CHEN Dongxia, LI Meijun, et al. A novel approach for evaluating the transport capacity of sandstone carriers and determining effective hydrocarbon migration channels: application to the Pinghu Slope Belt of the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2024, 259: 105923. [26] 吕照, 潘丽燕, 郝丽华, 等. 砂泥岩互层水力压裂裂缝穿层扩展影响因素数值模拟[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(6): 729-738.LYU Zhao, PAN Liyan, HAO Lihua, et al. Numerical simulation of factors influencing hydraulic fracture propagation in sandstone-mudstone interbedded reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(6): 729-738. [26] WANG Wenyang, PANG Xiongqi, CHEN Zhangxin, et al. Quantitative evaluation of transport efficiency of fault-reservoir composite migration pathway systems in carbonate petroliferous basins[J]. Energy, 2021, 222: 119983. [27] WANG Fuwei, CHEN Dongxia, WANG Qiaochu, et al. Quantitative evaluation of sandstone carrier transport properties and their effects on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation: a case study of the Es32 in the southern slope of Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 126: 104937. [28] 李爱山, 孔国英, 陈亮, 等. 墨西哥博格斯盆地深水挤压区复杂双层盐岩识别与解释[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(2): 42-48.LI Aishan, KONG Guoying, CHEN Liang, et al. Identification and interpretation of complex double-layered salt rocks in deepwater compression area of Burgos Basin, Mexico[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(2): 42-48. [29] VAZQUEZ-GARCIA O. Tectonic synthesis of the deepwater Lamprea thrust and fold belt, offshore Burgos Basin, western Gulf of Mexico[D]. Colorado: Colorado School of Mines, 2018. [30] 杨帆, 胡望水, 蔡文杰, 等. Burgos盆地Perdido构造带盐泥底辟构造特征及形成机制[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(6): 31-38.YANG Fan, HU Wangshui, CAI Wenjie, et al. Characteristics and their forming mechanisms of the salt-mud diapiric structure in Perdido Structure Belt of Burgos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(6): 31-38. [31] VAN AVENDONK H J A, CHRISTESON G L, NORTON I O, et al. Continental rifting and sediment infill in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(7): 631-634. http://doc.paperpass.com/foreign/rgArti20151790166.html [32] CUNNINGHAM R, SNEDDEN J W, NORTON I O, et al. Upper Jurassic Tithonian-centered source mapping in the deepwater northern Gulf of Mexico[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(1): SC97-SC123. [33] NGUYEN L C, MANN P. Gravity and magnetic constraints on the Jurassic opening of the oceanic Gulf of Mexico and the location and tectonic history of the western main transform fault along the eastern continental margin of Mexico[J]. Interpretation, 2016, 4(1): SC23-SC33. [34] WANG Junpeng, WANG Hongyan, ZHANG Ronghu, et al. Improvement of reservoir quality of ultra-deep tight sandstones by tectonism and fluid: a case study of Keshen gas field in Tarim Basin, western China[J]. Petroleum, 2023, 9(1): 124-134. [35] 李双林, 张生银. 墨西哥及墨西哥湾盆地构造单元及其演化[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(3): 14-21.LI Shuanglin, ZHANG Shengyin. Tectonic units and their evolution in Mexico orogen and Gulf of Mexico Basin[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2010, 26(3): 14-21. [36] 朱钇同, 李爱山, 陈亮, 等. 墨西哥Burgos盆地Perdido构造带深浅双层盐分布特征及南北差异构造形变[J]. 中国海上油气, 2021, 33(6): 62-70.ZHU Yitong, LI Aishan, CHEN Liang, et al. Distribution characteristics of deep/shallow bi-layered salt and the north-south differential structural deformation in the Perdido structural belt of Burgos Basin, Mexico[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2021, 33(6): 62-70. -





 下载:
下载:















 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号