Optimization design of geothermal field development schemes based on hydraulic, thermal and chemical coupled numerical simulation: a case study of karst thermal reservoir in Xiong'an New Area, Hebei Province
-
摘要: 为优化河北雄安新区岩溶热储的地热资源开发方案,在构建三维地质模型的基础上,对地热田开采状态进行水—热—化多场耦合数值模拟。通过敏感性分析,探讨开采时间、采灌流量、井距、回灌温度和回灌率等关键参数对地热田开发效果的影响。结果表明,地热井开采时间延长会导致温度下降和热突破现象,在现有开发场景下,100年开采周期内雄县及容城地区部分地热井温度下降可达4 ℃。减少开采流量或增加井距能有效延缓热突破,延长地热田寿命。在雄县地区,建议井距保持在500~600 m。回灌温度对地热田整体温度场影响不大,但降低回灌温度可提高热利用率。回灌率对地下水位影响显著,100%回灌率能维持地下水位稳定,而90%回灌率会导致地下水位持续下降。总之,合理调整开采周期、采灌流量、井距和回灌策略,可以有效延长地热田的使用寿命,并提高资源利用效率。
-
关键词:
- 地热田开发方案 /
- 水—热—化耦合数值模拟 /
- 岩溶热储 /
- 雄安新区 /
Abstract: For the optimization design of geothermal resource development schemes in karst thermal reservoirs of the Xiong'an New Area, Hebei Province, a hydraulic, thermal and chemical multi-field coupled numerical simulation was conducted on the geothermal field's extraction status based on a three-dimensional geological model. The influence of key parameters such as extraction duration, extraction and recharge flow rates, well spacing, recharge temperature, and recharge rate on the effectiveness of geothermal field development was discussed using sensitivity analysis. The results showed that the extension of the extraction time of geothermal wells led to temperature decline and thermal breakthrough. In the current development scenario, the temperature of some geothermal wells in Xiongxian and Rongcheng areas could decrease by up to 4 ℃ over a 100-year extraction cycle. Reducing extraction flow rates and increasing well spacing could effectively delay thermal breakthrough and ensure the longevity of geothermal fields. In Xiongxian area, it was recommended that the well spacing should be kept from 500 to 600 m. The recharge temperature had little effect on the overall temperature field of the geothermal field, but reducing the recharge temperature could improve thermal utilization. The recharge rate had a significant impact on groundwater levels. A 100% recharge rate could maintain water level stability, while a 90% recharge rate could lead to a continuous decline in groundwater levels. In general, reasonable adjustment of the extraction cycle, extraction and recharge flow rates, well spacing, and recharge strategy can effectively extend the service life of geothermal fields and improve resource utilization efficiency. -
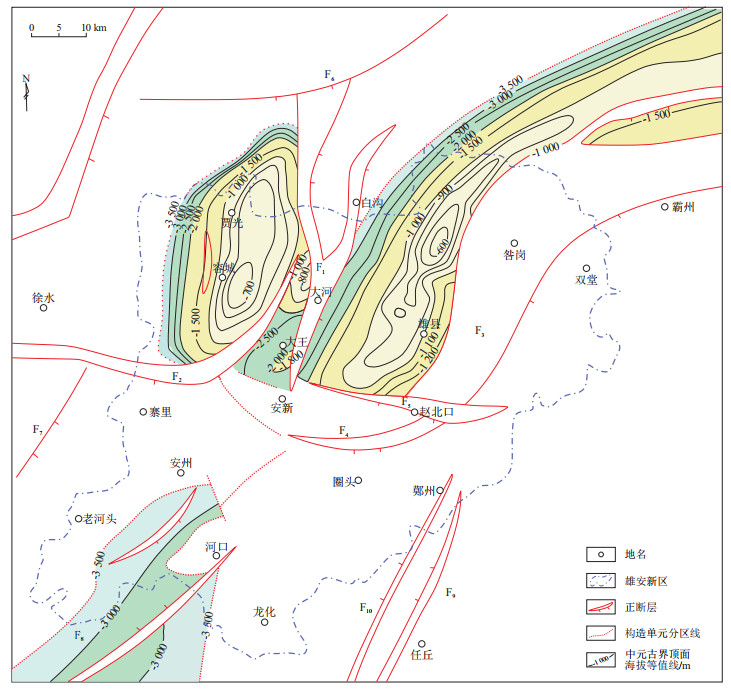
图 1 河北雄安新区区域地质概况据参考文献[10]修改。
Figure 1. Geological map of Xiong'an New Area, Hebei Province
-
[1] 汪集暘, 邱楠生, 胡圣标, 等. 中国油田地热研究的进展和发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(3): 1-12.WANG Jiyang, QIU Nansheng, HU Shengbiao, et al. Advancement and developmental trend in the geothermics of oil fields in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(3): 1-12. [2] 多吉, 王贵玲, 郑克棪. 中国地热资源开发利用战略研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.DUO Ji, WANG Guilin, ZHENG Keyan. Research on the development and utilization strategy of geothermal resources in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. [3] 周训, 陈明佑, 方斌, 等. 埋藏型岩溶地下水源地的三维数值模拟: 以天津市宁河北岩溶地下水源地为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2006, 25(1): 6-11.ZHOU Xun, CHEN Mingyou, FANG Bin, et al. 3-D numerical modeling to groundwater wellhead in buried karst area: a case study to the Ninghebei karst wellhead in Tianjin[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2006, 25(1): 6-11. [4] 宋美钰, 刘杰, 于彦, 等. 天津地区雾迷山组热储数值模拟研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2018, 41(4): 306-311.SONG Meiyu, LIU Jie, YU Yan, et al. Numerical simulation of Wumishan Formation thermal reservoir in Tianjin area[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2018, 41(4): 306-311. [5] 李俊峰, 贾志, 张芬娜, 等. 天津市蓟县系雾迷山组热储层水位动态变化及趋势预测研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2013, 36(3): 221-225.LI Junfeng, JIA Zhi, ZHANG Fenna, et al. Research on the change and trend prediction of the water level of Wumishan geothermal reservoir in Jixian system, Tianjin[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2013, 36(3): 221-225. [6] KIRYUKHIN A V, SHADRINA S V, PUZANKOV M Y. Modeling the thermohydrogeochemical conditions for the generation of productive reservoirs in volcanogenic rocks[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Seismology, 2013, 7(2): 170-183. [7] PANDEY S N, CHAUDHURI A, KELKAR S, et al. Investigation of permeability alteration of fractured limestone reservoir due to geothermal heat extraction using three-dimensional thermo-hydro-chemical (THC) model[J]. Geothermics, 2014, 51: 46-62. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2013.11.004 [8] PANDEY S N, CHAUDHURI A, KELKAR S. A coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of fracture aperture alteration and reservoir deformation during heat extraction from a geothermal reservoir[J]. Geothermics, 2017, 65: 17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2016.08.006 [9] 陈继良, 黄文博, 曹文炅, 等. 增强型地热系统中液—岩化学作用数值模拟研究[J]. 新能源进展, 2016, 4(1): 48-55.CHEN Jiliang, HUANG Wenbo, CAO Wenjiong, et al. A numerical study on the effect of fluid-rock reaction during enhanced geothermal system heat extraction processes[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2016, 4(1): 48-55. [10] 戴明刚, 马鹏鹏, 雷海飞, 等. 雄安新区雾迷山组岩溶热储特征与有利区[J]. 地质科学, 2020, 55(2): 487-505.DAI Minggang, MA Pengpeng, LEI Haifei, et al. Distribution characteristics and favorable targets of karst geothermal reservoir of Wumishan Formation in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2020, 55(2): 487-505. [11] 刘峰, 王贵玲, 姜光政, 等. 我国陆区大地热流测量新进展与新认识[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(6): 19-30.LIU Feng, WANG Guiling, JIANG Guangzheng, et al. Recent advances in heat flow measurement and new understanding of terrestrial heat flow distribution in terrestrial areas of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(6): 19-30. [12] 王贵玲, 马峰, 张薇, 等. 华北古潜山优势传热机制研究: 以雄安新区为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(6): 52-66.WANG Guiling, MA Feng, ZHANG Wei, et al. Dominant heat transfer mechanism in buried-hill reservoirs in North China: a case study in Xiong'an new area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(6): 52-66. [13] 孙焕泉, 毛翔, 吴陈冰洁, 等. 地热资源勘探开发技术与发展方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(1): 400-411.SUN Huanquan, MAO Xiang, WU Chenbingjie, et al. Geothermal resources exploration and development technology: current status and development directions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(1): 400-411. [14] 李卫卫, 饶松, 唐晓音, 等. 河北雄县地热田钻井地温测量及地温场特征[J]. 地质科学, 2014, 49(3): 850-863.LI Weiwei, RAO Song, TANG Xiaoyin, et al. Borehole temperature logging and temperature field in the Xiongxian geothermal field, Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2014, 49(3): 850-863. [15] HE Lijuan. Thermal regime of the North China Craton: implications for craton destruction[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2015, 140: 14-26. [16] 常健, 邱楠生, 赵贤正, 等. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷现今地热特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(3): 1003-1016.CHANG Jian, QIU Nansheng, ZHAO Xianzheng, et al. Present-day geothermal regime of the Jizhong Depression in Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(3): 1003-1016. [17] 姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理报, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910.JIANG Guangzheng, GAO Peng, RAO Song, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China (4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910. [18] JIANG Guangzheng, HU Shengbiao, SHI Yizuo, et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019, 753: 36-48. [19] WANG Zhuting, RAO Song, XIAO Hongping, et al. Terrestrial heat flow of Jizhong Depression, China, western Bohai Bay Basin and its influencing factors[J]. Geothermics, 2021, 96: 102210. [20] 何登发, 单帅强, 张煜颖, 等. 雄安新区的三维地质结构: 来自反射地震资料的约束[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(9): 1207-1222.HE Dengfa, SHAN Shuaiqiang, ZHANG Yuying, et al. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong'an New Area: constraints from seismic reflection data[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(8): 1007-1022. [21] 朱吉昌, 冯有良, 孟庆任, 等. 渤海湾盆地晚中生代构造地层划分及对比: 对燕山运动的启示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50(1): 28-49.ZHU Jichang, FENG Youliang, MENG Qingren, et al. Late Mesozoic tectonostratigraphic division and correlation of the Bohai Bay Basin: implications for the Yanshanian Orogeny[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2019, 62(11): 1783-1804. [22] SUN Ziyong, MA Rui, WANG Yanxin, et al. Using isotopic, hydrogeochemical-tracer and temperature data to characterize recharge and flow paths in a complex karst groundwater flow system in northern China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(6): 1393-1412. [23] LI Jie, PANG Zhonghe, YANG Guomin, et al. Million-year-old groundwater revealed by krypton-81 dating in Guanzhong Basin, China[J]. Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(17): 1181-1184. [24] KONG Yanlong, PANG Zhonghe, PANG Jumei, et al. Fault-affected fluid circulation revealed by hydrochemistry and isotopes in a large-scale utilized geothermal reservoir[J]. Geofluids, 2020(24): 1-13. [25] PANG Jumei, PANG Zhonghe, LV Min, et al. Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of fluids in the Niutuozhen geothermal field, North China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 77(1): 12. [26] GUO Sasa, ZHU Chuanqing, QIU Nansheng, et al. Present geothermal characteristics and influencing factors in the Xiong'an New Area, North China[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(20): 3884. [27] WANG Zhuting, JIANG Guangzheng, ZHANG Chao. Thermal regime of the lithosphere and geothermal potential in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2019, 37(2): 787-810. [28] 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 庞菊梅, 等. 雄安新区地热资源与开发利用研究[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2017, 32(11): 1224-1230.PANG Zhonghe, KONG Yanlong, PANG Jumei, et al. Geothermal resources and development in Xiongan New Area[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017, 32(11): 1224-1230. [29] KOLDITZ O, GÖRKE U J, SHAO Hua, et al. Thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical processes in porous media: benchmarks and examples[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. [30] 王树芳, 刘久荣, 林沛, 等. 岩溶热储回灌实验与示踪试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(6): 129-133.WANG Shufang, LIU Jiurong, LIN Pei, et al. A study of reinjection experiment and tracer test in a karst geothermal reservoir[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(6): 129-133. [31] KONG Yanlong, PANG Zhonghe, SHAO Haibin, et al. Optimization of well-doublet placement in geothermal reservoirs using numerical simulation and economic analysis[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(3): 118. [32] 马峰, 高俊, 王贵玲, 等. 雄安新区容城地热田碳酸盐岩热储采灌数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2023, 53(5): 1534-1548.MA Feng, GAO Jun, WANG Guiling, et al. Numerical simulation of exploitation and reinjection of carbonate geothermal reservoir in Rongcheng geothermal field, Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1534-1548. -





 下载:
下载:















 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号