Main controlling factors on oblique extensional deformations in multiphase rift basins: insights from analogue experiments
-
摘要: 为了探讨多期裂陷盆地中先存断裂及其与不同伸展方向之间夹角(斜度α)对斜向伸展变形和洼槽结构的影响,利用砂箱物理模拟实验,基于相似性原理,设计了三组物理模拟实验,即不同斜度(α)斜向伸展物理模拟实验和两组斜向伸展—走滑叠加变形物理模拟实验。实验结果表明:(1)多期裂陷盆地中,伸展方向与先存断裂之间的夹角变化控制着走向滑动分量和倾向滑动分量的比例,影响洼槽结构,夹角越大,倾向滑动分量越大,洼槽宽度越大;反之,洼槽宽度减小。(2)受先存断裂分布的影响,不同演化阶段,先存断裂再活动方式不同,对于斜向伸展—走滑叠加变形过程,先存走滑断裂与边界断裂之间的距离较大时,洼槽呈单断半地堑特征;二者间距较小时,走滑断裂也控陷,洼槽呈现双断地堑结构。(3)多方位展布的先存边界断裂再活动控制形成的洼槽深度和压扭褶皱幅度也受二者距离的影响,随着先存边界断裂与走滑断裂距离的增加,张扭区洼槽深度逐渐增大,压扭区褶皱幅度逐渐增加;反之,洼槽深度越小,褶皱幅度越低。Abstract: In order to investigate the influence of pre-existing faults and their angle (α) with different extension directions on oblique extension deformation and sag structure in multiphase rift basins, three sets of analogue experiments were designed based on the similarity theory, including oblique extensional physical simulation experiments with different angles (α), and two sets of physical simulation experiments of oblique extensional and strike-slip deformations. The experiment results showed that: (1) In multiphase rift basins, the angles between the extension direction and pre-existing faults controlled the ratio between the strike-slip component and the dip-slip components, affecting the sag structure. As the angle increased, the dip-slip component and the width of the sag increased. Conversely, when the angle decreased, the sag width decreased. (2) Affected by the distribution of pre-existing faults, the reactivation style of pre-existing faults differed at different evolutionary stages. During the oblique extensional and strike-slip deformation, when the distance between the pre-existing strike-slip fault and the boundary fault was large, the sag showed a single-fault half-graben characteristic. When the distance between them was small, the strike-slip fault also controlled subsidence, and the sag presented a double-fault graben structure. (3) Sag depth and the amplitude of the compression and shear folds controlled by the reactivation of pre-existing boundary faults with multi-directional extension were also influenced by the distance between the faults. As the distance between the pre-existing boundary faults and strike-slip faults increased, the depth of the sag in the extensional-shear zone gradually increased, and the amplitude of the folds in the compressional-shear zone gradually increased. Conversely, the sag depth and fold amplitude decreased.
-
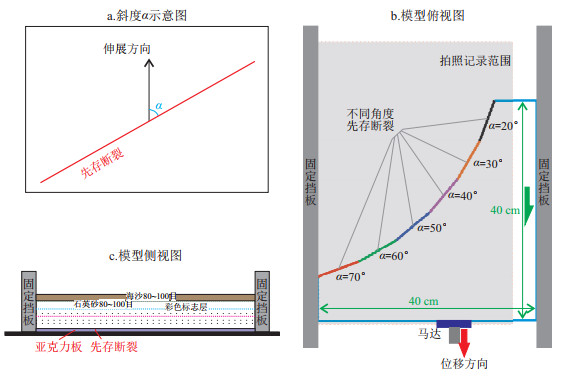
图 3 不同角度斜向伸展变形物理模拟实验平面结果
平面拍摄范围见图 1b。
Figure 3. Planar results of physical simulation experiments on oblique extensional deformation at different angles
图 4 不同角度斜向伸展变形物理模拟实验剖面结果
剖面位置见图 3。
Figure 4. Cross-sectional results of physical simulation experiments on oblique extensional deformation at different angles
图 5 多走向先存断裂斜向伸展物理模拟实验(a)和斜向伸展—走滑叠加变形物理模拟实验(b)平面结果
拍摄范围见图 2。
Figure 5. Planar results of physical simulation of oblique extension along multi-strike pre-existing faults (a) and physical simulation of superposed deformation of oblique extension and strike-slip (b)
图 6 多走向先存断裂斜向伸展物理模拟实验(a)和斜向伸展—走滑叠加变形物理模拟实验(b)剖面结果
剖面位置见图 5。
Figure 6. Cross-sectional results of physical simulation of oblique extension along multi-strike pre-existing faults (a) and physical simulation of superposed deformation of oblique extension and strike-slip (b)
-
[1] GIBA M, WALSH J J, NICOL A. Segmentation and growth of an obliquely reactivated normal fault[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2012, 39: 253-267. [2] FOSSEN H, KHANI H F, FALEIDE J I, et al. Post-Caledonian extension in the west Norway-northern North Sea region: the role of structural inheritance[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2017, 439(1): 465-486. [3] DENG C, FOSSEN H, GAWTHORPE R L, et al. Influence of fault reactivation during multiphase rifting: the Oseberg area, northern North Sea rift[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 1252-1272. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.025 [4] 童亨茂, 范彩伟, 孟令箭, 等. 中国东—南部裂陷盆地断裂系统复杂性的表现形式及成因机制: 以南堡凹陷和涠西南凹陷为例[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765.TONG Hengmao, FAN Caiwei, MENG Lingjian, et al. Manifestation and origin mechanism of the fault system complexity in rift basins in eastern-southern China: case study of the Nanbu and Weixinan sags[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765. [5] PONGWAPEE S, MORLEY C K, WON-IN K. Impact of pre-existing fabrics and multi-phase oblique extension on Cenozoic fault patterns, Wichianburi sub-basin of the Phetchabun rift, Thailand[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2019, 118: 340-361. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2018.11.012 [6] 张继标, 邓尚, 韩俊, 等. 多期构造应力控制走滑断控储层发育机理与差异性研究: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(4): 775-785.ZHANG Jibiao, DENG Shang, HAN Jun, et al. Study on development mechanism and variability of strike-slip fault-controlled reservoirs regulated by multi-stage structural stress: a case study of the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(4): 775-785. [7] 杨宪彰, 能源, 徐振平, 等. 塔里木盆地三大构造旋回油气成藏特征[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(2): 287-299.YANG Xianzhang, NENG Yuan, XU Zhenping, et al. Characteristics of the hydrocarbon accumulation formed through the three structural cycles in Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(2): 287-299. [8] 丁文龙, 王垚, 张子游, 等. 页岩储层构造裂缝活动期次及开启性研究进展与展望[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 1-16.DING Wenlong, WANG Yao, ZHANG Ziyou, et al. Tectonic fracturing and fracture initiation in shale reservoirs: research progress and outlooks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 1-16. [9] 吕古贤, 张宝林, 焦建刚, 等. 新华夏构造体系地块的多层次"构造隆起—拆离凹陷"特征: 大兴安岭造山带例析[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(4): 853-864.LÜ Guxian, ZHANG Baolin, JIAO Jiangang, et al. Multi-order characteristics of the "tectonic uplift-detachment depression" in blocks of the Neocathaysian tectonic system: a study of the Greater Khinganling Orogenic Belt[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(4): 853-864. [10] WITHJACK M O, JAMISON W R. Deformation produced by oblique rifting[J]. Tectonophysics, 1986, 126(2/4): 99-124. [11] BELLAHSEN N, FOURNIER M, D'ACREMONT E, et al. Fault reactivation and rift localization: northeastern gulf of Aden margin[J]. Tectonics, 2006, 25(1): TC1007. [12] 刘露, 孙永河, 陈昌, 等. 南堡凹陷4号构造带断裂活化及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(4): 716-727.LIU Lu, SUN Yonghe, CHEN Chang, et al. Fault reactivation in No.4 structural zone and its control on oil and gas accumulation in Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(4): 716-727. [13] TRON V, BRUN J P. Experiments on oblique rifting in brittle-ductile systems[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 188(1/2): 71-84. [14] AGOSTINI A, CORTI G, ZEOLI A, et al. Evolution, pattern, and partitioning of deformation during oblique continental rifting: inferences from lithospheric-scale centrifuge models[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2009, 10(11). doi: 10.1029/2009GC002676. [15] ZWAAN F, SCHREURS G, ROSENAU M. Rift propagation in rotational versus orthogonal extension: insights from 4D analogue models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2020, 135: 103946. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2019.103946 [16] ZWAAN F, SCHREURS G. Analogue modeling of continental rifting: an overview[M]//PERON-PINVIDIC G. Continental rifted margins 1: definition and methodology. Hoboken: Wiley, 2022: 309-343. [17] ZWAAN F, SCHREURS G. Analog models of lithospheric-scale rifting monitored in an X-ray CT scanner[J]. Tectonics, 2023, 42(3): e2022TC007291. [18] HENZA A A, WITHJACK M O, SCHLISCHE R W. Normal-fault development during two phases of non-coaxial extension: an experimental study[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2010, 32(11): 1656-1667. [19] LELOUP P H, LACASSIN R, TAPPONNIER P, et al. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone (Yunnan, China), Tertiary transform boundary of Indochina[J]. Tectonophysics, 1995, 251(1/4): 3-84. [20] 任健, 吕丁友, 陈兴鹏, 等. 渤海东部先存构造斜向拉伸作用及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3): 530-541.REN Jian, LYU Dingyou, CHEN Xingpeng, et al. Oblique extension of pre-existing structures and its control on oil accumulation in eastern Bohai Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3): 530-541. [21] 刘露. 渤海海域蓬莱25-31区块走滑—斜向伸展断裂变形机制及对油气成藏控制作用研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2022.LIU Lu. Study on the deformation mechanism of strike-slip and oblique extension faults and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation in Penglai 25-31 area, Bohai Sea[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2022. [22] MA Xiao. The characteristics of combined strike-slip and extension fault system in western offshore Bohai Bay Basin and its control on basin fillings[J]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020. [23] WANG Qi, SUN Yonghe, ZHANG Wanfu, et al. Cenozoic evolution and deformation in the eastern and western depression of the Liaohe Subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin: insights from seismic data[J]. Basin Research, 2023, 35(5): 1880-1907. [24] 邱旭明, 陈伟, 李鹤永, 等. 苏北盆地走滑构造与复杂断块油气成藏[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 393-401.QIU Xuming, CHEN Wei, LI Heyong, et al. strike-slip structures and hydrocarbon accumulation in complex fault blocks in Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 393-401. [25] 左亮, 能源, 黄少英, 等. 哈拉哈塘地区超深层走滑断裂构造变形特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(2): 270-282.ZUO Liang, NENG Yuan, HUANG Shaoyin, et al. Deformation characteristics of ultra-deep glide faults in the Halahatang area and their petroleum geological significance[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(2): 270-282. [26] 张仲培, 徐勤琪, 刘士林, 等. 塔里木盆地巴麦地区东段北东向走滑断裂体系特征及油气地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 761-769.ZHANG Zhongpei, XU Qinqi, LIU Shilin, et al. Characteristics of NE strike-slip fault system in the eastern section of Bachu-Maigaiti area, Tarim Basin and its oil-gas geological significance[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 761-769. [27] 张波. 济阳坳陷孤西潜山带构造演化及其对油气差异富集的控制[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(2): 29-38.ZHANG Bo. Tectonic evolution and its control on differential hydrocarbon enrichment of Guxi Buried Hill, Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(2): 29-38. [28] 王启超, 刘光祥, 吴疆, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地旬宜地区下古生界走滑断裂特征与油气勘探意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(2): 342-353.WANG Qichao, LIU Guangxiang, WU Jiang, et al. Characteristics of Lower Paleozoic strike-slip faults and their significance for oil and gas exploration in Xunyi-Yijun area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(2): 342-353. [29] 马海陇, 蒋林, 姜应兵, 等. 塔里木盆地先巴扎地区走滑断裂特征及石油地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2024, 31(2): 266-275.MA Hailong, JIANG Lin, JIANG Yingbing, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip faults in Xianbazha area of Tarim Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2024, 31(2): 266-275. [30] 张希晨, 刘晓波, 杜长江, 等. 松辽盆地王府断陷边界正断层差异变形特征及成因机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 455-465.ZHANG Xichen, LIU Xiaobo, DU Changjiang, et al. Differential deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of boundary normal faults in Wangfu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 455-465. [31] KATZ Y, WEINBERGER R, AYDIN A. Geometry and kinematic evolution of Riedel shear structures, Capitol Reef National Park, Utah[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2004, 26(3): 491-501. [32] SCHREURS G. Fault development and interaction in distributed strike-slip shear zones: an experimental approach[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2003, 210(1): 35-52. [33] WILCOX RONALD E, HARDING T P, SEELY D R. Basic wrench tectonics[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(1): 74-96. [34] KEEP M, MCCLAY K R. Analogue modelling of multiphase rift systems[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 273(3/4): 239-270. [35] BONINI M, SOURIOT T, BOCCALETTI M, et al. Successive orthogonal and oblique extension episodes in a rift zone: laboratory experiments with application to the Ethiopian Rift[J]. Tectonics, 1997, 16(2): 347-362. [36] JACKSON C A L, ROTEVATN A. 3D seismic analysis of the structure and evolution of a salt-influenced normal fault zone: a test of competing fault growth models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2013, 54: 215-234. [37] 张关龙, 王越. 准噶尔盆地早二叠世构造—沉积格局及石油地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(1): 35-48.ZHANG Guanlong, WANG Yue. Tectono-sedimentary framework of Early Permian in Junggar Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(1): 35-48. [38] 姜鹍鹏, 刘亚雷, 周新桂, 等. 塔里木盆地柯坪断隆早古生代断裂构造特征: 以柯坪南地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1248-1257.JIANG Kunpeng, LIU Yalei, ZHOU Xingui, et al. Fault structural characteristics of the Early Paleozoic in the Keping Fault-Uplift, Tarim Basin: a case study in the southern Keping area[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(5): 1248-1257. [39] 冯军. 走滑断层形成演化主控因素物理模拟研究及应用[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2022.FENG Jun. Physical analog modeling of main controlling factors of strike-slip fault formation and evolution and its application[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2022. [40] 童亨茂, 孟令箭, 蔡东升, 等. 裂陷盆地断层的形成和演化: 目标砂箱模拟实验与认识[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(6): 759-774.TONG Hengmao, MENG Lingjian, CAI Dongsheng, et al. Fault formation and evolution in rift basins: sandbox modeling and cognition[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(6): 759-774. [41] REBER J E, COOKE M L, DOOLEY T P. What model material to use?A review on rock analogs for structural geology and tectonics[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 202: 103107. [42] 代兰, 邬光辉, 陈鑫, 等. 共轭走滑断裂形成演化的控制因素及物理模拟实验[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 43-50.DAI Lan, WU Guanghui, CHEN Xin, et al. Controlling factors and physical simulation experiments on formation and evolution of conjugate strike-slip faults[J]. Xinjiang Petroloeum Geology, 2023, 44(1): 43-50. [43] 隆辉, 曾溅辉, 刘亚洲, 等. 可视化三维物理模拟实验技术在油气成藏研究中的应用: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区S53-2井为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(5): 1110-1122. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024051110LONG Hui, ZENG Jianhui, LIU Yazhou, et al. Application of visual 3D physical simulation experiment technology in oil and gas accumulation research: a case study of well S53-2 in Shunbei area of Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(5): 1110-1122. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024051110 [44] PANIEN M, SCHREURS G, PFIFFNER A. Mechanical behaviour of granular materials used in analogue modelling: insights from grain characterisation, ring-shear tests and analogue experiments[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28(9): 1710-1724. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号