Microscopic pore structure characteristics and mobility of shale oil reservoirs in Liushagang Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin
-
摘要: 页岩油储层致密且非均质性较强,微观孔隙结构影响着页岩油在储层中的储集与流动,但常规单一手段往往难以准确表征微观孔隙结构。为揭示页岩油储层的微观孔隙结构与可动性特征,指导后续海上页岩油的高效勘探开发,以北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组基质型、纹层型和夹层型3种类型的页岩油储层为研究对象,综合运用铸体薄片、扫描电镜、高压压汞、氮气吸附、核磁共振等分析测试方法,对孔隙结构参数、压汞形态、吸附曲线特征等进行了分析。结果表明:基质型与纹层型储层粒度较细,孔隙相对不发育,孔隙形态多以平板狭缝形为主,发育层理缝、有机孔、黏土矿物片间孔、黄铁矿晶间孔等;夹层型储层孔隙形态多以墨水瓶形为主,发育矿物粒间孔、溶蚀孔、网状缝等,孔径分布及储层连通性较好。荧光薄片、核磁共振对页岩油可动性分析表明,基质型和纹层型储层可动性相对较差,可动孔隙度分别为0.72%和4.62%,可动油含量相对较低;夹层型储层可动孔隙度为6.37%,烃类组分更轻,可动性更好,可动油含量更高,是涠西南凹陷最大的页岩油勘探有利储层。Abstract: Shale oil reservoirs are characterized by tightness and strong heterogeneity, and the microscopic pore structures affect the storage and flow of shale oil in reservoirs. However, conventional single analytical methods often fail to accurately characterize these microscopic pore structures. This study aims to reveal the microscopic pore structure and mobility characteristics of shale oil reservoirs, thereby guiding efficient exploration and development of offshore shale oil. Three types of shale oil reservoirs—matrix-type, laminated-type and interbedded-type—in the Liushagang Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin were selected as the research objects. Integrated analytical and testing methods were employed, including cast thin-sections, scanning electron microscopy, high-pressure mercury intrusion, nitrogen adsorption, and nuclear magnetic resonance, to analyze pore structure parameters, mercury intrusion morphology, and adsorption curve characteristics. The results showed that the matrix-type and laminated-type reservoirs exhibited finer grain sizes and relatively underdeveloped pores, dominated by slit-shaped pore morphologies. These reservoirs commonly featured bedding fractures, organic pores, interlayer pores within clay minerals, and intercrystalline pores within pyrite. The interbedded-type reservoirs mainly had ink-bottle-shaped pore morphologies, along with intergranular pores within mineral particles, dissolution pores, and fracture networks, showing good pore size distribution and reservoir connectivity. Analysis of shale oil mobility through fluorescence thin sections and nuclear magnetic resonance revealed that the matrix-type and laminated-type reservoirs exhibited relatively poorer mobility, with movable porosities of 0.72% and 4.62%, respectively, along with lower movable oil content. The interbedded-type reservoir exhibited a movable porosity of 6.37%, with lighter hydrocarbon components, better mobility, and higher movable oil content, making it the most favorable reservoir type for shale oil exploration in the Weixinan Sag.
-
Key words:
- reservoir pore structure /
- shale oil mobility /
- Liushagang Formation /
- Paleogene /
- Weixinan Sag /
- Beibu Gulf Basin
-
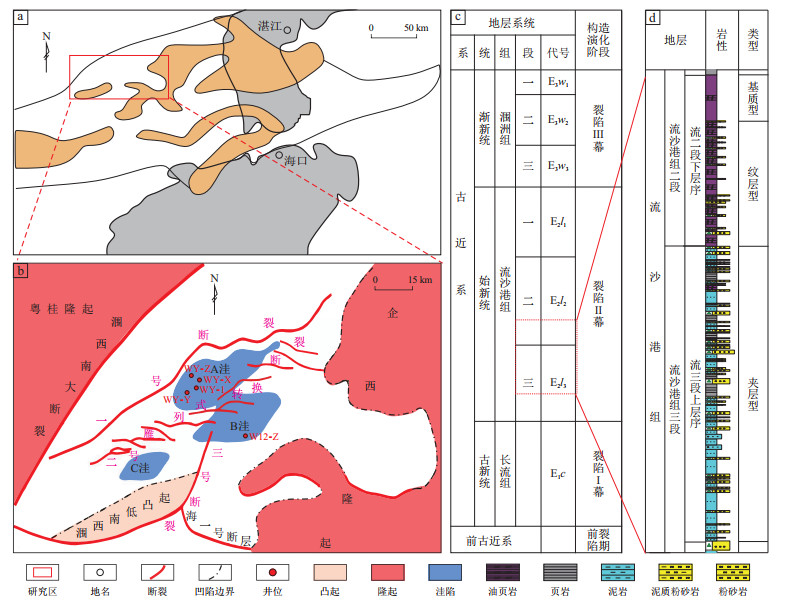
图 5 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组不同类型页岩油储层铸体薄片与扫描电镜照片
a.WY-X井,2 959 m,基质型铸体薄片,微裂缝;b.WY-X井,2 959 m,基质型铸体薄片,团状黄铁矿顺层发育;c.W12-Z井,3 161.1 m,基质型扫描电镜,黄铁矿晶间孔、黄铁矿伴生有机孔;d.WY-1井,3 164.9 m,基质型扫描电镜,黏土矿物顺层微裂缝;e.WY-X井,3 016.3 m,纹层型铸体薄片,微裂缝;f.WY-X井,2 998.3 m,纹层型铸体薄片,见铁方解石;g.WY-X井,3 556.9 m,纹层型扫描电镜,矿物粒间孔;h.WY-X井,3 556.9 m,纹层型扫描电镜,方解石与微晶石英;i.WY-Z井,3 496.52 m,夹层型铸体薄片网状缝;j.WY-X井,3 059.8 m,夹层型铸体薄片,溶蚀孔、铸模孔;k.WY-X井,3 126.8 m,夹层型扫描电镜,见微裂缝、碎屑矿物溶蚀;l.WY-X井,3 233 m,夹层型,碎屑矿物溶蚀。
Figure 5. Cast thin-sections and scanning electron microscopy images of different shale oil reservoir types in Liushagang Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin
图 8 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组不同类型页岩油储层荧光薄片尺度下的发育特征
a.W12-Z井,3 164.9 m,基质型,层理缝;b.W12-Z井,3 159.7 m,基质型,层理缝;c.W12-Z井,3 159.7 m,基质型,网状缝;d.WY-X井,3 561.7 m,纹层型,层理缝;e.WY-X井,3 560.25 m,纹层型,网状缝;f.WY-X井,3 556.9 m,纹层型,层理缝;g.WY-Z井,3 496.52 m井,夹层型,网状缝;h.WY-Z井,3 397.5 m,夹层型,高角度构造缝;i.WY-Z井,3 413.69 m井,层理缝与网状缝。
Figure 8. Development characteristics of different shale oil reservoir types at fluorescence thin-section scale in Liushagang Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin
表 1 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷不同类型页岩油储层孔隙结构及可动性发育特征
Table 1. Pore structure and mobility development characteristics of different shale oil reservoir types in Weixinan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin
类型 主要孔缝类型 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 孔喉连通性 回滞环形态 ω(TOC)/% S1/(mg/g) 荧光薄片 可动孔隙度/% OSI/(mg/g) 基质型 矿物颗粒粒间孔、层理缝、黏土矿物层间缝、黄铁矿晶间孔、有机孔 $\frac{0.49 \sim 4.75}{2.68}$ $\frac{0.022 \sim 1.700}{0.25}$ 较差 H3型 $\frac{2.71 \sim 7.49}{5.19}$ $\frac{5.92 \sim 8.96}{7.51}$ 淡蓝色 0.72 $\frac{86.60 \sim 297.04}{154}$ 纹层型 层理缝、黄铁矿晶间孔、矿物颗粒粒间孔、碳酸盐胶结孔 $\frac{1.70 \sim 16.66}{7.47}$ $\frac{0.011 \sim 2.750}{0.36}$ 中等 H3型 $\frac{2.55 \sim 6.31}{4.67}$ $\frac{4.61 \sim 9.49}{7.12}$ 淡蓝色 4.62 $\frac{97.57 \sim 200.28}{142}$ 夹层型 杂基微孔、黏土矿物晶间孔、铸模孔、网状裂缝 $\frac{0.21 \sim 20.79}{14.61}$ $\frac{0.080 \sim 36.000}{20.79}$ 较好 H2型 $\frac{1.26 \sim 4.50}{2.40}$ $\frac{4.08 \sim 4.48}{4.34}$ 蓝色 6.37 $\frac{99.56 \sim 323.81}{243}$ 注:表中分式意义为$\frac{\text { 最小值~最大值}}{\text { 平均值}}$。 -
[1] 邹才能, 潘松圻, 荆振华, 等. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(1): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2020.01.001ZOU Caineng, PAN Songqi, JING Zhenhua, et al. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2020.01.001 [2] 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26.ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, CUI Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. [3] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 等. 中国陆相页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(1): 155-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.01.013MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration practices of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(1): 155-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.01.013 [4] 何文渊, 蒙启安, 张金友. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油富集主控因素及分类评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(5): 1-12.HE Wenyuan, MENG Qi'an, ZHANG Jinyou. Controlling factors and their classification-evaluation of Gulong shale oil enrichment in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. [5] 刘伟新, 史志华, 朱樱, 等. 扫描电镜/能谱分析在油气勘探开发中的应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2001, 23(3): 341-343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2001.03.017LIU Weixin, SHI Zhihua, ZHU Ying, et al. Application of SEM/EDX analysis in petroleum exploration and production[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2001, 23(3): 341-343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2001.03.017 [6] 崔景伟, 邹才能, 朱如凯, 等. 页岩孔隙研究新进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(12): 1319-1325.CUI Jingwei, ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, et al. New advances in shale porosity research[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(12): 1319-1325. [7] 杜金虎, 胡素云, 庞正炼, 等. 中国陆相页岩油类型、潜力及前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 560-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.003DU Jinhu, HU Suyun, PANG Zhenglian, et al. The types, potentials and prospects of continental shale oil in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 560-568. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.003 [8] 王倩茹, 陶士振, 关平. 中国陆相盆地页岩油研究及勘探开发进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(3): 417-427.WANG Qianru, TAO Shizhen, GUAN Ping. Progress in research and exploration & development of shale oil in continental basins in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(3): 417-427. [9] 徐长贵, 邓勇, 范彩伟, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷页岩油地质特征与资源潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(5): 1-12.XU Changgui, DENG Yong, FAN Caiwei, et al. Geological characteristics and resource potential of shale oil in Weixinan Sag of Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(5): 1-12. [10] 孙殿强, 姜洪丰, 周刚. 我国海上首口页岩油探井压裂测试成功并获商业油流: 海上页岩油开启新纪元[J]. 中国石油石化, 2022(18): 50-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7708.2022.18.017SUN Dianqiang, JIANG Hongfeng, ZHOU Gang. China's first offshore shale oil exploration well successfully fractured and obtained commercial oil flow—opening a new era for offshore shale oil[J]. China Petrochem, 2022(18): 50-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7708.2022.18.017 [11] 徐新德, 王碧维, 李旭红, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流沙港组隐蔽油气藏油源及成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(1): 92-98.XU Xinde, WANG Biwei, LI Xuhong, et al. Oil sources of concealed reservoirs in Liushagang Formation of the Weixinan Sag and accumulation feature, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(1): 92-98. [12] 杨希冰, 胡林, 金秋月. 乌石凹陷中—东区油气来源及成藏时间分析[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2016, 40(5): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.05.002YANG Xibing, HU Lin, JIN Qiuyue. Analysis of hydrocarbon origin and its accumulation time in the middle and east zone of Wushi Sag[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2016, 40(5): 9-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.05.002 [13] 胡德胜, 宫立园, 满晓, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷雁列断层变换带发育特征及其控储作用: 以古近系流沙港组一段重力流沉积为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1359-1369.HU Desheng, GONG Liyuan, MAN Xiao, et al. Development pattern of en echelon fault transition zone in Weixi'nan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of gravity flow deposits in the Palaeogene Liu 1 Member[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1359-1369. [14] 秦春雨, 王华, 姜平, 等. 涠西南凹陷边界断层演化及其对地层充填的控制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(2): 318-327.QIN Chunyu, WANG Hua, JIANG Ping, et al. Boundary fault evolution of Weixinan Sag and its effect on strata filling[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2020, 49(2): 318-327. [15] 魏小松, 陆江, 刘蕾, 等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组一段天文旋回识别及高频层序划分[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(6): 99-108.WEI Xiaosong, LU Jiang, LIU Lei, et al. Astronomical cycle identification and high frequency sequence division of the 1st member of Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(6): 99-108. [16] 曹磊. 北部湾盆地流二段烃源岩的有机质富集机理及发育模式[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.CAO Lei. Organic matter enrichment mechanism and development model of source rocks in the 2nd member of Liushagang Formation in Beibuwan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. [17] 高树生, 胡志明, 刘华勋, 等. 不同岩性储层的微观孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 248-256.GAO Shusheng, HU Zhiming, LIU Huaxun, et al. Microscopic pore characteristics of different lithological reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 248-256. [18] 马云峰, 赵建国, 孙龙, 等. 应力作用下气藏水体微观赋存特征及渗流规律: 以鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田二叠系盒8段致密储层为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 466-473. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303466MA Yunfeng, ZHAO Jianguo, SUN Long, et al. Microscopic occurrence characteristics and seepage law of water bodies in gas reservoir under stress: a case study of tight reservoirs in the eighth member of Permian Shihezi Formation, Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 466-473. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303466 [19] 姜在兴, 张文昭, 梁超, 等. 页岩油储层基本特征及评价要素[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(1): 184-196.JIANG Zaixing, ZHANG Wenzhao, LIANG Chao, et al. Characteristics and evaluation elements of shale oil reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 184-196. [20] 王羽君, 赵晓东, 周伯玉, 等. 基于高压压汞—恒速压汞的低渗砂岩储层孔隙结构评价[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 824-830.WANG Yujun, ZHAO Xiaodong, ZHOU Boyu, et al. Evaluation of pore structure in low permeability sandstone reservoir based on high pressure-constant velocity mercury injection[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 824-830. [21] 罗锦昌, 田继军, 贺小标, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组储层介—宏孔孔隙结构特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科学, 2023, 58(3): 1008-1029.LUO Jinchang, TIAN Jijun, HE Xiaobiao, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of meso-macropore pore structure of Permian Lucaogou Formation reservoir in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2023, 58(3): 1008-1029. [22] IUPAC. Manual of symbol sand terminology[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1972, 31: 578. [23] 孙照通, 辛红刚, 吕成福, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长73亚段泥页岩型页岩油赋存状态与有机地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(8): 1304-1318.SUN Zhaotong, XIN Honggang, LV Chengfu, et al. Occurrence states and organic geochemical characteristics of shale-type shale oil from Chang 73 sub-member in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(8): 1304-1318. [24] 杨正明, 苗盛, 刘先贵, 等. 特低渗透油藏可动流体百分数参数及其应用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 22(2): 96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2007.02.025YANG Zhengming, MIAO Sheng, LIU Xiangui, et al. Percentage parameter of the movable fluid in ultra-low permeability reservoir and its application[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 22(2): 96-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2007.02.025 [25] 陈佳伟. 东营凹陷页岩油可动性及有利区优选方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2017.CHEN Jiawei. Research on the movability of shale oil in Dongying Sag and the optimization method of favorable zone[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2017. [26] LIU Guoheng, LIU Bo, LIU Keyu, et al. Silica crystallinity: characteristics and controlling factors in marine shale of the Upper Yangtze area, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 143: 105833. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105833 [27] TIAN Shansi, BOWEN L, LIU Bo, et al. A method for automatic shale porosity quantification using an Edge-Threshold Automatic Processing (ETAP) technique[J]. Fuel, 2021, 304: 121319. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121319 [28] 冯国奇, 李吉君, 刘洁文, 等. 泌阳凹陷页岩油富集及可动性探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6): 1236-1246.FENG Guoqi, LI Jijun, LIU Jiewen, et al. Discussion on the enrichment and mobility of continental shale oil in Biyang Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1236-1246. [29] 赵贤正, 周立宏, 蒲秀刚, 等. 断陷湖盆湖相页岩油形成有利条件及富集特征: 以渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔店组二段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(9): 1013-1029.ZHAO Xianzheng, ZHOU Lihong, PU Xiugang, et al. Favorable formation conditions and enrichment characteristics of lacustrine facies shale oil in faulted lake basin: a case study of member 2 of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(9): 1013-1029. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号