Quantitative characterization of adsorbed and free shale oil microscopic distribution based on nuclear magnetic resonance: a case study of Chang 7 member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 页岩油赋存状态及其可动性定量评价是当前页岩油地质研究的核心和难点问题。以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段(简称长7段)页岩为研究对象,采用饱和—离心—核磁共振实验方法,结合前人提出的页岩油吸附比例方程,对页岩油吸附/游离含量、比例、微观分布及可动性特征等开展了综合研究。在饱和正十二烷及20 ℃离心温度的条件下,长7段页岩游离/吸附油量平均分别为1.981 4 mg/g和1.548 1 mg/g,吸附油比例平均为0.430 7。页岩油吸附相/游离相平均密度比为1.171 3,吸附相平均密度为0.877 8 cm3/g,平均吸附层厚度为0.980 2 nm。吸附油主要赋存于微小孔(小于100 nm),游离油在微小、中、大孔中的赋存含量依次减少。高有机质页岩由于生烃增压微裂缝的存在和较不发育的有机质孔使得总体具有较高的游离油量和较低的吸附油量。石英相关孔隙会明显增大孔隙比表面积进而为吸附油提供更多赋存点位,而黏土矿物含量的增加会显著减少游离油赋存的孔隙体积。游离油量(Qf)与中值离心力(ΔPL)的比值(Qf/ΔPL)是评价页岩油可动性的新型有效参数,该值越高,反映页岩油可动性越好。对于长7段页岩而言,Qf/ΔPL=1.339 4 mg/(g·MPa)是页岩油可动性发生显著变化的阈值,大于该值,页岩油可动性明显变好。通过吸附比例方程计算的游离油理论赋存孔径下限介于1.960 4~5.881 2 nm之间,具体大小与孔隙形态有关。Abstract: Quantitative evaluation of shale oil occurrence states and mobility is a key and challenging issue in current shale oil geological research. Taking the shale from the seventh member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation (Chang 7 member) in the Ordos Basin as the research object, this study combined nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments with saturation-centrifugal tests, using the shale oil adsorption ratio equation proposed by previous research. It conducted a comprehensive study on the adsorbed and free oil amount, ratio, microscopic distribution, and mobility characteristics of shale oil. The results showed that under conditions of saturation with n-dodecane and centrifugation at 20 ℃, the average amounts of free oil and adsorbed oil in shale of the Chang 7 member were 1.981 4 mg/g and 1.548 1 mg/g, respectively. The average proportion of adsorbed oil was 0.430 7. The average density ratio between the adsorbed and free phases of shale oil was 1.171 3, the average density of adsorption phase was 0.877 8 cm3/g, and the average thickness of the adsorption layer was 0.980 2 nm. Adsorbed oil mainly exist in micropores (< 100 nm), and the amount of free oil in micropores, mesopores, and macropores sequentially decreases. Organic-matter-rich shale generally contain higher amount of free oil and lower amount of adsorbed oil due to the existence of hydrocarbon generation-induced microfractures and less developed organic pores. Quartz-related pores significantly increase the specific surface area of pores, thus providing more occurrence sites for adsorbed oil, whereas an increase in clay mineral content significantly reduces the pore volume available for free oil. The ratio of free oil amount (Qf) to median centrifugal force (ΔPL) is identified as a new and effective parameter for evaluating shale oil mobility. Higher ratio indicates better shale oil mobility. For shale in Chang 7 member, Qf/ΔPL=1.339 4 mg/(g·MPa) represents the threshold at which shale oil mobility undergoes a significant change. Above this threshold, the shale oil mobility significantly improves. The lower limit of theoretical pore size of free oil, calculated using the adsorption ratio equation, is between 1.960 4 nm and 5.881 2 nm, and the specific size is related to pore morphology.
-
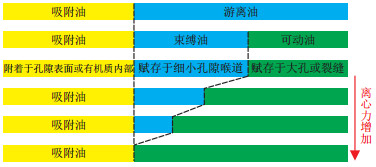
图 1 页岩油赋存状态及离心过程中转换过程示意图
据参考文献[27]修改。
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of shale oil occurrence states and conversion process during centrifugation
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段烃源岩厚度(a)及延长组地层综合柱状图(b)
图b据参考文献[21]修改。
Figure 2. Hydrocarbon source rock thickness in Triassic Chang 7 member (a) and stratigraphic histogram of Yanchang Formation (b) in Ordos Basin
图 8 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段页岩样品1/Qm与1/ΔP相关关系(a)及不同离心力下实测可动油量与模型拟合趋势的对应关系(b)
Figure 8. Correlation relationship between 1/Qm and 1/ΔP (a) and corresponding relationship between measured movable oil volume and model fitting trend under different centrifugal forces (b) of shale samples from Triassic Chang 7 member in Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段3亚段页岩样品有机地化及矿物组分特征
Table 1. Organic geochemical and mineral composition characteristics of shale samples from 3rd submember of Triassic Chang 7 member in Ordos Basin
样品号 深度/m ω(TOC)/% Tmax/℃ S1/(mg/g) S2/(mg/g) IH/(mg/g) 全岩矿物含量/% 黏土矿物含量/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 黏土矿物 伊蒙混层 伊利石 绿泥石 高岭石 YJ1-2 2 069.00 3.95 450 1.14 6.57 166 22.9 2.9 10.9 0.0 12.1 4.0 46.9 15.3 23.2 5.5 2.9 Yu22-2 2 666.70 9.86 448 1.58 32.42 329 24.1 1.9 8.7 0.0 0.5 4.1 59.5 19.2 28.0 4.8 7.5 D81-2 1 655.12 3.70 448 0.53 11.05 299 20.3 3.5 12.1 0.4 0.0 0.6 63.1 19.6 11.5 15.2 16.8 Zh22-4 1 653.10 1.02 477 0.23 0.64 63 33.6 0.5 13.7 0.5 0.6 1.0 48.6 14.1 25.9 5.4 3.2 W100-1 2 010.40 13.60 449 2.34 50.40 371 18.7 0.9 11.9 0.0 0.0 23.0 45.5 12.2 20.3 7.3 5.7 F75-3 2 763.90 8.00 445 3.61 29.09 364 24.4 1.7 2.7 0.0 1.8 2.9 66.5 18.4 30.1 8.3 9.7 Y22-2 2 642.92 0.79 449 0.16 0.47 59 29.2 0.9 2.9 9.6 11.2 1.1 42.1 7.2 24.2 7.4 3.4 B522-2 1 947.75 9.07 444 3.33 13.11 145 17.7 3.0 12.0 2.8 0.0 27.0 37.5 9.0 24.9 2.3 1.3 Zh233-1 1 802.70 22.20 440 7.28 91.66 413 31.3 1.4 10.4 1.2 1.3 36.1 15.2 4.8 8.7 1.2 0.6 G347-1 2 421.51 2.28 446 0.80 5.24 230 28.1 16.2 16.4 0.0 3.2 0.0 36.1 8.7 6.9 13.0 7.4 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段页岩样品离心实验拟合结果及孔隙结构参数
Table 2. Pore structural parameters and fitting results of centrifugal experiments on shale samples from Triassic Chang 7 member in Ordos Basin
样品号 Qf/(mg/g) Qa/(mg/g) ΔPL/MPa ra Qa/Qf Qf/ΔPL Vo/So YJ1-2 3.058 1 0.679 0 0.466 7 0.181 7 0.222 0 6.553 1 5.123 7 Yu22-2 1.327 3 0.603 7 0.665 8 0.312 6 0.454 8 1.993 6 3.276 8 D81-2 1.026 9 1.085 3 1.289 6 0.513 8 1.056 8 0.796 3 1.626 0 Zh22-4 0.818 4 5.993 2 1.142 4 0.879 9 7.323 1 0.716 4 1.118 6 W100-1 1.933 9 0.712 2 0.819 4 0.269 2 0.368 3 2.360 2 4.802 9 F75-3 1.051 0 0.822 9 0.674 1 0.439 1 0.783 0 1.559 1 2.900 8 Y22-2 0.410 0 2.246 2 0.986 8 0.845 7 5.479 1 0.415 4 0.542 1 B522-2 4.456 3 0.756 6 0.582 4 0.145 1 0.169 8 7.651 1 8.118 0 Zh233-1 4.454 3 1.404 1 0.712 7 0.239 7 0.315 2 6.250 0 4.650 2 G347-1 1.277 6 1.178 3 0.583 5 0.479 8 0.922 3 2.189 6 3.022 2 -
[1] 金之钧, 朱如凯, 梁新平, 等. 当前陆相页岩油勘探开发值得关注的几个问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(6): 1276-1287.JIN Zhijun, ZHU Rukai, LIANG Xinping, et al. Several issues worthy of attention in current lacustrine shale oil exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6): 1276-1287. [2] 杨智, 邹才能, 吴松涛, 等. 从源控论到源储共生系统: 论源岩层系油气地质理论认识及实践[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(3): 618-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.03.002YANG Zhi, ZOU Caineng, WU Songtao, et al. From source control theory to source-reservoir symbiosis system: on the theoretical understanding and practice of source rock strata oil and gas geology in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(3): 618-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.03.002 [3] 邹才能, 杨智, 董大忠, 等. 非常规源岩层系油气形成分布与前景展望[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(5): 1517-1533.ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, DONG Dazhong, et al. Formation, distribution and prospect of unconventional hydrocarbons in source rock strata in China[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(5): 1517-1533. [4] 郭秋麟, 米石云, 张倩, 等. 中国页岩油资源评价方法与资源潜力探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 402-412. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303402GUO Qiulin, MI Shiyun, ZHANG Qian, et al. Assessment methods and potential of shale oil resources in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 402-412. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303402 [5] 孙志刚, 于春磊, 陈辉, 等. 陆相页岩油开发实验技术现状与展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(5): 186-198.SUN Zhigang, YU Chunlei, CHEN Hui, et al. Progress and prospect of experimental technologies for continental shale oil development[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(5): 186-198. [6] 梅启亮, 郭睿良, 周新平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长73亚段纹层型页岩油储层孔隙结构特征与影响因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(5): 851-867.MEI Qiliang, GUO Ruiliang, ZHOU Xinping, et al. Pore structure characteristics and impact factors of laminated shale oil reservoir in Chang 73 sub-member of Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(5): 851-867. [7] 吴凯, 高娟琴, 解古巍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段页岩气储层特征及其勘探开发前景[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(6): 1298-1311. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024061298WU Kai, GAO Juanqin, XIE Guwei, et al. Characteristics of Chang 7 shale gas reservoirs in Triassic Yanchang Formation of Ordos Basin and its exploration and development prospects[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(6): 1298-1311. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024061298 [8] 王剑, 刘金, 潘晓慧, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油生烃母质及其生烃机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 253-261.WANG Jian, LIU Jin, PAN Xiaohui, et al. Precursor and mechanism of hydrocarbon generation for shale oil in Lucaogou formation, Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(3): 253-261. [9] 周家全, 王越, 宋子怡, 等. 准噶尔盆地博格达地区中二叠统芦草沟组热液硅质结核特征及页岩油意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(3): 789-800.ZHOU Jiaquan, WANG Yue, SONG Ziyi, et al. Characterizing hydrothermal siliceous nodules to guide shale oil exploration in the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation, Bogda area, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(3): 789-800. [10] 刘胜男, 朱如凯, 靳军, 等. 油气运移约束陆相页岩油富集: 以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(6): 932-946.LIU Shengnan, ZHU Rukai, JIN Jun, et al. Hydrocarbon migration constraints on continental shale oil enrichment: a case study of Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(6): 932-946. [11] 彭君, 孙宁亮, 鹿坤, 等. 东濮凹陷古近系沙河街组页岩油储层岩石学及微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 128-141.PENG Jun, SUN Ningliang, LU Kun, et al. Shale oil reservoir of the Palaeogene Shahejie Formation in the Dongpu Sag: petrology and pore microstructural characteristics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4): 128-141. [12] 李军亮, 刘惠民, 王勇, 等. 济阳陆相断陷盆地页岩油研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(4): 60-72.LI Junliang, LIU Huimin, WANG Yong, et al. Research progress of shale oil in Jiyang continental faulted basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(4): 60-72. [13] 柳波, 孙嘉慧, 张永清, 等. 松辽盆地长岭凹陷白垩系青山口组一段页岩油储集空间类型与富集模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 521-535.LIU Bo, SUN Jiahui, ZHANG Yongqing, et al. Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling Sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration & Development, 2021, 48(3): 521-535. [14] 肖佃师, 郭雪燚, 王猛, 等. 砂岩夹层储层分级评价及展布特征: 以松辽盆地长岭凹陷大情字井地区青山口组一段为例[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2024, 14(5): 714-726.XIAO Dianshi, GUO Xueyi, WANG Meng, et al. Classification evaluation and distribution characteristics of sandstone interlayer reservoirs: a case study of the first member of Qingshankou Formation in Daqingzijing area, Changling Sag, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2024, 14(5): 714-726. [15] 赵贤正, 周立宏, 蒲秀刚, 等. 断陷湖盆湖相页岩油形成有利条件及富集特征: 以渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔店组二段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(9): 1013-1029.ZHAO Xianzheng, ZHOU Lihong, PU Xiugang, et al. Favorable formation conditions and enrichment characteristics of lacustrine facies shale oil in faulted lake basin: a case study of member 2 of Kongdian Formation in Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(9): 1013-1029. [16] 赵文智, 朱如凯, 胡素云, 等. 陆相富有机质页岩与泥岩的成藏差异及其在页岩油评价中的意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1079-1089.ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, HU Suyun, et al. Accumulation contribution differences between lacustrine organic-rich shales and mudstones and their significance in shale oil evaluation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1079-1089. [17] 于燕, 林刚, 卓龙成, 等. 浅谈页岩油效益开发[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2023, 16(2): 144-148.YU Yan, LIN Gang, ZHUO Longcheng, et al. Discussion on the benefit development of shale oil[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2023, 16(2): 144-148. [18] 钟红利, 卓自敏, 张凤奇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地甘泉地区长7页岩油储层非均质性及其控油规律[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(4): 10-18.ZHONG Hongli, ZHUO Zimin, ZHANG Fengqi, et al. Heterogeneity of Chang 7 shale oil reservoir and its oil control law in Ganquan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil &Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(4): 10-18. [19] 金之钧, 王冠平, 刘光祥, 等. 中国陆相页岩油研究进展与关键科学问题[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 821-835.JIN Zhijun, WANG Guanping, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Research progress and key scientific issues of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 821-835. [20] 李政, 包友书, 朱日房, 等. 页岩油赋存特征、可动性实验技术及研究方法进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(4): 84-95.LI Zheng, BAO Youshu, ZHU Rifang, et al. Progress in experimental techniques and research methods for shale oil occurrence characteristics and mobility[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(4): 84-95. [21] GUO Ruliang, LI Shixiang, ZHOU Xinping, et al. Multi-isothermal stage pyrolysis of the Chang 73 shale oil reservoirs, Ordos Basin: implications for oil occurrence states and in situ conversion exploitation[J]. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 2022, 6(4): 1143-1162. [22] LI Shutong, LI Shixiang, GUO Ruiliang, et al. Occurrence state of soluble organic matter in shale oil reservoirs from the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin, China: insights from multipolarity sequential extraction[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2021, 30(6): 4379-4402. [23] 李士祥, 周新平, 郭芪恒, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长73亚段页岩油可动烃资源量评价方法[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1771-1784.LI Shixiang, ZHOU Xinping, GUO Qiheng, et al. Research on evaluation method of movable hydrocarbon resources of shale oil in the Chang 73 sub-member in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1771-1784. [24] 宫厚健, 姜振学, 朱峰, 等. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜宁组二段页岩油赋存状态定量表征及控制因素[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2024, 48(2): 59-71.GONG Houjian, JIANG Zhenxue, ZHU Feng, et al. Quantitative characterization and control factors of shale oil occurrence state in the shale of member 2 of Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2024, 48(2): 59-71. [25] 李俊乾, 卢双舫, 张婕, 等. 页岩油吸附与游离定量评价模型及微观赋存机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 583-592.LI Junqian, LU Shuangfang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Quantitative evaluation models of adsorbed and free shale oil and its microscopic occurrence mechanism[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 583-592. [26] 李俊乾, 宋兆京, 王民, 等. 页岩基质孔隙油微观赋存及可动性定量表征: 以东营凹陷沙河街组为例[J]. 石油科学通报, 2024, 9(1): 1-20.LI Junqian, SONG Zhaojing, WANG Min, et al. Quantitative characterization of microscopic occurrence and mobility of oil in shale matrix pores: a case study of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2024, 9(1): 1-20. [27] ZHANG Pengfei, LU Shuangfang, LI Junqian, et al. Evaluating microdistribution of adsorbed and free oil in a lacustrine shale using nuclear magnetic resonance: a theoretical and experimental study[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 212: 110208. [28] 王子萌, 蒋裕强, 付永红, 等. 基于核磁共振表征渝西地区五峰组—龙一1亚段页岩储层孔隙结构及非均质性[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(2): 490-504.WANG Zimeng, JIANG Yuqiang, FU Yonghong, et al. Characterization of pore structure and heterogeneity of shale reservoir from Wufeng Formation-sublayers Long-11 in western Chongqing based on nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(2): 490-504. [29] LI Junqian, WANG Siyuan, LU Shuangfang, et al. Microdistribution and mobility of water in gas shale: a theoretical and experimental study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 496-507. [30] 中国石油天然气股份有限公司勘探开发研究院, 大庆油田有限责任公司勘探开发研究院, 中海油能源发展股份有限公司工程技术公司, 等. 岩石毛管压力曲线的测定: GB/T 29171-2023[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2023.PetroChina Exploration and Development Research Institute, Daqing Oilfield Co., Ltd. Exploration and Development Research Institute, CNOOC Energy Development Co., Ltd. Engineering Technology Company, et al. Rock capillary pressure measurement: GB/T 29171-2023[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2023. [31] 王岚, 李文厚, 刘群, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7黑色页岩岩相分类与沉积环境恢复[J]. 古地理学报, 2023, 25(3): 598-613.WANG Lan, LI Wenhou, LIU Qun, et al. Lithofacies characteristics and sedimentary environment of Chang 7 black shale in the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography Chinese Edition), 2023, 25(3): 598-613. [32] LI Jinbu, LU Shuangfang, JIANG Chunqing, et al. Characterization of shale pore size distribution by NMR considering the influence of shale skeleton signals[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(7): 6361-6372. [33] 覃莹瑶, 张宫, 罗超, 等. 吉木萨尔页岩油储层二维核磁响应特征[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3387-3400.QIN Yingyao, ZHANG Gong, LUO Chao, et al. Two-dimensional NMR characteristics of Jimsar shale oil reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3387-3400. [34] 解德录, 赵贤正, 金凤鸣, 等. 沧东凹陷深湖亚相纹层状页岩成因及页岩油可动性影响因素[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(5): 804-816.XIE Delu, ZHAO Xianzheng, JIN Fengming, et al. Genesis of deep lacustrine subfacies laminated shale and influence factors on shale oil mobility in Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(5): 804-816. [35] 方锐, 蒋裕强, 杨长城, 等. 四川盆地侏罗系凉高山组不同岩性组合页岩油赋存状态及可动性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(3): 752-769.FANG Rui, JIANG Yuqiang, YANG Changcheng, et al. Occurrence states and mobility of shale oil in different lithologic assemblages in the Jurassic Lianggaoshan Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(3): 752-769. [36] 姜振学, 李廷微, 宫厚健, 等. 沾化凹陷低熟页岩储层特征及其对页岩油可动性的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(12): 1587-1600.JIANG Zhenxue, LI Tingwei, GONG Houjian, et al. Characteristics of low-mature shale reservoirs in Zhanhua Sag and their influence on the mobility of shale oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 1587-1600. [37] JARVIE D M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: part 2—Shale-oil resource systems[C]//Shale reservoirs—Giant resources for the 21st Century. AAPG, 2012. [38] 赵文智, 朱如凯, 刘伟, 等. 中国陆相页岩油勘探理论与技术进展[J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(4): 373-390.ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, LIU Wei, et al. Advances in theory and technology of non-marine shale oil exploration in China[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(4): 373-390. [39] 王民, 马睿, 李进步, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组湖相页岩油赋存机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 789-802.WANG Min, MA Rui, LI Jinbu, et al. Occurrence mechanism of lacustrine shale oil in the Paleogene Shahejie Formation of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 789-802. [40] 党伟, 张金川, 聂海宽, 等. 页岩油微观赋存特征及其主控因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延安地区延长组7段3亚段陆相页岩为例[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 507-523.DANG Wei, ZHANG Jinchuan, NIE Haikuan, et al. Microscopic occurrence characteristics of shale oil and their main controlling factors: a case study of the 3rd submember continental shale of member 7 of Yanchang Formation in Yan'an area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 507-523. -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号