Geological characteristics and exploration suggestions for shale in Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation of Biyang and Nanyang sags, Nanxiang Basin
-
摘要: 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷古近系核桃园组页岩层与已突破的东部断陷盆地的页岩层系存在明显的地质差异。目前对该区页岩油地质特征形成机制认识不清,制约了其勘探开发进程。通过岩心、X衍射、薄片、扫描电镜和激光共聚焦等分析手段,系统研究了南襄盆地不同凹陷核桃园组页岩地质特征的差异,并提出下一步勘探建议。南襄盆地核桃园组页岩以纹层状混合质页岩为主,其中泌阳凹陷以纹层状云灰质—长英质混积页岩为主,发育基质型页岩油;南阳凹陷以纹层状长英质—黏土质混合页岩为主,砂岩夹层发育,主要为夹层型页岩油。泌阳凹陷页岩具有常压、中—低演化程度、中—高丰度特征,表现为储集性能中等—好、含油性好、可压性好以及可动性中等;南阳凹陷页岩具有常压、中等演化程度、中—低丰度的特点,储集性能中等、含油性中等—好、可压性及可动性中等。对比研究表明,边界断层及古水深控制不同凹陷湖盆类型;湖盆类型与古沉积环境的协同作用影响了页岩的岩相类型;有机质组分和成烃生物类型控制了页岩丰度。南阳凹陷淡水湖盆中—低丰度夹层型页岩油、泌阳凹陷咸化湖盆常压基质型页岩油均具备良好的成藏条件。针对泌阳凹陷页岩层含油性好、甜点相对集中的特点,建议加强低成本工程工艺攻关,探索夹层型页岩油直斜井效益开发模式;针对南阳凹陷页岩层纵向跨度大、断层复杂的特点,建议采用大斜度井实现纵向多层大规模压裂改造。Abstract: The shale layers in the Paleogene Hetaoyuan Formation of the Biyang and Nanyang sags in the Nanxiang Basin show significant geological differences from the shale strata in the eastern rift basins where breakthroughs have been achieved. The limited understanding of the formation mechanism of shale oil and its geological characteristics in this area constrains its exploration and development. Through core analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD), thin-section observation, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), the geological differences of the shale in the Hetaoyuan Formation across various sags in the Nanxiang Basin were systematically studied, and suggestions for future exploration were proposed. The Hetaoyuan Formation in the Nanxiang Basin mainly develops laminated mixed shale. Particularly, the Biyang Sag mainly develops laminated dolomitic and felsic mixed shale and is abundant in matrix-type shale oil. The Nanyang Sag mainly develops laminated felsic and argillaceous mixed shale with well-developed sandstone interlayers, primarily containing sandwich-type shale oil. The shale in the Biyang Sag exhibits normal pressure, medium to low evolution degree, and medium to high organic matter abundance, with medium to good reservoir property, good oil-bearing capacity, good compressibility, and medium mobility. The shale in the Nanyang Sag exhibits normal pressure, medium evolution degree, and medium to low organic matter abundance, with medium reservoir property, medium to good oil-bearing capacity, and medium compressibility and mobility. Comparative analysis revealed that boundary faults and paleo-water depth controlled the types of lake basins in different sags. Lake basin types and the paleo-depositional environment collectively affected shale lithofacies types. The organic matter components and hydrocarbon-generating organism types controlled the abundance of organic matter in shale. The sandwich-type shale oil with medium to low organic matter abundance in the freshwater lake basin of the Nanyang Sag and the matrix-type shale oil under normal pressure in the salt lake basin of the Biyang Sag possess favorable reservoir-forming conditions. For the shale layers in the Biyang Sag, which have good oil-bearing properties and relatively concentrated sweet spots, it is recommended to strengthen research on low-cost engineering technologies and explore efficient development models for sandwich-type shale oil through vertical and deviated wells. For the shale layers in the Nanyang Sag, which feature large vertical spans and complex faults, highly deviated wells are recommended for large-scale, multi-layer vertical fracturing.
-
Key words:
- rift basin /
- shale oil /
- paleo-depositional environment /
- Hetaoyuan Formation /
- Nanxiang Basin
-
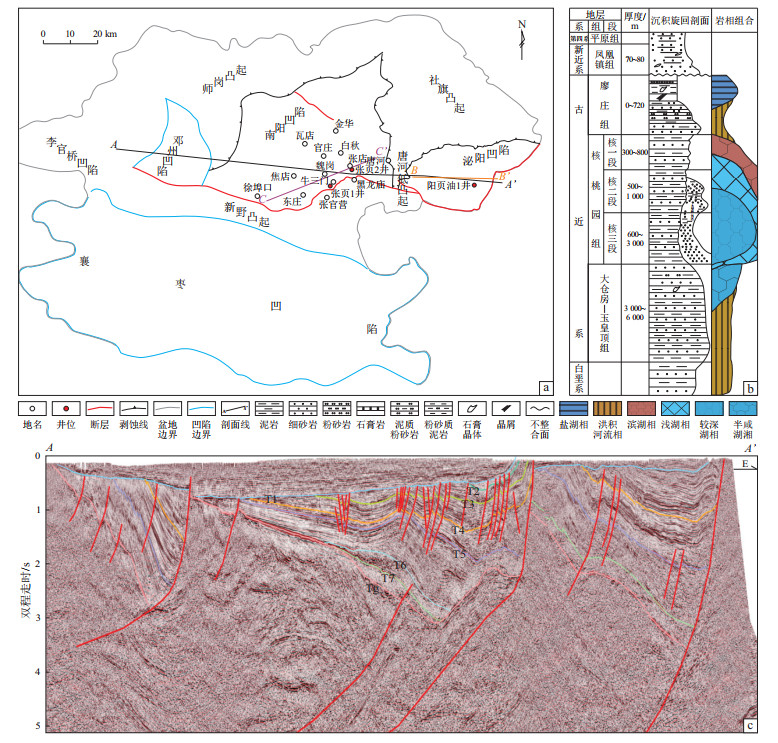
图 1 南襄盆地构造分区(a)、地层柱状图(b)及东西向地震剖面(c)
据参考文献[20],有修改。
Figure 1. Tectonic division (a), stratigraphic column (b), and EW-trending seismic profile (c) of Nanxiang Basin
图 3 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷岩心及岩石薄片照片
a.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 748.38 m,纹层状长英质页岩;b.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 753.02 m,纹层状混合质页岩;c.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 784.36 m,纹层状黏土质页岩;d.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 786.09 m,纹层状云灰质页岩;e.南阳凹陷,张页2井,2 878.55 m,纹层状长英质页岩;f.南阳凹陷,张页2井,3 025.93 m,纹层状黏土质页岩;g.张页2井,3 026.32 m,纹层状混合质页岩;h.南阳凹陷,张页2井,3 102.57 m,纹层状云灰质页岩。
Figure 3. Core samples and thin-section photomicrographs from Biyang and Nanyang sags of Nanxiang Basin
图 9 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷页岩有机质分布特征
a.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 742.01 m,含碎屑云质页岩,微裂缝发育,微裂缝以重质烃类显示为主,含油体积比10.41%;b.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 796 m,页岩,烃类分布受纹层控制,含油体积比11.82%;c.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 892.3 m,含粉砂云质泥岩。烃类呈星点状、线条状分布,局部富集,含油体积比8.11%;d.南阳凹陷,张页1井,3 023.24 m, 纹层状页岩,轻重质有机组分相对均匀地分布在泥质、灰质层中,连续性较差,有机质体积比3.23%;e.南阳凹陷,张页1井,2 961.53 m,纹层状页岩,轻质有机组分分布在泥质、灰质纹层中呈连续性分布,体积比2.85%;f.南阳凹陷,张页2井,3 090.45 m,粉细砂岩,烃类物质主要在颗粒周边的孔隙内呈环状分布,含油体积4.52%。
Figure 9. Organic matter distribution characteristics of shales in Biyang and Nanyang sags of Nanxiang Basin
图 11 南襄盆地过泌阳凹陷东—西向(a)和过南阳凹陷北东—南西向(b)地震剖面
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 11. EW-trending seismic profile across Biyang Sag (a) and NE-trending seismic profile across Nanyang Sag (b), Nanxiang Basin
图 15 南襄盆地各泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷页岩有机显微组分及成烃生物
a.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 804.8 m,纹层状混合质页岩(TOC含量为3.2%),密集线性藻类薄层,每层厚度在1 μm左右,黄色荧光;b.泌阳凹陷,阳页油1井,2 814.6 m,纹层状云灰质页岩(TOC含量为1.9%),结构藻类体,表面蜂窝或海绵状,发黄色荧光;c.南阳凹陷,张页1井,2 936.88 m,纹层状混合质页岩(TOC含量为1.4%),有机质以镜质组为主,腐泥组中见层状藻类体,部分降解为沥青质体,常呈细小的纹层状或基质状产出;d.南阳凹陷,张页1井,2 989.57 m,纹层状云灰质页岩(TOC含量为0.6%),镜质组以正常镜质体为主,见少量富氢镜质体,疑似被油浸染,条带状或不规则的透镜状,具褐色至暗褐色弱荧光,惰性组以惰屑体为主。
Figure 15. Organic macerals and hydrocarbon-generating organisms of shales in Biyang and Nanyang sags of Nanxiang Basin
表 1 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷和南阳凹陷页岩岩相分类
Table 1. Shale lithofacies classification of Biyang and Nanyang sags in Nanxiang Basin
凹陷 三端元分类 沉积构造 发育厚度/m 占比/% 泌阳凹陷 长英质页岩 层状 9.8 4.6 纹层状 95.4 30.1 云灰质页岩 层状 2.4 2.2 纹层状 150.0 7.9 黏土质页岩 纹层状 15.5 6.4 混合质页岩 层状 8.2 3.5 纹层状 125.3 45.3 南阳凹陷 长英质页岩 层状 18.2 6.0 纹层状 93.6 22.6 云灰质页岩 层状 3.2 2.5 纹层状 12.7 4.9 黏土质页岩 纹层状 9.4 4.0 混合质页岩 层状 13.2 3.1 纹层状 231.1 56.9 -
[1] 王敏, 陈祥, 严永新, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征与评价[J]. 古地理学报, 2013, 15(5): 663-671.WANG Min, CHEN Xiang, YAN Yongxin, et al. Geological characteristics and evaluation of continental shale oil in Biyang Sag of Nanxiang Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013, 15(5): 663-671. [2] 陈祥, 严永新, 章新文, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷陆相页岩气形成条件研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(2): 137-141.CHEN Xiang, YAN Yongxin, ZHANG Xinwen, et al. Generation conditions of continental shale gas in Biyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(2): 137-141. [3] 章新文, 李吉君, 朱景修, 等. 泌阳凹陷页岩油富集段资源评价及有利区预测[J]. 断块油气田, 2014, 21(3): 301-304.ZHANG Xinwen, LI Jijun, ZHU Jingxiu, et al. Resource evaluation and favorable area prediction on rich section of shale oil in Biyang Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2014, 21(3): 301-304. [4] 倪良田, 杜玉山, 蒋龙, 等. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷陆相断陷湖盆中—低成熟度页岩"富烃—成储—富集—高产"的理论认识与开发实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(5): 1417-1430.NI Liangtian, DU Yushan, JIANG Long, et al. Medium-to-low maturity shales in the faulted lacustrine basin in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin: theoretical understanding of their hydrocarbon generation, reservoir formation, and shale oil enrichment and high-yield nature and exploitation practices[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(5): 1417-1430. [5] 孙雅雄, 梁兵, 邱旭明, 等. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜二段页岩天然裂缝发育特征及其对页岩油富集和保存的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 61-74.SUN Yaxiong, LIANG Bing, QIU Xuming, et al. Characteristics of natural fractures and its influence on shale oil enrichment and preservation in member 2 of Funing Formation in Gaoyou sag, Subei Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 61-74. [6] 赵晨旭, 李忠诚, 郭世超, 等. 松辽盆地南部长岭断陷青一段陆相页岩地球化学和沉积环境特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(6): 55-61.ZHAO Chenxu, LI Zhongcheng, GUO Shichao, et al. Characteristics of geochemistry and depositional environment of terrestrial shales in the first member of Qingshankou Formation of Changling Fault Depression in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(6): 55-61. [7] 白斌, 戴朝成, 侯秀林, 等. 松辽盆地白垩系青山口组页岩层系非均质地质特征与页岩油甜点评价[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 846-856.BAI Bin, DAI Chaocheng, HOU Xiulin, et al. Geological heterogeneity of shale sequence and evaluation of shale oil sweet spots in the Qingshankou Formation, Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 846-856. [8] 何鑫, 陈世加, 胡琮, 等. 陆相页岩层系岩性组合模式及其对原油差异性富集的控制作用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1325-1337.HE Xin, CHEN Shijia, HU Cong, et al. lithological combination model of the continental shale series and its controls on differential crude oil enrichment: a case study of the Chang 7 member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(5): 1325-1337. [9] 王大兴, 曾治平, 胡海燕, 等. 准噶尔盆地中部下乌尔禾组深层陆相页岩孔隙结构分形特征及其地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(1): 23-35.WANG Daxing, ZENG Zhiping, HU Haiyan, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore structure of deep continental shale of Lower Wuerhe Formation in central Junggar Basin and its geological significance[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(1): 23-35. [10] 胡宗全, 刘忠宝, 李倩文, 等. 基于变尺度岩相组合的陆相页岩源—储耦合机理探讨: 以四川盆地侏罗系页岩层段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(4): 893-909.HU Zongquan, LIU Zhongbao, LI Qianwen, et al. Exploring source rock-reservoir coupling mechanisms in lacustrine shales based on varying-scale lithofacies assemblages: a case study of the Jurassic shale intervals in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(4): 893-909. [11] 蒋代琴, 李平平, 邹华耀. 川东北元坝地区侏罗系陆相页岩天然裂缝发育特征及其对页岩油气富集和保存的影响[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(2): 362-372.JIANG Daiqin, LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao. Characteristics of natural fractures and their influence on oil and gas enrichment and preservation of the Jurassic continental shale in the Yuanba Area, northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(2): 362-372. [12] 张奎华, 孙中良, 张关龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区下二叠统风城组泥页岩优势岩相与页岩油富集模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 593-605.ZHANG Kuihua, SUN Zhongliang, ZHANG Guanlong, et al. Shale dominant lithofacies and shale oil enrichment model of Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 593-605. [13] 余文端, 高玉巧, 昝灵, 等. 溱潼凹陷阜宁组二段泥页岩含油性及页岩油富集层段分布[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2024, 14(5): 688-698.YU Wenduan, GAO Yuqiao, ZAN Ling, et al. Distribution of oil bearing and shale oil-rich strata in the second member of Funing Formation in Qintong Sag[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2024, 14(5): 688-698. [14] 孙龙德, 王小军, 冯子辉, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩纳米孔缝形成机制与页岩油富集特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1350-1365.SUN Longde, WANG Xiaojun, FENG Zihui, et al. Formation mechanisms of nano-scale pores/fissures and shale oil enrichment characteristics for Gulong shale, Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1350-1365. [15] 李志明, 金芸芸, 李楚雄, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷渐新统核桃园组三Ⅲ亚段页岩油富集模式: 以中部深凹带YYY1井取心段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 952-962.LI Zhiming, JIN Yunyun, LI Chuxiong, et al. Discussion on shale oil enrichment pattern in the Ⅲ submember of the third member of Oligocene Hetaoyuan Formation, Biyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin: a case study of cored interval of well YYY1 in the central deep sag zone[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 952-962. [16] 王濡岳, 聂海宽, 胡宗全, 等. 压力演化对页岩气储层的控制作用: 以四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(10): 1-11.WANG Ruyue, NIE Haikuan, HU Zongquan, et al. Controlling effect of pressure evolution on shale gas reservoirs: a case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(10): 1-11. [17] 李智, 张志业, 李双建, 等. 南襄盆地地质结构与形成演化[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(2): 116-127.LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, LI Shuangjian, et al. Geological architecture and tectonic evolution of Nanxiang Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(2): 116-127. [18] 解东宁, 何明喜, 周立发, 等. 东秦岭—大别造山带北缘逆冲推覆构造特征及油气前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(1): 48-55.XIE Dongning, HE Mingxi, ZHOU Lifan, et al. Characteristics of overthrust structures on northern edge of East Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt and hydrocarbon potentials[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(1): 48-55. [19] 李海泉. 南襄盆地地热成因机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016.LI Haiquan. Mechanism study of geothermal resources in the Nanxiang Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2016. [20] 金芸芸, 李艳然, 李圯, 等. 陆相断陷咸化湖盆细粒沉积岩特征及沉积环境: 以泌阳凹陷核桃园组H3Ⅲ亚段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2024, 31(2): 289-298.JIN Yunyun, LI Yanran, LI Yi, et al. Characteristics and sedimentary environment of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in continental rift-subsidence saline lacustrine basin: a case study of H3Ⅲ submember of Hetaoyuan Formation in Biyang Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2024, 31(2): 289-298. [21] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷与南阳凹陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 74-84.LI Zhi, ZHANG Zhiye, HE Dengfa, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Biyang Depression and Nanyang Depression in Nanxiang Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 74-84. [22] 常佳琦, 姜振学, 高之业, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组不同岩相页岩含油性及可动性特征[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3354-3367.CHANG Jiaqi, JIANG Zhenxue, GAO Zhiye, et al. Oil bearing and mobility characteristics of different lithofacies shales in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3354-3367. [23] 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等. 页岩油分类与评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 322-331.ZHANG Jinchuan, LIN Lamei, LI Yuxi, et al. Classification and evaluation of shale oil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 322-331. [24] 李思佳, 唐玄, 昝灵, 等. 溱潼凹陷阜二段页岩岩相组合特征及其对含油性的影响[J]. 中国海上油气, 2024, 36(2): 37-49.LI Sijia, TANG Xuan, ZAN Ling, et al. Shale lithofacies combinations and their influence on oil bearing property in the 2nd member of Funing Formation, Qintong Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2024, 36(2): 37-49. [25] 蒲秀刚, 马超, 郭彬程, 等. 渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷歧北次凹沙三上亚段页岩岩相特征及含油性差异[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2023, 47(2): 55-69.PU Xiugang, MA Chao, GUO Bincheng, et al. Shale lithofacies characteristics and shale oil bearing differences in the Es3s of Qibei Subsag, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2023, 47(2): 55-69. [26] 许琳, 常秋生, 杨成克, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组页岩油储层特征及含油性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 535-549.XU Lin, CHANG Qiusheng, YANG Chengke, et al. Characteristics and oil-bearing capability of shale oil reservoir in the Permian Lucaogou Formation, Jimusaer Sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 535-549. [27] 康淑娟, 仰云峰, 王华建, 等. 松辽盆地中央坳陷区三肇凹陷上白垩统青山口组一段页岩含油性特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(1): 89-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301089KANG Shujuan, YANG Yunfeng, WANG Huajian, et al. Oil-bearing capacity of shale in the first member of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, Sanzhao Sag, Central Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(1): 89-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301089 [28] 张林晔, 包友书, 李钜源, 等. 湖相页岩油可动性: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(6): 641-649.ZHANG Linye, BAO Youshu, LI Juyuan, et al. Movability of lacustrine shale oil: a case study of Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(6): 641-649. [29] 姜振学, 李廷微, 宫厚健, 等. 沾化凹陷低熟页岩储层特征及其对页岩油可动性的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(12): 1587-1600.JIANG Zhenxue, LI Tingwei, GONG Houjian, et al. Characteristics of low-mature shale reservoirs in Zhanhua Sag and their influence on the mobility of shale oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 1587-1600. [30] JARVIE D M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: Part 2—shale-oil resource systems[C]//BREYET J. Shale reservoirs—giant resources for the 21st century. Houston: AAPG, 2012: 89-119. [31] 史璨, 林伯韬, 谢勃勃, 等. 基于双甜点的页岩储层可压性评价方法[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2024, 41(2): 183-191.SHI Can, LIN Botao, XIE Bobo, et al. Evaluation method of shale reservoir fracability based on double sweet spots[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2024, 41(2): 183-191. [32] 万有余, 王小琼, 雷丰宇, 等. 柴达木盆地英雄岭E32页岩油可压性评价及应用[J]. 非常规油气, 2024, 11(3): 120-129.WAN Youyu, WANG Xiaoqiong, LEI Fengyu, et al. Compressibility evaluation and application of E32 shale oil in Yingxiongling area, Qaidam Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2024, 11(3): 120-129. [33] 石正勇, 金芸芸, 罗家群. 泌阳凹陷核桃园组优质烃源岩发育古环境特征及地质意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 51-58.SHI Zhengyong, JIN Yunyun, LUO Jiaqun. Paleo-environmental characteristics of the development of high-quality hydrocarbon source rocks in Hetaoyuan Formation of Biyang Sag and geological significance[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(1): 51-58. [34] 李红磊, 张云献, 周勇水, 等. 东濮凹陷优质烃源岩生烃演化机理[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2): 143-148.LI Honglei, ZHANG Yunxian, ZHOU Yongshui, et al. Hydrocarbon evolution mechanism of high quality source rock in Dongpu Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(2): 143-148. [35] 郭汝泰, 杨凤丽. 藻类有机质的成烃机制探讨[J]. 同济大学学报, 2002, 30(1): 41-45.GUO Rutai, YANG Fengli. Inquisition to the hydrocarbon generation mechanism for algal organic matter[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2002, 30(1): 41-45. [36] 孟庆强, 马亮帮, 邹安德, 等. 不同藻类热模拟实验的生烃特征对比[J]. 石油实验地质, 2008, 30(3): 281-285.MENG Qingqiang, MA Liangbang, ZOU Ande, et al. Comparison of characteristics of hydrocarbon generation for different ALGA[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2008, 30(3): 281-285. -





 下载:
下载:














 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号