Differential diagenetic evolution of Sinian Dengying Formation reservoirs in Anyue gas field, Central Sichuan Uplift, Sichuan Basin
-
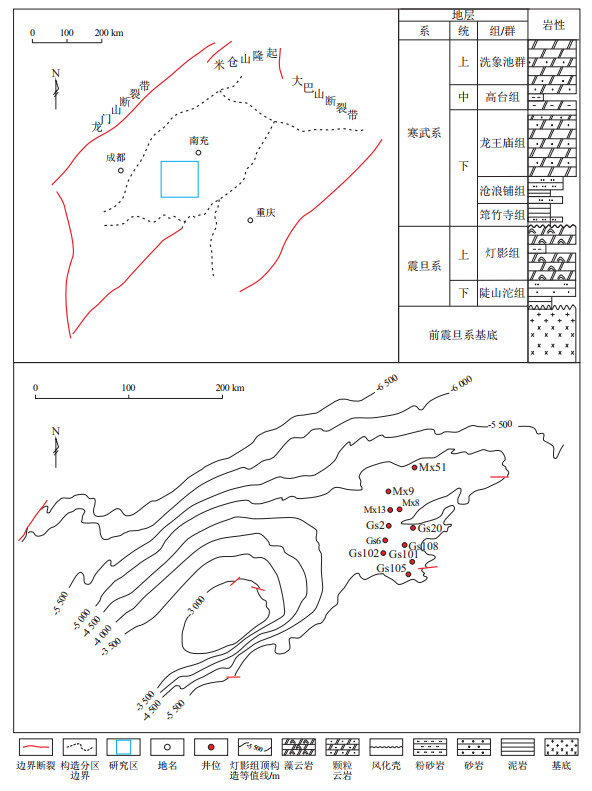
摘要: 四川盆地川中隆起震旦系灯影组白云岩中发育大型原位裂解气藏,研究其沉积和成岩作用对储层的影响可为古老的深层碳酸盐岩储层评价与预测提供重要依据。通过岩心样品的手标本观察、薄片鉴定、阴极发光以及扫描电镜分析,系统研究了灯影组四段白云岩储层的岩性差异、成岩作用类型、成岩序列以及不同岩性对成岩作用过程的约束作用。川中隆起灯影组储层主要岩性为具骨架—填充结构的藻叠层云岩、颗粒云岩和以细粒白云石堆积为主的泥—粉晶云岩;主要的成岩作用类型依次为压实作用、同生—准同生期以及表生期的溶蚀和胶结作用、埋藏期的亮晶胶结作用以及晚期热液作用,油气的充注时间晚于亮晶胶结作用,而油气的裂解与热液作用时期相近。灯影组四段白云岩储层为典型的T型碳酸盐工厂形成的台地藻丘体建造沉积,其中藻叠层云岩和颗粒云岩受到的压实作用较弱,但同生—准同生期以及表生期胶结与溶蚀作用较强。亮晶胶结作用造成孔隙大幅减少,残余粒间孔得以保存至油气充注期,随着晚期热液的侵入,热液矿物和裂解形成的焦沥青又进一步充填了孔隙。泥—粉晶云岩遭受了较强的压实作用,同生—准同生期以及表生期胶结作用较弱,亮晶胶结进一步减少了孔隙,残余孔隙同样保留至液态烃充注,泥—粉晶白云岩中未见明显的热液侵入痕迹,但热液传递的高温仍促使液态烃裂解进而形成了焦沥青。Abstract: Large in-situ pyrolysis gas reservoirs have developed in the dolomites of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Central Sichuan Uplift, Sichuan Basin. Investigating the effects of sedimentation and diagenesis on these reservoirs provides important insights for evaluating and predicting ancient deep carbonate reservoirs. Through hand specimen observation, thin-section identification, cathodoluminescence, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of core samples, the study systematically analyzed the lithological variations, diagenetic types, diagenetic sequences, and the constraints imposed by different lithologies on diagenetic processes in the dolomite reservoirs of the fourth member of the Dengying Formation. The results showed that the main lithologies of the Dengying Formation reservoirs in the Central Sichuan Uplift were algal stromatolite dolomite with a skeleton-filling structure, granular dolomite, and mud-fine crystalline dolomite mainly composed of fine-grained dolomite accumulations. The main types of diagenesis followed the sequence of compaction, dissolution, and cementation during the syngenetic-penecontemporaneous and supergene stages, sparry cementation at the burial stage, and late-stage hydrothermal activity. Hydrocarbon charging occurred after sparry cementation, while hydrocarbon pyrolysis coincided with hydrothermal activity. The dolomite reservoirs in the fourth member of the Dengying Formation were algal mound platform deposits formed by typical T-type carbonate factories. The algal stromatolite dolomite and granular dolomite experienced weak compaction but stronger cementation and dissolution during the syngenetic-penecontemporaneous and supergene stages. Sparry cementation significantly reduced porosity, and residual intergranular pores were preserved until the hydrocarbon charging period. With the intrusion of late-stage hydrothermal fluids, these pores were further filled with hydrothermal minerals and pyrobitumen formed through pyrolysis. In contrast, the mud-fine crystalline dolomite underwent strong compaction and weaker cementation during the syngenetic-penecontemporaneous and supergene stages. Sparry cementation further reduced porosity, and residual pores were also preserved until liquid hydrocarbon charging. No obvious signs of hydrothermal intrusion were observed in mud-fine crystalline dolomite, but the high temperature of hydrothermal fluids still promoted liquid hydrocarbon pyrolysis, leading to pyrobitumen formation.
-
Key words:
- reservoir /
- diagenesis /
- carbonate factory /
- Dengying Formation /
- Central Sichuan Uplift /
- Sichuan Basin
-
图 2 四川盆地安岳气田Gs102井震旦系灯影组四段储层岩性特征
a.颗粒云岩岩心,粒间孔层状较发育,5 192.1 m;b.颗粒云岩岩心,粒间孔层状较发育,5 182.6 m;c.颗粒云岩岩心,5 101.8 m;d.粉晶云岩岩心,顺层裂缝、窗棱孔发育,5178.3 m;e.颗粒云岩,可见内碎屑颗粒、藻碎屑和胶结物,5 100.7 m,薄片单偏透射光;f.泥粉晶云岩岩心,可见裂缝,无碎屑颗粒及胶结物,5 182.3 m。
Figure 2. Lithological characteristics of reservoir in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in well Gs102, Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin
图 3 四川盆地安岳气田震旦系灯影组四段储层岩性微观特征
a.颗粒云岩,Mx9井,5 192.1 m,单偏透射光;b.席状的藻类碎屑,Gs108井,5 182.6 m,单偏透射光;c.颗粒云岩两期胶结,Gs6井,5 101.8 m,单偏透射光;d.致密粉晶云岩,Mx51井,5178.3 m,单偏透射光;e.发育窗棱孔隙的粉晶云岩,孔隙多被焦沥青充填,Gs2井,5 100.7 m,单偏透射光;f.泥粉晶云岩,窗棱孔隙被胶结物充填,Mx13井,5 182.3 m,单偏透射光。
Figure 3. Microscopic lithological characteristics of reservoirs in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin
图 4 四川盆地安岳气田震旦系灯影组四段储层成岩作用微观特征
a.颗粒云岩内三期胶结物相互关系,Mx9井,5 421.34 m,单透射偏光;b.不同期次胶结物,Gs20井,5 253.83 m,单偏透射光;c.高自形度的白云石胶结物内孔隙中充填表面突起的焦沥青,Mx9井,5 033.62 m,扫描电镜;d.多期胶结物及孔隙中心充填的焦沥青,Mx13井,5 104.78 m,单偏透射光;e.不同期次的胶结物(与照片b同视域),Gs20井,5 253.83 m,阴极发光;f.焦沥青充填孔隙,孔隙内壁为高自形度的白云石晶体,Mx8井,5 425.22 m,单偏反射光;g.多期胶结物及孔隙中心充填的焦沥青,早期胶结物呈较亮的黄—红棕色内部无环带,晚期的亮晶胶结物呈鲜亮红色并具有环带结构,本样品中缺乏热液白云石,Gs101井,5 498.8 m,阴极发光;h.不同期次的胶结物(与照片i同视域),Gs108井,5 248.46 m,单偏透射光;i.本样品中缺乏早期胶结物,具有环带结构亮晶胶结物紧贴围岩,亮晶胶结后残余孔隙内为巨大的热液白云石,呈明暗变化的红褐色,不具有明显的环带结构,Gs108井,5 248.46 m,阴极发光。
Figure 4. Microscopic diagenetic characteristics of reservoirs in the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Anyue gas field, Sichuan Basin
-
[1] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣. 深层、超深层碳酸盐岩油气储层形成机理研究综述[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(4): 181-192.MA Yongsheng, CAI Xuynyu, ZHAO Peirong. The research status and advances in porosity evolution and diagenesis of deep carbonate reservoir[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(4): 181-192. [2] 杨云坤, 刘波, 秦善, 等. 碳酸盐矿物随埋深增加的溶蚀响应机制及其储层意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 49(5): 859-866.YANG Yunkun, LIU Bo, QIN Shan, et al. Dissolution response mechanism of the carbonate mineral with the increase of depth and its reservoir significance[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2013, 49(5): 859-866. [3] 杨德彬, 鲁新便, 鲍典, 等. 塔里木盆地北部奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩断溶体油藏成因类型及特征再认识[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(2): 357-366.YANG Debin, LU Xinbian, BAO Dian, et al. New insights into the genetic types and characteristics of the Ordovician marine fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in the northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(2): 357-366. [4] 蔡振忠, 赵海涛, 王彭, 等. 考虑流固耦合作用的超深缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层连通性表征: 以塔里木盆地富满油田满深区块为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 301-312.CAI Zhenzhong, ZHAO Haitao, WANG Peng, et al. Characterization of connectivity in ultra-deep fractured-caveate reservoirs considering fluid-solid coupling: a case study of the Manfen Block in the Fuman Oil Field of the Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 301-312. [5] 王璐, 罗瑞兰, 张林, 等. 超深层碳酸盐岩气藏产能预测模型及影响因素研究[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(3): 88-98.WANG Lu, LUO Ruilan, ZHANG Lin, et al. Investigation of productivity prediction model and influencing factors of ultradeep carbonate gas reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(3): 88-98. [6] 卢子兴, 董国栋, 裴文超, 等. 致密碳酸盐岩储层微观结构特征及发育影响因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东部马五1+2亚段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(3): 372-380, 388.LU Zixing, DONG Guodong, PEI Wenchao, et al. Microstructure characteristics and development influencing factors of tight carbonate reservoirs: a case study of the Ma 5 1+2 sub-member in eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(3): 372-380, 388. [7] 杜仲元, 李相文, 李青霖, 等. 不同序级走滑断裂对碳酸盐岩储集层发育的控制差异[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(4): 425-431.DU Zhongyuan, LI Xiangwen, LI Qinglin, et al. Differential controls of strike-slip faults of different orders on carbonate reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(4): 425-431. [8] WANG J B, HE Z L, ZHU D Y, et al. Petrological and geochemical characteristics of the botryoidal dolomite of Dengying Formation in the Yangtze Craton, South China: constraints on terminal Ediacaran "dolomite seas"[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 406: 105722. [9] 黄思静, 张雪花, 刘丽红, 等. 碳酸盐成岩作用研究现状与前瞻[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(5): 219-231.HUANG Sijing, ZHANG Xuehua, LIU Lihong, et al. Progress of research on carbonate diagenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(5): 219-231. [10] LISEROUDI M H, ARDAKANI O H, PEDERSEN P K, et al. Fluid flow and water/rock interaction during the Early Triassic evolution of the western Canada sedimentary Basin as revealed by carbonate diagenesis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 142: 105765. [11] 李云涛, 丁文龙, 韩俊, 等. 顺北地区走滑断裂带奥陶系碳酸盐岩裂缝分布预测与主控因素研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5): 263-287.LI Yuntao, DING Wenlong, HAN Jun, et al. Fractures in Ordovician carbonate rocks in strike-slip fault zone, Shunbei area: fracture distribution prediction and fracture controlling factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5): 263-287. [12] 单秀琴, 张静, 张宝民, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组白云岩岩溶储层特征及溶蚀作用证据[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(1): 17-29.SHAN Xiuqin, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Baomin, et al. Dolomite karst reservoir characteristics and dissolution evidences of Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 17-29. [13] EHRENBERG S N, EBERLI G P, KERAMATI M, et al. Porosity-permeability relationships in interlayered limestone-dolostone reservoirs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(1): 91-114. [14] SALLER A H, LOUNSBURY K, BIRCHARD M. Facies control on dolomitization and porosity in the Devonian Swan Hills Formation in the Rosevear area, west-central Alberta[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 2001, 49(4): 458-471. [15] 莫静, 王兴志, 谢林, 等. 川中震旦系灯影组碳酸盐岩成岩作用及储层孔隙演化[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(8): 32-38.MO Jing, WANG Xingzhi, XIE Lin, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of carbonate in Sinian Dengying Formation in central Sichuan province[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(8): 32-38. [16] 魏国齐, 王志宏, 李剑, 等. 四川盆地震旦系、寒武系烃源岩特征、资源潜力与勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017.28(1): 1-13.WEI Guoqi, WANG Zhihong, LI Jian, et al. Characteristics of source rocks, resource potential and exploration direction of Sinian and Cambrian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(1): 1-13. [17] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293.ZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. [18] 徐春春, 沈平, 杨跃明, 等. 乐山—龙女寺古隆起震旦系—下寒武统龙王庙组天然气成藏条件与富集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3): 1-7.XU Chunchun, SHEN Ping, YANG Yueming, et al. Accumulation conditions and enrichment patterns of natural gas in the Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Fm reservoirs of the Leshan-Longnüsi Paleohigh, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 1-7. [19] 杨雨, 文龙, 宋泽章, 等. 川中古隆起北部蓬莱气区多层系天然气勘探突破与潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(10): 1351-1368.YANG Yu, WEN Long, SONG Zezhang, et al. Breakthrough and potential of natural gas exploration in multi-layer system of Penglai gas area in the north of central Sichuan paleo-uplift[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(10): 1351-1368. [20] 刘树根, 马永生, 黄文明, 等. 四川盆地上震旦统灯影组储集层致密化过程研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(4): 485-496.LIU Shugen, MA Yongsheng, HUANG Wenming, et al. Densification process of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(4): 485-496. [21] 许海龙, 魏国齐, 贾承造, 等. 乐山—龙女寺古隆起构造演化及对震旦系成藏的控制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 406-416.XU Hailong, WEI Guoqi, JIA Chengzao, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Leshan-Longnüsi paleo-uplift and its control on gas accumulation in the Sinian strata, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 406-416. [22] 文龙, 王文之, 张健, 等. 川中高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组碳酸盐岩岩石类型及分布规律[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(4): 1285-1294.WEN Long, WANG Wenzhi, ZHANG Jian, et al. Classification of Sinian Dengying Formation and sedimentary evolution mechanism of Gaoshiti-Moxi area in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(4): 1285-1294. [23] 王文之, 文龙, 姚军, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组层序划分及多期台缘带的发现[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2019, 42(4): 46-54.WANG Wenzhi, WEN Long, YAO Jun, et al. Sequence classification and discovery of multi-stage platform margin belts of Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2019, 42(4): 46-54. [24] 陈艺娴, 廖明光, 王文之, 等. 四川盆地上震旦统灯影组四段典型碳酸盐岩类型及沉积模式[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2021, 44(1): 38-45.CHEN Yixian, LIAO Mingguang, WANG Wenzhi, et al. Typical carbonate rock types and sedimentary models of the 4th member of the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2021, 44(1): 38-45. [25] FOLK R L. Practical petrographic classification of limestones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1959, 43(1): 1-38. [26] 张荫本, 唐泽尧, 陈季高. 粘结岩分类及应用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 1996, 19(4): 24-33.ZHANG Yinben, TANG Zeyao, CHEN Jigao. Classification and application of caking rock[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 1996, 19(4): 24-33. [27] BURNE R V, MOORE L S. Microbialites: organosedimentary deposits of benthic microbial communities[J]. Research Palaios, 1987, 2(3): 241-254. [28] 张玺华, 李勇, 张本健, 等. 四川盆地中江—蓬莱地区灯二段储层特征及优质储层成因机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(3): 301-312.ZHANG Xihua, LI Yong, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of high quality reservoir of the second member of the Dengying Formation in Zhongjiang-Penglai area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 50(3): 301-312. [29] DAVIES G R, SMITH JR L B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: an overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1641-1690. [30] 杨威, 魏国齐, 赵蓉蓉, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组岩溶储层特征及展布[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3): 55-60.YANG Wei, WEI Guoqi, ZHAO Rongrong, et al. Characteristics and distribution of karst reservoirs in the Sinian Dengying Fm, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 55-60. [31] 蒋裕强, 谷一凡, 朱讯, 等. 四川盆地川中地区震旦系灯影组热液白云岩储集相[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(3): 17-24.JIANG Yuqiang, GU Yifan, ZHU Xun, et al. Hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies in the Sinian Dengying Fm, central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(3): 17-24. [32] 朱东亚, 金之钧, 孙冬胜, 等. 南方震旦系灯影组热液白云岩化及其对储层形成的影响研究: 以黔中隆起为例[J]. 地质科学, 2014, 49(1): 161-175.ZHU Dongya, JIN Zhijun, SUN Dongsheng, et al. Hydrothermally dolomitized reservoir bed in Sinian Dengying Formation, northern China: an example from Central Guizhou Uplift[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2014, 49(1): 161-175. [33] 姜华, 汪泽成, 杜宏宇, 等. 乐山—龙女寺古隆起构造演化与新元古界震旦系天然气成藏[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(2): 192-200.JIANG Hua, WANG Zecheng, DU Hongyu, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Leshan-Longnvsi paleo-uplift and reservoir formation of Neoproterozoic Sinian gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(2): 192-200. [34] 李伟, 余华琪, 邓鸿斌. 四川盆地中南部寒武系地层划分对比与沉积演化特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 681-690.LI Wei, YU Huaqi, DENG Hongbin. Stratigraphic division and correlation and sedimentary characteristics of the Cambrian in central-southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 39(6): 681-690. [35] 姚建军, 陈孟晋, 华爱刚, 等. 川中乐山—龙女寺古隆起震旦系天然气成藏条件分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(4): 7-9.YAO Jianjun, CHEN Mengjin, HUA Aigang, et al. Formation of the gas reservoirs of the Leshan-Longnvsi Sinian palaeo-uplift in central Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(4): 7-9. [36] 黄文明, 刘树根, 王国芝, 等. 四川盆地下古生界油气地质条件及气藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(3): 465-476.HUANG Wenming, LIU Shugen, WANG Guozhi, et al. Geological conditions and gas reservoir features in Lower Paleozoic in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(3): 465-476. [37] ZHU Guangyou, WANG Tongshan, XIE Zengye, et al. Giant gas discovery in the Precambrian deeply buried reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin, China: implications for gas exploration in old cratonic basins[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 262: 45-66. [38] YANG Chengyu, NI Zhiyong, WANG Tieguan, et al. A new genetic mechanism of natural gas accumulation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 8336. [39] MEYERS W J, LU F H, ZACHARIAH J K. Dolomitization by mixed evaporative brines and freshwater, Upper Miocene carbonates, Nijar, Spain[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1997, 67(5): 898-912. [40] OELKERS E H, SCHOTT J. Geochemical aspects of CO2 sequestration[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 217(3/4): 183-186. [41] CAI Chunfang, XIANG Lei, YUA Yuyang, et al. Sulfur and carbon isotopic compositions of the Permian to Triassic TSR and non-TSR altered solid bitumen and its parent source rock in NE Sichuan Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 105: 1-12. [42] CHEN Jian, JIA Wanglu, YU Chiling, et al. Bound hydrocarbons and structure of pyrobitumen rapidly formed by asphaltene cracking: implications for oil-source correlation[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2020, 146: 104053. [43] LIU Quanyou, ZHU Dongya, JIN Zhijun, et al. Coupled alteration of hydrothermal fluids and thermal sulfate reduction (TSR) in ancient dolomite reservoirs: an example from Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin, southern China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 285: 39-57. [44] WORDEN R H, SMALLEY P C, OXTOBY N H. The effects of thermochemical sulfate reduction upon formation water salinity and oxygen isotopes in carbonate gas reservoirs[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3925-3931. [45] 杨程宇, 文龙, 王铁冠, 等. 川中隆起安岳气田古油藏成藏时间厘定[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3): 492-502.YANG Chengyu, WEN Long, WANG Tieguan, et al. Timing of hydrocarbon accumulation for paleo-oil reservoirs in Anyue gas field in Chuanzhong Uplift[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(3): 492-502. [46] 颜佳新, 孟琦, 王夏, 等. 碳酸盐工厂与浅水碳酸盐岩台地: 研究进展与展望[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(2): 232-253.YAN Jiaxin, MENG Qi, WANG Xia, et al. Carbonate factory and carbonate platform: progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(2): 232-253. [47] WILSON J L. Carbonate facies in geologic history[M]. New York: Springer, 1975: 1-471. [48] JAMES N P. Facies models 7. Introduction to carbonate facies models[J]. Geoscience Canada, 1977, 4(3): 123-125. [49] WALKER R G. Facies models 1. General introduction[J]. Geoscience Canada, 1976, 3(1): 21-24. [50] TUCKER M E, WRIGHT V P, DICKSON J A D. Carbonate sedimentology[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Science, 1990: 1-482. [51] SCHLAGER W. Benthic carbonate factories of the Phanerozoic[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2003, 92(4): 445-464. [52] SCHLAGER W. Carbonate sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy[M]. Tulsa: SEPM, 2005: 1-208 [53] 何冰辉. 关于峨眉山大火成岩省一些问题的研究现状[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(1): 23-42.HE Binghui. Research progress on some issues on the Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2016, 31(1): 23-42. [54] HE Bin, XU Yigang, CHUNG S L, et al. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 213(3/4): 391-405. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号