Helium accumulation characteristics and main controlling factors of helium depletion in Daniudi Gas Field, Ordos Basin
-
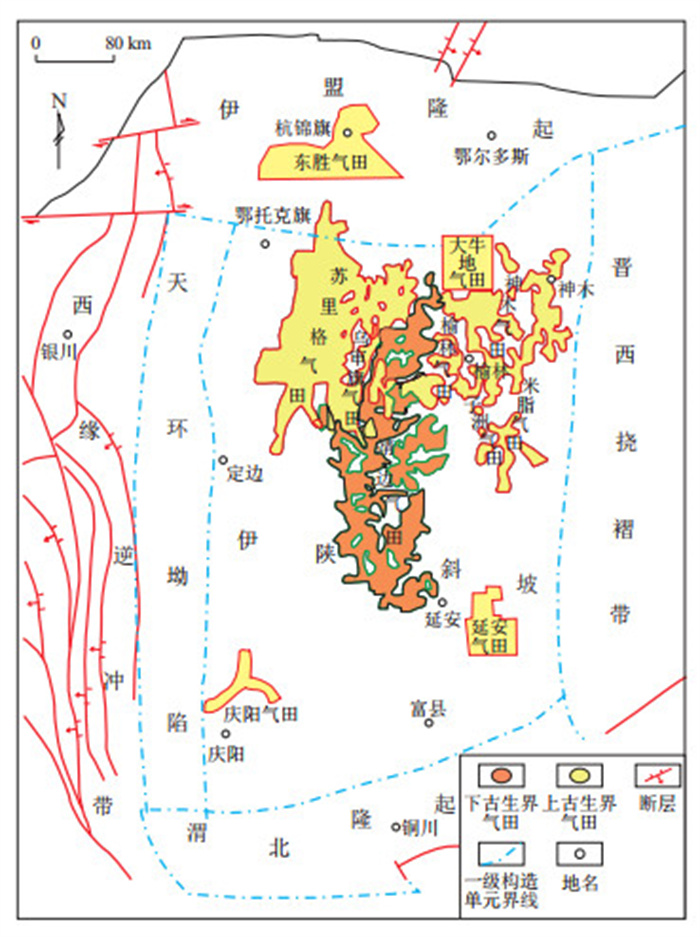
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗东胜气田和大牛地气田的天然气中发现一定含量的氦气,但大牛地气田氦气平均含量仅为东胜气田的1/4左右,那么在盆地基底和构造背景相似的情况下,究竟是何因素造成二者氦气含量差异如此之大。为此,基于天然气伴生氦气地球化学特征与氦气成藏关键要素的系统分析,发现大牛地古生界天然气中氦气含量介于0.000 1%~0.15%,为低氦—中氦气田;上古生界氦气含量相对较高,纵向上从下往上氦气含量逐渐增加,显示出浅部相对富集的特征。大牛地古生界氦气为典型壳源氦,主要来源于盆地基底的太古宇—中元古界变质岩—花岗岩系,上古生界潜在氦源岩所生成的氦气成藏贡献很小。对比大牛地气田上古生界与东胜气田上古生界氦气的发育地质条件与成藏特征,发现两者基底氦源岩的岩石类型、矿物组成、厚度及U、Th含量均相近,推测基底氦源岩不是造成氦气含量差异如此之大的原因。大牛地仅发育一条二级基底深大断裂,且在燕山—喜马拉雅期活动较弱,造成次一级断裂活动也较弱,氦气由基底氦源岩向上运移以及纵向输导和横向调整都缺乏有效通道;氦气与常规气成藏关键要素组合的时空配置不匹配,氦气仅靠扩散进入大牛地古生界气藏中,造成大牛地气田氦气含量偏低。大牛地气田氦气贫化的主要因素为基底深大断裂及次一级断裂不发育且活动强度弱、氦气与常规气成藏要素组合不匹配、缺乏有效输导体系、氦气运移仅靠浓度扩散。Abstract: A certain amount of helium is found in the natural gas of both the Dongsheng and Daniudi gas fields in the Hangjinqi area of the Ordos Basin. However, the average helium content in the Daniudi Gas Field is only about one-fourth of that in the Dongsheng Gas Field. Given the similar basement geology and tectonic background of the basin, it is necessary to investigate the factors leading to this significant difference. A systematic analysis of the geochemical characteristics of associated helium in natural gas and the key factors controlling helium accumulation was conducted. The results revealed that the helium content in the Paleozoic natural gas of the Daniudi Gas Field ranged from 0.000 1% to 0.15%, classifying it as a low- to medium-helium gas field. Helium content in the Upper Paleozoic was relatively higher, and vertically, it gradually increased from the lower to the upper layers, showing relative enrichment in shallower layers. The helium in the Paleozoic source rocks of the Daniudi Gas Field was typical crust-source helium, mainly derived from the Archean-middle Paleoproterozoic metamorphic rock-granite series in the basin basement. The contribution of helium generated by potential helium source rocks in the Upper Paleozoic was minimal. By comparing the geological conditions and accumulation characteristics of the Upper Paleozoic between the Daniudi and Dongsheng gas fields, it was found that the basement helium source rocks in both gas fields were similar in rock type, mineral composition, thickness, and uranium (U) and thorium (Th) contents, suggesting that the differences in source rock were not responsible for the significant difference in helium content. In the Daniudi area, only one second-level deep fault was developed in the basement of the Daniudi area, and its activity during the Yanshanian-Himalayan period was relatively weak, resulting in limited activity of secondary faults. This led to a lack of effective channels for helium to migrate upward from the basement helium source rocks, as well as vertical transport and lateral adjustment. Due to the mismatch in spatiotemporal configuration of key accumulation factors for helium and conventional gas, helium entered the Paleozoic gas reservoirs in Daniudi only by diffusion, resulting in low helium content. Therefore, the main factors contributing to helium depletion in the Daniudi Gas Field are the underdevelopment and weak activity of deep faults and secondary faults in the basement, the mismatch between helium and conventional gas accumulation conditions, the lack of an effective transport system, and the reliance on concentration-driven diffusion for helium migration.
-
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田不同层系氦气含量分布
Table 1. Distribution of helium content in different rock sequences of Daniudi Gas Field, Ordos Basin
层位 气样/件 氦气含量分布/% 平均氦气含量/% 盒三段 4 0.029~0.059 0.038 盒二段 3 0.029~0.127 0.064 盒一段 11 0.032~0.062 0.042 山二段 9 0.028~0.052 0.037 山一段 6 0.000 1~0.037 0.028 太二段 10 0.022~0.042 0.032 太一段 2 0.029~0.040 0.035 本溪组 1 0.030 0.030 马五段 43 0.002~0.150 0.025 马四段 4 0.004~0.034 0.015 混层 10 0.017~0.045 0.035 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地和杭锦旗地区潜在氦源岩特征
Table 2. Characteristics of potential helium source rocks in Daniudi and Hangjinqi areas, Ordos Basin
地区 潜在氦源岩 U含量/(μg/g) Th含量/(μg/g) 生氦强度/(10-13cm3/g/a) 厚度/m 年龄/Ma 杭锦旗 上古生界煤层 1.27~9.27/5.61 3.62~18.94/13.09 10.52 5~25/10 275~307 上古生界铝土岩 14.45~37.61/21.52 20.62~99.85/62.69 43.93 0~10/4 289~315 古—中元古界石英砂岩—石英岩 0.81~7.31/3.07 3.42~28.93/13.77 7.65 0~1 100/500 1 400~2 500 中元古界板岩 2.64~5.15/3.9 11.34~18.07/14.71 8.92 5~20 1 400~1 800 太古宇花岗岩、变质岩 0.88~2.89/1.49 3.47~8.94/5.44 3.36 >1 000 2 500~4 600 大牛地 上古生界煤层 2.35~22.92/6.79 3.04~53.35/16.39 12.89 10~20/15 275~307 上古生界铝土岩 8.42~39.97/20.35 25.57~95.25/57.11 40.92 2.0~21.6/12.6 289~315 古—中元古界石英砂岩 0.77~7.25/2.98 3.06~26.39/12.14 7.08 30~150/60 1 400~2 500 太古宇花岗岩、变质岩 0.57~6.90/2.37 0.89~32.17/13.09 6.61 >1 000 2 500~4 600 注:表中数据意义为最小值~最大值/平均值。 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地地区不同层级断裂发育特征
Table 3. Characteristics of fault development at different levels in Daniudi area, Ordos Basin
断裂分级 数量/条 断裂名称 规模/km 活动期次 断裂性质 二级 1 鄂托克—乌审召 >200 早元古代、加里东期、海西期 基底深大断裂(早期正断层,晚期走滑断裂) 三级 4 小壕兔、石板太、秃尾河、台格庙 >22 加里东—海西期、印支期、燕山期 通基底断裂(高角度逆断层、走滑、逆冲断裂) 四级 7 D14、E5、D99、PG24、D98、D81、D65-4 6~22 加里东—海西期、印支期、燕山期 通基底断裂(高角度走滑断裂) 五级 23 分布较为广泛 3~15 加里东—海西期、印支期、燕山期 层间断裂(高角度走滑断裂) -
[1] USGS.U.S. Geological survey mineral commodity summaries 2024[R]. Reston: National Minerals Information Center, 2024: 88-89. [2] 王杰, 贾会冲, 陶成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区东胜气田氦气成因来源及富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 566-575.WANG Jie, JIA Huichong, TAO Cheng, et al. Source and enrichment regularity of helium in Dongsheng Gas Field of Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 566-575. [3] 刘成林, 丁振刚, 范立勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地含氦天然气地球化学特征与富集影响因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(2): 384-392.LIU Chenglin, DING Zhengang, FAN Liyong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and enrichment factors of helium-bearing natural gas in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(2): 384-392. [4] 陶士振, 杨怡青, 高建荣, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密砂岩气及伴生氦气形成演化特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 551-565.TAO Shizhen, YANG Yiqing, GAO Jianrong, et al. The formation and evolution characteristics of tight sandstone gas and associated helium in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 551-565. [5] 惠洁, 康锐, 赵伟波, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地氦气特征及生成潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(9): 1688-1698.HUI Jie, KANG Rui, ZHAO Weibo, et al. Helium characteristics and potential in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(9): 1688-1698. [6] 孙晓, 王杰, 陶成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地下古生界天然气地球化学特征及其来源综合判识[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102307SUN Xiao, WANG Jie, TAO Cheng, et al. Evaluation of geochemical characteristics and source of natural gas in Lower Paleozoic, Daniudi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102307 [7] 王杰, 陈践发, 王铁冠, 等. 双城-太平川地区稀有气体同位素特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(10): 24-26.WANG Jie, CHEN Jianfa, WANG Tieguan, et al. Isotopic characteristics of rare gas in Shuangcheng-Taipingchuan area in the Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(10): 24-26. [8] 何发岐, 王付斌, 王杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜气田氦气分布规律及特大型富氦气田的发现[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201001HE Faqi, WANG Fubin, WANG Jie, et al. Helium distribution of Dongsheng Gas Field in Ordos Basin and discovery of a super large helium-rich gas field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201001 [9] 陈燕燕, 陶士振, 杨秀春, 等. 页岩气和煤层气中氦气的地球化学特征和富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 684-696.CHEN Yanyan, TAO Shizhen, YANG Xiuchun, et al. The geochemical characteristics and enrichment of helium in shale gas and coalbed methane[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 684-696. [10] XU Sheng, XU Yongchang, SHEN Ping, et al. Noble gas isotopes in natural gases from central and northwest China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(10): 838-841. [11] 刘成林, 丁振刚, 陈践发, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地氦源岩特征及生氦潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1546-1554.LIU Chenglin, DING Zhengang, CHEN Jianfa, et al. Characteristics and helium-generating potential of helium source rocks in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1546-1554. [12] 刘文辉, 潘和平, 李健伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地气田铝土质泥岩储层的测井评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(5): 24-30.LIU Wenhui, PAN Heping, LI Jianwei, et al. Well logging evaluation on bauxitic mudstone reservoirs in the Daniudi Gasfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(5): 24-30. [13] BROWN A A. Formation of high helium gases: a guide for explorationists[C]//AAPG Convention. New Orleans, Louisiana, 2010: 11-14. [14] 赵振宇, 郭彦如, 王艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化及古地理特征研究进展[J]. 特种油气藏, 2012, 19(5): 15-20.ZHAO Zhenyu, GUO Yanru, WANG Yan, et al. Study progress in tectonic evolution and paleogeography of Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2012, 19(5): 15-20. [15] 翟明国, 张艳斌, 李秋立, 等. 克拉通、下地壳与大陆岩石圈: 庆贺沈其韩先生百年华诞[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(1): 1-23.ZHAI Mingguo, ZHANG Yanbin, LI Qiuli, et al. Cratonization, lower crust and continental lithosphere[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(1): 1-23. [16] 田刚, 杨明慧, 宋立军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地基底结构特征及演化过程新认识[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(1): 123-139.TIAN Gang, YANG Minghui, SONG Lijun, et al. New understanding of basement structural characteristics and its evolution process in Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(1): 123-139. [17] 张威, 杨明慧, 李春堂, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地区块板内走滑断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(6): 2267-2280.ZHANG Wei, YANG Minghui, LI Chuntang, et al. Structural characteristics and evolution of intraplate strike-slip faults in Daniudi block, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(6): 2267-2280. [18] 李竞赢, 杨明慧, 田刚, 等. 陆内走滑断裂构造特征及活动性分析[J]. 地质论评, 2023, 69(S1): 73-75.LI Jingying, YANG Minghui, TIAN Gang, et al. Structural characteristics and activity analysis of intracontinental strike-slip fault[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69(S1): 73-75. [19] 何发岐, 王杰, 赵永强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜富氦气田成藏特征及其大地构造背景[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(5): 937-950.HE Faqi, WANG Jie, ZHAO Yongqiang, et al. Accumulation characteristics of Dongsheng helium-rich gas field in Ordos Basin and its tectonic background[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2022, 24(5): 937-950. [20] 李剑, 罗霞, 单秀琴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界天然气成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4): 54-59.LI Jian, LUO Xia, SHAN Xiuqin, et al. Natural gas accumulation in the Upper Paleozoic of Ordos Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 54-59. [21] 郝蜀民, 李良, 尤欢增. 大牛地气田石炭-二叠系海陆过渡沉积体系与近源成藏模式[J]. 中国地质, 2007, 34(4): 606-611.HAO Shumin, LI Liang, YOU Huanzeng. Permo-Carboniferous paralic depositional systems in the Daniudi Gas Field and its near-source box-type gas accumulation-forming model[J]. Geology in China, 2007, 34(4): 606-611. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号