Characteristics and controlling factors of shale oil reservoirs in the seventh member of Triassic Yanchang Formation, western Mahuangshan area, Ordos Basin
-
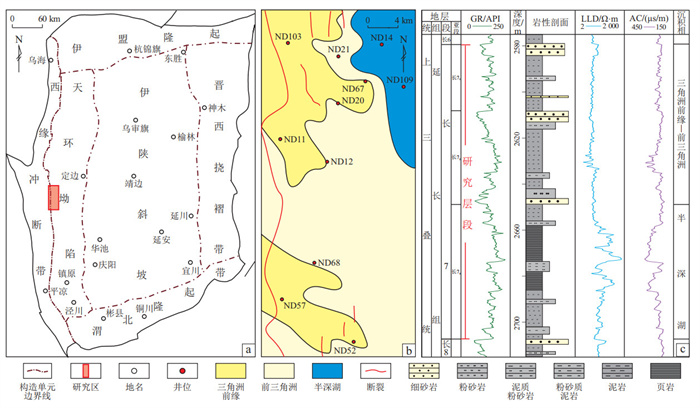
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段(简称长7段)页岩油资源丰富,但湖盆边缘和湖盆中心页岩油储层特征存在显著差异。目前,湖盆边缘麻黄山西地区页岩油储层研究程度较低,制约了该区页岩油的勘探进展。通过扫描电镜、高压压汞、低场核磁共振、氮气吸附和微米CT等分析手段,结合岩心观察和薄片鉴定等资料,对该区长7段页岩油储层特征进行精细刻画,同时利用碳氧同位素及常量、微量元素分析了优质储层发育机制。结果表明:麻黄山西地区长7段页岩油储层岩性主要为细砂岩、粉砂岩和泥页岩,长英质和黏土矿物含量较高,长英质矿物普遍达到50%以上;储层储集空间类型多样,不同岩性之间孔隙发育具有差异性,其中细砂岩以粒间孔和黏土矿物晶间孔为主,孔径集中分布于1~2 μm;粉砂岩(主要为泥质粉砂岩) 发育无机孔隙和有机质孔,主孔径分布在3 nm和500 nm附近;泥页岩以有机质黏土复合体孔隙和微裂缝为主,小于10 nm和数十纳米的孔径均有发育。储层物性与孔隙结构分析表明,夹层型细砂岩储层为优质储层类型,成岩压实过程中减孔约26%~33%,其储层砂体中部受成烃流体改造作用显著,现今孔隙度普遍大于5%;而夹层型砂体边缘和纹层型储层因胶结物的大量沉淀,物性相对较差。Abstract: The seventh member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation (Chang 7) in the Ordos Basin is abundant in shale oil resources. However, there are significant differences in reservoir characteristics between the basin margin and the basin center. Currently, research on shale oil reservoirs in the western Mahuangshan area at the basin margin remains insufficient, which has constrained shale oil exploration in this area. In this study, a detailed characterization of the shale oil reservoirs of Chang 7 member in this area was conducted using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high-pressure mercury injection, low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), nitrogen adsorption, and micro-CT, combined with core observations and thin-section identification. Additionally, carbon and oxygen isotope and major and trace element analyses were conducted to investigate the development mechanism of high-quality reservoirs. The results showed that: (1) The shale oil reservoir in the Chang 7 member of the western Mahuangshan area is mainly composed of fine sandstone, siltstone, and mud shale. The mineral composition is characterized by high contents of felsic and clay minerals, with felsic minerals generally exceeding 50%. (2) The reservoir exhibits diverse space types, and the pore development differs among lithologies. In fine sandstone, intergranular pores and clay mineral intercrystalline pores are dominant, with pore sizes mainly distributed in the 1 to 2 μm range. In siltstone (mainly argillaceous siltstone), both inorganic pores and organic matter pores are developed, with dominant pore sizes near 3 nm and 500 nm. Mud shale is mainly composed of pores with organic-clay composites matter and microfractures, developed with pores below 10 nm and those in the range of tens of nanometers. (3) Analysis of reservoir physical properties and pore structure indicated that interbedded-type fine sandstone reservoirs represent the high-quality reservoir type. During compaction diagenesis, the porosity was reduced by approximately 26% to 33%. Hydrocarbon-generating fluids significantly modified the central parts of the sandstone bodies of reservoirs, and the current porosity generally exceeds 5%. In contrast, the edges of sandstone bodies and laminated-type reservoirs experienced substantial cement sedimentation, resulting in relatively poor physical properties.
-
Key words:
- shale oil /
- reservoir characteristics /
- controlling factor /
- Triassic /
- western Mahuangshan area /
- Ordos Basin
-
图 4 鄂尔多斯盆地麻黄山西地区三叠系延长组7段不同岩性铸体薄片及氩离子抛光扫描电镜下储集空间类型特征
a.ND103井,2 729.5 m,长71亚段,灰白色细砂岩,粒间和粒内溶孔;b.ND103井,2 759.2 m,长72亚段,灰白色细砂岩含泥质纹层,粒间溶孔、微裂缝;c.ND103井,2 771.07 m,长72亚段,细砂岩,残余粒间孔、晶间孔;d.ND21井,2 678.57 m,长73亚段,灰白色粉砂岩夹泥质纹层,微裂缝;e.ND103井,2 771.07 m,长72亚段,灰白色粉砂岩夹泥质纹层,晶间孔;f.ND18井,2 576.67 m,长71亚段,灰黑色泥质粉砂岩,绿泥石纳米级晶间孔;g.ND18井,2 576.67 m,长71亚段,灰黑色泥质粉砂岩含灰质纹层,有机质孔隙;h.DP1井,2 757.82 m,长73亚段,泥岩,条带状、块状有机质,发育收缩缝;i.DP1井,2 757.82 m,长73亚段,黑色泥岩,有机质黏土复合体孔隙发育。
Figure 4. Reservoir space type characteristics of different lithologies in cast thin sections and argon ion polishing SEM images of the seventh member of Triassic Yanchang Formation, western Mahuangshan area, Ordos Basin
图 5 鄂尔多斯盆地麻黄山西地区研究区延长组7段不同类型页岩油储层样品压汞孔径分布(a-c)和氮气吸附孔径分布(d)
Figure 5. Mercury intrusion pore size distribution (a-c) and nitrogen adsorption pore size distribution (d) of different types of shale oil reservoir samples from the seventh member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in the study area, western Mahuangshan area, Ordos Basin
图 9 鄂尔多斯盆地麻黄山西地区研究区三叠系延长组7段机械压实特征照片
a.ND103井,2 729.5 m,长71亚段,石英颗粒压溶;b.ND15井,2 760.5 m,长72亚段,灰黑色泥质粉砂岩石英颗粒定向排列;c.ND6井,2 382.05 m,长71亚段,灰黑色泥质纹层细砂岩中云母变形。
Figure 9. Photographs of mechanical compaction characteristics in the seventh member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in the study area, western Mahuangshan area, Ordos Basin
图 10 鄂尔多斯盆地麻黄山西地区研究区三叠系延长组7段胶结物及交代特征显微照片
a.ND44井,2 603.82 m,长73亚段,石英次生加大;b.ND103井,2 771.07 m,长72亚段,书页状高岭石、绿泥石胶结充填粒间孔;c.ND18井,2 576.67 m,长71亚段,灰黑色泥质粉砂岩,绿泥石集合体;d.ND6井,2 382.05 m,长71亚段,灰白色含泥质纹层粉砂岩碳酸盐胶结;e.ND103井,2 758.0 m,长72亚段,灰白色含泥质纹层细砂岩碳酸盐胶结;f.ND15井,2 759.98 m,长73亚段,灰白色细砂岩碳酸盐胶结;g.ND103井,2 758.2 m,长72亚段,长石蚀变碳酸盐见溶孔;h.ND21井,2 580.87 m,长71亚段,碳酸盐交代;i.ND53井,2 578.83 m,长73亚段,长石被碳酸盐交代仍保留双晶特征。
Figure 10. Photomicrographs of cementation and alternation characteristics in the seventh member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in the study area, western Mahuangshan area, Ordos Basin
-
[1] 杨雷, 金之钧. 全球页岩油发展及展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 553-559.YANG Lei, JIN Zhijun. Global shale oil development and prospects[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 553-559. [2] 张廷山, 彭志, 杨巍, 等. 美国页岩油研究对我国的启示[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(3): 1-10.ZHANG Tingshan, PENG Zhi, YANG Wei, et al. Enlightenments of American shale oil research towards China[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(3): 1-10. [3] 郭旭升, 马晓潇, 黎茂稳, 等. 陆相页岩油富集机理探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1333-1349.GUO Xusheng, MA Xiaoxiao, LI Maowen, et al. Mechanisms for lacustrine shale oil enrichment in Chinese sedimentary basins[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1333-1349. [4] 孙志刚, 于春磊, 陈辉, 等. 陆相页岩油开发实验技术现状与展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(5): 186-198.SUN Zhigang, YU Chunlei, CHEN Hui, et al. Progress and prospect of experimental technologies for continental shale oil development[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(5): 186-198. [5] 金之钧, 张谦, 朱如凯, 等. 中国陆相页岩油分类及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 801-819.JIN Zhijun, ZHANG Qian, ZHU Rukai, et al. Classification of lacustrine shale oil reservoirs in China and its significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 801-819. [6] 吴凯, 高娟琴, 解古巍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段页岩气储层特征及其勘探开发前景[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(6): 1298-1311. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024061298WU Kai, GAO Juanqin, XIE Guwei, et al. Characteristics of Chang 7 shale gas reservoirs in Triassic Yanchang Formation of Ordos Basin and its exploration and development prospects[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(6): 1298-1311. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2024061298 [7] 付金华, 郭雯, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段多类型页岩油特征及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1749-1761.FU Jinhua, GUO Wen, LI Shixiang, et al. Characteristics and exploration potential of muti-type shale oil in the 7th member of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1749-1761. [8] 何鑫, 陈世加, 胡琮, 等. 陆相页岩层系岩性组合模式及其对原油差异性富集的控制作用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段为例[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(5): 1325-1337.HE Xin, CHEN Shijia, HU Cong, et al. Lithological combination model of the continental shale series and its controls on differential crude oil enrichment: a case study of the Chang 7 member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(5): 1325-1337. [9] 付锁堂, 金之钧, 付金华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段从致密油到页岩油认识的转变及勘探开发意义[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(5): 561-569.FU Suotang, JIN Zhijun, FU Jinhua, et al. Transformation of understanding from tight oil to shale oil in the member 7 of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and its significance of exploration and development[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 561-569. [10] 付锁堂, 付金华, 牛小兵, 等. 庆城油田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(7): 777-795.FU Suotang, FU Jinhua, NIU Xiaobing, et al. Accumulation conditions and key exploration and development technologies in Qingcheng oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(7): 777-795. [11] 马艳丽, 辛红刚, 马文忠, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北地区长7段页岩油富集主控因素及甜点区预测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1822-1829.MA Yanli, XIN Honggang, MA Wenzhong, et al. The main controlling factors on the enrichment and sweet-spot area prediction of Chang 7 member shale oil in northern Shaanxi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1822-1829. [12] 庞正炼, 陶士振, 张琴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段夹层型页岩层系石油富集规律与主控因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4): 152-163.PANG Zhenglian, TAO Shizhen, ZHANG Qin, et al. Interbedded shale formation of the 7th member of the Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin: petroleum accumulation patterns and controlling factors[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4): 152-163. [13] 胡宗全, 王濡岳, 路菁, 等. 陆相页岩及其夹层储集特征对比与差异演化模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1393-1404.HU Zongquan, WANG Ruyue, LU Jing, et al. Storage characteristic comparison of pores between lacustrine shales and their interbeds and differential evolutionary patterns[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1393-1404. [14] 邓秀芹, 付金华, 姚泾利, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中及上三叠统延长组沉积相与油气勘探的突破[J]. 古地理学报, 2011, 13(4): 443-455.DENG Xiuqin, FU Jinhua, YAO Jingli, et al. Sedimentary facies of the Middle-Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin and breakthrough in petroleum exploration[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2011, 13(4): 443-455. [15] 马文忠, 王永宏, 张三, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北地区长7段页岩油储层微观特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1810-1821.MA Wenzhong, WANG Yonghong, ZHANG San, et al. Microscopic characteristics and controlling factors of Chang 7 member shale oil reservoir in northern Shaanxi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1810-1821. [16] 徐黎明, 郭芪恒, 刘元博, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长73亚段深水重力流砂岩储层特征及控制因素: 以华池地区CY1井为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1797-1809.XU Liming, GUO Qiheng, LIU Yuanbo, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of deep-water gravity flow sandstone reservoir in the Chang 73 sub-member in Ordos Basin: case study of well CY1 in Huachi area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1797-1809. [17] 尤源, 梁晓伟, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段致密储层主要黏土矿物特征及其地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(8): 1233-1241.YOU Yuan, LIANG Xiaowei, FENG Shengbin, et al. Features and geological significance of main clay minerals in Chang 7 tight sandstone reservoir, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(8): 1233-1241. [18] 祝海华, 钟大康, 姚泾利, 等. 鄂尔多斯西南地区长7段致密油储层微观特征及成因机理[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(5): 853-863.ZHU Haihua, ZHONG Dakang, YAO Jingli, et al. Microscopic characteristics and formation mechanism of Upper Triassic Chang 7 tight oil reservoir in the southwest Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2014, 43(5): 853-863. [19] Cui X, Kou X, Feng S, et al. In-situ stress analysis in the Chang 7 reservoir of northern Shannxi region[J]. Unconventional Resources 2024, 4, 100051. [20] 李辉, 张涛, 侯雨庭, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段陆相页岩层系致密储层充注物性下限及其控制因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(6): 1498-1510.LI Hui, ZHANG Tao, HOU Yuting, et al. Lower limit of physical properties of filling materials in tight reservoirs of the Chang 7 Member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, and their controlling factors[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(6): 1498-1510 [21] 付金华, 李士祥, 牛小兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5): 870-883.FU Jinhua, LI Shixiang, NIU Xiaobing, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration of shale oil in Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(5): 870-883. [22] 李士祥, 牛小兵, 柳广弟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7段页岩油形成富集机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 719-729.LI Shixiang, NIU Xiaobing, LIU Guangdi, et al. Formation and accumulation mechanism of shale oil in the 7th member of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 719-729. [23] 葸克来, 李克, 操应长, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长73亚段富有机质页岩纹层组合与页岩油富集模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1244-1255.XI Kelai, LI Ke, CAO Yingchang, et al. Laminae combination and shale oil enrichment patterns of Chang 73 sub-member organic-rich shales in the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1244-1255. [24] 张凤奇, 孙越, 刘思瑶, 等. 构造抬升区泥页岩脆性破裂泄压特征及对页岩油富集的影响: 以延安地区延长组长73亚段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 936-951.ZHANG Fengqi, SUN Yue, LIU Siyao, et al. Characteristics of pressure relief induced by shale brittle fracture in tectonic uplift area and its influence on shale oil enrichment: a case study of Chang 73 sub-member of Yanchang Formation in Yan'an area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 936-951. [25] 付锁堂, 姚泾利, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组陆相页岩油富集特征与资源潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 698-710.FU Suotang, YAO Jingli, LI Shixiang, et al. Enrichment characteristics and resource potential of continental shale oil in Mesozoic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 698-710. [26] 杨华, 牛小兵, 徐黎明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 511-520.YANG Hua, NIU Xiaobing, XU Liming, et al. Exploration potential of shale oil in Chang 7 member, Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 511-520. [27] 薛婷, 黄天镜, 成良丙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆城油田页岩油水平井产能主控因素及开发对策优化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1880-1888.XUE Ting, HUANG Tianjing, CHENG Liangbing, et al. Dominating factors on shale oil horizontal well productivity and development strategies optimization in Qingcheng Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1880-1888. [28] 刘显阳, 杨伟伟, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组湖相页岩油赋存状态评价与定量表征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(12): 1762-1770.LIU Xianyang, YANG Weiwei, LI Shixiang, et al. Occurrence states and quantitative characterization of lacustrine shale oil from Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(12): 1762-1770. [29] 张福礼. 鄂尔多斯盆地早古生代复合的古构造体系与天然气[J]. 地质力学学报, 2002, 8(3): 193-200.ZHANG Fuli. Compound ancient tectonic system and natural gas of Early Paleozoic in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2002, 8(3): 193-200. [30] 赵文智, 胡素云, 侯连华. 页岩油地下原位转化的内涵与战略地位[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(4): 537-545.ZHAO Wenzhi, HU Suyun, HOU Lianhua. Connotation and strategic role of in-situ conversion processing of shale oil underground in the onshore China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(4): 537-545. [31] 邵广辉, 高衍武, 蔺敬旗, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油储层微观孔隙结构精细表征[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 20(1): 48-55.SHAO Guanghui, GAO Yanwu, LIN Jingqi, et al. The fine characterization of micro-pore structure of shale oil reservoir in Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 20(1): 48-55. [32] SCHERER M. Parameters influencing porosity in sandstones: a model for sandstone porosity prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71(5): 485-491. [33] BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369. [34] EHRENBERG S N. Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones: discussion; compaction and porosity evolution of Pliocene sandstones, Ventura Basin, California: discussion[J]. The American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1989, 73(10): 1274-1276. [35] DUTTON S P. Calcite cement in Permian deep-water sandstones, Delaware Basin, west Texas: origin, distribution, and effect on reservoir properties[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(6): 765-787. [36] ZHOU Yong, JI Youliang, XU Liming, et al. Controls on reservoir heterogeneity of tight sand oil reservoirs in Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Longdong area, southwest Ordos Basin, China: implications for reservoir quality prediction and oil accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 78: 110-135. [37] IRWIN H, CURTIS C, COLEMAN M. Isotopic evidence for source of diagenetic carbonates formed during burial of organic-rich sediments[J]. Nature, 1977, 269(5625): 209-213. [38] LORENS R B. Sr, Cd, Mn and Co distribution coefficients in calcite as a function of calcite precipitation rate[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1981, 45(4): 553-561. [39] LANZ M D R, AZMY K, CESARETTI N N, et al. Diagenesis of the Vaca Muerta Formation, Neuquén Basin: evidence from petro-graphy, microthermometry and geochemistry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 124: 104769. [40] FRIEDMAN I, O'NEIL J R. Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest[J]. US Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1977, 40-KK: 49. -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号