Gas injection capacity of low permeability reservoirs considering microscopic characteristics
-
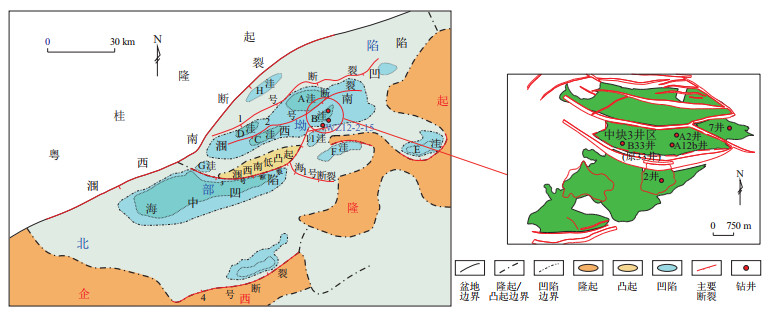
摘要: 注气是提高低渗油藏采收率的重要手段,但现有注气能力的评价方法未充分考虑微观孔隙特征的影响,为此以北部湾盆地涠洲B油田中块3井区渐新统涠洲组四段的低渗储层为研究对象,综合考虑微观孔喉结构特征(如分形维数、喉道半径、曲折度等)和束缚水膜厚度的影响,建立了基于静态测井渗透率动态校正的气相有效渗透率评价模型,同时结合岩心多倍气驱实验确定评价模型的精度,协同分析了微观特征因素影响下的注气渗流规律。研究结果表明,低渗油藏的注气能力呈现3种演化阶段:注气初期(0~100 PV)气体优先驱替较大孔隙原油,使束缚水饱和度快速下降,气相渗透率跃升显著提升气驱效率;注气中期(100~1 200 PV)气相有效渗透率呈线性增长,束缚水因微喉道毛管力限制进入平稳期;注气后期(>1 200 PV)气体开始突破微孔隙水膜,使束缚水饱和度缓慢降低,但受储层亲水性与非均质性影响,导致残余油滞留形成孤立相,气相渗透率及驱油效率(极限52%)趋于稳定,油藏开发潜力受限。根据涠洲B油田实例井证明,注气初期提升注入压力可有效改善吸气指数,而后期需控制注气量以避免非均质储层中油相孤立化及生产井含水上升,保证油相析出,从而提高油藏整体气驱效率。Abstract: Gas injection is a crucial method for enhancing oil recovery in low permeability reservoirs, but current evaluation methods for gas injection capacity have not fully considered microscopic pore characteristics. Therefore, taking the low permeability reservoirs in the fourth member of the Oligocene Weizhou Formation in well block 3 in the middle block of the Weizhou B Oilfield, Beibuwan Basin as the research object, a gas-phase effective permeability evaluation model was established based on dynamic correction of static logging permeability, comprehensively considering microscopic pore-throat structural characteristics (such as fractal dimension, throat radius, and tortuosity) and the thickness of bound water film. At the same time, core multiple-cycle gas flooding experiments were used to verify the accuracy of the evaluation model, and the seepage patterns of gas injection under the influence of microscopic characteristics were analyzed. The results showed that the gas injection capacity in low permeability reservoirs undergoes three evolutionary stages: In the initial stage of gas injection (0 to 100 PV), gas preferentially displaces crude oil in larger pores, leading to a rapid reduction in bound water saturation and a sharp increase in gas-phase permeability, which significantly improves gas flooding efficiency. In the middle stage of gas injection (100 to 1 200 PV), the gas-phase effective permeability increases linearly, and the bound water enters a stable phase due to capillary force constraints in microscopic throats. In the later stage of gas injection (>1 200 PV), gas begins to break through the water film in microscopic pores, causing a slow decrease in bound water saturation. However, due to the hydrophilicity and heterogeneity of reservoirs, residual oil are trapped as an isolated phase, leading to the stabilization of gas-phase permeability and displacement efficiency (with a maximum of 52%), and limiting the development potential of reservoirs. Field verification in the Weizhou B Oilfield demonstrated that increasing injection pressure in the initial stage can effectively improve gas injectivity index, while in the later stage, it is necessary to control the gas injection amount to prevent oil phase isolation in heterogeneous reservoirs and rising water cut in production wells, thereby ensuring oil phase precipitation and improving the overall reservoir gas flooding efficiency.
-
表 1 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷涠洲B油田岩心实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters of cores from Weizhou B Oilfield of Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin
项目 参数 井号 WZ12-1-B33 岩心编号 WM2-10 井深/m 3 680.51 长度/cm 6.122 直径/cm 2.535 孔隙体积/mL 4.49 孔隙度/% 14.5 渗透率/10-3μm2 15.7 主流喉道半径下限/μm 0.5 迂曲度/% 4.287 排驱压力/MPa 0.066 分形维数 2.961 2 气黏度/(mPa·s) 0.015 油黏度/(mPa·s) 3.958 3 实验温度/℃ 室温 实验压力/MPa 室压 饱和油量/mL 27.5 束缚水饱和度/% 38.752 8 饱和水矿化度/(mg/L) 13 000 表 2 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷涠洲B油田注入气组分含量
Table 2. Compositional content of injected gas in Weizhou B Oilfield, Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin
组分 含量/% C2 14.62 C3 9.63 iC4 1.26 nC4 2.38 CO2 3.96 iC5 0.62 nC5 0.45 H2S 0.85 C6+ 0.85 C1 66.23 -
[1] 贺承祖, 华明琪. 油气藏中水膜的厚度[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(2): 75-77.HE Chengzu, HUA Mingqi. The thickness of water film in oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998, 25(2): 75-77. [2] 俞杨锋, 康毅力, 游利军, 等. 特低渗透油层边界层—双电层微流调控研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2010, 17(6): 85-89.YU Yangfeng, KANG Yili, YOU Lijun, et al. Review on advances of microflow regulation in ultra-low permeable oil reservoir from interface layer to electric double layer[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2010, 17(6): 85-89. [3] 王鸣川, 王燃, 岳慧, 等. 页岩油微观渗流机理研究进展[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 98-110. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401098WANG Mingchuan, WANG Ran, YUE Hui, et al. Research progress of microscopic percolation mechanism of shale oil[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(1): 98-110. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401098 [4] SMITH A, JOHNSON D, LEE S. Numerical simulation of gas injection performance in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 190: 106865. [5] LUO Z, KANG Y, ZHANG M. Experimental study on gas injection in low permeability reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Research Journal, 2022, 12(3): 345-358. [6] ZENG Daqian, ZHANG Guangquan, YANG Xiaosong, et al. Design method of key parameters of gas reservoir engineering for complex reservoir type underground gas storages[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(10): 24-33. [7] 白玉湖, 王苏冉, 徐兵祥, 等. 致密砂岩束缚水饱和度和微观孔喉结构关系实验研究[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(4): 65-71.BAI Yuhu, WANG Suran, XU Bingxiang, et al. Experimental study on the relationship between irreducible water saturation and micro pore throat in tight sandstone[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(4): 65-71. [8] 王立新, 高青松, 周家林, 等. 黏土矿物类型对杭锦旗下石盒子组致密砂岩储层束缚水饱和度的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2024, 43(6): 821-835.WANG Lixin, GAO Qingsong, ZHOU Jialin, et al. The impact of different clay mineral types on the irreducible water saturation in tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of the Lower Shihezi Formation in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2024, 43(6): 821-835. [9] WANG Rujun, ZHANG Chengze, CHEN Dong, et al. Microscopic seepage mechanism of gas and water in ultra-deep fractured sandstone gas reservoirs of low porosity: a case study of Keshen Gas Field in Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin, China[J]Front. Earth Sci., 2022, 10: 893701. [10] 孙建孟, 闫国亮. 渗透率模型研究进展[J]. 测井技术, 2012, 36(4): 329-335.SUN Jianmeng, YAN Guoliang. Review on absolute permeability model[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2012, 36(4): 329-335. [11] 宋泽章, 吕明阳, 赵力彬, 等. 基于分形理论的致密砂岩渗透率预测模型[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(6): 1847-1858.SONG Zezhang, LÜ Mingyang, ZHAO Libin, et al. Fractal-based permeability prediction model for tight sandstone[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(6): 1847-1858. [12] 李昊远, 庞强, 魏克颖, 等. 致密砂岩储层孔隙结构分形特征对气水渗流规律的影响[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 177-185.LI Haoyuan, PANG Qiang, WEI Keying, et al. Influence of pore structure fractal features of tight sandstone reservoir on gas-water seepage law[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 177-185. [13] 唐玄, 郑逢赞, 梁国栋, 等. 黔北寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩孔隙分形表征[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3): 110-123.TANG Xuan, ZHENG Fengzan, LIANG Guodong, et al. Fractal characterization of pore structure in Cambrian Niutitang shale in northern Guizhou, southwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 110-123. [14] 刘志楠, 张贵才, 王增林, 等. 致密储层束缚水膜厚度计算方法及影响因素研究进展[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(4): 1-9.LIU Zhinan, ZHANG Guicai, WANG Zenglin, et al. Research progress on calculation methods and influencing factors of tight reservoir irreducible water film thickness[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(4): 1-9. [15] 李春雷, 曹小朋, 张林凤, 等. 基于机器学习算法的水驱储层相渗曲线仿真预测[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(6): 138-142.LI Chunlei, CAO Xiaopeng, ZHANG Linfeng, et al. Simulation and prediction of water-flooding reservoir relative permeability curve based on machine learning[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(6): 138-142. [16] 李童, 龙安林, 刘波, 等. 低渗透砂岩油藏隔夹层注气突破压力及注气开发策略: 以柴达木盆地尕斯库勒油田E31油藏为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(10): 1364-1372.LI Tong, LONG Anlin, LIU Bo, et al. Breakthrough pressure and development strategy for gas injection in interlayers in low-permeability sandstone reservoirs: a case study of the Gasikule E31 reservoir, Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(10): 1364-1372. [17] 于忠良, 熊伟, 高树生, 等. 致密储层应力敏感性及其对油田开发的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 95-98.YU Zhongliang, XIONG Wei, GAO Shusheng, et al. Stress sensitivity of tight reservoir and its influence on oilfield development[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 95-98. [18] 胡德胜, 孙文钊, 满晓, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷涠洲组断裂—岩性复合圈闭发育模式与勘探实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(2): 215-227. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202402215HU Desheng, SUN Wenzhao, MAN Xiao, et al. Development model and exploration practice of fault-lithologic composite traps in Oligocene Weizhou Formation, Weixinan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(2): 215-227. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202402215 [19] 杨朝蓬. 李星民. 刘尚奇. 等. 苏里格低渗致密气藏阈压效应[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(3): 347-354.YANG Zhaopeng, LI Xingmin, LIU Shangqi, et al. Threshold pressure effect of low permeability tight gas reservoirs in Sulige Gas Field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(3): 347-354. [20] 章莉娟. 郑忠. 胶体与界面化学[M]. 2版. 广州: 华南理工大学出版社, 2006: 23-165.ZHANG Lijuan, ZHENG Zhong. Colloid and interface chemistry[M]. 2nd ed. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press, 2006: 23-165. [21] 陈洪才, 李哲, 金忠康, 等. 苏北盆地石港特低渗储层微观特征及提高采收率对策研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(3): 638-646. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202403638CHEN Hongcai, LI Zhe, JIN Zhongkang, et al. Microscopic characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoirs in the Shigang Oilfield of the Subei Basin and strategies for enhancing oil recovery[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(3): 638-646. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202403638 [22] 吴小斌, 杜支文, 强小龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段致密砂岩二元孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(6): 45-56.WU Xiaobin, DU Zhiwen, QIANG Xiaolong, et al. Binary pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight sandstone: a case study of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(6): 45-56. [23] 陈科贵, 温易娜, 何太洪, 等. 低孔低渗致密砂岩气藏束缚水饱和度模型建立及应用: 以苏里格气田某区块山西组致密砂岩储层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(2): 273-277.CHEN Kegui, WEN Yina, HE Taihong, et al. Irreducible water saturation models of tight sandstone gas reservoirs with low porosity and permeability and its application: taking a block of Shanxi Formation tight sandstone reservoir in Sulige Gas Field as an example[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(2): 273-277. [24] 周宗良, 张凡磊, 王怀忠, 等. 低渗砂岩储层毛管孔道应力与孔隙水膜赋存状态探讨[J]. 新疆地质, 2017, 35(3): 320-324.ZHOU Zongliang, ZHANG Fanlei, WANG Huaizhong, et al. Study of capillary channel pressure and pore water-film occurrence of low permeability sandstone reservoir[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2017, 35(3): 320-324. [25] LI Yudan, KALANTARI-DAHAGHI A, ZOLFAGHARI A, et al. Fractal-based real gas flow model in shales: an interplay of nano-pore and nano-fracture networks[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 127: 1188-1202. [26] 马勇新, 雷霄, 张乔良, 等. 低渗透油藏有效渗透率计算新模型: 以珠江口盆地海相低渗透砂岩为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(1): 117-122.MA Yongxin, LEI Xiao, ZHANG Qiaoliang, et al. A new model for calculating effective permeability in low permeability reservoirs: a case study of low permeability marine sediments reservoir in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2016, 28(1): 117-122. [27] 陈少云, 杨勇强, 邱隆伟, 等. 致密砂岩孔喉结构分析与渗透率预测方法: 以川中地区侏罗系沙溪庙组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 202-214. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401202CHEN Shaoyun, YANG Yongqiang, QIU Longwei, et al. Pore throat structure analysis and permeability prediction method of tight sandstone: a case study of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(1): 202-214. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401202 [28] 李东升, 高平, 盖海峰, 等. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩有机质纳米孔隙结构表征[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(5): 1293-1305.LI Dongsheng, GAO Ping, GAI Haifeng, et al. Organic nano-pore textural characteristics of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(5): 1293-1305. [29] 刘印华, 杨英, 马文涛, 等. 海陆过渡相页岩孔隙结构表征及页岩气渗流规律模拟[J]. 断块油气田, 2024, 31(2): 207-215.LIU Yinhua, YANG Ying, MA Wentao, et al. Pore structure characterization of marine-continental transitional shale and seepage law simulation of shale gas[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2024, 31(2): 207-215. [30] KANG Yili, LI Peisong, CAO Wangkun, et al. Investigation of pore structure alteration and permeability enhancement of shale matrix by supercritical water treatment after hydraulic fracturing[J]. Petroleum, 2024, 10(2): 265-274. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号