Utilization strategies for deep coal-measure reservoirs with different stacking patterns in Linxing block, Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块已进入致密气、煤层气协同开发阶段,致密砂岩与煤层的叠置模式直接影响开发方式。通过对叠置关系的研究,并从临兴区块不同开发方式生产动态出发,进行深部煤系储层动用策略研究。基于致密砂岩与煤层发育沉积特征和相对位置关系,临兴区块砂煤叠置模式主要包括砂煤互层型和上砂下煤型。对比不同叠置模式下的开发现状,水平井是深层煤层气单独开发时的首选井型,煤层气与致密气两气合采井初期产气能力高于单采煤层直井定向井。进一步建立了以经济效益为优化目标的不同叠置模式下深层煤系储层动用策略优选图版:当煤层丰度小于1.1×108 m3/km2、且致密气层为一类或二类气层时,采用两气合采方式进行开发;当煤层丰度介于(1.1~1.5)×108 m3/km2时,若致密气层不发育,采用水平井单独动用煤层,若致密气层为一类或二类气层时,则采用致密气—煤层气两气合采方式进行开发;当煤层丰度大于1.5×108 m3/km2时,若致密气层不发育或为二类、三类气层,采用水平井单独动用煤,若致密气层为一类气层,则采用致密气、煤层气单独开发方式进行开发。该研究为临兴区块及相似区块等深层煤层气资源两气协同高效开发提供技术支撑。Abstract: The Linxing block in the Ordos Basin has entered the stage of co-production of tight gas and coalbed methane (CBM), and the stacking patterns of tight sandstone and coal seams directly affect the production methods. By analyzing the stacking relationships and production dynamics using different development methods in the Linxing block, the utilization strategies for deep coal-measure reservoirs were investigated. Based on the sedimentary characteristics and relative spatial positions of tight sandstone and coal seams, the sand-coal stacking patterns in the Linxing block were mainly categorized into interbedded sand-coal type and upper sand-lower coal type. By comparing the development status under different stacking patterns, it was found that horizontal wells were preferred for the independent development of deep CBM, and wells co-producing CBM and tight gas had higher initial gas production capacity than vertical or directional wells producing CBM alone. An optimization chart of deep coal-measure reservoir utilization strategies under different stacking patterns was further established, with economic efficiency as the optimization objective. When CBM abundance is less than 1.1×108 m3/km2 and the tight gas reservoir is classified as a Class Ⅰ or Class Ⅱ, a co-production approach should be adopted. Under the condition that CBM abundance ranges from 1.1×108 to 1.5×108 m3/km2, if the tight gas reservoir is underdeveloped, horizontal wells should be used for the independent utilization of CBM; if the tight gas reservoir is classified as Class Ⅰ or Ⅱ, a co-production method should be adopted. Under the condition that CBM abundance exceeds 1.5×108 m3/km2, if the tight gas reservoir is underdeveloped or classified as Class Ⅱ or Ⅲ, horizontal wells should be used to develop the coal seams solely; if the tight gas reservoir is classified as Class Ⅰ, tight gas and CBM should be developed separately. The research provides technical support for the efficient co-production of deep CBM resources in the Linxing block and other similar blocks.
-
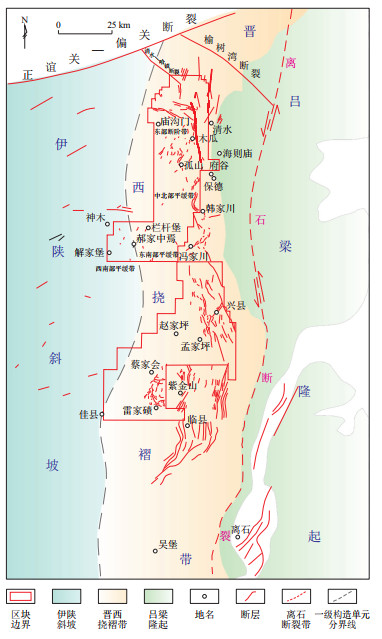
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块构造位置[28]
Figure 1. Tectonic location of Linxing block, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块LX1-79井及相邻井组投产井信息
Table 1. Production well information of well LX1-79 and adjacent well groups in Linxing block, Ordos Basin
井名 含气量/(m3/t) 煤层厚度/m 相邻气层
厚度/m90天峰值平均
产气量/(m3/d)LX1-79-1D 14.3 13.0 0 2 913 LX1-79-2D 14.5 12.1 0 2 352 LX1-79-3D 14.5 12.5 0 2 633 LX1-79-4D 14.5 12.5 2.2 7 115 LXC1-67-5D 14.1 12.7 1.5 6 199 LXC1-67-6D 14.1 12.9 2.5 5 264 LXC1-67-7D 14.1 13.2 2.2 4 769 LXC1-67-8D 14.8 13.0 0 2 698 LXC1-67-9D 14.8 12.8 0 3 352 LXC1-67-10D 14.8 12.8 3.8 5 523 LXC1-67-11D 14.8 12.9 4.5 6 741 LX1-85 14.3 13.1 0 2 908 LX1-85-1D 14.3 13.2 0 3 321 LX1-85-2D 14.3 13.2 0 3 154 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块6口新井预测90天峰值产量与实际90天峰值产量对比
Table 2. Comparison between predicted and actual 90-day peak production of six new wells in Linxing block, Ordos
钻井 含气量/(m3/t) 压裂砂量/m3 排量/(m3/min) 压裂液量/m3 煤层厚度/m 构造高度/m 实测产量/(m3/d) 预测产量/(m3/d) 误差/% A井 14.83 220 13 2 066 14 -791 2 723 2 906 7.63 B井 10.20 496 20 4 123 16 -763 6 214 6 666 7.52 C井 8.19 276 16 2 801 13 -802 2 263 2 222 1.24 D井 15.52 219 15 2 026 14 -810 3 274 3 120 2.50 E井 17.07 401 22 3 024 15 -782 7 105 6 637 5.19 F井 18.44 240 20 2 300 16 -758 4 951 4 587 7.34 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地大宁—吉县深层煤层气井3年平均产气量与峰值产气量的比例
Table 3. Ratios of three-year average gas production to peak gas production of deep CBM wells in Daning-Jixian area, Ordos Basin
井号 排采时间/d 3年平均产气量/(m3/d) 峰值产气量/(m3/d) 比例 大吉-1 674 2 620 5 791 0.45 大吉-2 454 3 490 4 469 0.78 大吉-3 360 4 940 5 193 0.95 大吉-4 217 3 844 4 300 0.89 大吉-5 217 3 536 4 050 0.87 大吉-6 361 2 033 3 167 0.64 大吉-7 344 1 550 2 425 0.64 大吉-8 390 990 2 142 0.46 大吉-9 459 1 530 2 824 0.54 大吉-10 459 1 320 1 915 0.69 大吉-11 241 1 400 1 810 0.77 大吉-12 459 1 450 2 864 0.51 平均 2 295 3 430 0.67 表 4 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块典型井数值模型参数
Table 4. Numerical model parameters of typical wells in Linxing block, Ordos Basin
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 煤层厚度/m 8.6 割理渗透率/10-3 μm2 0.08 孔隙度/% 5 地层压力/MPa 19.8 裂缝半长/m 70 裂缝导流能力/(10-3 μm2·m) 250 兰氏压力/MPa 2.3 兰氏体积/(m3/t) 15.2 含气量/(m3/t) 12.2 临界解吸压力/MPa 18.5 表 5 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块致密气储量分类划分标准
Table 5. Classification criteria for tight gas reserves in Linxing block, Ordos Basin
类别 砂岩
厚度/m渗透率/10-3 μm2 地层特征参数/(10-3 μm2·m) 单层无阻流量/(104 m3/d) Ⅰ类 >4.0 >1.0 >2 164 >1.5 Ⅱ类 2.0~4.0 0.3~1.0 750~2 164 0.3~1.5 Ⅲ类 <2.0 <0.3 <750 <0.3 表 6 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块不同叠置模式下不同开发方式经济效益
Table 6. Economic benefits of different development approaches under different stacking patterns in Linxing block, Ordos Basin
煤层丰度/108 m3/km2 致密气地层
特征参数/(10-3 μm2·m)煤层气
累产/104 m3致密气
累产/104 m3不同开发方式经济指标/104 m3 判断结果 水平井
单采煤层直井单采
致密气层以煤层气为主
的两气合采以致密气为主
的两气合采两气
单独开发0.80 500 2 040 193 -1 747 -2 119 -4 689 -770 -3 866 无效益 0.80 1 000 2 040 386 -1 747 -1 583 -4 153 -233 -3 329 无效益 0.80 2 000 2 040 773 -1 747 -509 -3 080 840 -2 256 以致密气为主的两气合采 0.80 4 000 2 040 1 545 -1 747 1 637 -934 2 986 -110 以致密气为主的两气合采 0.80 8 000 2 040 3 090 -1 747 5 929 3 359 7 278 4 182 以致密气为主的两气合采 0.80 10 000 2 040 3 863 -1 747 8 075 5 505 9 424 6 328 以致密气为主的两气合采 1.50 500 3 825 193 2 830 -2 119 32 410 711 水平井单采煤层 1.50 1 000 3 825 386 2 830 -1 583 569 947 1 247 水平井单采煤层 1.50 2 000 3 825 773 2 830 -509 1 642 2 020 2 320 水平井单采煤层 1.50 4 000 3 825 1 545 2 830 1 637 3 788 4 166 4 466 两气单独开发 1.50 8 000 3 825 3 090 2 830 5 929 8 080 8 458 8 759 两气单独开发 1.50 10 000 3 825 3 863 2 830 8 075 10 226 10 605 10 905 两气单独开发 -
[1] 郑民, 李建忠, 吴晓智, 等. 我国主要含油气盆地油气资源潜力及未来重点勘探领域[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 833-847.ZHENG Min, LI Jianzhong, WU Xiaozhi, et al. Potential of oil and natural gas resources of main hydrocarbon-bearing basins and key exploration fields in China[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 833-847. [2] 刘池洋, 王建强, 张东东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地油气资源丰富的成因与赋存—成藏特点[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5): 1011-1029.LIU Chiyang, WANG Jianqiang, ZHANG Dongdong, et al. Genesis of rich hydrocarbon resources and their occurrence and accumulation characteristics in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5): 1011-1029. [3] 王建, 郭秋麟, 赵晨蕾, 等. 中国主要盆地页岩油气资源潜力及发展前景[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(12): 2033-2044.WANG Jian, GUO Qiulin, ZHAO Chenlei, et al. Potentials and prospects of shale oil-gas resources in major basins of China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(12): 2033-2044. [4] 秦勇, 申建, 史锐. 中国煤系气大产业建设战略价值与战略选择[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(1): 371-387.QIN Yong, SHEN Jian, SHI Rui. Strategic value and choice on construction of large CMG industry in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 371-387. [5] 郭旭升, 赵培荣, 申宝剑, 等. 中国深层煤层气地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(6): 1511-1523.GUO Xusheng, ZHAO Peirong, SHEN Baojian, et al. Geological features and exploration practices of deep coalbed methane in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(6): 1511-1523. [6] 张鹏飞, 张仲达, 邱贻博, 等. 华北地区煤系地层油气资源研究现状及启示[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(4): 96-111.ZHANG Pengfei, ZHANG Zhongda, QIU Yibo, et al. Research progress of oil and gas resources in coal-bearing strata in North China and its implications[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(4): 96-111. [7] 郭晨, 秦勇, 易同生, 等. 煤层气合采地质研究进展述评[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(3): 42-57.GUO Chen, QIN Yong, YI Tongsheng, et al. Review of the progress of geological research on coalbed methane co-production[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 42-57. [8] 张健, 申建, 朱苏阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘煤系气合采接替方案优化[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(11): 3965-3974.ZHANG Jian, SHEN Jian, ZHU Suyang, et al. Productivity prediction and gas production technology of superimposed coal measure gas in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(11): 3965-3974. [9] 王志壮, 吴鹏, 孙强, 等. 临兴区块深部煤层气井生产特征及影响因素[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(8): 69-78.WANG Zhizhuang, WU Peng, SUN Qiang, et al. Production characteristics of deep coalbed methane wells in the Linxing block and associated their influencing factors[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(8): 69-78. [10] 闫涛滔, 邓志宇, 吴鹏, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴东区杨家坡区块煤层气井产能特征及主控因素[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(6): 1545-1556.YAN Taotao, DENG Zhiyu, WU Peng, et al. Characteristics and key control factors of coalbed methane well productivity in the Yangjiapo block, eastern Linxing district, Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(6): 1545-1556. [11] 刘建忠, 朱光辉, 刘彦成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘深部煤层气勘探突破及未来面临的挑战与对策: 以临兴—神府区块为例[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1827-1839. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311006LIU Jianzhong, ZHU Guanghui, LIU Yancheng, et al. Breakthrough, future challenges and countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the eastern margin of Ordos Basin: a case study of Linxing-Shenfu block[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1827-1839. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311006 [12] 徐长贵, 季洪泉, 王存武, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴—神府区块深部煤层气富集规律与勘探对策[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(8): 1-11.XU Changgui, JI Hongquan, WANG Cunwu, et al. Enrichment patterns and exploration countermeasures of deep coalbed methane in the Linxing-Shenfu block on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(8): 1-11. [13] 秦勇, 宋全友, 傅雪海. 煤层气与常规油气共采可行性探讨: 深部煤储层平衡水条件下的吸附效应[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(4): 492-498.QIN Yong, SONG Quanyou, FU Xuehai. Discussion on reliability for co-mining the coalbed gas and normal petroleum and natural gas: absorptive effect of deep coal reservoir under condition of balanced water[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(4): 492-498. [14] 郭本广, 许浩, 孟尚志, 等. 临兴地区非常规天然气合探共采地质条件分析[J]. 中国煤层气, 2012, 9(4): 3-6.GUO Benguang, XU Hao, MENG Shangzhi, et al. Geology condition analysis for unconventional gas co-exploration and concurrent production in Linxing area[J]. China Coalbed Methane, 2012, 9(4): 3-6. [15] 陈尚斌, 侯晓伟, 屈晓荣, 等. 煤系气叠置含气系统与天然气成藏特征: 以沁水盆地榆社—武乡示范区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(5): 12-22.CHEN Shangbin, HOU Xiaowei, QU Xiaorong, et al. Superimposed gas-bearing system of coal measure gas and its natural gas accumulation characteristics: a case study of Yushe-Wuxiang demonstration area in the Qinshui Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(5): 12-22. [16] 姜杉钰, 王峰. 中国煤系天然气共探合采的战略选择与发展对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 152-159.JIANG Shanyu, WANG Feng. Strategic choice and development countermeasures for the commingled exploration and exploitation of coal measure natural gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 152-159. [17] 郑力会, 陶秀娟, 魏攀峰, 等. 多储层产量伤害物理模拟系统及其在煤系气合采中的应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(8): 2501-2509.ZHENG Lihui, TAO Xiujuan, WEI Panfeng, et al. Multi-reservoir production damage physical simulation system and its application in coal-measure gas production[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(8): 2501-2509. [18] 邵奎宇, 鞠玮, 王胜宇, 等. 临兴地区山西组煤系复合储层压裂改造优化研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(11): 14-18.SHAO Kuiyu, JU Wei, WANG Shengyu, et al. Study on Fracturing optimization of coal measure composite reservoir of Shanxi Formation in Linxing area[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(11): 14-18. [19] ZHOU Jun, FU Tiantian, WU Kunyi, et al. Optimization design of multi-gathering mode for the surface system in coalbed methane field[J]. Petroleum, 2023, 9(2): 237-247. [20] 彭威龙, 庞雄奇, 范立勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界烃源岩排烃特征及资源潜力评价[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2014, 36(7): 40-46.PENG Weilong, PANG Xiongqi, FAN Liyong, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon expulsion of Upper Paleozoic source rocks and resource potential assessment in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2014, 36(7): 40-46. [21] ZHANG Yu, MENG Xianghong, WANG Duoyun. Provenance analysis of the Middle Triassic Ordos Basin: constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Geochemistry, 2019, 80(1): 125521. [22] 于兴河, 王香增, 王念喜, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部上古生界层序地层格架及含气砂体沉积演化特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(6): 935-954.YU Xinghe, WANG Xiangzeng, WANG Nianxi, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary evolution characteristics of gas-bearing sandbody in the Upper Paleozoic in southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(6): 935-954. [23] 李芙蓉, 刘文汇, 王晓锋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地古生界天然气地球化学特征与成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 809-820. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304809LI Furong, LIU Wenhui, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Paleozoic natural gas in the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 809-820. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304809 [24] 张英男, 白青林, 束青林, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘浅埋藏储层致密化成因[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(2): 24-36.ZHANG Yingnan, BAI Qinglin, SHU Qinglin, et al. Mechanism of tight sandstone reservoirs with shallow burial in southwest of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2024, 48(2): 24-36. [25] 姚泾利, 刘晓鹏, 赵会涛, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地盒8段致密砂岩气藏储层特征及地质工程一体化对策[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(2): 186-195.YAO Jingli, LIU Xiaopeng, ZHAO Huitao, et al. Characteristics of He 8th member tight sandstone gas reservoir and solution based on geology-engineering integration in Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(2): 186-195. [26] 陈诚, 齐宇, 喻梓靓, 等. 浅水三角洲河道砂体叠置关系的地震识别: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴S区为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(5): 772-779.CHEN Cheng, QI Yu, YU Ziliang, et al. Seismic identification of superposition relationship of the shallow water delta channel sand bodies: case study of Linxing S area in eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(5): 772-779. [27] 刘畅, 张道旻, 李超, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块上古生界致密砂岩气藏成藏条件及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5): 1146-1158.LIU Chang, ZHANG Daomin, LI Chao, et al. Upper Paleozoic tight gas sandstone reservoirs and main controls, Linxing block, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5): 1146-1158. [28] 孙立春, 刘佳, 李娜, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神府区块深部煤层气井产量主控因素及合理压裂规模优化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2025, 47(1): 43-53. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2025010043SUN Lichun, LIU Jia, LI Na, et al. Main controlling factors of production and reasonable fracturing scale optimization of deep coalbed methane wells in Shenfu block, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2025, 47(1): 43-53. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2025010043 [29] 田永净, 吴和源, 姜雄鹰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴地区上石盒子组成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(11): 1664-1672.TIAN Yongjing, WU Heyuan, JIANG Xiongying, et al. Accumulation characteristics research of Shangshihezi Formation in Linxing block, eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(11): 1664-1672. [30] 杜佳, 朱光辉, 李勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆缘致密砂岩气藏勘探开发挑战与技术对策: 以临兴—神府气田为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(1): 114-124.DU Jia, ZHU Guanghui, LI Yong, et al. Exploration and development challenges and technological countermeasures for tight sandstone gas reservoirs in Ordos Basin margin: a case study of Linxing-Shenfu gas field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(1): 114-124. [31] 沈柏坪, 李荣相, 白洪涛, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地宜川地区本溪组8号煤岩特征及成煤环境分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2024, 31(6): 32-38.SHEN Baiping, LI Rongxiang, BAI Hongtao, et al. Analysis of coal rock characteristics and coal-forming environment of the No. 8 coal seam in the Benxi Formation in Yichuan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2024, 31(6): 32-38. [32] 张涛, 巩肖可, 黄朝, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组低品质气藏储层微观特征及形成机理[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 32-45. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401032ZHANG Tao, GONG Xiaoke, HUANG Chao, et al. Micro characteristics and formation mechanism of low-quality gas reservoirs in Taiyuan Formation of Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(1): 32-45. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401032 [33] 王金伟, 许浩, 刘一楠, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴—神府地区深部煤储层储渗空间发育特征及产水能力评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2025, 47(1): 54-63. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2025010054WANG Jinwei, XU Hao, LIU Yinan, et al. Storage and permeation space development characteristics and water production capacity evaluation of deep coal reservoirs in Linxing-Shenfu area of Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2025, 47(1): 54-63. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2025010054 -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号