Carbon isotope fractionation characteristics during shale gas release
-
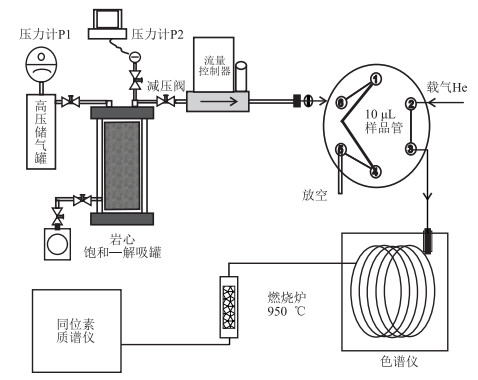
摘要: 钻井现场开展页岩岩心解吸气同位素监测,由于损失气样品缺失,而不能得到岩心气体释放全过程同位素的变化规律。通过加工岩心甲烷高压饱和-解吸装置,并接入色谱-同位素质谱联机系统,满足在线实时监测解吸气甲烷碳同位素变化的要求。在此基础上,开展页岩岩心释气的正演模拟实验,发现了解吸气甲烷碳同位素先期稳定、后期变轻后逐渐变重的变化规律,揭示了岩心中游离气和吸附气的相态转化、二者混合比例的动态演化与同位素变化趋势的相关性,表明同位素在页岩气开发状态的示踪方面具有应用潜力。Abstract: The isotope monitoring of desorption gas from shale cores was carried out at the drill site. Gas is lost during core recovery and thus the isotope variation for the whole process of gas release from shale cores cannot be obtained. A high pressure methane saturation-desorption device was developed and connected to the chromatographic-isotope mass spectrometry system to monitor the carbon isotope change of released CH4 on-line. The isotopic curves of releaed methane were initially stable, and then tended to become lighter and finally heavier, which was related to the phase transformation and the mixing ratio of free gas and adsorbed gas. Isotopes have potential applications in monitoring shale gas development.
-
Key words:
- carbon isotope /
- isotopic fractionation /
- methane /
- shale gas
-
表 1 在线连续流甲烷碳同位素重复性检测
Table 1. On-line continuous flow methane isotope repeatability measurement
序号 信号强度44 mV 信号强度45 mV δ13CCH4/‰ 序号 信号强度44 mV 信号强度45 mV δ13CCH4/‰ 1 20 042 22 619 -42.00 7 19 940 22 497 -41.92 2 20 056 22 633 -41.92 8 19 916 22 470 -41.92 3 19 994 22 563 -41.94 9 19 951 22 510 -41.92 4 19 775 22 313 -42.01 10 20 002 22 565 -41.95 5 19 733 22 264 -41.96 11 19 757 22 285 -41.94 6 19 882 22 435 -41.96 12 20 005 22 567 -41.94 -
[1] WANG Xiaofeng, LI Xiaofu, WANG Xianzeng, et al. Carbon isotopic fractionation by desorption of shale gases[J]. Marine and Petro-leum Geology, 2015, 60: 79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.11.003 [2] 孟强, 王晓锋, 王香增, 等. 页岩气解析过程中烷烃碳同位素组成变化及其地质意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡东南部长7页岩为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(2): 333-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201502018.htmMENG Qiang, WANG Xiaofeng, WANG Xiangzeng, et al. Variation of carbon isotopic composition of alkanes during the shale gas desorption process and its geological significance: a case study of Chang7 shale of Yanchang Formation in Yishan Slope, southeast of Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(2): 333-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201502018.htm [3] 韩辉, 李大华, 马勇, 等. 四川盆地东北地区下寒武统海相页岩气成因: 来自气体组分和碳同位素组成的启示[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(3): 453-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201303006.htmHAN Hui, LI Dahua, MA Yong, et al. The origin of marine shale gas in the northeastern Sichuan Basin, China: implications from chemical composition and stable carbon isotope of desorbed gas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(3): 453-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201303006.htm [4] 秦华, 范小军, 刘明, 等. 焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩解吸气地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(7): 846-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201607003.htmQIN Hua, FAN Xiaojun, LIU Ming, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of desorbed shale gas in Longmaxi Formation, Jiaoshiba area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(7): 846-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201607003.htm [5] 杨振恒, 魏志红, 何文斌, 等. 川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩现场解吸气特征及其意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(1): 156-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701017.htmYANG Zhenheng, WEI Zhihong, HE Wenbin, et al. Characteristics and significance of onsite gas desorption from Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(1): 156-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201701017.htm [6] 高和群, 曹海虹, 曾隽. 页岩气解吸规律新认识[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(2): 81-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902011.htmGAO Hequn, CAO Haihong, ZENG Jun. New understanding of shale gas desorption law[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(2): 81-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902011.htm [7] 李凯, 孟志勇, 吉婧, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组解吸气特征及影响因素分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1): 90-96. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201801090LI Kai, MENG Zhiyong, JI Jing, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of desorption gas in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(1): 90-96. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201801090 [8] 尹观, 倪师军. 同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.YIN Guan, NI Shijun. Isotope geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geologic Press, 2009. [9] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 地质样品有机地球化学分析方法第2部分: 有机质稳定碳同位素测定同位素质谱法: GB/T 18340.2-2010[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. Organic geochemical analysis method for geological samples, part 2: determination of organic carbon stable isotopic component, isotopic mass spectrometry: GB/T 18340.2-2010[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2011. [10] 刘强, 朱铭, 张福松, 等. 氩同位素分馏的实验研究[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(3): 297-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200003004.htmLIU Qiang, ZHU Ming, ZHANG Fusong, et al. Experimental study on argon isotopic fractionation[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 2000, 35(3): 297-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200003004.htm [11] XIA Xinyu, TANG Yongchun. Isotope fractionation of methane during natural gas flow with coupled diffusion and adsorption/desorption[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 77: 489-503. [12] 俞凌杰, 范明, 腾格尔, 等. 埋藏条件下页岩气赋存形式研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(4): 438-444. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201604438YU Lingjie, FAN Ming, TENGER, et al. Shale gas occurrence under burial conditions[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(4): 438-444. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201604438 [13] 韩伟, 艾宁, 李玉宏, 等. 六盘山盆地页岩吸附气赋存条件及其影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 127-133. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901127HAN Wei, AI Ning, LI Yuhong, et al. Occurrence and controls of shale absorbed gas in Liupanshan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1): 127-133. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901127 -





 下载:
下载:

 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号