Microbial characteristics of low-amplitude structures and prediction of favorable target areas in Xinhe area, Tarim Basin
-
摘要: 对塔里木盆地新和地区油气微生物异常特征进行了研究,为该地区油气预测和油气微生物勘探技术的推广和应用提供依据。主要采用平板培养计数法、16SrRNA基因克隆文库法与高通量测序法对土壤样品中的油气微生物进行定量检测,利用这些方法研究了新和地区油气微生物种群构成及数量异常情况,构建出研究区油气区的油气微生物异常模式。以此为依据,对新和及三道桥地区低幅度圈闭线索区域的油气微生物进行检测,根据油气微生物异常特征预测油气有利区。最终识别出5个微生物异常区,并结合构造圈闭认识结果及油气微生物数量异常,优选出5个潜在的有利勘探目标区。Abstract: The Microbial Prospecting for Oil and Gas (MPOG) is an exploration method based on the seepage of light gaseous hydrocarbons from oil/gas reservoirs to the surface and their utilization by hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria. By studying the abnormal characteristics of oil and gas microorganisms in Xinhe area of the Tarim Basin, this project provides a solid scientific basis for oil and gas prediction and the validation and application of oil and gas microbial exploration technology in this area. Soil samples were collected to investigate prospects for hydrocarbon exploration. The amount of cultivable soil microorganisms in different soil samples were analyzed using the agar plating method. High-throughput sequencing has been used directly to study the composition of microbial population in soil samples. Based on the data from Xinhe area, an abnormal pattern of oil and gas microorganisms has been established. By using this pattern, five abnormal microbial areas were identified in the Xinhe and Sandaoqiao area. Combined with the results of structural traps and the abnormal number of hydrocarbon microorganisms, five potential favorable exploration target areas were identified.
-
图 2 塔里木盆地新和地区XH5井东北向采样线油藏剖面与微生物数量异常对应关系
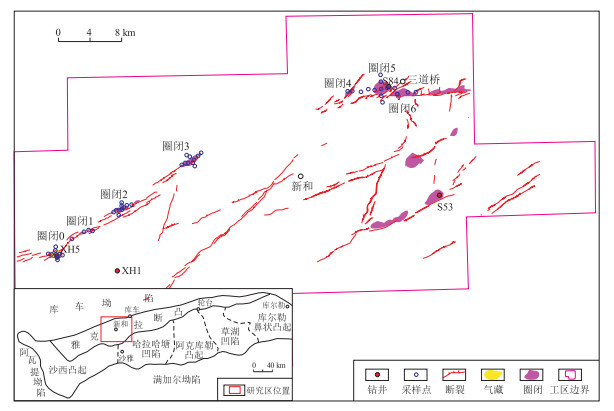
圈闭位置见图 1。
Figure 2. NE-oriented geological section crossing well XH5 in Xinhe area of Tarim Basin and correspondence with microbial quantity
表 1 塔里木盆地新和地区采样点信息
Table 1. Sample information in Xinhe area, Tarim Basin
采样点 油气成藏 圈闭(位置见图 1) 地表环境 高通量分组 1-9号 近XH5井,油气已知区 圈闭0 农田 XH-y 10~13号 油气预测区 圈闭1 沙漠 XH-s 14~18号,44~48号 油气预测区 圈闭2 沙漠 XH-s 34~43号 油气预测区 圈闭3 果树 XH-gs 19~21号 油气预测区 圈闭4 农田 XH-nt 22~30号 油气预测区 圈闭5 农田 XH-nt 31~33号 油气预测区 圈闭6 农田 XH-nt 表 2 塔里木盆地新和地区微生物异常样品点及异常值
Table 2. Abnormal sample points and abnormal values in Xinhe area, Tarim Basin
高异常样品点号 数量异常值 种群异常值 异常值总和 异常样品点号 数量异常值 种群异常值 异常值总和 11 1.025 -0.012 1.013 12 0.675 -0.025 0.650 27 1.565 -0.153 1.412 35 0.585 -0.036 0.549 40 2.145 -0.347 1.798 32 1.525 -0.824 0.701 46 1.845 -0.326 1.519 -
[1] 梅博文, 袁志华. 地质微生物技术在油气勘探开发中的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(2): 156-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200402012.htmMEI Bowen, YUAN Zhihua. Application of geo-microbiological techniques to oil and gas exploration and development[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2004, 15(2): 156-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200402012.htm [2] 梅博文, 袁志华, 王修垣. 油气微生物勘探法[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2002, 7(3): 42-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200203007.htmMEI Bowen, YUAN Zhihua, WANG Xiuyuan. Microbiological prospecting of oil and gas[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2002, 7(3): 42-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200203007.htm [3] WAGNER M, PISKE J, SMIT R. Case histories of microbial prospection for oil and gas, onshore and offshore in northwest Europe[J]. AAPG Studies in Geology No. 48 and SEG Geophysical Refe-rence Series, 2002, 11: 453-479. [4] LIEBNER S, RUBLACK K, STUEHRMANN T, et al. Diversity of aerobic methanotrophic bacteria in a permafrost active layer soil of the Lena Delta, Siberia[J]. Microbial Ecology, 2009, 57(1): 25-35. doi: 10.1007/s00248-008-9411-x [5] 吴传芝. 油气勘查中的微生物测量法[J]. 国外地质勘探技术, 1995(5): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDK199505006.htmWU Chuanzhi. Microbiological measurement in oil and gas exploration[J]. Foreign Geoexploration Technology, 1995(5): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWDK199505006.htm [6] JANEZIC G G. Biogenic light hydrocarbon production related to near-surface geochemical prospecting for petroleum[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1983, 67(3): 340-351. [7] 张春林, 庞雄奇, 梅海, 等. 微生物油气勘探技术的实践与发展[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2010, 31(3): 320-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201003037.htmZHANG Chunlin, PANG Xiongqi, MEI Hai, et al. Application and progress of microbial oil survey technique (MOST)[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2010, 31(3): 320-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201003037.htm [8] 梅廉夫, 叶加仁, 周江羽, 等. 油气勘查与评价[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2010: 61-63.MEI Lianfu, YE Jiaren, ZHOU Jiangyu, et al. Oil and gas exploration and evaluation[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geo-sciences Press, 2010: 61-63. [9] COLBY J, DALTON H. Some properties of a soluble methane mono-oxygenase from methylococcus capsulatus strain bath[J]. Biochemical Journal, 1976, 157(2): 495-497. doi: 10.1042/bj1570495 [10] 韩冰, 苏涛, 李信, 等. 甲烷氧化菌及甲烷单加氧酶的研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报, 2008, 24(9): 1511-1519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHWU200809005.htmHAN Bing, SU Tao, LI Xin, et al. Research progresses of methanotrophs and methane monooxygenases[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2008, 24(9): 1511-1519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHWU200809005.htm [11] SHENNAN J L. Utilisation of C2-C4 gaseous hydrocarbons and isoprene by microorganisms[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2006, 81(3): 237-256. [12] 肖学, 胡俊卿, 吴建平, 等. 塔里木盆地阿北顺北区块古近系油气成藏条件[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2006, 20(6): 16-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200606006.htmXIAO Xue, HU Junqing, WU Jianping, et al. Oil and gas accumulation conditions of Paleogene in Abei-Shunbei Block, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2006, 20(6): 16-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200606006.htm [13] 向廷生, 汪保卫. 油田地表土壤甲烷氧化菌的分离鉴定及活性测定[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2005, 27(2): 324-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX2005S2015.htmXIANG Tingsheng, WANG Baowei. Isolation, identification and characterization of methane oxidizing bacteria from the soil of oilfields and its activity[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2005, 27(2): 324-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX2005S2015.htm [14] 满鹏, 齐鸿雁, 呼庆, 等. 利用PCR-DGGE分析未开发油气田地表微生物群落结构[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(1): 305-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201201053.htmMAN Peng, QI Hongyan, HU Qing, et al. Microbial community structure analysis of unexploited oil and gas fields by PCR-DGGE[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(1): 305-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201201053.htm [15] RASHEED M A, LAKSHMI M, SRINU D, et al. Bacteria as indicators for finding oil and gas reservoirs: a case study of the Bikaner-Nagaur Basin, Rajasthan, India[J]. Petroleum Science, 2011, 8(3): 264-268. [16] 丁力, 吴宇兵, 刘芬芬. 中拐凸起火山岩油气藏微生物地球化学勘探研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(4): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201804005.htmDING Li, WU Yubing, LIU Fenfen. Microbiological and geochemical exploration for hydrocarbon reservoirs in volcanic rocks of Zhongguai Uplift[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(4): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201804005.htm [17] LUNDBERG D S, YOURSTONE S, MIECZKOWSKI P, et al. Practical innovations for high-throughput amplicon sequencing[J]. Nature Methods, 2013, 10(10): 999-1002. [18] LOZUPONE C, KNIGHT R. UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(12): 8228-8235. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号