The influence of water flooding multiples on reservoir micro pore structure
-
摘要: 目前针对大庆油田某区块水驱倍数对储层微观孔隙结构特征的研究还不系统,缺少岩心微观孔隙结构参数、孔渗以及矿物含量等参数随不同水驱倍数变化规律的量化研究,严重制约了对储层水驱微观机理的揭示。基于核磁共振技术和压汞相结合的方法,建立了随岩石物性变化而变化的核磁共振转换系数C值的确定方法,充分克服压汞法不能重复利用相同位置样品而造成的误差,以及核磁法不能准确确定转换系数C值的弊端。利用该方法分析了岩心在不同水驱倍数下孔径大小及岩心矿物成分的变化规律。不同物性岩心的孔隙度和渗透率随水驱倍数增加均出现不同程度的增大;岩心原始孔隙度和渗透率越大,岩心孔径增加的幅度越大。水驱后黏土含量降低,高岭石的相对含量降低幅度最大,黏土矿物变化和微粒运移是导致岩石物性和孔径变化的主要原因。Abstract: Recent research on the micro-pore structure characteristics of reservoirs during long-term water flooding in a block of the Daqing Oilfield is non-systematic and falls short on the quantitative research on the micro-pore structure parameters at different water flooding multiples. This poses a challenge for revealing the mechanism of reservoir alteration. To resolve this problem, this paper develops and presents a method, combining nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) with mercury intrusion, to determine the value of nuclear magnetic resonance conversion coefficient (C) with corresponding changes of rock physical properties. Utilizing high pressure mercury intrusion to calibrate the pore diameter by NMR overcomes the shortcomings that the samples in the same position are unable to be reused by mercury intrusion and the conversion coefficient, C value, of NMR can not be accurately determined. By the new method the core diameter and the change of core mineral composition under different water injection multiples, the porosity and permeability of all experimental cores increase to different degrees during long-term water flooding. Long term water flooding of the core increases the pore size and lowers the clay content. Furthermore, the experiments show that kaolinite is affected most. Clay mineral variation and particle migration are the main reasons for the change of rock physical properties and pore size.
-
Key words:
- water flooding /
- micro pore structure /
- pore size /
- clay /
- microscopic mechanism
-
表 1 大庆油田某区块岩心原始孔隙度和渗透率以及随注水倍数的变化
Table 1. Changes of core porosity and permeability with water injection multiples in a block of Daqing Oilfield
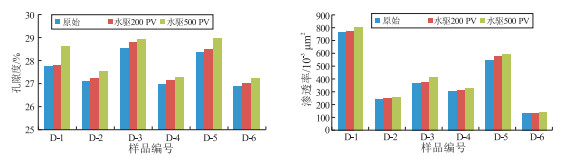
样品编号 岩性 不同注水倍数下孔隙度/% 不同注水倍数下渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 原始 200 PV 500 PV 原始 200 PV 500 PV D-1 砂岩 27.76 27.82 28.63 760.9 765.8 793.0 D-2 砂岩 27.13 27.24 27.54 241.1 249.0 256.7 D-3 砂岩 28.52 28.82 28.96 366.0 377.6 412.8 D-4 砂岩 27.01 27.16 27.31 299.2 314.1 329.0 D-5 砂岩 28.37 28.51 28.96 539.3 576.0 588.5 D-6 泥质砂岩 26.91 27.03 27.26 131.4 133.1 136.6 表 2 大庆油田某区块实验岩心的基础物性参数和矿物含量
Table 2. Basic physical parameters and mineral contents of experimental cores in a block of Daqing Oilfield
样品编号 岩性 渗透率/(10-3 μm2) 孔隙度/% 矿物含量/% 黏土矿物相对含量/% 混层比/% 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 黏土总量 伊蒙混层 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 X-1 泥质砂岩 836.2 29.36 58.0 8.2 24.9 1.1 7.9 27 9 58 6 20 X-2 砂岩 254.4 24.31 59.6 7.2 26.6 1.4 5.2 32 11 24 33 26 X-3 砂岩 380.5 26.88 56.5 8.5 27.0 1.6 6.3 15 6 75 4 28 X-4 砂岩 143.6 25.17 52.6 8.1 30.6 1.9 6.8 23 8 61 8 21 X-5 砂岩 480.7 27.35 59.6 9.4 24.9 1.7 4.3 15 7 73 5 30 X-6 泥质砂岩 123.2 25.67 50.8 7.6 31.3 1.8 8.5 41 18 24 17 21 -
[1] 王志章, 蔡毅. 开发中后期油藏参数变化规律及变化机理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1999.WANG Zhizhang, CAI Yi. The change rule and mechanism of reservoir parameters in the middle and late stage of development[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1999. [2] 吴欣松, 苏小军, 吴宗来. 注水开发过程中储层参数变化规律的测井地质评价[J]. 测井技术, 2002, 26(4): 311-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200204011.htmWU Xinsong, SU Xiaojun, WU Zonglai. Logging geology evaluation of reservoir parameter changes in water flooding production[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2002, 26(4): 311-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200204011.htm [3] 林光荣, 邵创国, 王小林. 洗油时间对低渗特低渗储层孔渗的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2005, 12(3): 86-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200503029.htmLIN Guangrong, SHAO Chuangguo, WANG Xiaolin. Impact of cleaning time on poroperm of low and extra-low permeability reservoir[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2005, 12(3): 86-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ200503029.htm [4] 陈聪, 陈容, 陈勇良, 等. 长期注水对大港油田中高渗储层物性的影响[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2012, 32(7): 125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201207118.htmCHEN Cong, CHEN Rong, CHEN Yongliang, et al. Effect of long-term water injection on physical properties of high permeability reservoirs in Dagang Oilfield[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standards and Quality, 2012, 32(7): 125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGBJ201207118.htm [5] 于靖之. 长期注水对低渗透储层物性影响的实验研究新方法[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2017, 43(6): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMSH201706046.htmYU Jingzhi. New method of experimental research on the influence of long-term water flooding on low reservoir physical pro-perties[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2017, 43(6): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMSH201706046.htm [6] 杜庆龙. 长期注水开发砂岩油田储层渗透率变化规律及微观机理[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(9): 1159-1164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201609010.htmDU Qinglong. Variation law and microscopic mechanism of permeability in sandstone reservoir during long-term water flooding deve-lopment[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(9): 1159-1164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201609010.htm [7] 胡治华, 马奎前, 刘宗宾, 等. 海上S油田注水开发后期储层物性变化规律及应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(15): 164-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201415035.htmHU Zhihua, MA Kuiqian, LIU Zongbin, et al. Research and application of the properties variation regularity of water injection reservoirs in S offshore oilfield[J]. Science Technology and Enginee-ring, 2014, 14(15): 164-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201415035.htm [8] 王博, 陈小凡, 刘峰, 等. 长期注水冲刷对储层渗透率的影响[J]. 重庆科技学院学报(自然科学版), 2011, 13(2): 37-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQSG201102013.htmWANG Bo, CHEN Xiaofan, LIU Feng, et al. Influence of long-term water flooding on reservoir permeability[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 2011, 13(2): 37-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CQSG201102013.htm [9] 陈红伟, 冯其红, 张先敏, 等. 多层非均质油藏注水开发指标预测方法[J]. 断块油气田, 2018, 25(4): 473-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201804014.htmCHEN Hongwei, FENG Qihong, ZHANG Xianmin, et al. Prediction method of waterflooding development indexes for multi-layer heterogeneous reservoir[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2018, 25(4): 473-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201804014.htm [10] 房娜, 张占女, 程明佳, 等. 基于不同裂缝发育程度下周期注水注采参数优化研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(1): 131-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901023.htmFANG Na, ZHANG Zhannü, CHENG Mingjia, et al. Injection-production parameter optimization study of cyclic water injection at different development levels of fractures[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(1): 131-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901023.htm [11] 陈蒲礼, 王烁, 王丹, 等. 恒速压汞法与常规压汞法优越性比较[J]. 新疆地质, 2013, 31(S1): 139-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI2013S1032.htmCHEN Puli, WANG Shuo, WANG Dan, et al. Comparing the constant-speed mercury injection technique with the conventional mercury injection technique[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2013, 31(S1): 139-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI2013S1032.htm [12] PRAMMER M G, DRACK E D, BOUTON J C, et al. Measurements of clay-bound water and total porosity by magnetic resonance logging[C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Denver, Colorado: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1996: 311-320. [13] VOLOKITIN Y, LOOYESTIJN W J, SLIJKERMAN W F J, et al. A practical approach to obtain primary drainage capillary pressure curves from NMR core and log data[J]. Petrophysics, 2001, 42(4): 334-343. [14] 阙洪培, 雷卞军. 核磁共振T2谱法估算毛管压力曲线综述[J]. 西南石油学院学报, 2003, 25(6): 9-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY200306002.htmQUE Hongpei, LEI Bianjun. Deriving capillary presure curves from NMR T2 spectra[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum Institute, 2003, 25(6): 9-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY200306002.htm [15] 刘堂宴, 马在田, 傅容珊. 核磁共振谱的岩石孔喉结构分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2003, 18(4): 737-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200304026.htmLIU Tangyan, MA Zaitian, FU Rongshan. Analysis of rock pore structure with NMR spectra[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2003, 18(4): 737-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200304026.htm [16] 李红南, 王德军. 油藏动态模型和剩余油仿真模型[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(5): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200605015.htmLI Hongnan, WANG Dejun. Dynamic model of oil reservoir and simulation model of remaining oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(5): 83-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200605015.htm [17] 李海波, 朱巨义, 郭和坤. 核磁共振T2谱换算孔隙半径分布方法研究[J]. 波谱学杂志, 2008, 25(2): 273-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PPXZ200802017.htmLI Haibo, ZHU Juyi, GUO Hekun. Methods for calculating pore radius distribution in rock from NMR T2 spectra[J]. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2008, 25(2): 273-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-PPXZ200802017.htm [18] 徐云林, 陈星星, 周耐强, 等. 注水对轮南油田储层微观孔隙结构影响实验研究[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2015, 11(2): 54-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201502013.htmXU Yunlin, CHEN Xingxing, ZHOU Naiqiang, et al. The experiment study on waterflooding impact for reservoir microscopic pore structure in Lunnan Oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2015, 11(2): 54-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201502013.htm [19] 文鑫, 戴宗, 王华, 等. 海相砂岩油藏长期水驱后储层物性变化规律[J]. 特种油气藏, 2017, 24(1): 157-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201701032.htmWEN Xin, DAI Zong, WANG Hua, et al. Physical properties of marine sandstone reservoir after long-term waterflooding[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2017, 24(1): 157-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201701032.htm [20] 刘明涛, 杨珊珊, 张玮, 等. 低孔低渗油藏注水开发后孔隙结构的变化研究[J]. 石化技术, 2018, 25(2): 134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJS201802103.htmLIU Mingtao, YANG Shanshan, ZHANG Wei, et al. Study on the change of pore structure after water-flood development of low porosity and permeability reservoirs[J]. Petrochemical Industry Techno-logy, 2018, 25(2): 134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJS201802103.htm -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号