Shale gas exploration potential and target of Permian Dalong Formation in northern Sichuan
-
摘要: 综合利用地质、地球物理等资料,对川北地区二叠系大隆组富有机质泥页岩的时空展布特征及基本地质条件进行研究,明确了川北地区大隆组页岩储层具有“高有机碳含量,高孔隙度,高脆性矿物含量,高含气量”的有利地质条件,勘探潜力大,有望形成川北地区新的勘探领域。一是川北地区大隆组深水陆棚有利相带发育,泥页岩厚度20~45 m,分布广泛;二是大隆组富有机质泥页岩脆性矿物含量平均为82.3%,有机碳含量平均达到8.32%,有机质类型以腐殖腐泥型为主,热演化程度(Ro)平均为2.43%,孔隙度平均为3.0%,总含气量平均为4.62 m3/t;三是研究区与控盆米仓山断裂有断洼相隔,往盆内方向保存条件好。南江地区大隆组深水陆棚相富有机质泥页岩发育,保存条件好,埋深适中(2 000~5 000 m),是近期有望实现勘探突破的最有利区。Abstract: The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and basic geological conditions of organic rich shale in the Permian Dalong Formation in northern Sichuan Basin were studied based on the comprehensive analysis of geological and geophysical data. The Dalong Formation shale reservoir in the northern Sichuan region has favorable geological conditions of "high TOC content, high porosity, high brittle mineral content, and high gas content", showing a great exploration potential. The first significant property is the development of favorable facies belts in the deep-water shelf of the Dalong Formation in the northern Sichuan, with a thickness of 20-45 m and a wide areal distribution. Secondly, the average brittle mineral content of organic rich shale in the Dalong Formation is 82.3%, the organic matter type is humic-sapropel type, the average organic carbon content is 8.32%, the average thermal evolution degree(Ro) is 2.43%, the average porosity is 3.0%, and the average total gas content is 4.62 m3/t. The third positive factor is that the study area is separated from the basin-controlled Micangshan Fault by fault depressions, and the preservation conditions in the direction of the basin are good. It is proposed that the deep-water shelf facies of the organic-rich mud shale of the Dalong Formation in Nanjiang area is well-preserved, and the burial depth is moderate (2 000-5 000 m). It is a most favorable area for exploration in the near future.
-
Key words:
- shale gas /
- exploration direction /
- Dalong Formation /
- Permian /
- northern Sichuan area
-
图 2 川北地区大隆组深水陆棚相沉积特征
a.灰黑色硅质页岩, 大隆组, 长江沟; b.灰黑色硅质页岩, 大隆组, LB1井; c.水平层理发育, 大隆组, 长江沟; d.发育黄铁矿团块, 大隆组, LB1井; e.硅质页岩, 大隆组, HB1井(单偏光); f.灰质页岩, 大隆组, HB1井(单偏光); g.硅质页岩, 含放射虫, 大隆组, 长江沟(单偏光); h.骨针, 大隆组长江沟(单偏光)
Figure 2. Sedimentary characteristics of deep water shelf facies in Dalong Formation, northern Sichuan area
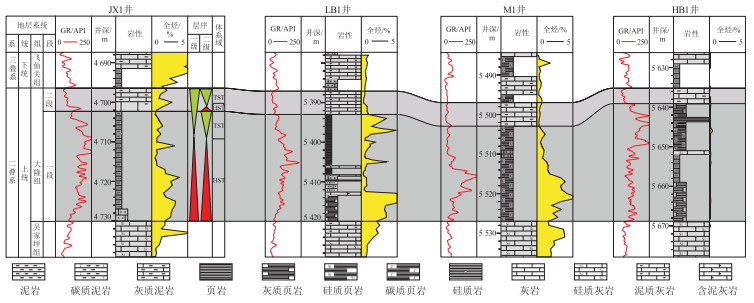
表 1 四川盆地大隆组与五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of shale gas parameters between Dalong and Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Sichuan Basin
区块 页岩层位 w(TOC)/% 有机质类型 Ro/% 孔隙度/% 硅质矿物含量/% 黏土矿物含量/% 含气量/(m3·t-1) 日产气量/104 m3 川北 大隆组 8.32 腐殖腐泥型 2.43 3.0 44.7 17.1 4.62 川东南 五峰组—龙马溪组 3.54 腐泥型 2.65 4.81 44.4 34.5 2.65 20.3(焦页1井) -
[1] 梁狄刚, 郭彤楼, 陈建平, 等. 中国南方海相生烃成藏研究的若干新进展(一): 南方四套区域性海相烃源岩的分布[J]. 海相油气地质, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200902003.htmLIANG Digang, GUO Tonglou, CHEN Jianping, et al. Some progresses on studies of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in marine sedimentary regions, Southern China (part 1): distribution of four suits of regional marine source rocks[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2008, 13(2): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200902003.htm [2] 赵培荣, 高波, 郭占峰, 等. 四川盆地上二叠统海陆过渡相和深水陆棚相页岩气的勘探潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 335-344. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003335ZHAO Peirong, GAO Bo, GUO Zhanfeng, et al. Exploration potential of marine-continental transitional and deep-water shelf shale gas in Upper Permian, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 335-344. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003335 [3] 朱洪发, 秦德余, 刘翠章. 论华南孤峰组和大隆组硅质岩成因、分布规律及其构造机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 1989, 11(4): 341-348. doi: 10.11781/sysydz198904341ZHU Hongfa, QIN Deyu, LIU Cuizhang. On the origin distributive pattern and tectonic control of siliceous rocks in Gufeng and Dalong formations, South China[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 11(4): 341-348. doi: 10.11781/sysydz198904341 [4] 胡世忠. 对孤峰组的新认识[J]. 火山地质与矿产, 2000, 21(1): 63-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ200001010.htmHU Shizhong. New consideration of Gufeng Formation by strati-graphy check up[J]. Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 2000, 21(1): 63-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ200001010.htm [5] 李平平, 郭旭升, 郝芳, 等. 四川盆地元坝气田长兴组古油藏的定量恢复及油源分析[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(3): 452-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201603011.htmLI Pingping, GUO Xusheng, HAO Fang, et al. Paleo-oil-reservoirs reconstruction and oil correlation of Changxing Formation in the Yuanba Gas Field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(3): 452-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201603011.htm [6] 郭彤楼. 元坝气田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(6): 748-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202201011.htmGUO Tonglou. Gas accumulation conditions and key exploration & development technologies in Yuanba Gas Field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(6): 748-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202201011.htm [7] 郭旭升. 南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律: 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htmGUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichment for marine shale gas in Southern China: understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htm [8] 马永生, 陈洪德, 王国力. 中国南方构造-层序岩相古地理图集(震旦纪-新近纪)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 246-278.MA Yongsheng, CHEN Hongde, WANG Guoli. Atlas of tectonic-lithofacies paleogeography in South China (Sinian-Neogene)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 246-278. [9] 李国辉, 李翔, 宋蜀筠, 等. 四川盆地二叠系三分及其意义[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2005, 28(3): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200503004.htmLI Guohui, LI Xiang, SONG Shujun, et al. Dividing Permian into 3 series and its significance in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2005, 28(3): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200503004.htm [10] 冯纯江, 张继庆, 官举铭, 等. 四川盆地上二叠统沉积相及其构造控制[J]. 岩相古地理, 1998, 34(2): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD198802000.htmFENG Chunjiang, ZHANG Jiqing, GUAN Juming, et al. The Upper Permian sedimentary facies in Sichuan Basin and their tectonic controls[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1998, 34(2): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD198802000.htm [11] 王一刚, 文应初, 张帆, 等. 川东地区上二叠统长兴组生物礁分布规律[J]. 天然气工业, 1998, 18(6): 10-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG806.002.htmWANG Yigang, WEN Yingchu, ZHANG Fan, et al. Distribution law of organic reefs in Changxing Formation of Upper Permian in East Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1998, 18(6): 10-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG806.002.htm [12] 何鲤, 罗潇, 刘莉萍, 等. 试论四川盆地晚二叠世沉积环境与礁滩分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(1): 28-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200801006.htmHE Li, LUO Xiao, LIU Liping, et al. A discussion on depositional environment in Late Permian and distribution of reef-bank in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(1): 28-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200801006.htm [13] 王一刚, 文应初, 洪海涛, 等. 四川盆地及邻区上二叠统-下三叠统海槽的深水沉积特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(5): 702-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200605022.htmWANG Yigang, WEN Yingchu, HONG Haitao, et al. Petroleum geological characteristics of deep water deposits in Upper Permian-Lower Triassic trough in Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(5): 702-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200605022.htm [14] AHR W M. The carbonate ramp: an alternative to the shelf model[J]. Transactions of the Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies, 1973, 23: 221-225. [15] 威尔逊J L. 地质历史中的碳酸盐相[M]. 冯增昭, 等, 译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1981: 17.WILSON J L. Carbonate rocks in geological history[M]. FENG Zengzhao, et al, trans. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1981: 17. [16] READ J F. Carbonate platforms of passive (extensional) continental margins: types, characteristics and evolution[J]. Tectonophysics, 1982, 81(3/4): 195-212. [17] READ J F. Carbonate platform facies models[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(1): 1-21. [18] TUCKER M E, WRIGHT V P. Carbonate sedimentology[M]. Oxford, London: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1990: 28-69. [19] 马永生, 牟传龙, 谭钦银, 等. 关于开江-梁平海槽的认识[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(3): 326-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200603005.htmMA Yongsheng, MOU Chuanlong, TAN Qinyin, et al. A discussion on Kaijiang-Liangping Ocean Trough[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(3): 326-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200603005.htm [20] 蔡雄飞, 顾松竹, 罗中杰. 陆棚环境与大陆斜坡环境的识别标志和研究意义[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2009, 25(6): 10-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200906002.htmCAI Xiongfei, GU Songzhu, LUO Zhongjie. Identification feature mark and research significance of continental shelf and slope environments[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2009, 25(6): 10-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200906002.htm [21] 蒲泊伶, 董大忠, 王凤琴, 等. 川南地区龙马溪组沉积亚相精细划分及地质意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(3): 15-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202003002.htmPU Boling, DONG Dazhong, WANG Fengqin, et al. Re-division and evolution of sedimentary subfacies of Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2020, 44(3): 15-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202003002.htm [22] 王宁, 许峰, 王喆, 等. 上扬子地台北缘下寒武统牛蹄塘组海相页岩气地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(3): 329-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202003006.htmWANG Ning, XU Feng, WANG Zhe, et al. Geological conditions and exploration potential of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation marine-facies shale gas in the northern margin of Upper Yangtze platform, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(3): 329-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX202003006.htm [23] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 魏志红, 等. 涪陵页岩气田的发现与勘探认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(3): 24-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603003.htmGUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, WEI Zhihong, et al. Discovery and exploration of Fuling Shale Gas Field[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(3): 24-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603003.htm [24] 谢邦华, 陈盛吉, 黄纯虎, 等. 米仓山山前带油气成藏地质条件分析[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2007, 30(2): 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200702003.htmXIE Banghua, CHEN Shengji, HUANG Chunhu, et al. Reservoir-forming geological conditions of Micangshan Foreland Thrust Belt[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2007, 30(2): 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200702003.htm [25] 李飞, 尚长健, 楼章华, 等. 米仓-大巴山海相地层古流体地球化学特征与油气保存[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(3): 365-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201403011.htmLI Fei, SHANG Changjian, LOU Zhanghua, et al. Geochemical characteristics of paleofluid and hydrocarbon preservation in marine strata of Micang-Daba Piedmont and its adjacent areas[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(3): 365-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201403011.htm [26] 徐旭辉, 方成名, 刘金连, 等. 中国中西部山前构造变形结构分带模式与油气[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 779-790. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906779XU Xuhui, FANG Chengming, LIU Jinlian, et al. Deformation zoning model of piedmont thrust, Western China, and its petroleum response[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 779-790. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906779 -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号