Deep thermal state and hydrocarbon accumulation potential of Cenozoic sedimentary basins in East China: a case study of Subei-South Yellow Sea basin
-
摘要: 中国东部新生代盆地有一个值得关注的现象:裂后热沉降量大小与油气资源贫富之间存在密切的相关性。为探究这一现象潜在的成因机制,探讨沉积盆地深部热地质作用与油气富集分布的相关性,以磁异常反演的居里面深度作为沉积盆地深部热状态一级约束,建立其与干酪根裂解的油气生成反应速度之间的定量关系,并以苏北—南黄海盆地为例证,揭示了沉积盆地烃源岩有机质生烃与深部热状态之间具有显著的正相关性。该认识有助于更好地理解沉积盆地构造—热体制与生烃过程,可为油气成藏规律与资源潜力评价提供研究新视角。Abstract: A remarkable phenomenon of the Cenozoic basins in East China is that there is a close correlation between the amount of post-rift thermal subsidence and the petroleum resources. In order to explore the underlying mechanism of this phenomenon and the correlation between deep thermal processes of sedimentary basins and the distribution of oil and gas resources, this paper takes the Curie interface depth estimated by the magnetic data as the first-order constraint for the deep thermal state to determine the quantitative relationship between it and the reaction rate of hydrocarbon generation from the cracking of kerogen. Moreover, the Subei-South Yellow Sea basin is an example of the outstanding positive correlation between hydrocarbon generation from source rocks and the deep thermal state, which could help to understand the tectonic-thermal system of sedimentary basin and hydrocarbon generation process, and offer a new research perspective for hydrocarbon accumulation and evaluation of petroleum potential.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary basin /
- thermal state /
- petroleum potential /
- Subei-South Yellow Sea basin /
- East China
-
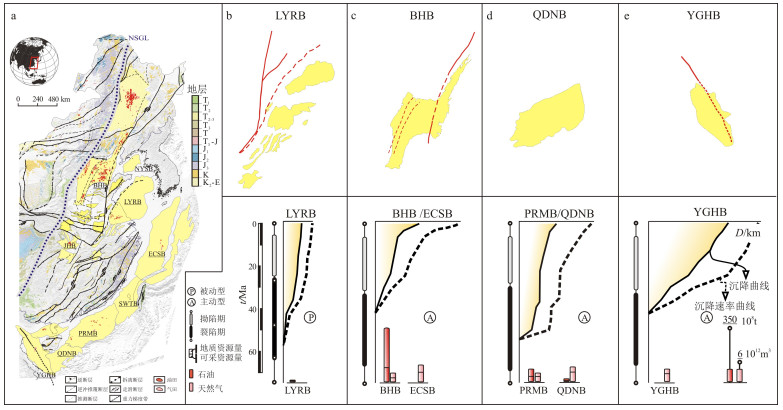
图 1 中国东部新生代沉积盆地的空间展布与油气地质特征
a.油气田分布位置[2],NSGL.重力梯度带,BHB.渤海湾盆地,NYSB.北黄海盆地,LYRB.下扬子伸展盆地,JHB.江汉盆地,ECSB.东海盆地,SWTB.台西南盆地,PRMB.珠江口盆地,QDNB.琼东南盆地,YGHB.莺歌海盆地;b.下扬子伸展盆地(苏北—南黄海);c.渤海湾盆地;d.琼东南盆地;e.莺歌海盆地[3-10]
Figure 1. Spatial distribution and petroleum geological features of Cenozoic sedimentary basins in East China
图 2 下扬子区苏北—南黄海盆地构造
构造单元注释:SKB.中朝块体;LYB.下扬子块体;SCB.华南块体;SLO.苏鲁造山带;DBO.大别造山带;JLO.九岭造山带;JNO.江南造山带;NSYSB.南黄海北部盆地;SSSYSB.苏北—南黄海南部盆地;LYFBS.下扬子断陷盆地系统;YJBS.沿江盆地群棕色区域为下扬子区新生代盆地凸起,黄色区域为下扬子区新生代伸展断陷;黑色实线为断裂单元,红色色块为油气田,彩色圆点为热流值数据点[17, 20-25]。HF为地表热流值,TOPO为地形。
Figure 2. Structural framework of Subei-South Yellow Sea basin in Lower Yangtze region
图 4 下扬子区居里面与油气田关系
a.下扬子区总磁△T异常图;b.下扬子区居里面深度数字地形图;c.下扬子区居里面深度立体阴影图;d.下扬子区居里面等值线与油气田分布图。居里面深度数据来源于李春峰等[30]
Figure 4. Correlation between Curie surface and oil-gas fields across the Lower Yangtze region
表 1 中国东部新生代盆地热状态特征与油气资源潜力[6-10]
Table 1. Thermal state and petroleum potential of Cenozoic basins in East China
盆地 烃源岩 热场 最大埋深/m 大地位置 形成机制 成因类型 勘探潜力 苏北—南黄海 湖相泥岩,0.4%<Ro < 2% 温盆 7 000 大陆内缘 侧向伸展 被动 中等油气 渤海湾 深湖盆泥岩,0.3%<Ro < 3% 热盆 10 000 大陆内缘 走滑拉分+幔隆 被动+主动 特富油气 东海 海陆过渡相泥岩,Ro>2% 热盆 18 000 大陆外缘 弧后伸展 主动 特富油气 莺歌海 海陆过渡相泥岩,Ro>4% 超热盆 17 000 大陆外缘 走滑拉分 被动+主动 特富油气 -
[1] REN Jianye, TAMAKI K, LI Sitian, et al. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic rifting and its dynamic setting in eastern China and adjacent areas[J]. Tectonophysics, 2002, 344(3/4): 175-205. [2] 朱伟林, 米立军. 中国海域含油气盆地图集[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.ZHU Weilin, MI Lijun. Atlas of oil and gas basins, China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [3] 李运振, 邓运华, 徐强, 等. 板块运动对中国近海新生代盆地沉降及充填的控制作用[J]. 现代地质, 2010, 24(4): 719-726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201004012.htmLI Yunzhen, DENG Yunhua, XU Qiang, et al. Controls of plate motions on subsidence and filled characteristics of the Cenozoic in Chinese offshore basins[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(4): 719-726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201004012.htm [4] 能源, 杨桥, 张克鑫, 等. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷晚白垩世-新生代构造沉降史分析与构造演化[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2009, 29(2): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200902003.htmNENG Yuan, YANG Qiao, ZHANG Kexin, et al. Tectonic subsidence and evolution of the Gaoyou Depression in Northern Jiangsu Basin during the Late Cretaceous to the Cenozoic[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2009, 29(2): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200902003.htm [5] 舒良树, 王博, 王良书, 等. 苏北盆地晚白垩世-新近纪原型盆地分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(4): 534-543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504009.htmSHU Liangshu, WANG Bo, WANG Liangshu, et al. Analysis of Northern Jiangsu prototype basin from Late Cretaceous to Neogene[J]. Geological of China Universities, 2005, 11(4): 534-543. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504009.htm [6] 张功成, 朱伟林, 米立军, 等. "源热共控论": 来自南海海域油气田"外油内气"环带有序分布的新认识[J]. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(5): 987-1005. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005018.htmZHANG Gongcheng, ZHU Weilin, MI Lijun, et al. The theory of hydrocarbon genernation controlled by source rock and heat from circle distribution of outside-oil fields and inside-gas fields in South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(5): 987-1005. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201005018.htm [7] 张功成, 陈国俊, 张厚和, 等. "源热共控"中国近海盆地油气田"内油外气"有序分布[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(1): 1-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201002.htmZHANG Gongcheng, CHEN Guojun, ZHANG Houhe, et al. Regular distribution of inside-oil fields and outside-gas fields controlled by source rocks and heat in China offshore basins[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(1): 1-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201002.htm [8] 张功成, 谢晓军, 王万银, 等. 中国南海含油气盆地构造类型及勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(4): 611-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201304001.htmZHANG Gongcheng, XIE Xiaojun, WANG Wanyin, et al. Tectonic types of petroliferous basins and its exploration potential in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 611-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201304001.htm [9] 徐曦, 高顺莉, 王兴建, 等. 下扬子区新生代伸展构造变形及其区域构造意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2015, 40(12): 1968-1986. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201512003.htmXU Xi, GAO Shunli, WANG Xingjian, et al. Cenozoic deformation of extensional tectonics in the Lower Yangtze region and its tectonic significance[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2015, 40(12): 1968-1986. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201512003.htm [10] 徐曦, 高顺莉. 扬子区新生代断陷盆地的构造与形成[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(6): 148-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201506013.htmXU Xi, GAO Shunli. The structure and formation of the Cenozoic fault basin in the Lower Yangtze region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(6): 148-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201506013.htm [11] 黄建军, 牛华伟. 南黄海盆地南部坳陷对冲挤压变形与拉张断陷叠加特征分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(4): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.04.003HUANG Jianjun, NIU Huawei. Superposition characterization between hedging extrusion deformation and tensile fault-depression in the Southern Depression of the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(4): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.04.003 [12] 张震, 徐春强, 郭瑞, 等. 渤海秦南凹陷新生代断裂体系与构造演化[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(2): 158-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201902006.htmZHANG Zhen, XU Chunqiang, GUO Rui, et al. Cenozoic fault system and tectonic evolution of Qinan Sag in Bohai Sea[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(2): 158-161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201902006.htm [13] 刘雨晴, 吴智平, 张杰, 等. 南海南部陆缘盆地反转构造及其油气成藏意义: 以礼乐盆地北部坳陷为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2018, 25(1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201801001.htmLIU Yuqing, WU Zhiping, ZHANG Jie, et al. Characteristics of inversion tectonic and its impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in southern continental basins of South China Sea: a case study of Northern Depression, Reed Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2018, 25(1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201801001.htm [14] 郭明刚, 朱继田, 曾小宇, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区流体势场恢复与有利区带研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(3): 36-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903007.htmGUO Mingang, ZHU Jitian, ZENG Xiaoyu, et al. Fluid potential field restoration and favorable zone optimization in the deep-water area of Southeast Hainan Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(3): 36-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903007.htm [15] 国土资源部油气资源战略研究中心. 全国油气资源动态评价(2015)[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2017.Strategic Research Center of Oil and Gas Resources, Ministry of Land and resources. National petroleum resource assessment[M]. Beijing: China Land Press, 2017. [16] SLEEP N H. Thermal effects of the formation of Atlantic continental margins by continental break up[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1971, 24(4): 325-350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1971.tb02182.x [17] 姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201608015.htmJIANG Guangzheng, GAO Peng, RAO Song, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China (4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(8): 2892-2910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201608015.htm [18] 唐晓音, 胡圣标, 张功成, 等. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地地热特征与油气富集[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(2): 572-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201402021.htmTANG Xiaoyin, HU Shengbiao, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Geothermal characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation of the northern marginal basins, South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(2): 572-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201402021.htm [19] 唐晓音, 黄少鹏, 张功成, 等. 南海北部陆缘珠江口盆地岩石圈热结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(9): 3749-3759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201809022.htmTANG Xiaoyin, HUANG Shaopeng, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Lithospheric thermal structure of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(9): 3749-3759. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201809022.htm [20] POLLAK H N, HURTER S J, JOHNSON J R. A new global heat flow compilation[D]. Michigan: Department of Geological Sciences, University of Michigan, 1991. [21] WANG Jiyang, HU Shengbiao, YANG Wencai, et al. Geothermal measurements in the pilot-boreholes of the China continental scientific drilling[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(20): 1745-1748. [22] WANG Liangshu, LIU Shaowen, XIAO Weiyong, et al. Distribution feature of terrestrial heat flow densities in the Bohai Basin, East China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(10): 857-862. [23] 胡圣标, 何丽娟, 汪集旸. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第三版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 2001, 44(5): 611-626. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201608015.htmHU Shengbiao, HE Lijuan, WANG Jiyang. Compilation of heat flow data in the China continental area (3rd edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2001, 44(5): 611-626. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201608015.htm [24] 熊亮萍, 胡圣标, 汪集旸. 中国东南地区实测热流值[J]. 地球物理学报, 1993, 36(6): 784-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199306011.htmXIONG Liangping, HU Shengbiao, WANG Jiyang. Terrestrial heat flow values in southeastern China[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 1993, 36(6): 784-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199306011.htm [25] 许薇龄, 焦荣昌, 乐俊英, 等. 东海陆架区地热研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1995, 10(2): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ502.002.htmXU Weiling, JIAO Rongchang, YUE Junying, et al. Geothermal study on the continent shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1995, 10(2): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ502.002.htm [26] 翟亚楠, 冯仁朋. 东濮凹陷前梨园地区新生代热史: 基于磷灰石裂变径迹和镜质组反射率耦合反演[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(6): 693-696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906004.htmZHAI Ya'nan, FENG Renpeng. Cenozoic thermal history in Qianliyuan area of Dongpu Sag: using apatite fission track and vitrinite reflectance coupling inversion[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(6): 693-696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201906004.htm [27] 梁刚, 甘军, 李兴, 等. 琼东南盆地浅水区与深水区烃源岩热演化差异性影响因素研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(1): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901012.htmLIANG Gang, GAN Jun, LI Xing, et al. Influential factors of thermal evolution difference of source rocks in shallow and deep water areas of southeastern Hainan Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(1): 69-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901012.htm [28] CONNARD G, COUCH R, GEMPERLE M. Analysis of aeromagnetic measurements from the Cascade Range in central Oregon[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(3): 376-390. [29] TANAKA A, OKUBO Y, MATSUBAYASHI O. Curie point depth based on spectrum analysis of the magnetic anomaly data in East and Southeast Asia[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 306(3/4): 461-470. [30] 李春峰, 陈冰, 周祖翼. 中国东部及邻近海域磁异常数据所揭示的深部构造[J]. 中国科学(D辑地球科学), 2009, 39(12): 1770-1779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200912013.htmLI Chunfeng, CHEN Bing, ZHOU Zuyi. Deep crustal structures of eastern China and adjacent seas revealed by magnetic data[J]. Science in China (Series D Earth Sciences), 2009, 52(7): 984-993. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200912013.htm [31] WANG Jian, LI Chunfeng. Curie point depths in Northeast China and their geothermal implications for the Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 163: 177-193. [32] ARTEMIEVA I M, MOONEY W D. Thermal thickness and evolution of Precambrian lithosphere: a global study[J]. Journal of Geophy-sical Research: Solid Earth, 2001, 106(B8): 16387-16414. [33] HU Shengbiao, HE Lijuan, WANG Jiyang. Heat flow in the continental area of China: a new data set[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 179(2): 407-419. [34] GOUTORBE B, POORT J, LUCAZEAU F, et al. Global heat flow trends resolved from multiple geological and geophysical proxies[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2011, 187(3): 1405-1419. [35] HASTEROK H, CHAPMAN D S. Heat production and geotherms for the continental lithosphere[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 307(1/2): 59-70. [36] MARESCHAL J C, JAUPART C. Variations of surface heat flow and lithospheric thermal structure beneath the North American craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 223(1/2): 65-77. [37] HIERONYMUS C F, GOES S. Complex cratonic seismic structure from thermal models of the lithosphere: effects of variations in deep radiogenic heating[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 180(3): 999-1012. [38] LI Chunfeng, SHI Xiaobin, ZHOU Zuyi, et al. Depths to the magnetic layer bottom in the South China Sea area and their tectonic implications[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010, 182(3): 1229-1247. [39] LI Chunfeng, WANG Jialin, ZHOU Zuyi, et al. 3D geophysical characterization of the Sulu-Dabie orogen and its environs[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2012, 192-193: 35-53. [40] LI Chunfeng. An integrated geodynamic model of the Nankai subduction zone and neighboring regions from geophysical inversion and modeling[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2011, 51(1): 64-80. [41] LI Chunfeng, WANG Jian, LIN Jian, et al. Thermal evolution of the North Atlantic lithosphere: new constraints from magnetic anomaly inversion with a fractal magnetization model[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2013, 14(12): 5078-5105. [42] XIONG Shengqing, TONG Jing, DING Yanyun, et al. Aeromagnetic data and geological structure of continental China: a review[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2016, 13(2): 227-237. [43] TISSOT B P, PELET R, UNGERER P H. Thermal history of sedimentary basins, maturation indices, and kinetics of oil and gas generation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71(12): 1445-1466. [44] 王必金, 林畅松, 陈莹, 等. 江汉盆地幕式构造运动及其演化特征[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2006, 41(2): 226-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200602023.htmWANG Bijin, LIN Changsong, CHEN Ying, et al. Episodic tectonic movement and evolutional character in Jianghan Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2006, 41(2): 226-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200602023.htm [45] 高顺莉, 徐曦, 周祖翼. 南黄海北部盆地晚白垩世以来构造变形与盆地成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(6): 924-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201506009.htmGAO Shunli, XU Xi, ZHOU Zuyi. Structural deformation and genesis of the northern sub-basin in South Yellow Sea since Late Cretaceous[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(6): 924-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201506009.htm [46] ZHU Rixiang, ZHENG Tianyu. Destruction geodynamics of the North China Craton and its Paleoproterozoic plate tectonics[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(19): 3354-3366. [47] 朱伟林, 米立军, 钟锴, 等. 油气并举再攀高峰: 中国近海2010年勘探回顾及"十二五"勘探展望[J]. 中国海上油气, 2011, 23(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201101000.htmZHU Weilin, MI Lijun, ZHONG Kai, et al. Developing simultaneously oil and gas exploration and scaling new heights again: a review of hydrocarbon exploration offshore China in 2010 and an outlook for the twelfth "Five-Year Plan"[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2011, 23(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201101000.htm [48] LIU Qiongying, HE Lijuan, CHEN Lichun. Tectono-thermal modeling of Cenozoic multiple rift episodes in the Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China and its geodynamic implications[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 107(1): 53-69. [49] DUAN Yonghong, WANG Fuyun, ZHANG Xiankang, et al. Three-dimensional crustal velocity structure model of the middle-eastern North China Craton (HBCrust1.0)[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59(7): 1477-1488. [50] 赖晓玲, 李松林, 孙译. 渤海及邻区3次7级以上地震的深部构造背景[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2007, 27(1): 31-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200701006.htmLAI Xiaoling, LI Songlin, SUN Yi. Deep tectonic background of three Ms>7.0 strong earthquakes in Bohai and its adjacent region[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2007, 27(1): 31-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB200701006.htm [51] 王巍, 陈高, 王家林, 等. 苏北南黄海盆地区域构造特征分析[J]. 地震学刊, 1999(1): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK901.007.htmWANG Wei, CHEN Gao, WANG Jialin, et al. Analysis for regional structural characteristics of North Jiangsu-South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Seismology, 1999(1): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK901.007.htm [52] 张功成, 金莉, 兰蕾, 等. "源热共控"中国油气田有序分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(5): 1-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201405001.htmZHANG Gongcheng, JIN Li, LAN Lei, et al. Analysis of the regular distribution of oil and gas fields in China based on the theory of hydrocarbon generation controlled by source rocks and geothermal heat[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(5): 1-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201405001.htm [53] 韩波, 张训华, 徐晓达. 东海磁场特征及居里面分析[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2011, 26(2): 519-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201102016.htmHAN Bo, ZHANG Xunhua, XU Xiaoda. Features of the magnetic features and the curie interface in the East China Sea[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2011, 26(2): 519-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201102016.htm [54] YUAN Yusong, ZHU Weilin, MI Lijun, et al. "Uniform geothermal gradient" and heat flow in the Qiongdongnan and Pearl River Mouth Basins of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(7): 1152-1162. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lijuan_He6/publication/232390227_Uniform_geothermal_gradient_and_heat_flow_in_the_Qiongdongnan_and_Pearl_River_Mouth_Basins_of_the_South_China_Sea/links/53f14d350cf2711e0c45d861 [55] 金博, 刘震, 李绪深, 等. 莺歌海盆地地温-地压系统特征及其对天然气成藏的意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(1): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801013.htmJIN Bo, LIU Zhen, LI Xushen, et al. Relationship between accumulation of natural gas and geotemperature-geopressure system in Yinggehai Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(1): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801013.htm [56] MAULE C F, PURUCKER M E, OLSEN N, et al. Heat flux anomalies in antarctica revealed by satellite magnetic data[J]. Science, 2005, 309(5733): 464-467. [57] 焦立果. 由卫星岩石圈磁场研究地震活动性及居里等温面反演[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所, 2014.JIAO Liguo. Study seismicity by satellite lithospheric magnetic field and curie isotherm depth inversion[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, 2014. [58] WOOD D A. Relationships between thermal maturity indices calculated using Arrhenius equation and Lopatin method: implications for petroleum exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1988, 72(2): 115-134. [59] 邱楠生, 李善鹏, 曾溅辉. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷热历史及构造-热演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2004, 78(2): 263-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402015.htmQIU Nansheng, LI Shanpeng, ZENG Jianhui. Thermal history and tectonic-thermal evolution of the Jiyang Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(2): 263-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200402015.htm [60] 刘玉瑞. 苏北盆地与南黄海盆地中-新生界成烃对比浅析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(6): 541-546. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201006541LIU Yurui. Comparison analysis of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon generation between the North Jiangsu Basin and the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(6): 541-546. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201006541 [61] 徐曦, 杨风丽, 赵文芳. 下扬子区海相中、古生界上油气成藏组合特征分析[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(4): 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201104012.htmXU Xi, YANG Fengli, ZHAO Wenfang. Analysis of characteristics of upper hydrocarbon play of Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine group, Lower Yangtze region[J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(4): 48-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201104012.htm [62] JIANG Guangzheng, HU Shengbiao, SHI Yizuo, et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China: updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019, 753: 36-48. -





 下载:
下载:



 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号