Discovery and geochemical characteristics of Chang 7 source rocks from the eastern margin of a Triassic lacustrine basin in the Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 以往对鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系主力烃源岩的研究主要集中于盆地内部的湖盆中心及其周围地区,对湖盆“边缘”特别是东缘地区的烃源岩则鲜有研究。为弥补以往研究的空白,解决鄂尔多斯盆地东缘三叠系是否发育有效烃源岩这一问题,选择七里村油田为研究区,通过岩心观察、测井曲线特征分析、地化测试分析等手段,对该油田三叠系长7段烃源岩特征进行了详细研究。七里村油田长7段烃源岩分布范围广,面积超过2 500 km2;可分为黑色泥页岩和暗色泥岩2种类型,平均厚度分别为9.2 m和28.9 m;烃源岩有机质丰度高,黑色泥页岩TOC含量平均为2.73%,可达到“最好”烃源岩标准,暗色泥岩TOC含量平均为1.98%,达到“中等—好”烃源岩标准;有机质类型总体为Ⅰ—Ⅱ1型,以生油为主;多项成熟度参数表明黑色泥页岩和暗色泥岩成熟度无明显差别,均已达到成熟,处于主要生油阶段。根据烃源岩生物标志化合物特征,分析其沉积环境为陆相淡水还原环境,且黑色泥页岩所处沉积环境还原性比暗色泥岩更强;烃源岩母质来源主要为低等水生生物,其次为陆源高等植物;暗色泥岩较黑色泥页岩有更多陆源高等植物的贡献。综合分析认为,鄂尔多斯盆地东缘七里村油田长7段烃源岩是本地区油藏的主力烃源岩,而且优质烃源岩的发现表明本区长7段页岩油和致密油也具有良好勘探前景。Abstract: Previous studies of source rocks in the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin were mainly focused on the inner part of the basin, especially on the depocenter and its surrounding areas. Few investigations have been made with regard to source rocks on the "margin" of the lacustrine basin, particularly on the eastern margin. In order to make up for the limitations of previous work and determine whether effective source rocks are developed on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin, we chose the Qilicun Oilfield in Yanchang County as our study area. The characteristics of the Chang 7 source rocks from the Qilicun Oilfield were studied through core observations, logging curve analyses and geochemical tests. The Chang 7 source rocks in the Qilicun Oilfield were widespread, with an area of over 2 500 km2. They were subdivided into two types: black shale and dark mudstone, averaging 9.2 m and 28.9 m thick, respectively. The average TOC content of the black shale is 2.73%, which is in accordance with the "best" source rock standard. The average TOC content of the dark mudstone is 1.98%, which falls into the "good" source rock category. The organic matter is of types Ⅰ-Ⅱ1, mainly generating oils. Maturity parameters show that there is no significant difference between the black shale and the dark mudstone, and both have entered the main oil generation stage. Biomarker analyses indicate that the Chang 7 source rocks were deposited in continental fresh water in a reducing environment. The black shale depositional environment was more reducing than that of the dark mudstone. The source organic matter is mainly derived from lower ranked aquatic organisms, with some higher land plants. Compared with the black shale, the dark mudstone has more contribution from terrestrial higher plants. The Chang 7 source rocks from the Qilicun Oilfield on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin is the major source rock for hydrocarbon accumulation in this area. Moreover, the discovery of good quality source rocks suggests that the Chang 7 section on the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin such as the Qilicun field has significant potential for shale oil/tight oil exploration.
-
Key words:
- source rock /
- geochemical characteristics /
- Yanchang Formation /
- Qilicun Oilfield /
- Ordos Basin
-
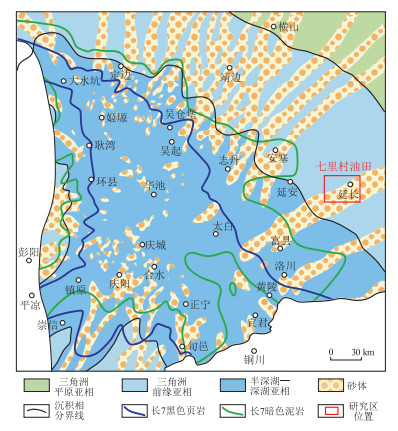
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地长7烃源岩分布及沉积环境与研究区分布位置
据参考文献[6]修改。
Figure 1. Distribution and deposition environment of Chang 7 source rocks and location of study area, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地七里村油田长7烃源岩干酪根有机显微组分、类型指数及各族组成稳定碳同位素分布
Table 1. Organic microscopic composition and types of kerogen, and stable carbon isotopes of each composition of Chang 7 source rocks in Qilicun Oilfield, Ordos Basin
井名 深度/m 层位 岩性 腐泥组/% 壳质组/% 镜质组/% 惰性组/% 类型指数 类型 δ13C/‰ 干酪根 饱和烃 芳香烃 非烃 沥青质 DT016 442.0 长72 泥岩 61.3 0 38.0 0.7 32.1 Ⅱ2 -29.45 -33.25 -32.88 -30.18 -30.66 454.2 长73 泥页岩 61.0 0 38.7 0.3 31.7 Ⅱ2 -29.58 -33.77 -32.94 -30.90 -31.03 456.5 长73 泥页岩 57.3 0 36.7 0.3 25.3 Ⅱ2 -28.30 -32.60 -32.26 -29.58 -29.45 462.0 长73 泥岩 54.7 0 45.0 0.3 20.7 Ⅱ2 -29.27 -32.48 -32.60 -30.20 -29.89 Z085 522.8 长72 泥岩 62.3 0 37.7 0 34.0 Ⅱ2 -29.46 -32.49 -29.97 -29.39 -28.36 524.7 长72 泥岩 58.0 0 42.0 0 26.5 Ⅱ2 -29.56 -32.15 -29.92 -29.82 -29.57 526.4 长72 泥岩 56.3 0 43.7 0 23.5 Ⅱ2 -30.48 -33.27 -30.48 -29.83 -29.59 527.6 长72 泥岩 43.7 0 56.3 0 1.5 Ⅱ2 -29.54 -33.21 -30.27 -29.47 -29.57 530.2 长72 泥岩 58.0 0 42.0 0 26.5 Ⅱ2 -30.26 -31.50 -28.08 -28.14 -28.31 533.9 长73 泥页岩 64.0 0 35.7 0.3 36.9 Ⅱ2 -30.02 -32.73 -32.97 -30.90 -30.76 535.0 长73 泥页岩 57.3 0 42.3 0.3 25.3 Ⅱ2 -29.20 -33.50 -32.85 -30.28 -30.63 537.7 长73 泥页岩 62.0 0 37.7 0.3 33.4 Ⅱ2 -29.71 -32.94 -32.77 -30.63 -31.12 540.9 长73 泥页岩 65.7 0 34.3 0 40.0 Ⅱ1 -31.86 -32.31 -32.50 -30.64 -31.12 543.2 长73 泥页岩 69.0 0 31.0 0 45.8 Ⅱ1 -29.55 -31.08 -30.84 -29.72 -29.88 546.7 长73 泥岩 64.7 0 35.3 0 38.2 Ⅱ2 -28.84 -30.96 -30.59 -29.73 -29.36 554.8 长73 泥岩 63.7 0 36.3 0 36.5 Ⅱ2 -27.78 -29.80 -28.31 -28.29 -27.48 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地七里村油田长7烃源岩饱和烃色谱及主要生物标志化合物特征
Table 2. Saturated hydrocarbon chromatography and main biomarker compound characteristics of Chang 7 source rocks in Qilicun Oilfield, Ordos Basin
井名 深度/m 层位 岩性 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N DT016 442.0 长72 泥岩 1.95 0.25 0.11 1.82 0.76 1.05 0.95 C20 6.17 0.32 0.51 0.38 0.39 0.40 454.2 长73 泥页岩 1.76 0.21 0.11 1.76 0.84 1.04 1.05 C19 3.12 0.32 0.52 0.60 0.51 0.46 456.5 长73 泥页岩 1.67 0.42 0.2 1.22 0.53 1.04 1.09 C19 4.00 0.15 0.57 0.50 0.59 0.42 462.0 长73 泥岩 1.96 0.38 0.16 1.53 0.67 1.05 1.01 C19 3.64 0.28 0.54 0.55 0.53 0.45 Z085 522.8 长72 泥岩 0.65 0.36 0.32 2.81 0.56 1.26 1.47 C23 2.96 0.19 0.51 0.61 0.60 0.46 524.7 长72 泥岩 1.61 0.36 0.18 2.11 0.84 1.08 1.14 C20 0.71 0.11 0.53 0.11 0.16 0.43 526.4 长72 泥岩 2.18 0.47 0.17 1.9 0.78 1.05 1.10 C19 7.23 0.23 0.49 0.60 0.50 0.64 527.6 长72 泥岩 1.77 0.34 0.15 1.78 0.65 1.03 1.10 C21 3.77 0.18 0.53 0.48 0.65 0.33 530.2 长72 泥岩 1.42 0.67 0.28 3.49 0.85 1.08 1.14 C19 5.12 0.12 0.53 0.35 0.43 0.21 533.9 长73 泥页岩 1.66 0.20 0.11 1.94 0.88 1.06 1.09 C19 0.77 0.08 0.57 0.40 0.64 0.45 535.0 长73 泥页岩 1.25 0.17 0.10 2.16 1.06 1.07 1.11 C19 6.35 0.24 0.47 0.63 0.55 0.50 537.7 长73 泥页岩 1.74 0.21 0.11 1.84 0.77 1.07 1.11 C19 6.65 0.22 0.48 0.61 0.61 0.45 540.9 长73 泥页岩 1.83 0.24 0.12 1.48 0.73 1.07 1.07 C19 5.49 0.23 0.48 0.50 0.28 0.55 543.2 长73 泥页岩 1.92 0.30 0.13 2.07 0.85 1.02 1.10 C19 3.39 0.28 0.48 0.62 0.62 0.46 546.7 长73 泥岩 1.82 0.29 0.14 1.73 0.81 1.06 0.96 C19 5.12 0.26 0.49 0.68 0.68 0.38 554.8 长73 泥岩 2.82 1.41 0.34 2.98 1 1.05 1.09 C19 0.60 0.07 0.55 0.48 0.50 0.59 平均值 1.77 0.39 0.17 2.04 0.79 1.07 1.10 4.07 0.20 0.52 0.51 0.52 0.45 注:A.Pr/Ph;B.Pr/nC17;C.Ph/nC18;D.(C21+C22)/(C28+C29);E.∑C21-/∑C22+;F.OEP;G.CPI;H.主峰碳数;I.Ts/Tm;J.伽马蜡烷指数;K.C31藿烷22S/(22S+22R);L.重排甾烷/规则甾烷;M.αααC29甾烷20S/(20S+20R);N.C29甾烷ββ/(ββ+αα)。 -
[1] 刘显阳, 惠潇, 李士祥. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界低渗透岩性油藏形成规律综述[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(5): 964-974. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2012.05.007LIU Xianyang, HUI Xiao, LI Shixiang. Summary of formation rule for low permeability lithologic reservoir of Mesozoic in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(5): 964-974. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2012.05.007 [2] 赵靖舟, 白玉彬, 曹青, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地准连续型低渗透-致密砂岩大油田成藏模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(6): 811-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201206000.htmZHAO Jingzhou, BAI Yubin, CAO Qing, et al. Quasi-continuous hydrocarbon accumulation: a new pattern for large tight sand oilfields in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(6): 811-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201206000.htm [3] 杨华, 张文正. 论鄂尔多斯盆地长7段优质油源岩在低渗透油气成藏富集中的主导作用: 地质地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(2): 147-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200502006.htmYANG Hua, ZHANG Wenzheng. Leading effect of the seventh member high-quality source rock of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin during the enrichment of low-penetrating oil-gas accumulation: geology and geochemistry[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(2): 147-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200502006.htm [4] 赵靖舟, 付金华, 曹青, 等. 致密油气成藏理论与评价技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2017.ZHAO Jingzhou, FU Jinhua, CAO Qing, et al. Tight oil and gas accumulation: geological theories and evaluation technologies[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Press, 2017. [5] 张文正, 杨华, 李剑锋, 等. 论鄂尔多斯盆地长7段优质油源岩在低渗透油气成藏富集中的主导作用: 强生排烃特征及机理分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(3): 289-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200603005.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, LI Jianfeng, et al. Leading effect of high-class source rock of Chang 7 in Ordos Basin on enrichment of low permeability oil-gas accumulation: hydrocarbon generation and expulsion mechanism[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(3): 289-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200603005.htm [6] 杨华, 牛小兵, 徐黎明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htmYANG Hua, NIU Xiaobing, XU Liming, et al. Exploration potential of shale oil in Chang 7 Member, Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2016, 43(4): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htm [7] 张文正, 杨华, 杨奕华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩的岩石学、元素地球化学特征及发育环境[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.01.008ZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, YANG Yihua, et al. Petrology and element geochemistry and development environment of Yanchang Formation Chang-7 high quality source rocks in Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.01.008 [8] 郭彦如, 刘俊榜, 杨华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组低渗透致密岩性油藏成藏机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 417-425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201204005.htmGUO Yanru, LIU Junbang, YANG Hua, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism of low permeable tight lithologic oil reservoirs in the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 417-425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201204005.htm [9] 楚美娟, 李士祥, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长8油层组石油成藏机理及成藏模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(4): 683-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201304016.htmCHU Meijuan, LI Shixiang, LIU Xianyang, et al. Accumulation mechanisms and modes of Yanchang Formation Chang 8 interval hydrocarbons in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(4): 683-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201304016.htm [10] 付金华. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油勘探理论与技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.FU Jinhua. Theory and technology of tight oil exploration in Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. [11] PASSEY Q R, CREANEY S, KULLA J B, et al. A practical model for organic richness from porosity and resistivity logs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(12): 1777-1794. [12] 王贵文, 朱振宇, 朱广宇. 烃源岩测井识别与评价方法研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(4): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200204015.htmWANG Guiwen, ZHU Zhenyu, ZHU Guangyu. Logging identification and evaluation of Cambrian-Ordovician source rocks in syneclise of Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2002, 29(4): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200204015.htm [13] 中国石油天然气总公司. SY/T 5735-1995, 陆相烃源岩地球化学评价方法[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1995.China National Petroleum Corporation. SY/T 5735-1995, geochemical evaluation of terrestrial source rock[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1995. [14] 卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010.LU Shuangfang, ZHANG Min. Oil and gas geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010. [15] 黄第藩, 李晋超. 干酪根类型划分的X图解[J]. 地球化学, 1982(1): 21-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198201002.htmHUANG Difan, LI Jinchao. X-diagram of kerogen classification and the characters of kerogen of standard humic type[J]. Geochimica, 1982(1): 21-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX198201002.htm [16] 邬立言, 顾信章. 热解技术在我国生油岩研究中的应用[J]. 石油学报, 1986, 7(2): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB198602002.htmWU Liyan, GU Xinzhang. The application of pyrolysis technique in source rocks research[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1986, 7(2): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB198602002.htm [17] 杨伟伟, 石玉江, 李剑峰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华池地区X96井长7烃源岩地球化学特征及其对致密油成藏的意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(1): 115-125.YANG Weiwei, SHI Yujiang, LI Jianfeng, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Chang-7 source rocks from well X96 in Huachi area of Ordos Basin and their significance on tight oil accumulation[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2016, 38(1): 115-125. [18] 陈建渝, 郝芳. 有机岩石学研究有机质类型和成熟度的改进[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(4): 426-431. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004426CHEN Jianyu, HAO Fang. Improvement on study of organic types and maturation with organic petrology[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1990, 12(4): 426-431. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199004426 [19] 王强, 付晓文, 徐志明, 等. 稳定碳同位素在油气地球化学中的应用及存在的问题[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(2): 233-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200502021.htmWANG Qiang, FU Xiaowen, XU Zhiming, et al. Development and application of stable carbon iostopes in natural gas and oil geochemistry[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(2): 233-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200502021.htm [20] 胡见义, 黄第藩, 徐树宝, 等. 中国陆相石油地质理论基础[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1991.HU Jianyi, HUNG Difan, XU Shubao, et al. The foundation of China continental petroleum geology theory[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1991. [21] 侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.HOU Dujie, FENG Zihui. Oil and gas geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011. [22] JARVIE D M, HILL R J, RUBLE T E, et al. Unconventional shale-gas systems: the Mississippian Barnett shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 475-499. [23] 唐建云, 王志维, 也尔哈那提·黑扎提, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地旬邑探区延长组烃源岩及原油地球化学特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(2): 107-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201702013.htmTANG Jianyun, WANG Zhiwei, YEERHANATI Heizhati, et al. Source rocks and geochemical characteristics of crude oil of the Yanchang Formation in Xunyi exploration area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(2): 107-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201702013.htm [24] PHILIPPI G T. The influence of marine and terrestrial source material on the composition of petroleum[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1974, 38(6): 947-966. [25] 程鹏, 肖贤明, 田辉, 等. 成熟度对陆相烃源岩可溶有机质Pr/Ph比值的影响[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1): 182-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401021.htmCHENG Peng, XIAO Xianming, TIAN Hui, et al. Effects of maturity on the Pr/Ph ratio of the soluble organic matters in the terrestrial source rocks[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 182-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401021.htm [26] 孙林, 李剑锋, 姬鹏程, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘上古生界泥岩饱和烃Pr/Ph值特征及其地质应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(6): 1116-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201206019.htmSUN Lin, LI Jianfeng, JI Pengcheng, et al. Pr/Ph value of saturated hydrocarbon from the Upper Paleozoic mudstone in western Ordos Basin and its applications[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(6): 1116-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201206019.htm [27] 朱扬明, 钟荣春, 蔡勋育, 等. 川中侏罗系原油重排藿烷类化合物的组成及成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(3): 253-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200703003.htmZHU Yangming, ZHONG Rongchun, CAI Xunyu, et al. Composition and origin approach of rearranged hopanes in Jurassic oils of central Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2007, 36(3): 253-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200703003.htm [28] 鲁银涛, 栾锡武, 史卜庆, 等. 加里曼丹岛库泰盆地海相成藏组合特征及油气富集区分带性分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(1): 38-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX201901004.htmLU Yintao, LUAN Xiwu, SHI Boqing, et al. Characteristics of Lower Miocene marine petroleum play and prospective petroleum accumulation region in the Kutei Basin, the Kalimantan Island[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(1): 38-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYKX201901004.htm [29] 张立平, 黄第藩, 廖志勤. 伽马蜡烷: 水体分层的地球化学标志[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htmZHANG Liping, HUANG Difan, LIAO Zhiqin. Gammacerane: geochemical indicator of water column stratification[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htm [30] SEIFERT W K, MOLDOWAN J M. The effect of thermal stress on source-rock quality as measured by hopane stereochemistry[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 1980, 12: 229-237. [31] 张海, 雷华伟, 张涛, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地靖边油田西部延9原油地球化学特征与油源[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(6): 836-842. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201806836ZHANG Hai, LEI Huawei, ZHANG Tao, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Yan 9 crude oil and oil-source correlation in western Jingbian Oil Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(6): 836-842. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201806836 [32] SEIFERT W K, MOLDOWAN J M. Methods in geochemistry and geophysics[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1986. [33] 唐建云, 史政, 宋红霞, 等. 富黄探区延长组烃源岩评价与油源对比[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 38(3): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201603002.htmTANG Jianyun, SHI Zheng, SONG Hongxia, et al. Hydrocarbon source evaluation and oil source contrast of the Yanchang Formation in Fu-Huang Exploration area, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 38(3): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201603002.htm [34] 白玉彬, 赵靖舟, 高振东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杏子川油田长9烃源岩特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(4): 38-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201304007.htmBAI Yubin, ZHAO Jingzhou, GAO Zhendong, et al. Characteristics of Chang 9 member source rocks and its significance of hydrocarbon exploration in Xingzichuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2013, 37(4): 38-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201304007.htm [35] 朱扬明, 张春明, 张敏, 等. 沉积环境的氧化还原性对重排甾烷形成的作用[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(4): 104-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB704.017.htmZHU Yangming, ZHANG Chunming, ZHANG Min, et al. The effect of oxidation reduction nature of depositional environments on the formation of diasteranes[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(4): 104-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB704.017.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号