Hypothesis of organic-inorganic coupling causes for petroleum generation and its significance
-
摘要: 明确油气的成因及其分布具有重要的理论与现实意义。针对目前石油成因研究中的关键科学问题,以全球构造学、石油地质学的一般原理为指导,对各种石油成因假说进行梳理、融合和集成创新,形成了石油的双机(有机—无机)耦合成因假说框架。其主要观点是,石油(或天然气)是一种多成因的可再生资源,储量巨大。石油的形成与分布是盆地与地幔隆起、深部流体与浅部流体、有机生烃机制与无机生烃机制、深大断裂与封盖条件4对成烃成藏要素相互耦合的结果。双机耦合程度越好,油气越丰富。盆地及其基底以下区域是耦合程度最好的领域,其次是盆地周边区域封盖条件较好的深大断裂发育区;深大断裂与封盖条件的匹配是控制油气聚集的重要因素;长期、多期或近期活跃的深大断裂发育区封盖条件好的大型圈闭,是最可能取得重大勘探突破的区域。Abstract: It has important theoretical and practical significance to clarify the causes and distribution of oil and gas. This paper focused on the key scientific issues in the current petroleum genesis research, guided by the general principles of global tectonics and petroleum geology. Various petroleum genesis hypotheses have been sorted out, merged, integrated and innovated, thus a hypothesis framework of organic-inorganic coupling causes for petroleum was introduced. The main factors are that oil (including natural gas) is a renewable resource with multiple origins and has huge reserves. The formation and distribution of petroleum is the result of the coupling of four pairs of hydrocarbon-forming factors, including basin and mantle uplift, deep and shallow fluids, organic and inorganic hydrocarbon generation mechanisms, deep faults and sealing conditions. The higher degree of organic-inorganic cause coupling indicates the richer the oil and gas. The basin and the area below its basement are the locations with the best degree of coupling, followed by the deep and large fault development areas with good sealing conditions in the surrounding areas of the basin. The matching of deep and large faults with sealing conditions is an important factor constraining hydrocarbon accumulation. Large-scale traps with good sealing conditions in long-term, multi-period or recent active deep and large fault development areas are the most favorable targets for major exploration successes.
-
Key words:
- petroleum /
- organic cause /
- inorganic cause /
- organic-inorganic coupling causes /
- hypothesis /
- exploration concept
-
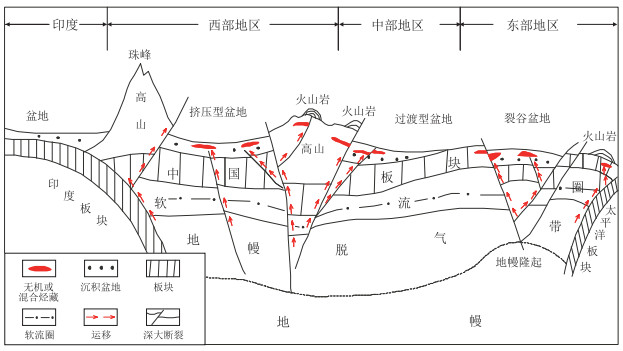
图 3 中国大陆、近海油气盆地与深大断裂、无机烃藏预测示意
据参考文献[51]修改。
Figure 3. Prediction of oil and gas basins and deep faults and inorganic hydrocarbon reservoirs in mainland and offshore of China
学派 主要人物 学说 核心观点 时间 无机成因说 门捷列夫[2] 碳化铁生烃说 石油是地下深处的重金属碳化物与下渗水相互作用生成的 1876 索可洛夫[3] 宇宙说 随着地球不断冷却,地球诞生时被吸收的碳氢化合物逐渐冷凝埋藏在地壳中形成石油 1889 沃里沃夫斯基[3] 费—托合成说 地幔脱气生成的CO2、CO、H2沿玄武岩的破裂带上升到超基性的蛇纹岩带,发生著名的费—托合成反应,形成烃类 1930 库得梁采夫[4-5] 岩浆成因说 石油是基性岩浆在冷却过程中C、H元素在高温高压条件下合成的碳氢化合物 1949 ROBINSON[6] 费—托合成说 地球上原始石油可能是在20亿年前通过费—托合成反应而生成 1963 耶兰斯基[6] 蛇纹石化成油理论 蛇纹石化作用多发生在地壳深部的坳陷,蛇纹石化生成的油气沿裂隙升入沉积岩中形成油藏 1966 GOLD[7] 地幔脱气说 在地球深部存在大量甲烷,这些气体可通过断裂、火山活动得到释放,在断裂附近形成无机成因的油气藏 1982 杜乐天[8-9] 烃碱幔汁说 烃碱幔汁流体是HACONS流体,油气是由“幔汁”从地球深部带来的。幔汁中的C-H系统才是油气的主要来源 1988 李扬鉴[9] 大陆层控构造理论 严重缺氢的干酪根演变成氢含量非常丰富的烃,氢来自地球深部,干酪根生烃的主要能量也来自地球深部 1996 罗群[10] 深大断裂说 断裂输导地幔脱气带各类成因的无机烃向上运移,并聚集在沿深大断裂带分布的各类圈闭中形成无机烃藏 1998 刘先志[11] 地下放电放光说 石油、天然气是地下无机物因地下放电放光合成形成的 2006 徐晓宁[12] 二氧化碳基源学说 高温高压下,CO2能够很容易地与H2反应,生成CH4 2012 张景廉[5, 13] 油气深部起源说 在传统干酪根晚期降解生烃学说划定的油气“经济死亡线”以下(地球深部),油气仍有很高的热力学稳定性 2013 周宁超[14] 成因模式说 提出了3种无机成因油气成因模式:“缺花岗岩”型盆地油气模式、板块俯冲带油气模式和洋中脊热液油气模式 2014 虞震东[15] 地下核燃烧学 地下核燃烧导致碳元素和地下水自动发生化学反应,生成大量的碳氢氧化合物 2016 崔永强[9] 幔源油气理论 以烃类为主的挥发分和以钾钠为主的碱金属两大类组分构成了地幔烃碱流体;烃类组分进入圈闭形成油气藏 2017 有机成因说 罗蒙诺索夫[1, 3, 16] 蒸馏说 石油是煤在地热作用下干馏产生的 1763 美国学者[4] 海相生油说 石油都形成于海相地层中,由动物、植物死亡后的遗体经过高温高压作用形成的 19世纪 潘钟祥等[4, 17] 陆相生油说 石油可以在淡水沉积物中生成,陆相生油是多期次的,而且可能形成油田 1941 二元—多元成因说 罗志立[18] 地裂运动控烃说 地裂盆地可以富集由有机物质演化而成的油气,也可以接纳无机成因的深层油气资源 1991 何志高[19] 二元碳酸盐决定论 湿封闭体系微生物和碳酸盐主导生油,没有碳酸盐古物源沉积物的任何沉积盆地都不可能有石油 2000 陈发亮[20] 二元—元素循环说 石油和天然气只是元素循环过程中的一种中间产物,其生成是多方面的而没有一个统一的模式 2001 滕吉文[21] 双机混合成因说 承认在以有机物成油为主体的前提下,无机物亦可生成部分石油 2017 郭占谦[7] 多元成因说 石油、天然气的生成具有一次性与可再生的两种属性;有机生烃、无机生烃与混合生烃3种机制 2008 表 2 石油无机成因论与有机成因论的主要证据与缺陷
Table 2. Main evidences and defects of inorganic and organic cause theories for petroleum
无机成因论 有机成因论 证据 缺陷 证据 缺陷 (1)不含生物的地层或盆地外地层中也能找到石油。
(2)油气和热液矿床共处于统一的共生序列中。
(3)现代火山活动有大量烃类物质喷出。
(4)实验室用无机物模拟出了石油(费—托合成烃实验)。
(5)许多天体中存在碳氢化合物(1)不能直接指导油气勘探。
(2)多以化学反应结果为依据,缺少实际地质材料。
(3)在中国还没有发现一个商业无机成因油气藏。
(4)学说繁多,大多相互割裂,甚至矛盾,不统一。
(5)不能解释石油中含大量生物标志化合物(1)99%油气藏都存在于沉积盆地之中。
(2)99%油气藏都是通过有机成因论指导找到的。
(3)石油中含有生物标记化合物,有旋光性。
(4)干酪根热模拟实验获得烃类物质(1)不能解释巨量石油的来源,与生物数量不匹配。
(2)不能解释严重缺氢的干酪根演变成氢含量非常丰富的烃,氢从何来?
(3)有些陨石中的石油也发现含有生物标记化合物,有旋光性。
(4)干酪根生烃热解模拟实验的热解产物在组成上与天然原油、天然气的组成差异很大。
(5)不能解释镜质体反射率Ro值为3.0%、温度超过300 ℃时,仍有液态烃的存在 -
[1] 李祖刚. 石油成因研究中的辩证法[J]. 华东石油学院学报(社会科学版), 1987(1): 40-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSK198701014.htmLI Zugang. Dialectics in the study of petroleum genesis[J]. Journal of East China Petroleum Institute (Social Science Edition), 1987(1): 40-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSK198701014.htm [2] 邵丽英. 门捷列夫的石油无机成因学说及其现代影响[J]. 西安石油大学学报(社会科学版), 2015, 24(6): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASS201506004.htmSHAO Liying. Medeleev's petroleum inorganic cause theory and its modern influence[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Social Science Edition), 2015, 24(6): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASS201506004.htm [3] 密洛诺夫C И, 李祖刚. 石油成因研究中的辩证法[J]. 科学通报, 1952(9): 618-624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSK198701014.htmMILONOV C И, LI Zugang. dialectics in the study of petroleum genesis[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1952(9): 618-624. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSK198701014.htm [4] 王大锐. "石油无机成因"说立足未稳[J]. 石油知识, 2014(4): 4-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZS201404002.htmWANG Darui. "Petroleum inorganic cause" said the foothold is not stable[J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2014(4): 4-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZS201404002.htm [5] 张景廉, 李相博, 刘化清. "石油无机成因说"的理论与实践[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 28(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201301002.htmZHANG Jinglian, LI Xiangbo, LIU Huaqing. Theory and practice of petroleum inorganic origin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 28(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201301002.htm [6] SZATMARI P, 陈德卿. 板块构造中的费-特合成法石油生成假说[J]. 地质科学译丛, 1990, 7(3): 51-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB199003013.htmSZATMARI P, CHEN Deqing. Petroleum formation by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in plate tectonics[J]. Journal of Geoscience Translations, 1990, 7(3): 51-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB199003013.htm [7] 郭占谦. 论石油与天然气的多元成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2008, 29(6): 768-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200806034.htmGUO Zhanqian. On multifactor origin of crude oil and natural gas[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2008, 29(6): 768-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200806034.htm [8] 杜乐天. 新地球科学原理导论[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 2017: 259-285.DU Letian. Introduction to novel geoscience principles[M]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 2017: 259-285. [9] 崔永强, 陈丹江. 幔源油气理论, 打开石油开发新天地[J]. 中国石油和化工, 2017(5): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYFG201705016.htmCUI Yongqiang, CHEN Danjiang. Mantle-derived oil and gas theory opens up a new world of oil development[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Industry, 2017(5): 41-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYFG201705016.htm [10] 罗群, 白新华. 断裂控烃理论与实践: 断裂活动与油气聚集研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1998: 86-89.LUO Qun, BAI Xinhua. The theory and practice of fault controlling hydrocarbon-fault activity and hydrocarbon accumulation[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1998: 86-89. [11] 刘先志. 石油、天然气、金刚石地下放电放光成因说[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2006, 27(1): 121-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200601034.htmLIU Xianzhi. Hypotheses of origins of oil, natural gas and diamond by underground discharge/radiation[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geo-logy, 2006, 27(1): 121-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200601034.htm [12] 徐晓宁. 关于石油、天然气和煤炭的成因机理的探讨[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2012, 2(2): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201202017.htmXU Xiaoning. Discussion about the formation mechanism of petro-leum, natural gas and coal[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2012, 2(2): 76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201202017.htm [13] 张景廉, 朱炳泉, 陈义贤, 等. 辽河断陷石油无机成因的地球化学证据[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(3): 192-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199903001.htmZHANG Jinglian, ZHU Bingquan, CHEN Yixian, et al. Geochemical evidences of inorganic origin for oils in Liaohe Faulted Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999, 20(3): 192-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199903001.htm [14] 周宁超, 南云. 无机成因油气的成因模式和鉴别特征研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 11(26): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201426013.htmZHOU Ningchao, NAN Yun. On the genetic mode and identification characteristics of inorganic oil and gas[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 11(26): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201426013.htm [15] 虞震东. 煤的无机成因学说: 兼论石油天然气和油页岩的成因[J]. 前沿科学, 2016, 10(3): 33-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QYKX201603005.htmYU Zhendong. Inorganic theory of coal origin also review the origins of petroleum, natural gas and oil shale[J]. Frontier Science, 2016, 10(3): 33-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QYKX201603005.htm [16] КАГРАМАНОВ Ю Р, ЕГИКЯН А Г. 论石油成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2002, 23(3): 265-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200203031.htmКАГРАМАНОВ Ю Р, ЕГИКЯН А Г. On petroleum origin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2002, 23(3): 265-269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200203031.htm [17] 王晓玲, 房乃珍, 陈娟, 等. 大庆油田无机成因油气藏的生成及勘探前景[J]. 西安石油大学学报(社会科学版), 2017, 26(4): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASS201704004.htmWANG Xiaoling, FANG Naizhen, CHEN Juan, et al. The generation of inorganic origin reservoir and its exploration prospects in Daqing oilfield[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Social Science Edition), 2017, 26(4): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASS201704004.htm [18] 罗志立. 地裂运动与中国油气分布[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1991: 22-58.LUO Zhili. Taphrogeny and distribution of oil and gas reservoir in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1991: 22-58. [19] 何志高. 关于石油成因理论发展历史若干问题的思考与评论[J]. 海相油气地质, 2000, 5(3/4): 118-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ2000Z2036.htmHE Zhigao. Thinking and commenting on several issues in the history of petroleum genesis theory[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2000, 5(3/4): 118-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ2000Z2036.htm [20] 陈发亮, 邓国振, 禹金营. 对石油与天然气成因的思考[J]. 断块油气田, 2001, 8(3): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200103002.htmCHEN Faliang, DENG Guozhen, YU Jinying. A consideration to the origin of petroleum and natural gas[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2001, 8(3): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200103002.htm [21] 滕吉文, 刘有山, 乔勇虎. 石油双机(有机+无机)混合成因的研究与探索[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(5): 1874-1892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201705022.htmTENG Jiwen, LIU Youshan, QIAO Yonghu. Study and exploration of the mixed-origin theories of organic and inorganic oil and gas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(5): 1874-1892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201705022.htm [22] HAZEN R M, SCHIFFRIES C M. Why deep carbon?[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2013, 75(1): 1-6. [23] JIN Zhijun, ZHANG Liuping, YANG Lei, et al. A preliminary study of mantle-derived fluids and their effects on oil/gas gene-ration in sedimentary basins[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2004, 41(1/3): 45-55. [24] LIU Quanyou, DAI Jinxing, JIN Zhijun, et al. Abnormal carbon and hydrogen isotopes of alkane gases from the Qingshen gas field, Songliao Basin, China, suggesting abiogenic alkanes?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 115: 285-297. [25] LIU Quanyou, ZHU Dongya, JIN Zhijun, et al. Effects of deep CO2 on petroleum and thermal alteration: the case of the Huangqiao oil and gas field[J]. Chemical Geology, 2017, 469: 214-229. [26] ZHU Dongya, LIU Quanyou, JIN Zhijun, et al. Effects of deep fluids on hydrocarbon generation and accumulation in Chinese petroliferous basins[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(1): 301-319. [27] DUAN Zhenhao, MØLLER N, WEARE J H. Molecular dynamics simulation of PVT properties of geological fluids and a general equation of state of nonpolar and weakly polar gases up to 2000 k and 20, 000 bar[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(10): 3839-3845. [28] DEMAISON G J, MOORE G T. Environment and oil source bed genesis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1979, 2: 9-31. [29] DUAN Zhenhao, MØLLER N, WEARE J H. A general equation of state for supercritical fluid mixtures and molecular dynamics simulation of mixture PVTX properties[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(7): 1209-1216. [30] JACQUEMYN C, EL DESOUKY H, HUNT D, et al. Dolomitization of the Latemar platform: fluid flow and dolomite evolution[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2014, 55: 43-67. [31] PAN Changchun, YU Linping, LIU Jinzhong, et al. Chemical and carbon isotopic fractionations of gaseous hydrocarbons during abiogenic oxidation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 246(1/2): 70-89. [32] PUEYO J J, SÁEZ A, GIRALT S, et al. Carbonate and organic matter sedimentation and isotopic signatures in lake Chungará, Chilean Altiplano, during the last 12.3 kyr[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2011, 307(1/4): 339-355. [33] 戴金星, 石昕, 卫延召. 无机成因油气论和无机成因的气田(藏)概略[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(6): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200106001.htmDAI Jinxing, SHI Xin, WEI Yanzhao. Summary of the abiogenic origin theory and the abiogenic gas pools(Fields)[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(6): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200106001.htm [34] 吴聿元, 陈贞龙. 延川南深部煤层气勘探开发面临的挑战和对策[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(4): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202004001.htmWU Yuyuan, CHEN Zhenlong. Challenges and countermeasures for exploration and development of deep CBM of South Yanchuan[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(4): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202004001.htm [35] 何治亮, 李双建, 刘全有, 等. 盆地深部地质作用与深层资源: 科学问题与攻关方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 767-779. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005767HE Zhiliang, LI Shuangjian, LIU Quanyou, et al. Deep geolo-gical processes and deep resources in basins: scientific issues and research directions[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 767-779. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005767 [36] STUART F M, BURNARD P G, TAYLOR R P, et al. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W Mo mine-ralisation, South Korea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(22): 4663-4673. [37] SIBSON R H. Crustal stress, faulting and fluid flow[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1994, 78(1): 69-84. [38] SUGISAKI R, MIMURA K. Mantle hydrocarbons: abiotic or biotic[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(11): 2527-2542. [39] SURDAM R C, CROSSEY L J, EGLINTON G, et al. Organic-inorganic reactions during progressive burial: key to porosity and permeability enhancement and preservation[and discussion] [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1985, 315(1531): 135-156. [40] SEEWALD J S. Organic-inorganic interactions in petroleum-producing sedimentary basins[J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6964): 327-333. [41] 乔世海, 李玉宏, 郭望, 等. 陕西铜川地区延长组长7油页岩无机地球化学特征及古环境恢复[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 121-126. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901121QIAO Shihai, LI Yuhong, GUO Wang, et al. Inorganic geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironment of Chang 7 oil shale in Yanchang Formation, Tongchuan area, Shaanxi Province[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1): 121-126. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901121 [42] 邱楠生, 何丽娟, 常健, 等. 沉积盆地热历史重建研究进展与挑战[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 790-802. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005790QIU Nansheng, HE Lijuan, CHANG Jian, et al. Research progress and challenges of thermal history reconstruction in sedimentary basins[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 790-802. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005790 [43] 郭占谦, 王先彬. 松辽盆地非生物成因气的探讨[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(3): 303-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199403012.htmGUO Zhanqian, WANG Xianbin. Study on inorganic origin gas in Songliao Basin[J]. Science in China(Series B), 1994, 24(3): 303-309. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199403012.htm [44] ROACH J W, 王曼. 石油的生物成因说[J]. 国外油气勘探, 1989, 1(3): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWQY198903004.htmROACH J W, WANG Man. The biological cause of oil[J]. Equipment for Geophysical Prospecting, 1989, 1(3): 41-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWQY198903004.htm [45] 乔桂林, 赵永强, 沙旭光, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中隆起南坡油气勘探领域[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 630-637. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905630QIAO Guilin, ZHAO Yongqiang, SHA Xuguang, et al. Oil and gas exploration domains on the southern slope of Central Tarim Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 630-637. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905630 [46] 康玉柱. 中国南方隆起区油气资源潜力及勘查方向[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(4): 409-411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202004002.htmKANG Yuzhu. Potential and exploration direction of oil and gas resources in the uplift regions of southern China[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(4): 409-411. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202004002.htm [47] 蒋其垲. 从石油成因学说的争论谈起[J]. 自然杂志, 1983, 6(7): 512-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ198307007.htmJIANG Qikai. Talking from the controversy about the theory of oil genesis[J]. Nature Magazine, 1983, 6(7): 512-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZZ198307007.htm [48] 刘远. 西方承认: 俄石油成因研究领先30年[J]. 国外测井技术, 2007, 22(6): 77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXZ202004015.htmLIU Yuan. Western recognition: Russia's oil genesis research is 30 years ahead[J]. World Well Logging Technology, 2007, 22(6): 77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJXZ202004015.htm [49] 于浩雨, 于明德, 李洲, 等. 洛伊凹陷西南部边界大断裂发育特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(5): 13-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005003.htmYU Haoyu, YU Mingde, LI Zhou, et al. Development characteristics of large fault in southwest boundary of Luoyi Sag and its controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(5): 13-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005003.htm [50] 王金铎, 曾治平, 宫亚军, 等. 深部超压储层发育机制及控制因素: 以准噶尔盆地永进油田为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(3): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003003.htmWANG Jinduo, ZENG Zhiping, GONG Yajun, et al. Development mechanism and controlling factors of deep overpressured reservoir: a case study of Yongjin Oilfield in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(3): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202003003.htm [51] 李德生. 中国含油气盆地构造学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版, 2002: 248-254.LI Desheng. Tectonics of petroliferous basins in China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, China, 2002: 248-254. [52] 黄瑞华. 石油无机成因说的新进展[J]. 石油实验地质, 1981, 3(1): 66-69. doi: 10.11781/sysydz198101066HUANG Ruihua. New development of the origin theory of petroleum inorganic[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1981, 3(1): 66-69. doi: 10.11781/sysydz198101066 -





 下载:
下载:



 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号