Simulation of crude oil cracking and gas generation with semi-open condition, Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
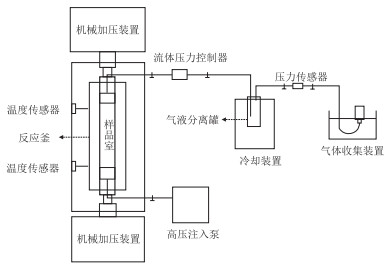
摘要: 为深入研究珠江口盆地白云凹陷原油裂解机制及产物变化特征,选取了白云凹陷渐新统珠海组原油样品,利用高温高压模拟实验,模拟了地下压力、地下流体介质及半开放条件下、不同升温速率的原油裂解过程,分析了气产率和气体组分特征。研究表明,原油样品在365℃开始裂解,裂解产率随温度增加而增加,在20℃/h的升温速率下,最终(550℃)裂解气体产率、烃气产率和非烃气体产率分别为580.13,394.25,185.88 mg/g;而在60℃/h的升温速率下,最终(550℃)裂解气体产率、烃气产率和非烃气体产率分别为707.68,485.77,221.91 mg/g。不同升温速率下最终产率的差异和烃气的组分差异均与不同温度下原油裂解机制差异有关。从原油裂解成气模拟实验的组分特征来看,大部分原油裂解气具有较高的重烃气含量,而较高重烃含量可作为判识原油裂解气和干酪根裂解气的辅助指标。Abstract: In order to study the mechanism and product compositions of oil cracking, crude oil samples from the Zhuhai Formation of the Baiyun Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin were carried out for the high-temperature, high-pressure pyrolysis with different heating rates with the pressure close to the conditions of underground. The underground fluid was also considered to be included with a semi-open condition for the pyrolysis, the gas yields and gas composition characteristics were then analyzed. Results showed that crude oils start to crack at 365 ℃, and the cracking yield increases with the increase of temperature. At a heating rate of 20 ℃/h, the final yields (at 550 ℃) of pyrolysis gas, hydrocarbon gas and non-hydrocarbon gas were 580.13, 394.25, and 185.88 mg/g, while at a heating rate of 60 ℃/h, these values increased to 707.68, 485.77, 221.91 mg/g, respectively. The composition of hydrocarbon gases at different heating rates also varied, and these variations were assumed to be related to the difference of cracking mechanisms of crude oils at different temperatures of pyrolysis. According to the composition characteristics of pyrolytic gas products, most of the gases from crude oil cracking has a relative higher content of high molecular weight hydrocarbon gas, thus these compounds can be used as an auxiliary index to distinguish crude oil cracked gas from kerogen cracked gas.
-
表 1 原油高温高压裂解模拟实验条件
Table 1. Conditions for simulation experiments of crude oil high temperature and high pressure cracking
实验步骤 温度/℃ 流体压力/MPa 静岩压力/MPa 模拟点1 250 25 60 模拟点2 300 30 72 模拟点3 335 33 79 模拟点4 365 35 84 模拟点5 400 38 91 模拟点6 450 40 96 模拟点7 500 43 103 模拟点8 550 45 108 表 2 珠江口盆地白云凹陷LH16井原油裂解气体产率数据
Table 2. Cracked gas yields of crude oil samples from well LH16, Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
升温速率/(℃·h-1) 温度/℃ 总气体产率/(mg·g-1) 烃气产率(mg·g-1) 非烃气产率/(mg·g-1) 非烃气占比/% C1 C2 C3 C1-C5 C2-C5 C3-C5 20 335 - - - - - - - - - 365 12.09 0.10 0.08 0.14 0.44 0.34 0.26 11.65 96.36 400 169.21 13.53 30.43 45.96 144.09 130.56 100.13 25.12 14.85 450 358.71 53.30 82.64 98.85 291.28 237.98 155.34 67.43 18.80 500 571.15 114.60 163.50 90.65 460.50 345.90 182.40 110.65 19.37 550 580.13 120.51 166.75 49.33 394.25 273.74 106.99 185.88 32.04 60 335 - - - - - - - - - 365 26.73 3.43 3.71 5.39 16.70 13.27 9.56 10.03 37.52 400 159.60 24.00 11.74 22.96 84.70 60.70 48.96 74.90 46.93 450 213.36 31.11 46.03 53.36 154.15 123.04 77.01 59.21 27.75 500 483.63 86.34 124.49 70.31 344.17 257.83 133.34 139.46 28.84 550 707.68 164.84 198.20 60.28 485.77 320.93 122.73 221.91 31.36 -
[1] 朱明, 张向涛, 黄玉平, 等. 珠江口盆地烃源岩特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(增刊1): 53-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1005.htmZHU Ming, ZHANG Xiangtao, HUANG Yuping, et al. Source rock characteristics and resource potential in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 53-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1005.htm [2] 米立军, 张忠涛, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部陆缘白云凹陷油气富集规律及主控因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5): 902-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805019.htmMI Lijun, ZHANG Zhongtao, PANG Xiong, et al. Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in Baiyun Sag at northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 902-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805019.htm [3] 朱俊章, 施和生, 庞雄, 等. 白云深水区东部油气成因来源与成藏特征[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2012, 17(4): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201204005.htmZHU Junzhang, SHI Hesheng, PANG Xiong, et al. Origins and accumulation characteristics of hydrocarbons in eastern Baiyun deepwater area[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2012, 17(4): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201204005.htm [4] 李美俊, 张忠涛, 陈聪, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷储层沥青成因及其对油藏调整改造的启示[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1): 133-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901014.htmLI Meijun, ZHANG Zhongtao, CHEN Cong, et al. Origin of reservoir bitumen and its implications for adjustment and reformation of hydrocarbon-accumulation in Baiyuan Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 133-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901014.htm [5] 卢晓林, 石宁, 李美俊, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷原油双杜松烷分布特征及地球化学意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 560-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904560LU Xiaolin, SHI Ning, LI Meijun, et al. Distribution patterns and geochemical implication of bicadinanes in crude oils from Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 560-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904560 [6] 陈亮, 庞雄, 韩晋阳, 等. 珠江口盆地白云深水区构造-岩性油气藏特征及成藏模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(1): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901006.htmCHEN Liang, PANG Xiong, HAN Jinyang, et al. Structural-lithologic hydrocarbon reservoir characterization and accumulation patterns in the Baiyun deep-water area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(1): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201901006.htm [7] 陈中红. 原油裂解成气研究进展[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 31(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201203004.htmCHEN Zhonghong. Research progress of oil cracking into gas[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2012, 31(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDKY201203004.htm [8] 侯读杰, 赵增迎, 唐友军, 等. 柯克亚地区原油裂解气的地质-地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2004, 15(2): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200402008.htmHOU Dujie, ZHAO Zengying, TANG Youjun, et al. The gelogical and geochemical characteristics of oil cracked gas in Kekeya region, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2004, 15(2): 137-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200402008.htm [9] 张敏, 黄光辉, 胡国艺, 等. 原油裂解气和干酪根裂解气的地球化学研究(Ⅰ): 模拟实验和产物分析[J]. 中国科学(D辑地球科学), 2008, 38(S2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S2002.htmZHANG Min, HUANG Guanghui, HU Guoyi, et al. Geochemical study on oil-cracked gases and kerogen-cracked gases(Ⅰ)-Experimental simulation and products analysis[J]. Science in China (Series D Earth Sciences), 2009, 52(S1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S2002.htm [10] 唐小强, 黄光辉, 张敏, 等. 原油裂解过程中正构烷烃的组成变化特征及其地球化学意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(6): 372-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200906047.htmTANG Xiaoqiang, HUANG Guanghui, ZHANG Min, et al. Compositional characteristics and geochemical significance of n-alkanes in process of crude oil cracking[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(6): 372-378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200906047.htm [11] 陈中红, 张守春, 查明. 压力对原油裂解成气影响的对比模拟实验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 36(6): 19-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201206005.htmCHEN Zhonghong, ZHANG Shouchun, ZHA Ming. Comparative simulation experiments regarding influence of pressure on crude oil cracking into gas[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2012, 36(6): 19-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201206005.htm [12] 陈中红, 张守春, 查明. 不同压力体系下原油裂解的地球化学演化特征[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2013, 43(11): 1807-1818.CHEN Zhonghong, ZHANG Shouchun, ZHA Ming. Geochemical evolution during the cracking of crude oil into gas under different pressure systems[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2014, 57(3): 480-490. [13] HILL R J, TANG Yongchun, KAPLAN I R. Insights into oil cra-cking based on laboratory experiments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(12): 1651-1672. [14] TIAN Hui, XIAO Xianming, YANG Liguo, et al. Pyrolysis of oil at high temperatures: gas potentials, chemical and carbon isotopic signatures[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(7): 1217-1224. [15] 田辉, 肖贤明, 李贤庆, 等. 海相干酪根与原油裂解气甲烷生成及碳同位素分馏的差异研究[J]. 地球化学, 2007, 36(1): 71-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200701007.htmTIAN Hui, XIAO Xianming, LI Xianqing, et al. Comparison of gas generation and carbon isotope fractionation of methane from marine kerogen- and crude oil-cracking gases[J]. Geochimica, 2007, 36(1): 71-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200701007.htm [16] 高生军, 陈义才, 李延钧, 等. 东营凹陷沙四段原油裂解热模拟实验及产物特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(1): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200901009.htmGAO Shengjun, CHEN Yicai, LI Yanjun, et al. Pyrolysis on crude oil and characteristics of Sha 4 member cracking gas, Dongying Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(1): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200901009.htm [17] 郭利果, 肖贤明, 田辉. 原油裂解气与干酪根裂解气差异实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(4): 428-436. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201104428GUO Liguo, XIAO Xianming, TIAN Hui. Laboratory studies of differences between oil-derived and kerogen maturation gases[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(4): 428-436. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201104428 [18] 李贤庆, 仰云峰, 冯松宝, 等. 塔里木盆地原油裂解生烃特征与生气过程研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2012, 41(3): 397-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201203012.htmLI Xianqing, YANG Yunfeng, FENG Songbao, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon and gas generation process from pyrolyzed crude oils in Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2012, 41(3): 397-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201203012.htm [19] 刘文汇, 罗厚勇, 腾格尔, 等. 碳酸盐岩储层中原油裂解及碳同位素演化模拟实验[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 627-633. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605003.htmLIU Wenhui, LUO Houyong, TENGER, et al. Simulation experiments on crude oil cracking and carbon isotopic evolution in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(5): 627-633. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201605003.htm [20] 王晓涛, 王铜山, 李永新, 等. 储层介质环境对原油裂解生气影响的实验研究[J]. 地球化学, 2015, 44(2): 178-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201502007.htmWANG Xiaotao, WANG Tongshan, LI Yongxin, et al. Experimental study on the effects of reservoir mediums on crude oil cracking to gas[J]. Geochimica, 2015, 44(2): 178-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201502007.htm [21] 徐陈杰, 叶加仁, 刘金水, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖组Ⅲ型干酪根暗色泥岩生排烃模拟[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002013.htmXU Chenjie, YE Jiaren, LIU Jinshui, et al. Simulation of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion for the dark mudstone with type-Ⅲ kerogen in the Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002013.htm [22] 包友书, 张林晔, 张守春, 等. 烃源岩生烃抑制模拟实验及机理[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(7): 753-762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201707003.htmBAO Youshu, ZHANG Linye, ZHANG Shouchun, et al. Simulation experiment and mechanism of hydrocarbon-generation retardation for source rocks[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(7): 753-762. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201707003.htm -





 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号