Experimental development and application of source rock thermal simulation for hydrocarbon generation and expulsion
-
摘要: 烃源岩生排烃模拟实验已成为研究烃源岩生、排、滞油气机理的重要技术手段。对生排烃模拟实验技术的研究现状及发展趋势进行了归纳与总结。目前根据反应体系的开放程度,生排烃模拟实验方法可分为开放体系、封闭体系和限制体系3类;模拟实验的方式主要有单温阶累计生排油气模拟和多温阶连续生排油气模拟2种;实验边界条件主要有模拟的温度、压力体系、时间、样品形态及无机反应介质等5类。生排烃模拟实验在明确油气生、排、滞过程及其主控因素,建立不同类型沉积有机质的油气演化模式,评价沉积盆地的油气资源潜力和进行油气源对比与示踪等方面起到了重要的作用。目前的生排烃模拟实验具有局限性,需要在实验边界条件、源-储-藏协同成烃成藏物理模拟和多因素共控作用下油气形成动力学模拟方面进行更深入的研究。Abstract: Simulation experiment was one of the most valuable methods for the study of hydrocarbon generation, expulsion and retention in source rocks. It was summarized in this paper that the progressing status and development significations of thermal simulation experiments. According to the open degree of reaction system, the experimental methods can be classified to three types, including open, closed and restricted systems. Cumulative generation and expulsion of oil and gas at a single temperature step and continuous generation and expulsion of oil and gas in multiple temperature steps were introduced. The main constrains included simulation temperature, pressure, time duration, sample morphology and inorganic reaction medium. The simulation experiments of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion have played an important role in clarifying the processes of oil and gas generation, expulsion and retention and their major controlling factors, establishing oil and gas evolution models of different types of sedimentary organic matter, evaluating the oil and gas resource potential of sedimentary basins, and performing oil and gas source comparison and correlation. The current hydrocarbon generation and expulsion simulation experiments have some limitations, and researches are needed in terms of experimental boundary conditions, physical simulation of hydrocarbon generation and accumulation of source-reservoir synergy, and dynamic calculation of hydrocarbon generation with various constrains.
-
表 1 不同生排烃模拟实验装置实验条件对比
Table 1. Experimental conditions of different thermal simulation experimental setup
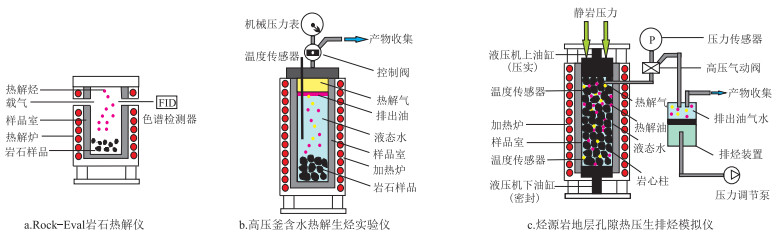
体系类型 典型设备 最高温度/℃ 上覆静岩压力 流体压力 装置中流体介质 反应空间 样品需求质量 开放体系 Rock-Eval岩石热解仪、热重仪、热解—色谱—质谱仪 800 无 常压 惰性气体 无限制 几毫克 封闭体系 金属高压釜 600 无 < 20 MPa 水蒸气,汽水平衡态或超临界水 几十至几百毫升 几十至一百多克粉碎岩石 玻璃管 600 无 < 5 MPa,不能实测 无水 几至几十毫升 零点几克 黄金管—高压釜 650 不确定 < 50 MPa,不能实测 无水 几至十几毫升 几十毫克 金刚石压腔 1 200 无 100 MPa~10 GPa 液态水、超临界水 零点几至几毫升 零点几毫克 限制体系 压实模拟装置,压力差热分析仪 600 130 MPa~2 GPa 常压或40 MPa 无水低压水蒸气 无限制或十几毫升 几克到几百克柱状岩石 地层孔隙热压模拟 600 常压至200 MPa 常压至150 MPa 液态水、超临界水 几至十几毫升 几十至一百多克柱状岩石 -
[1] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1978. [2] EISMA E, JURG E. Fundamental aspects of the diagenesis of organic matter and the formation of hydrocarbons[C]//Proceedings of 7th World Petroleum Congress. London: World Petroleum Congress, 1967. [3] 黄第藩. 陆相有机质演化和成烃机理[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1984.HUANG Difan. Evolution and hydrocarbon generation mechanism of terrestrial organic matter[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1984. [4] 张景亷. 论石油的无机成因[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001.ZHANG Jinglian. On the inorganic origin of petroleum[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001. [5] 张林晔, 张守春, 黄开权, 等. 半咸水湖相未熟油成因机理模拟实验研究[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(4): 361-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199904005.htmZHANG Linye, ZHANG Shouchun, HUANG Kaiquan, et al. Simulation experiment of immature oil genetic mechanism in lake facies of semi-salt water[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 44(11): 980-988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199904005.htm [6] 刘文汇, 王万春. 烃类的有机(生物)与无机(非生物)来源: 油气成因理论思考之二[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19(3): 179-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200003008.htmLIU Wenhui, WANG Wanchun. The organic (biogenic) and inorganic (non-biogenic) sources of hydrocarbons: thought on theory of oil and gas formation[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2000, 19(3): 179-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200003008.htm [7] 刘全有, 金之钧, 高波, 等. 四川盆地二叠系不同类型烃源岩生烃热模拟实验[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(5): 700-704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201005001.htmLIU Quanyou, JIN Zhijun, GAO Bo, et al. Characterization of gas pyrolysates from different types of Permian source rocks in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(5): 700-704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201005001.htm [8] 段毅, 周世新. 塔里木盆地石炭系烃源岩热模拟实验研究: Ⅱ. 生态标志化合物的组成和演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2001, 22(1): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200101002.htmDUAN Yi, ZHOU Shixin. Experimental study on thermal simulation of Carboniferous source rocks in Tarim Basin: Ⅱ. Composition and evolution of biomarkers[J]. Petroleum and Natural Gas Geology, 2001, 22(1): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200101002.htm [9] 张有生, 秦勇, 刘焕杰, 等. 沉积有机质二次生烃热模拟实验研究[J]. 地球化学, 2002, 31(3): 273-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200203007.htmZHANG Yousheng, QIN Yong, LIU Huanjie, et al. Investigation on the hydrocarbon regeneration from sedimentary organic matters by pyrolytic simulation[J]. Geochimica, 2002, 31(3): 273-282. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200203007.htm [10] 米敬奎, 张水昌, 王晓梅. 不同类型生烃模拟实验方法对比与关键技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(4): 409-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200904409MI Jingkui, ZHANG Shuichang, WANG Xiaomei. Comparison of different hydrocarbon generation simulation approaches and key technique[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(4): 409-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200904409 [11] 王治朝, 米敬奎, 李贤庆, 等. 生烃模拟实验方法现状与存在问题[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4): 592-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904019.htmWANG Zhichao, MI Jingkui, LI Xianqing, et al. Current situation and problems of simulation experiment approach of hydrocarbon generation[J]. Natural Gas Geosciences, 2009, 20(4): 592-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904019.htm [12] 刘宝泉, 蔡冰. 上元古界下马岭组页岩干酪根的油气生成模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(2): 147-161. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199002147LIU Baoquan, CAI Bing. A Simulation experiment of petroleum origin on kerogen from shales of the Lower Xiamalin Formation in the Upper Proterozoic[J]. Petroleum Experimental Geology, 1990, 12(2): 147-161. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199002147 [13] 王兆云, 程克明, 张柏生, 等. 泥灰岩的生、排烃模拟实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(1): 127-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB601.014.htmWANG Zhaoyun, CHENG Keming, ZHANG Baisheng, et al. The study on simulation experiments of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of mud limestone[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(1): 127-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB601.014.htm [14] 熊永强, 耿安松, 王云鹏, 等. 干酪根二次生烃动力学模拟实验研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(4): 315-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200104006.htmXIONG Yongqiang, GENG Ansong, WANG Yunpeng, et al. Kinetic simulating experiment on the secondary hydrocarbon generation of kerogen[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 2002, 45(1): 13-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200104006.htm [15] MONTHIOUX M, LANDAIS P, MONIN J C. Comparison between natural and artificial maturation series of humic coals from the Mahakam delta, Indonesia[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1985, 8(4): 275-292. [16] MONTHIOUX M, LANDAIS P, DURAND B. Comparison between extracts from natural and artificial maturation series of Mahakam delta coals[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(1/3): 299-311. [17] 刘金钟. 桂西北中三叠统板纳组的岩石学及地球化学[D]. 北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 1990.LIU Jinzhong. Petrology and geochemistry of the Middle Triassic Banna Formation in northwest Guangxi[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1990. [18] PRICE L C, WENGER L M. The influence of pressure on petroleum generation and maturation as suggested by aqueous pyrolysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 19(1/3): 141-159. [19] 郑伦举, 秦建中, 何生, 等. 地层孔隙热压生排烃模拟实验初步研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(3): 296-302. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200903296ZHENG Lunju, QIN Jianzhong, HE Sheng, et al. Preliminary study of formation porosity thermocompression simulation experiment of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(3): 296-302. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200903296 [20] LOPATIN N V. Temperatura geologicheskoye vema kak factory uglefikatsii (Temperature and geologic time as factors in calcification)[J]. Akademiia nauk SSSR. Izvestiia. Seriia khimicheskaia, 1971, 3, 95-106. [21] CONNAN J. Time-temperature relation in oil genesis: geologic notes[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1974, 58(12): 2516-2521. [22] LANDAIS P, MICHELS R, ELIE M. Are time and temperature the only constraints to the simulation of organic matter maturation?[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 22(3/5): 617-630. [23] 姜峰, 杜建国, 王万春, 等. 高温超高压模拟实验研究: Ⅱ. 高温高压下烷烃产物的演化特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1998, 16(4): 145-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB804.024.htmJIANG Feng, DU Jianguo, WANG Wanchun, et al. The study on high pressure high temperature aqueous pyrolysis Ⅱ. Evolutionary characteristics of alkane generated from organic matter under high temperature and high pressure[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998, 16(4): 145-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB804.024.htm [24] 王兆明, 罗晓容, 陈瑞银, 等. 有机质热演化过程中地层压力的作用与影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 2006, 21(1): 39-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200601005.htmWANG Zhaoming, LUO Xiaorong, CHEN Ruiyin, et al. Effects and influences of pore pressures on organic matter's maturation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2006, 21(1): 39-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200601005.htm [25] 陈晓东, 王先彬. 压力对有机质成熟和油气生成的影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(1): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ901.006.htmCHEN Xiaodong, WANG Xianbin. Pressure effect on organic matter maturation and petroleum generation[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(1): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ901.006.htm [26] 秦建中, 刘井旺, 刘宝泉, 等. 加温时间、加水量对模拟实验油气产率及地化参数的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2002, 24(2): 152-157. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200202152QIN Jianzhong, LIU Jingwang, LIU Baoquan, et al. Hydrocarbon yield and geochemical parameters affected by heating time and added water amount in the simulation test[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2002, 24(2): 152-157. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200202152 [27] LEWAN M D, WINTERS J C, MCDONALD J H. Generation of oil-like pyrolyzates from organic-rich shales[J]. Science, 1979, 203(4383): 897-899. [28] 王晓锋, 刘文汇, 徐永昌, 等. 水在有机质形成气态烃演化中作用的热模拟实验研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2006, 16(10): 1275-1281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200610011.htmWANG Xiaofeng, LIU Wenhui, XU Yongchang, et al. Experimental study on the role of water in the formation and evolution of gaseous hydrocarbons from organic matter[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2006, 16(10): 1275-1281. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200610011.htm [29] 王兆云, 程克明, 张柏生. 加水热模拟实验气态产物特征及演化规律研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(3): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK503.006.htmWANG Zhaoyun, CHENG Keming, ZHANG Bosheng. The study on the characteristics and evolution regularity of product of gas under pyrolysis simulation experiments[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1995, 22(3): 36-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK503.006.htm [30] 邹艳荣, 帅燕华, 孔枫, 等. 油气生成过程实验研究的思考与展望[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(4): 375-382. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200404375ZOU Yanrong, SHUAI Yanhua, KONG Feng, et al. Experiments on petroleum generation: considerations and outlook[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(4): 375-382. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200404375 [31] 陈安定, 张文正, 徐永昌. 沉积岩成烃热模拟实验产物的同位素特征及应用[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1993, 23(2): 209-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199302014.htmCHEN Anding, ZHANG Wenzheng, XU Yongchang. Isotopic characteristics and application of hydrocarbon generation thermal simulation products of sedimentary rocks[J]. Chinese Science(Series B), 1993, 23(2): 209-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199302014.htm [32] 程克明, 关德师, 陈建平, 等. 烃源岩产烃潜力的热压模拟实验及其在油气勘探中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1991(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199105002.htmCHENG Keming, GUAN Deshi, CHEN Jianping, et al. Laboratory thermal pressure modeling of the hydrocarbon generation potential of source rocks and its application in petroleum exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1991(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199105002.htm [33] 张文正, 裴戈, 关德师. 烃源岩轻烃生成与演化的热压模拟实验研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1991(3): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199103003.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YUAN Ge, GUAN Deshi. Thermal pressure simulation of the formation and evolution of light hydrocarbons of HGSR[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1991(3): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK199103003.htm [34] 祖小京, 妥进才, 张明峰, 等. 矿物在油气形成过程中的作用[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(2): 298-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200702018.htmZU Xiaojing, TUO Jincai, ZHANG Mingfeng, et al. The roles of inorganic minerals on the oil and gas generating processes[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(2): 298-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200702018.htm [35] 大庆石油学院. 有机质地化演化模拟实验装置: 87100918[P]. 1988-08-31.Daqing Institute of Petroleum. Organic texture evolution simulation test device: CN, 87100918[P]. 1988-08-31. [36] WANG Qianru, HUANG Haiping, ZHENG Lunjun. Thermal maturity parameters derived from tetra-, penta-substituted naphthalenes and organosulfur compounds in highly mature sediments[J]. Fuel, 2021, 288: 119626. [37] 关德范. 成盆成烃成藏理论思维[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.GUAN Defan. Theoretical thinking of basin and hydrocarbon accumulation[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004. [38] MAGOON L B, DOW W. The petroleum system[M]//MAGOON L B, DOW W G. The petroleum system: from source to trap. Tulsa, Okla: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1994. [39] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 黄仁春, 等. 四川盆地深层-超深层天然气勘探进展与展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(5): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202005002.htmGUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, HUANG Renchun, et al. Deep and ultra-deep natural gas exploration in the Sichuan Basin: progress and prospect[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(5): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202005002.htm [40] 庞雄奇, 林会喜, 郑定业, 等. 中国深层和超深层碳酸盐岩油气藏形成分布的基本特征与动力机制及发展方向[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(5): 673-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202005006.htmPANG Xiongqi, LIN Huixi, ZHENG Dingye, et al. Basic characteristics, dynamic mechanism and development direction of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs in China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(5): 673-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX202005006.htm -





 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号