Main controlling factors and exploration direction of Permian to Triassic reservior in the central sag of Junggar Basin
-
摘要: 准噶尔盆地近年在中央坳陷边缘斜坡区二叠系上乌尔禾组、三叠系百口泉组连续获得重大油气发现,但盆地中部凹陷区针对该领域的钻探仅2口井获低产而多口井目的层未见油气显示,因此亟需深化该地区的油气成藏认识,明确其主控因素。通过对中部凹陷区成藏条件的分析,结合已钻井成藏分析,明确凹陷区失利井未获油气发现的直接原因为局部“通源断裂”不发育和储层物性差。基于此,建立了凹陷区二叠系—三叠系油气藏“通源断裂”、“优质砂体”二元控藏的下生上储成藏模式。根据“通源断裂”与砂体的配置关系,明确地层超覆背景下的上乌尔禾组、百口泉组低位扇三角洲前缘砂体岩性油气藏是下步风险勘探的首选领域,有利区面积约3 600 km2;中—下二叠统烃源岩层系内的非常规油气和源外多层系常规油气综合勘探是未来主要勘探方向。Abstract: In recent years, significant oil and gas discoveries have been achieved in the Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation and the Triassic Baikouquan Formation on the marginal slope of oil generation sag, Junggar Basin. However, in the central sag of the basin, no oil or gas show has been discovered in target formations, and low production has been made only by two wells. As a result, it is necessary to deepen the understanding of the mechanisms of oil and gas accumulation and clarify the main controlling factors. The analyses of the accumulation conditions in the central sag and some wells show that the direct reason for the failure to find oil and gas in the sag is the lack of local source-connecting faults and poor reservoir properties. An accumulation model with source in the lower section and reservoir in the upper section controlled by both source-connecting faults and favorable sand bodies was established for the Permian and Triassic strata in the sag. The sandbody lithologic reservoirs of fan-delta front subfacies in the Upper Wuerhe and Baikouquan formations under the background of stratigraphic overlap are the primary direction of exploration, covering an area about 3 600 km2. The comprehensive exploration of unconventional oil and gas in the Middle-Lower Permian source rocks and conventional oil and gas in multiple layers outside the source area should be targeted.
-
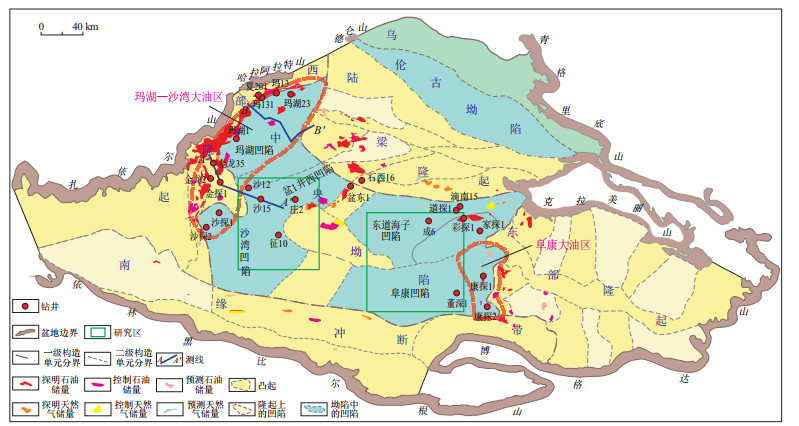
图 1 准噶尔盆地构造区划与研究区位置
据何文军等(2019)[5]。
Figure 1. Tectonic units of Junggar Basin and location of study area
图 2 准噶尔盆地西部金龙35—金探1—沙15井上二叠统上乌尔禾组储层沉积模式
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 2. Depositional model of Upper Wuerhe Formation in Upper Permian crossing wells Jinlong 35, Jintan 1 and Sha 15, western Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地中部凹陷区二叠系—三叠系已钻井钻探结果统计
Table 1. Drilling results in Permian-Triassic in central sag area of Junggar Basin
凹陷 井名 主探目的层 完钻层位 二叠系—三叠系录井显示 二叠系—三叠系综合解释 二叠系—三叠系试油层及结果 部署年份 盆1井西 庄2 T1b T1b 无 无 未试油 2003 沙12 T1b P3w T1b一级荧光 T1b油层4.8 m/2层 未试油 2015 沙15 T1b,P3w P2w 无 T3b差油层,T2k气水同层 T2k试油未见油气 2018 东道海子 成6 P3w,T1b P2w T3b荧光,T2k、P2w一级荧光 T3b油水同层,T2k油层,P2w气层、差气层 P3w峰值气100 m3/d;P2w日产气4 000 m3左右,峰值3.4×104 m3/d;T2k待试 2019 沙湾 征10 P3w P2w T3b、T1b、P3w见显示 T3b、T1b、P3w解释气层31.8 m P3w日产油1 m3、气600 m3,峰值油13 m3、气4.1×104 m3,试油未完 2020 阜康 董深1 P3w,P2w 正钻 2021 表 2 准噶尔盆地中部凹陷区烃源岩指标统计
Table 2. Parameters of source rocks in central sag, Junggar Basin
位置/井 地层 样品类型 ω(TOC)/% (S1+S2)/ (mg·g-1) 有机质类型 Ro/% 数据出处 阜康凹陷周缘 芦草沟组(P2l) $\frac{0.65 \sim 6.72}{2.16} $ $\frac{0.36 \sim 26.28}{7.0} $ Ⅱ1—Ⅱ2 0.83~1.52 据文献[1, 7] 东道海子凹陷/成6井 下乌尔禾组(P2w) 岩屑 ${\frac{{0.41\sim 4.3(179)}}{{1.27}}} $ $ {\frac{{1.24\sim 1.31(4)}}{{1.27}}}$ 岩心 ${\frac{{1.23\sim 1.37(9)}}{{1.27}}} $ ${\frac{{1.3\sim 1.31(2)}}{{1.31}}} $ 阜康凹陷周缘凸起 石炭系 煤系泥岩 $ {\frac{{0.54\sim 5.83}}{{2.12}}}$ $ {\frac{{0.21\sim 20.30}}{{2.83}}}$ Ⅱ2—Ⅲ 据文献[1] 碳质泥岩 $ {\frac{{8.74\sim 28.32}}{{13.50}}}$ $ {\frac{{9.06\sim 71.58}}{{38.1}}}$ Ⅱ2—Ⅲ 据文献[1] 注:表中分式意义为$\frac{\text { 最小值~ 最大值(样品数 })}{\text { 平均值 }} $。 表 3 准噶尔盆地白家海凸起彩探1H井与准东诸井天然气地球化学参数对比
Table 3. Comparison of natural gas geochemical parameters between well Caitan 1H on Baijiahai Uplift and wells in eastern Junggar Basin
天然气来源 井号 层位 天然气组成 C7轻烃组成/% 天然气碳同位素/‰ N2/ % CH4/ % C2H6/ % 干燥系数 正庚烷 甲基环己烷 二甲基环戊烷 CH4 C2H6 C3H8 高熟石炭系 彩探1H J2x 3.09 94.07 1.51 0.98 35 50 15 -30.20 -26.08 -25.56 彩17 J1b 1.90 96.79 0.89 0.99 37 60 3 -33.83 -25.67 -23.93 彩504 J2x 2.32 92.50 2.37 0.95 43 46 11 -30.22 -26.02 -26.53 滴西10 C 3.67 91.67 2.54 0.96 38 45 17 -30.06 -27.73 -24.47 家探1 C 3.81 93.70 1.38 0.98 -30.30 -27.66 -25.71 注:表中数据据参考文献[12]。 表 4 准噶尔盆地中部及周边钻井百口泉组、上乌尔禾组储层平均孔隙度及油气发现情况对比
Table 4. Comparison of average porosity of target formations and oil and gas drilling results of wells drilled in and around central Junggar Basin
储层物性及油气 准中凹陷区 沙湾、玛湖凹陷斜坡区 沙15井 沙12井 庄2井 成6井 沙探1井 玛131井 玛13井 夏201井 平均孔隙度/% T1b3 9.7 13.9 6.9~12.5 3.3~8.0 4.0~6.0 9.5 T1b2 7.5 8.8 7.1 T1b1 T1b油气发现 无油气显示 T1b3解释油层4.8 m/2层 未钻穿,无油气显示 无油气显示 试油自喷日油1.22 m3, 水13.99 m3 日产油11.1 m3 日产油1.24~6.29 m3,气2 010~8 640 m3 T1b2成藏,数据不详 储层物性及油气 准中凹陷区 沙湾、玛湖凹陷斜坡区 沙15井 沙12井 成6井 沙探1井 沙探2井 玛湖1井 玛湖23井 平均孔隙度/% P3w3 未钻穿 2.8~7.2 7~9 P3w2 11.6 9.1 6.7 10.6 P3w1 6.7 9.1 P3w油气发现 无油气显示 无油气显示 无油气显示 日产油30.25 m3 日产油106 m3、气6 842 m3 试油分别获得日产油12.84 t和5.54 t 试油日产10.84 t -
[1] 何海清, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷康探1井重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.02.001HE Haiqing, ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, et al. A great discovery of Well Kangtan 1 in the Fukang Sag in the Junggar Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.02.001 [2] 阿布力米提·依明, 唐勇, 曹剑, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下三叠统百口泉组源外"连续型"油藏成藏机理与富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(2): 241-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201602006.htmABLIMIT Imin, TANG Yong, CAO Jian, et al. Accumulation mechanism and enrichment rules of the continuous hydrocarbon plays in the Lower Triassic Baikouquan Formation of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(2): 241-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201602006.htm [3] 郑孟林, 邱小芝, 何文军, 等. 西北地区含油气盆地动力学演化[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(5): 1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.05.001ZHENG Menglin, QIU Xiaozhi, HE Wenjun, et al. Geodynamic evolution of petroliferous basins in Northwest China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2015, 37(5): 1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.05.001 [4] 商丰凯. 叠合盆地凸起区多期复杂断裂特征及形成机制: 以准噶尔盆地车排子凸起为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202003003.htmSHANG Fengkai. Characteristics and formation mechanism of multi-stage complex fault system of uplift in superimposed basin: a case study of Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202003003.htm [5] 何文军, 王绪龙, 邹阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.02.008HE Wenjun, WANG Xulong, ZOU Yang, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction of oil in Junggar Basin[J]. Marine Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.02.008 [6] 王小军, 宋永, 郑孟林, 等. 准噶尔盆地复合含油气系统与复式聚集成藏[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(4): 29-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.003WANG Xiaojun, SONG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Composite petroleum system and multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(4): 29-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.003 [7] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 邓春萍, 等. 准噶尔盆地烃源岩与原油地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(1): 37-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.01.003CHEN Jianping, WANG Xulong, DENG Chenping, et al. Geoche-mical features of source rocks and crude oil in the Junggar Basin, Northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(1): 37-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.01.003 [8] 郑孟林, 樊向东, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层地质结构叠加演变与油气赋存[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htmZHENG Menglin, FAN Xiangdong, HE Wenjun, et al. Superposition of deep geological structural evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htm [9] 陈磊, 杨镱婷, 汪飞, 等. 准噶尔盆地勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(5): 506-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202005001.htmCHEN Lei, YANG Yiting, WANG Fei, et al. Exploration history and enlightenment in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geoloy, 2020, 41(5): 506-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202005001.htm [10] 尹伟, 郑和荣, 孟闲龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地中部原油地球化学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(4): 461-466. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.04.011YIN Wei, ZHENG Herong, MENG Xianlong, et al. Geochemical behaviors of crude oils in central Junggar Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2005, 26(4): 461-466. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.04.011 [11] 王圣柱, 王千军, 张关龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地石炭系烃源岩发育模式及地球化学特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(4): 13-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004003.htmWANG Shengzhu, WANG Qianjun, ZHANG Guanlong, et al. Deve-lopment mode and geochemical characteristics of Carboniferous source rocks in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(4): 13-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004003.htm [12] 靳军, 付欢, 于景维, 等. 准噶尔盆地白家海凸起下侏罗统三工河组沉积演化及油气勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(1): 82-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201801009.htmJIN Jun, FU Huan, YU Jingwei, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Lower Jurassic Sangonghe Formation in Baijiahai uplift, Junggar Basin and its significance in oil and gas exploration[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1): 82-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201801009.htm [13] 唐勇, 曹剑, 何文军, 等. 从玛湖大油区发现看全油气系统地质理论发展趋势[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htmTANG Yong, CAO Jian, HE Wenjun, et al. Development tendency of geological theory of total petroleum system: insights from the discovery of Mahu large oil province[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htm [14] 唐勇, 徐洋, 李亚哲, 等. 玛湖凹陷大型浅水退覆式扇三角洲沉积模式及勘探意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 16-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801009.htmTANG Yong, XU Yang, LI Yazhe, et al. Sedimentation model and exploration significance of large-scaled shallow retrogradation fan delta in Mahu sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 16-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801009.htm [15] 卢红刚, 罗焕宏, 骆飞飞, 等. 玛湖凹陷MH1井区上乌尔禾组扇控大面积成藏条件与成藏模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101006.htmLU Honggang, LUO Huanhong, LUO Feifei, et al. Fan controlled large-area accumulation conditions and mode of upper Wuerhe Formation in MH1 well zone of Mahu Sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(1): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101006.htm [16] 杜金虎, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地上二叠统风险领域分析与沙湾凹陷战略发现[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(1): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201901004.htmDU Jinhu, ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, et al. Prospects in Upper Permian and strategic discovery in Shawan Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(1): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201901004.htm [17] 何文军, 费李莹, 阿布力米提·依明, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层油气成藏条件与勘探潜力分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 189-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901019.htmHE Wenjun, FEI Liying, ABLⅡNTI Yiming, et al. Accumulation conditions of deep hydrocarbon and exploration potential analysis in Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 189-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901019.htm [18] 张凤奇, 刘伟, 鲁雪松, 等. 喜马拉雅晚期构造应力场及其与油气分布的关系: 以准噶尔盆地南缘为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htmZHANG Fengqi, LIU Wei, LU Xuesong, et al. Late Himalayan tectonic stress field and its relationship with hydrocarbon distribution: a case study of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htm [19] 刘德志. 准中4区块侏罗系成藏动力子系统划分及勘探意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002004.htmLIU Dezhi. Division of dynamic subsystem for hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in Jurassic middle 4 Block of Jungar Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002004.htm [20] 陶国亮, 胡文瑄, 张义杰, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘北西向横断裂与油气成藏[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(4): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200604004.htmTAO Guoliang, HU Wenxuan, ZHANG Yijie, et al. NW-trending transverse faults and hydrocarbon accumulation in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(4): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200604004.htm [21] 支东明, 唐勇, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组常规—非常规油气有序共生与全油气系统成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htmZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htm [22] 杨智, 邹才能. "进源找油": 源岩油气内涵与前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 173-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901018.htmYANG Zhi, ZOU Caineng. "Exploring petroleum inside source kitchen": connotation and prospects of source rock oil and gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 173-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901018.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号