Geochemical characteristics and fluid origins of fracture- and cave-filling calcites of Ordovician in Yubei area, Tarim Basin
-
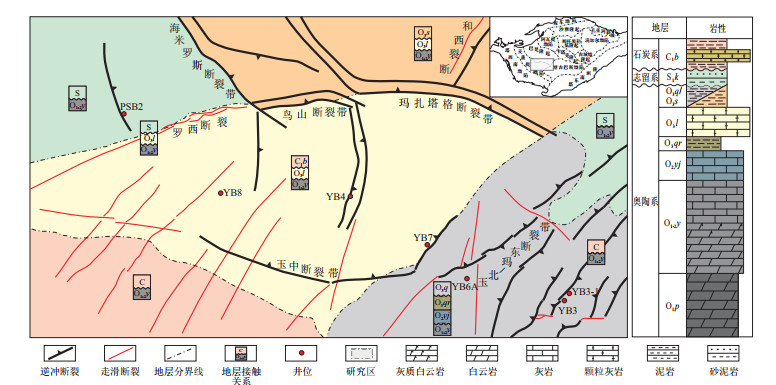
摘要: 塔里木盆地玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层的成因是该地区油气勘探研究的关键问题。通过分析玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩缝洞方解石的充填特征和地球化学特征,并结合区域构造背景,探讨了影响储层发育的流体期次、性质和作用类型。该区奥陶系缝洞充填方解石样品的稀土配分曲线呈现淡水和海水2种流体特征,由东向西分布的井中样品锶同位素比值逐渐减小,且高角度缝方解石的锶同位素值明显高于孔洞和水平缝洞方解石中的,显示了不同区域、不同产状样品中流体性质的差异。因此,玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩成岩系统具有一定开放性,由东向西淡水改造的程度逐渐减弱,这与加里东中期—海西早期东强西弱的构造活动特征相吻合,断裂活动强度影响了流体对储层的改造过程。Abstract: The genesis of carbonate reservoirs of the Lower-Middle Ordovician strata has been an important topic for petroleum exploration in the Yubei area, Tarim Basin. To investigate the stages and properties of paleo-fluid and discuss the reservoir origin, the geochemical and cathodoluminescence features of the Ordovician fracture- and cave-filling calcites from wells in the Yubei area were analyzed combining with the regional tectonic background. Results show that the REE distribution patterns and occurrences of samples from different wells have the characteristics of seawater and fresh water, respectively. The average values of Sr isotopes gradually decrease from east to west. Moreover, the average value of 87Sr/86Sr in high-angle fracture calcites is higher than those of cave-filling and horizontal-fracture calcites, suggesting obvious variations of fluid properties in different regions and sample occurrences. Therefore, the diagenetic environment of the Lower-Middle Ordovician carbonates in the Yubei area may be open. The decreases of meteoric alteration from east to west can be attributed to the Middle Caledonian and Early Hercynian tectonic setting. Moreover, the progress of reservoir modification by fluids is mainly affected by fault activity intensity.
-
Key words:
- strontium isotope /
- rare earth element /
- calcite /
- reservoir fluid /
- carbonate /
- Ordovician /
- Yubei area /
- Tarim Basin
-
图 2 塔里木盆地玉北地区缝洞充填方解石取样位置与镜下微观特征
a.泥晶灰岩高角度裂缝中充填的方解石,YB7井,5 810.39 m,O1-2y;b.泥晶灰岩孔洞中充填的方解石,YB8井,6 969.80 m,O1-2y;c.泥晶灰岩水平缝洞中充填的方解石,YB8井,6 919.96 m,O1-2y;d.高角度裂缝充填方解石,YB7井,5 810.39 m,O1-2y;e-f.图d红色圆圈处镜下与阴极发光特征
Figure 2. Positions and photomicrographs of fracture- and cave-filling calcite samples in Yubei area, Tarim Basin
图 3 塔里木盆地玉北地区缝洞充填方解石阴极发光特征
a-b.早期孔洞充填第一期方解石(C1),暗红色阴极发光,晚期高角度缝被第三期方解石(C3)充填,切穿C1方解石,C3发橙黄色阴极光,C1边缘可见少量第二期方解石(C2),玫瑰红色阴极发光,YB4井,5 838.97 m,O3l;c-d.早期孔洞充填C1方解石,可见破碎围岩颗粒,暗红色阴极发光,晚期裂缝被C3方解石充填,切穿C2方解石,C2发玫瑰红色阴极光,C3发橙黄色阴极光,YB3井,5 443.10 m,O1-2y;e-f.孔洞中主要充填C1方解石,不发光—暗红色阴极发光,YB8井,6 919.96 m,O1-2y;g-h孔洞中充填C1方解石,不发光—暗红色阴极发光,在围岩和C1颗粒边缘可见C2方解石充填,阴极发光颜色为玫瑰红色,YB6A井,6 531.65 m,O1-2y;i-j.孔洞中主要充填C2方解石,玫瑰红色阴极发光,YB8井,6 918.66 m,O1-2y;k-l.高角度裂缝中主要充填C3方解石,橙黄色阴极发光,YB7井,5 810.39 m,O1-2y
Figure 3. Characteristics of cathodoluminescence of fracture- and cave-filling calcite samples in Yubei area, Tarim Basin
表 1 塔里木盆地玉北地区奥陶系缝洞方解石稀土元素和锶同位素组成
Table 1. Rare earth elements and strontium isotope compositions of fracture- and cave-filling calcites of Lower-Middle Ordovician in Yubei area, Tarim Basin
样品号 地层 产状 La/La* Ce/Ce* Eu/Eu* ∑REE/10-6 LREE/HREE 87Sr/86Sr 2σ YB3-1-2-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.55 1.06 2.36 0.27 0.43 YB3-1-3-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.65 0.78 0.87 8.56 1.31 0.709 86 0.000 18 YB3-1-3-1* O1-2y 0.709 81 0.000 15 YB3-1-3-2 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.68 1.65 1.05 8.17 1.29 0.709 17 0.000 22 YB3-2-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.80 0.87 1.07 2.37 1.71 0.709 35 0.000 19 YB3-2-2 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.86 0.95 0.80 3.11 0.91 0.711 08 0.000 24 YB3-3-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 2.51 0.90 2.09 1.24 1.10 0.708 60 0.000 18 YB3-3-2 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.91 0.80 1.28 0.80 0.69 YB3-3-3 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.31 0.31 1.75 0.24 0.73 YB3-5-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.75 0.74 1.46 1.58 1.10 0.709 26 0.000 20 YB3-5-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.33 0.75 0.54 1.29 0.78 0.709 61 0.000 25 YB3-5-2* O1-2y 0.709 59 0.000 30 YB3-6-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.40 0.78 1.08 5.46 0.74 YB3-6-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.51 0.67 0.68 0.29 0.49 YB3-7-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.67 0.80 0.73 3.43 1.15 0.709 88 0.000 51 YB3-7-2 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.94 0.82 0.92 1.80 0.59 YB3-9-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.78 0.98 0.61 1.44 0.91 YB3-9-2 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.65 0.83 0.85 2.15 1.22 YB3-9-3 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.81 0.78 0.63 2.16 0.88 YB3-9-4 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.62 0.84 0.64 3.37 1.19 YB3-11-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.48 1.01 1.23 6.06 0.54 0.708 75 0.000 28 YB3-11-1* O1-2y 0.708 78 0.000 32 YB4-1-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.42 0.81 1.44 1.20 1.15 0.709 44 0.000 29 YB4-1-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.09 0.57 2.56 10.73 0.94 YB4-2-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.61 0.77 0.83 2.62 1.22 YB4-2-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 2.91 1.06 2.26 0.42 0.75 YB4-2-3 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.78 0.83 1.19 6.42 1.63 0.707 67 0.000 47 YB4-2-4 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.26 0.36 1.83 0.34 0.61 YB4-2-5 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.58 0.77 1.07 1.73 0.83 YB4-3-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.67 0.77 1.61 1.43 0.90 YB4-3-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.53 0.92 1.08 5.89 0.67 0.707 94 0.000 30 YB4-5-1 O3l 孔洞方解石 49.81 1.21 1.57 2.26 1.15 YB4-5-2 O3l 孔洞方解石 0.78 0.84 1.15 6.92 1.81 YB4-5-3 O3l 孔洞方解石 1.02 0.85 0.67 3.65 1.17 YB4-5-4 O3l 孔洞方解石 1.44 0.70 0.67 7.32 1.62 YB6A-5-34-1 O2yj 水平缝洞方解石 0.94 1.00 0.88 3.47 0.86 0.709 01 0.000 12 YB6A-7-66-1 O2yj 水平缝洞方解石 0.96 1.07 1.34 1.48 1.40 0.709 43 0.000 29 YB6A-8-6-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.74 0.91 1.01 2.67 0.84 YB6A-9-19-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 1.08 1.03 1.70 1.92 0.55 YB7-1-1 O1p 高角度缝方解石 0.64 0.69 1.52 1.08 0.26 YB7-4-1 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.79 0.96 1.00 4.40 0.48 0.709 08 0.000 55 YB7-4-2 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 1.42 0.88 0.95 1.40 0.63 0.709 69 0.000 16 YB7-4-3 O1-2y 高角度缝方解石 0.81 0.93 1.04 1.91 0.86 YB8-6-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.94 0.47 0.84 0.10 0.28 YB8-7-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.29 0.92 0.61 1.07 0.48 YB8-7-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.79 0.96 0.95 0.64 0.54 0.708 77 0.000 34 YB8-7-2* O1-2y 0.708 71 0.000 20 YB8-8-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.72 0.96 0.71 0.81 0.65 0.708 83 0.000 41 YB8-8-1* O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.709 47 0.000 61 YB8-9-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 1.00 0.92 1.22 2.08 0.71 0.708 49 0.000 33 YB8-10-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.60 0.27 1.43 0.12 0.49 YB8-10-2 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 1.11 0.45 1.25 0.21 0.31 YB8-11A-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.65 0.94 1.66 4.78 1.51 YB8-11A-2 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 1.71 0.34 1.50 2.71 0.67 0.708 68 0.000 21 YB8-11B-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 1.02 0.95 1.27 1.70 0.47 0.709 00 0.000 31 YB8-11B-2 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.90 0.99 0.61 2.10 0.61 0.708 62 0.000 35 YB8-12-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.63 1.07 0.94 1.74 0.91 YB8-13-1 O1-2y 水平缝洞方解石 0.75 2.81 5.02 6.30 2.64 0.708 78 0.000 50 YB8-14A-1 O3l 孔洞方解石 0.64 0.76 0.96 7.55 0.31 PSB2-4-55-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 1.68 0.84 1.58 0.42 0.77 PSB2-4-55-2 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 1.22 0.80 0.90 14.42 0.54 PSB2-3-38-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.46 0.70 1.48 0.85 0.89 PSB2-5-50-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.85 0.90 1.17 5.10 1.18 PSB2-5-3-1 O1-2y 孔洞方解石 0.82 0.92 0.77 10.00 1.31 -
[1] 钱一雄, 余腾孝, 周凌方, 等. 麦盖提斜坡东部构造带奥陶系岩相、成岩作用带与储层成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 870-882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406016.htmQIAN Yixiong, YU Tengxiao, ZHOU Lingfang, et al. Lithofacies, diagenesis zone and reservoir origin of the Ordovician in eastern tectonic belt of the Maigaiti slope[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 870-882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406016.htm [2] 牛君, 黄文辉, 蒋文龙, 等. 玉北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩风化壳岩溶储层特征及其主控因素[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2016, 40(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.01.001NIU Jun, HUANG Wenhui, JIANG Wenlong, et al. Reservoir characterization and controlling factors of Ordovician weathering crust reservoir in Yubei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2016, 40(1): 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2016.01.001 [3] 刘忠宝, 高山林, 岳勇, 等. 塔里木盆地麦盖提斜坡奥陶系储层成因与分布[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(4): 654-663. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201404005.htmLIU Zhongbao, GAO Shanlin, YUE Yong, et al. Formation and distribution of the Ordovician reservoir in Maigaiti slope, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(4): 654-663. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201404005.htm [4] 张旭光. 玉北地区碳酸盐岩储层地震响应特征研究[J]. 石油物探, 2012, 51(5): 493-501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2012.05.011ZHANG Xuguang. Study on seismic response characteristics of carbonate reservoir in Yubei area[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2012, 51(5): 493-501. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2012.05.011 [5] 黄太柱. 塔里木盆地玉北地区断裂系统解析[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401013.htmHUANG Taizhu. Analysis on the fault system of Yubei region, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401013.htm [6] 陈刚, 汤良杰, 余腾孝, 等. 塔里木盆地玉北地区断裂构造差异变形及其控制因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(3): 42-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.03.007CHEN Gang, TANG Liangjie, YU Tengxiao, et al. Differential deformation and control mechanism of fault structures in Yubei area of Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2015, 37(3): 42-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2015.03.007 [7] 李慧莉, 刘士林, 杨圣彬, 等. 塔中—巴麦地区构造沉积演化及其对奥陶系储层的控制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 883-892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406017.htmLI Huili, LIU Shilin, YANG Shengbin, et al. Tectonic-sedimentary evolution of Tazhong-Bachu-Maigaiti area and its control on the Ordovician reservoir[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 883-892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406017.htm [8] 马海陇, 王震, 邓光校, 等. 塔里木盆地和田河东地区断裂特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(3): 329-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202103009.htmMA Hailong, WANG Zhen, DENG Guangxiao, et al. Fault features in eastern Hetianhe area, Tarim Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(3): 329-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202103009.htm [9] 于浩雨, 于明德, 李洲, 等. 洛伊凹陷西南部边界大断裂发育特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(5): 13-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005003.htmYU Haoyu, YU Mingde, LI Zhou, et al. Development characteristics of large fault in southwest boundary of Luoyi Sag and its controlling effect on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(5): 13-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202005003.htm [10] 于爱暄, 王有功, 刘世瑞, 等. 真武—汉留断裂带分段生长及其油气意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(3): 27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.03.005YU Aixuan, WANG Yougong, LIU Shirui, et al. Segmented growth of Zhenwu-Hanliu fault zone and its hydrocarbon significance[J]. Specail Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(3): 27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2020.03.005 [11] 吴梅莲, 刘永福, 彭鹏, 等. 轮南古潜山走滑断裂特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 456-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104006.htmWU Meilian, LIU Yongfu, PENG Peng, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip faults in Lunnan buried hill and its influence on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 456-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104006.htm [12] 汤好书, 陈衍景, 武广, 等. 辽东辽河群大石桥组碳酸盐岩稀土元素地球化学及其对Lomagundi事件的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11): 3075-3093. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911036.htmTANG Haoshu, CHEN Yanjing, WU Guang, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of carbonates of Dashiqiao Formation, Liaohe Group, eastern Liaoning province: implications for Lomagundi Event[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(11): 3075-3093. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200911036.htm [13] 崔军文. 南阿尔金断裂的韧性剪切作用时代及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3422-3434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111021.htmCUI Junwen. Ductile shearing age of the South Altun fault and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(11): 3422-3434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111021.htm [14] 黄思静, 卿海若, 胡作维, 等. 川东三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩的阴极发光特征与成岩作用[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2008, 33(1): 26-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200801007.htmHUANG Sijing, QING Hairuo, HU Zuowei, et al. Cathodoluminescence and diagenesis of the carbonate rocks in Feixianguan Formation of Triassic, eastern Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2008, 33(1): 26-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200801007.htm [15] MCLENNAN S M. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, 2(4): 2000GC000109. [16] MCARTHUR J M, HOWARTH R J, BAILEY T R. Strontium isotope stratigraphy: LOWESS version 3: best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0-509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2001, 109(2): 155-170. [17] ELDERFIELD H, UPSTILL-GODDARD R, SHOLKOVITZ E R. The rare earth elements in rivers, estuaries, and coastal seas and their significance to the composition of ocean waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(4): 971-991. [18] BANNER J L, HANSON G N, MEYERS W J. Rare earth element and Nd isotopic variations in regionally extensive dolomites from the Burlington-Keokuk formation (Mississippian): implications for REE mobility during carbonate diagenesis[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1988, 58(3): 415-432. [19] QING Hairuo, MOUNTJOY E W. Rare earth element geochemistry of dolomites in the Middle Devonian Presqu'ile barrier, Western Canada Sedimentary Basin: implications for fluid-rock ratios during dolomitization[J]. Sedimentology, 1994, 41(4): 787-804. [20] PALMER M R. Rare earth elements in foraminifera tests[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1985, 73(2/4): 285-298. [21] MICHARD A, ALBARÈDE F. The REE content of some hydrothermal fluids[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 55(1/2): 51-60. [22] OLIVAREZ A M, OWEN R M. The europium anomaly of seawater: implications for fluvial versus hydrothermal REE inputs to the oceans[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 92(4): 317-328. [23] ALEXANDER B W, BAU M, ANDERSSON P, et al. Continentally-derived solutes in shallow Archean seawater: rare earth element and Nd isotope evidence in iron formation from the 2.9 Ga Pongola Supergroup, South Africa[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(2): 378-394. [24] DEBRUYNE D, HULSBOSCH N, MUCHEZ P. Unraveling rare earth element signatures in hydrothermal carbonate minerals using a source-sink system[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 232-252. [25] ROBBINS L J, LALONDE S V, PLANAVSKY N J, et al. Trace elements at the intersection of marine biological and geochemical evolution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2016, 163: 323-348. [26] BAU M, BALAN S, SCHMIDT K, et al. Rare earth elements in mussel shells of the Mytilidae family as tracers for hidden and fossil high-temperature hydrothermal systems[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 299(3/4): 310-316. [27] 王宇航, 朱园园, 黄建东, 等. 海相碳酸盐岩稀土元素在古环境研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(9): 922-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201809006.htmWANG Yuhang, ZHU Yuanyuan, HUANG Jiandong, et al. Application of rare earth elements of the marine carbonate rocks in paleoenvironmental researches[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(9): 922-932. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201809006.htm [28] BAU M, KOSCHINSKY A, DULSKI P, et al. Comparison of the partitioning behaviours of yttrium, rare earth elements, and titanium between hydrogenetic marine ferromanganese crusts and seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(10): 1709-1725. [29] SHIELDS G A, WEBB G E. Has the REE composition of seawater changed over geological time?[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 204(1/2): 103-107. [30] ZHANG Jing, NOZAKI Y. Rare earth elements and yttrium in seawater: ICP-MS determinations in the East Caroline, Coral Sea, and South Fiji Basins of the western South Pacific Ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(23): 4631-4644. [31] GARCÍA M G, LECOMTE K L, PASQUINI A I, et al. Sources of dissolved REE in mountainous streams draining granitic rocks, Sierras Pampeanas (Córdoba, Argentina)[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(22): 5355-5368. [32] BAU M, DULSKI P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: implications for Y and REE behaviour during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 155(1/2): 77-90. [33] WHEAT C G, MOTTL M J, RUDNICKI M. Trace element and REE composition of a low-temperature ridge-flank hydrothermal spring[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(21): 3693-3705. [34] DOUVILLE E, BIENVENU P, CHARLOU J L, et al. Yttrium and rare earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(5): 627-643. [35] SMEDLEY P L. The geochemistry of rare earth elements in groundwater from the Carnmenellis area, southwest England[J]. Geochi-mica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(10): 2767-2779. [36] 胡文瑄, 陈琪, 王小林, 等. 白云岩储层形成演化过程中不同流体作用的稀土元素判别模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(6): 810-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201006017.htmHU Wenxuan, CHEN Qi, WANG Xiaolin, et al. REE models for the discrimination of fluids in the formation and evolution of dolomite reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(6): 810-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201006017.htm [37] MCARTHUR J M, BURNETT J, HANCOCK J M. Strontium isotopes at K/T boundary[J]. Nature, 1992, 355(6355): 28. [38] PALMER M R, ELDERFIELD H. Sr isotope composition of sea water over the past 75 Myr[J]. Nature, 1985, 314(6011): 526-528. [39] PALMER M R, EDMOND J M. The strontium isotope budget of the modern ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1989, 92(1): 11-26. [40] MOORE C H, CHOWDHURY A, CHAN L. Upper Jurassic Smackover platform dolomitization, northwestern gulf of Mexico: a tale of two waters[M]//SHUKLA V, BAKER P A. Sedimentology and Geochemistry of Dolostones. Tulsa: SEPM, 1988: 175-189. [41] 游声刚. 塔里木盆地玉北地区古构造演化对奥陶系岩溶储层的控制作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.YOU Shenggang. Controlling effect of paleotectonic evolution on Ordovician karst reservoir in Yubei area of Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2013. [42] 陈刚, 汤良杰, 余腾孝, 等. 塔里木盆地玉北冲断带分期活动特征及其控油气作用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2014, 43(5): 870-879. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201405016.htmCHEN Gang, TANG Liangjie, YU Tengxiao, et al. Poly-phase fault activities and the control on hydrocarbon accumulation of Yubei thrust belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2014, 43(5): 870-879. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201405016.htm [43] 丁文龙, 漆立新, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地巴楚—麦盖提地区古构造演化及其对奥陶系储层发育的控制作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2542-2556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208021.htmDING Wenlong, QI Lixin, YUN Lu, et al. The tectonic evolution and its controlling effects on the development of ordovician reservoir in Bachu-Markit Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2542-2556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201208021.htm -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号