Types and features of diagenetic fluids in Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone in Shuntuoguole Low Uplift, Tarim Basin
-
摘要: 塔里木盆地顺托果勒低隆起顺北4号走滑断裂带是该地区重点勘探目标,中奥陶统碳酸盐岩是主要的含油气层系。断裂活动及伴随断裂活动的断裂流体活动控制了研究区内储层的分布,因此,研究断裂流体的活动特征对勘探工作至关重要。针对研究区顺北4号断裂带内中奥陶统碳酸盐岩裂缝中的方解石进行了岩石学、原位锶同位素、原位稀土元素和U-Pb测年研究。方解石的锶同位素比值为0.708 498~0.709 177,方解石稀土元素表现出明显的Ce负异常、Eu正异常和高Y/Ho比值。方解石U-Pb测年获得的年龄分别为(433±17) Ma和(449±15) Ma。方解石的原位锶同位素和稀土元素特征说明流体充分继承了碳酸盐岩围岩的特征且经历了高温;U-Pb年龄则说明顺北4号断裂带方解石记录的更可能是与阿尔金造山带挤压造山相关的加里东中期Ⅲ幕运动的断裂流体活动。Abstract: The Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone is an important exploration target in the Shuntuoguole Low Uplift of Tarim Basin, and the Middle Ordovician carbonate is a major hydrocarbon-bearing stratum. Fault structures and accompanied fluids play a key role for the distribution of carbonate reservoirs, and it is therefore important to study the fluids accompanied with fault evolution. Petrography, in situ Sr isotopic compositions, in situ rare earth elements (REE) and U-Pb dating were carried out to reveal the fluids from which the calcites in fractures precipitated. The calcites in fractures show 87Sr/86Sr ratios of 0.708 498-0.709 177, and the REE patterns of the calcites are characterized by negative Ce anomaly, positive Eu anomaly and high Y/Ho ratios. The calcite samples show U-Pb isochron age of (433±17) Ma and (449±15) Ma, respectively. The 87Sr/86Sr ratios and REE patterns of the calcites suggest that parent fluids experienced elevated temperature environment and buffered by carbonate host rocks. The U-Pb isochron age implies that the calcites may record the fault-related fluids during the Ⅲ stage of the Middle Caledonian Movement, which might be associated with the Altyn orogeny.
-
Key words:
- strike-slip fault /
- diagenetic fluid /
- carbonates /
- geochemistry /
- Shunbei area /
- Tarim Basin
-
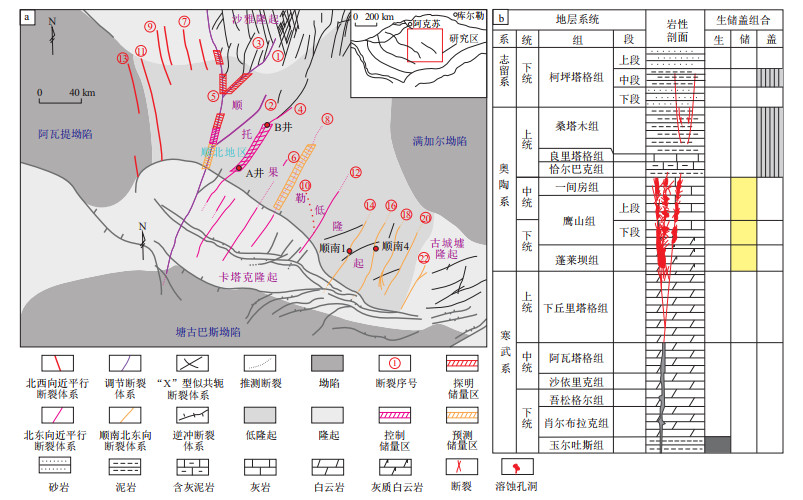
图 1 塔里木盆地顺北油气田构造位置(a)与地层柱状图(b)
据马永生等[12]修改。
Figure 1. Tectonic units (a) and stratigraphic column (b) of Shunbei oil & gas field, Tarim Basin
图 3 塔里木盆地顺北4号走滑断裂带中—下奥陶统碳酸盐岩缝洞充填物特征
a.岩心照片,孔洞中充填巨晶方解石(VC),另可见近层面发育的裂缝被方解石(C1)充填,其中VC方解石切割缝合线,而缝合线切割C1方解石,顺北A井,7 412.03 m,O2yj;b,c为a中红框区域的单偏光和阴极光照片,可见C1方解石在阴极射线下具有橙色的发光性;d.岩心照片,缝合线切割两期裂缝,顺北A井,O2yj;e.岩心照片,高角度裂缝被方解石充填,顺北B井;f,g为d红框中的单偏光和阴极光照片,其中,裂缝中沿边缘向中心依次分布两期方解石(C1、C2)、鞍形白云石(SD)和石英(QZ);h,i为e红框中的单偏光和阴极光照片,见裂缝被方解石(C2)充填,在阴极射线下具有中等橙色的发光性
Figure 3. Charcteristics of fracture-pore cements in Lower-Middle Ordovician carbonates in Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone, Tarim Basin
表 1 塔里木盆地顺北4号带方解石C2的原位87Sr/86Sr比值
Table 1. In situ Sr-isotope analysis of calcite C2 cement in Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone, Tarim Basin
样品编号 87Sr/86Sr 相对误差 SHB4-1-01 0.708 498 0.000 058 SHB4-1-02 0.708 705 0.000 074 SHB4-1-03 0.708 608 0.000 072 SHB4-2-01 0.709 040 0.000 043 SHB4-2-02 0.709 174 0.000 037 SHB4-2-03 0.708 937 0.000 040 SHB4-3-01 0.709 115 0.000 044 SHB4-3-02 0.709 175 0.000 045 SHB4-3-03 0.709 177 0.000 064 SHB4-4-01 0.709 049 0.000 074 SHB4-4-02 0.709 051 0.000 069 SHB4-4-03 0.709 145 0.000 059 SHB4-4-04 0.709 083 0.000 075 SHB4-6-01 0.709 127 0.000 072 SHB4-6-02 0.708 847 0.000 178 SHB4-6-03 0.709 111 0.000 097 表 2 塔里木盆地顺北4号段裂带方解石C2的原位微量元素含量
Table 2. In situ trace element contents of calcite C2 cement in Shunbei No. 4 strike-slip fault zone, Tarim Basin
微量元素 样品 SHB4-2-1 SHB4-2-2 SHB4-3-1 SHB4-3-2 SHB4-3-3 SHB4-4-5 SHB4-4-3 SHB4-4-8 SHB4-4-9 SHB4-4-10 SHB4-4 SHB4-5 Al/10-6 0.167 0.003 0.086 0.172 9.576 0.031 0.175 0.090 0.100 Sc/10-6 0.017 0.049 0.070 0.119 0.098 0.061 0.062 0.051 0.077 0.057 0.550 0.490 Mn/10-6 79.0 73.5 73.8 118.1 108.4 69.3 125.2 59.0 106.6 117.4 210.7 213.0 Sr/10-6 301.1 497.8 599.3 421.6 184.7 381.4 105.4 543.8 511.8 223.9 174.0 181.0 Ba/10-6 0.058 0.340 0.341 0.262 0.063 0.165 0.037 0.265 0.025 0.059 0.190 La/10-6 0.007 0.012 0.006 0.022 0.005 0.007 0.072 0.206 0.675 1.113 2.460 1.670 Ce/10-6 0.013 0.024 0.008 0.030 0.010 0.028 0.161 0.272 1.368 2.703 6.240 4.240 Pr/10-6 0.002 0.005 0.001 0.005 0.003 0.006 0.026 0.045 0.251 0.529 0.773 0.512 Nd/10-6 0.012 0.015 0.006 0.021 0.014 0.018 0.123 0.204 1.080 2.437 2.890 1.900 Sm/10-6 0.001 0.008 0.003 0.005 0.003 0.006 0.030 0.041 0.273 0.706 0.640 0.410 Eu/10-6 0.001 0.003 0.002 0.008 0.002 0.003 0.013 0.011 0.169 0.245 0.163 0.105 Gd/10-6 0.003 0.008 0.002 0.006 0.005 0.008 0.037 0.051 0.362 0.995 0.624 0.385 Tb/10-6 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.001 0.001 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.052 0.169 0.081 0.054 Dy/10-6 0.002 0.004 0.003 0.006 0.006 0.008 0.023 0.028 0.326 1.137 0.448 0.318 Y/10-6 0.028 0.081 0.035 0.056 0.067 0.096 0.213 0.281 2.637 8.742 2.570 2.070 Ho/10-6 0.000 0.002 0.000 0.001 0.002 0.002 0.004 0.005 0.062 0.237 0.086 0.061 Er/10-6 0.001 0.004 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.005 0.013 0.010 0.153 0.627 0.218 0.154 Tm/10-6 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.001 0.015 0.073 0.031 0.019 Yb/10-6 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.002 0.003 0.007 0.003 0.079 0.388 0.166 0.135 Lu/10-6 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.000 0.008 0.049 0.023 0.020 ∑REE/10-6 0.05 0.09 0.04 0.11 0.06 0.10 0.52 0.89 4.87 11.41 14.84 9.98 Eu异常 4.18 2.35 4.52 8.39 1.86 1.96 2.28 1.40 2.84 1.44 1.35 1.34 Ce异常 0.72 0.71 0.64 0.67 0.58 0.85 0.83 0.65 0.75 0.76 1.03 1.05 Y/Ho 67.6 52.8 87.2 57.9 44.2 39.2 53.2 54.9 42.3 37.0 30.0 33.9 -
[1] 漆立新, 云露. 塔里木台盆区碳酸盐岩成藏模式与勘探实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 867-876. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005867QI Lixin, YUN Lu. Carbonate reservoir forming model and exploration in Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 867-876. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005867 [2] 云露. 顺北地区奥陶系超深断溶体油气成藏条件[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102002.htmYUN Lu. Hydrocarbon accumulation of ultra-deep Ordovician fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102002.htm [3] 邓尚, 刘雨晴, 刘军, 等. 克拉通盆地内部走滑断裂发育、演化特征及其石油地质意义: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(6): 1111-1126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202106003.htmDENG Shang, LIU Yuqing, LIU Jun, et al. Structural styles and evolution models of intracratonic strike-slip faults and the implications for reservoir exploration and appraisal: a case study of the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(6): 1111-1126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK202106003.htm [4] 王斌, 赵永强, 何生, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北5号断裂带北段奥陶系油气成藏期次及其控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 965-974. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005008.htmWANG Bin, ZHAO Yongqiang, HE Sheng, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation stages and their controlling factors in the northern Ordovician Shunbei 5 fault zone, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 965-974. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005008.htm [5] 曹自成, 路清华, 顾忆, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北油气田1号和5号断裂带奥陶系油气藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 975-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005009.htmCAO Zicheng, LU Qinghua, GU Yi, et al. Characteristics of Ordovician reservoirs in Shunbei 1 and 5 fault zones, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 975-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005009.htm [6] 林波, 张旭, 况安鹏, 等. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造变形特征及油气意义: 以顺北地区1号和5号断裂为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 906-923. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107007.htmLIN Bo, ZHANG Xu, KUANG Anpeng, et al. Structural deformation characteristics of strike-slip faults in Tarim Basin and their hydrocarbon significance: a case study of No. 1 fault and No. 5 fault in Shunbei area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 906-923. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107007.htm [7] 韩俊, 况安鹏, 能源, 等. 顺北5号走滑断裂带纵向分层结构及其油气地质意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 152-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102004.htmHAN Jun, KUANG Anpeng, NENG Yuan, et al. Vertical layered structure of Shunbei No. 5 strike-slip fault zone and its significance on hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 152-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102004.htm [8] 黄诚, 云露, 曹自成, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中—下奥陶统"断控"缝洞系统划分与形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 54-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201004.htmHUANG Cheng, YUN Lu, CAO Zicheng, et al. Division and formation mechanism of fault-controlled fracture-vug system of the Middle-to-Lower Ordovician, Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 54-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201004.htm [9] 漆立新, 云露, 曹自成, 等. 顺北油气田地质储量评估与油气勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102001.htmQI Lixin, YUN Lu, CAO Zicheng, et al. Geological reserves assessment and petroleum exploration targets in Shunbei oil & gas field[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102001.htm [10] 李映涛, 漆立新, 张哨楠, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中—下奥陶统断溶体储层特征及发育模式[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1470-1484. doi: 10.7623/syxb201912006LI Yingtao, QI Lixin, ZHANG Shaonan, et al. Characteristics and development mode of the Middle and Lower Ordovician fault-karst reservoir in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1470-1484. doi: 10.7623/syxb201912006 [11] 吕海涛, 韩俊, 张继标, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区超深碳酸盐岩断溶体发育特征与形成机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(1): 14-22. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101014LV Haitao, HAN Jun, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Development characte-ristics and formation mechanism of ultra-deep carbonate fault-dissolution body in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2021, 43(1): 14-22. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101014 [12] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, YUN Lu, et al. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htm [13] 金之钧, 朱东亚, 胡文瑄, 等. 塔里木盆地热液活动地质地球化学特征及其对储层影响[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(2): 245-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200602014.htmJIN Zhijun, ZHU Dongya, HU Wenxuan, et al. Geological and geochemical signatures of hydrothermal activity and their influence on carbonate reservoir beds in the Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(2): 245-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200602014.htm [14] 金之钧, 朱东亚, 孟庆强, 等. 塔里木盆地热液流体活动及其对油气运移的影响[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(3): 1048-1058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303026.htmJIN Zhijun, ZHU Dongya, MENG Qingqiang, et al. Hydrothermal activites and influences on migration of oil and gas in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(3): 1048-1058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201303026.htm [15] QING Hairuo, CHI Guoxiang, ZHANG Shaonan. Origin of coarse-crystalline calcite cement in Early Ordovician carbonate rocks, Ordos Basin, northern China: insights from oxygen and carbon isotopes and fluid inclusion microthermometry[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 89(1/3): 344-347. [16] DONG Shaofeng, CHEN Daizhao, QING Hairuo, et al. Hydrothermal alteration of dolostones in the Lower Ordovician, Tarim Basin, NW China: multiple constraints from petrology, isotope geochemistry and fluid inclusion microthermometry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 46: 270-286. [17] DONG Shaofeng, CHEN Daizhao, ZHOU Xiqiang, et al. Tectonically driven dolomitization of Cambrian to Lower Ordovician carbonates of the Quruqtagh area, north-eastern flank of Tarim Basin, north-west China[J]. Sedimentology, 2017, 64(4): 1079-1106. [18] 李映涛, 叶宁, 袁晓宇, 等. 塔里木盆地顺南4井中硅化热液的地质与地球化学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(6): 934-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201506010.htmLI Yingtao, YE Ning, YUAN Xiaoyu, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics of silicified hydrothermal fluids in well Shunnan 4, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(6): 934-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201506010.htm [19] LU Ziye, CHEN Honghan, QING Hairuo, et al. Petrography, fluid inclusion and isotope studies in Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in the Shunnan area, Tarim Basin, NW China: implications for the nature and timing of silicification[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 359: 29-43. [20] 滕建彬. 东营凹陷页岩油储层中方解石的成因及证据[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(2): 18-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002004.htmTENG Jianbin. Origin and evidence of calcite in shale oil reservoir of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(2): 18-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002004.htm [21] MORROW D W. Zebra and boxwork fabrics in hydrothermal dolomites of northern Canada: indicators for dilational fracturing, dissolution or in situ replacement?[J]. Sedimentology, 2014, 61(4): 915-951. [22] JIANG Lei, CAI Chunfang, WORDEN R H, et al. Multiphase dolomitization of deeply buried Cambrian petroleum reservoirs, Tarim Basin, north-west China[J]. Sedimentology, 2016, 63(7): 2130-2157. [23] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htmDENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm [24] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 韩俊, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断裂中段活动特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(5): 990-998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201905004.htmDENG Shang, LI Huili, HAN Jun, et al. Characteristics of the central segment of Shunbei 5 strike-slip fault zone in Tarim Basin and its geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(5): 990-998. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201905004.htm [25] LI Bing, ZHAO Rui, KONG Qiangfu, et al. An Ordovician carbonate reservoir in strike-slip structures producing from faultassociated fracture systems, 3D seismic region of northern Shun 8 block (Tarim Basin)[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites, 2019, 34(3): 545-556. [26] DENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Structural characte-rization of intracratonic strike-slip faults in the central Tarim Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(1): 109-137. [27] QIU Huabiao, DENG Shang, CAO Zicheng, et al. The evolution of the complex anticlinal belt with crosscutting strike-slip faults in the central Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Tectonics, 2019, 38(6): 2087-2113. [28] 陈槚俊, 何登发, 孙方源, 等. 塔北古隆起的三维地质结构及相关问题探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 121-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901014.htmCHEN Jiajun, HE Dengfa, SUN Fangyuan, et al. Three-dimensional geological modeling of the Tabei paleo-uplift and discussion on related issues[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 121-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901014.htm [29] 黄太柱, 蒋华山, 马庆佑. 塔里木盆地下古生界碳酸盐岩油气成藏特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 780-787. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406007.htmHUANG Taizhu, JIANG Huashan, MA Qingyou. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics in Lower Paleozoic carbonate reservoirs of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 780-787. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406007.htm [30] TONG Xirun, LIU Yongsheng, HU Zhaochu, et al. Accurate determination of Sr isotopic compositions in clinopyroxene and silicate glasses by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(1): 85-99. [31] PATON C, HELLSTROM J, PAUL B, et al. Iolite: freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(12): 2508-2518. [32] 沈安江, 胡安平, 程婷, 等. 激光原位U-Pb同位素定年技术及其在碳酸盐岩成岩—孔隙演化中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6): 1062-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906006.htmSHEN Anjiang, HU Anping, CHENG Ting, et al. Laser ablation in situ U-Pb dating and its application to diagenesis-porosity evolution of carbonate reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1062-1074. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906006.htm [33] VAN SMEERDIJK HOOD A, WALLACE M W. Extreme ocean anoxia during the Late Cryogenian recorded in reefal carbonates of southern Australia[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 261: 96-111. [34] BAU M, MÖLLER P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite[J]. Mineralogy & Petrology, 1992, 45(3): 231-246. [35] CAI Chunfang, LI Kaikai, LI Hongtao, et al. Evidence for cross formational hot brine flow from integrated 87Sr/86Sr, REE and fluid inclusions of the Ordovician veins in central Tarim, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23(8): 2226-2235. [36] BAU M. Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 93(3/4): 219-230. [37] GONG Qiaolin, LI Fei, LU Chaojin, et al. Tracing seawater- and terrestrial-sourced REE signatures in detritally contaminated, diagenetically altered carbonate rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 570: 120169. [38] BAU M, ROMER R L, LVDERS V, et al. Tracing element sources of hydrothermal mineral deposits: REE and Y distribution and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes in fluorite from MVT deposits in the Pennine Orefield, England[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(8): 992-1008. [39] BAU M, DULSKI P. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 119(2/3): 213-223. [40] MIGDISOV A, WILLIAMS-JONES A E, BRUGGER J, et al. Hydrothermal transport, deposition, and fractionation of the REE: experimental data and thermodynamic calculations[J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 439: 13-42. [41] MACHEL H. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings: old and new insights[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 140(1/2): 143-175. [42] LI Fei, YAN Jiaxin, BURNE R V, et al. Paleo-seawater REE compositions and microbial signatures preserved in laminae of Lower Triassic ooids[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 486: 96-107. [43] MCARTHUR J M, HOWARTH R J, BAILEY T R. Strontium isotope stratigraphy: LOWESS version 3: best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0-509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2001, 109(2): 155-170. [44] ZHU Dongya, LIU Quanyou, ZHANG Juntao, et al. Types of fluid alteration and developing mechanism of deep marine carbonate reservoirs[J]. Geofluids, 2019, 2019: 3630915. [45] GE Xiang, SHEN Chuanbo, ZHOU Renjie, et al. Tracing fluid evolution in sedimentary basins with calcite geochemical, isotopic and U-Pb geochronological data: implications for petroleum and mineral resource accumulation in the Nanpanjiang Basin, South China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1130/B36168.1. [46] 崔军文, 唐哲民. 塔里木盆地构造格架和构造应力场分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 231-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101016.htmCUI Junwen, TANG Zhemin. Tectonic framework of the Tarim Basin and its tectonic stress field analysis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(1): 231-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101016.htm [47] MACHEL H G, CAVELL P A. Low-flux, tectonically-induced squeegee fluid flow ("hot flash") into the Rocky Mountain Foreland Basin[J]. Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology, 1999, 47(4): 510-533. [48] WENZ Z J, APPOLD M S, SHELTON K L, et al. Geochemistry of Mississippi Valley-type mineralizing fluids of the Ozark Plateau: a regional synthesis[J]. American Journal of Science, 2012, 312(1): 22-80. [49] GABELLONE T, GASPARRINI M, IANNACE A, et al. Fluid channeling along thrust zones: the Lagonegro case history, southern Apennines, Italy[J]. Geofluids, 2013, 13(2): 140-158. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号