Application of visual 3D physical simulation experiment technology in oil and gas accumulation research: a case study of well S53-2 in Shunbei area of Tarim Basin
-
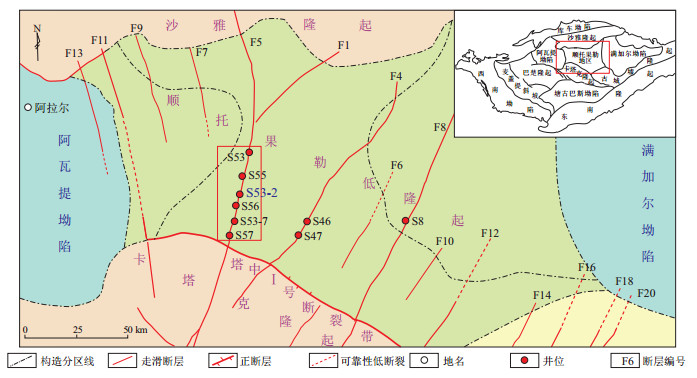
摘要: 油气成藏物理模拟实验技术是研究油气运移聚集过程的重要技术手段,可以在实验室条件下,实现油气运移成藏动态化、可视化、定量化研究。但传统二维物理模拟实验技术存在细微现象缺乏、含油性测量难、观察面单一等不足。针对这些问题,同时为了揭示超深层油气成藏特征,研发了一种可视化三维油气成藏物理模拟实验技术,并成功模拟了塔里木盆地顺北地区S53-2井的成藏过程。明确了超深断控油气藏油气成藏影响因素;揭示了断层和缝网系统在断控油气藏形成过程中扮演双重角色,其既作为油气运移通道,也是重要的油气储集空间;提出了主断层、缝网及缝网一侧的地堑断层是油气的优势聚集区;建立了“浮力垂向运移、先核部后破碎带、先主干后地堑、缝网输储一体、主次断裂各异”的油气成藏模式。新技术使实验过程更加清晰,实验参数更加准确,实验现象更加立体,可为实验室油气成藏模拟工作提供新的支撑。Abstract: The physical simulation experiment technology for oil and gas reservoir formation is an important technical means to study the process of oil and gas migration and accumulation. Under laboratory conditions, dynamic, visual, and quantitative research on oil and gas migration and reservoir formation can be achieved. However, traditional two-dimensional physics simulation experimental techniques have shortcomings such as a lack of subtle phenomena, difficulty in measuring oil content, and a single observation surface. To address these issues, and to reveal the characteristics of ultra-deep oil and gas accumulation, a visual 3D physical simulation experiment technology of oil and gas accumulation was developed, and the accumulation process of well S53-2 in Shunbei area of Tarim Basin was successfully simulated. The influencing factors of oil and gas accumulation in ultra-deep fault controlled oil and gas reservoirs have been clarified, revealing that faults and fracture network systems play a dual role in the formation process of fault controlled oil and gas reservoirs, serving as both oil and gas migration channels and important oil and gas storage spaces. It has been proposed that the main fault, fracture network, and the graben fault on one side of the fracture network are advantageous areas for oil and gas accumulation, and a "buoyancy vertical migration, first fault core and then damage zone, first main trunk and then graben, fracture network integrated transportation and storage, and different main and secondary faults" oil and gas accumulation model has been established. The new technology makes the experimental process clearer, the experimental parameters more accurate, and the experimental phenomena more three-dimensional, providing new support for laboratory oil and gas reservoir simulation work.
-
Key words:
- fault-controlled reservoir /
- oil and gas accumulation /
- physical simulation /
- Tarim Basin
-
表 1 模拟实验类型及特点
Table 1. Types and characteristics of simulation experiments
实验分类 装置组成 技术特点 缺点 主要应用 微观逾渗模拟实验 蚀刻玻璃、树脂 用于微观实验 模型制作困难、结果可信度差 用于孔隙尺度浮力运移特征模拟 一维管状模拟实验 玻璃管、钢管、玻璃珠 制作简单、应用广泛 玻璃管模型仅适合低温低压,钢管模型观察难、参数测定难 用于单一方向油气运移路径、机理研究 二维砂箱模拟实验 二维玻璃箱、石英砂 可模拟二维平面运移规律 密封差,仅适合低温低压 用于油气运移特征、方式与成藏影响因素研究 二维改良砂箱模拟实验 二维金属箱、钢板、推进杆、石英砂等 可加温加压、可手动动态模拟 密封差、含油性测定难、缺乏微观现象 用于研究油气运移过程与影响因素 可视化三维模拟实验 三维固结模型、核磁等 可模拟三维立体运移规律、实验过程立体可视、参数测定简单、模型密封 用于油气运移成藏过程与成藏机制研究 表 2 三维物理模拟实验参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters of three-dimensional physical simulation
编号 宽度/cm 粒径/目 密度/(g/cm3) 孔隙度/% 断层F1 1.5 40∶200(9∶1) 1.516 37.4 F1破碎带 3 60 1.625 34.5 断层F2 1 80 1.600 33.6 F2破碎带 2 60 2.074 28.4 断层F3 0.5 80 1.967 25.8 F3破碎带 1 80∶200(2∶1) 2.019 18.7 缝网 5 200 1.728 23.9 基质 200 2.082 15.1 盖层和隔层 橡胶 注:表中40∶200(9∶1)指40目和200目以9∶1的比例混合,80∶200(2∶1)指80目和200目以2∶1的比例混合。 -
[1] 曾溅辉, 金之钧, 王伟华. 油气二次运移和聚集实验模拟研究现状与发展[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 21(5): 94-97.ZENG Jianhui, JIN Zhijun, WANG Weihua. Status and advances of the studies on the experimental simulation of secondary hydrocarbon migration and accumulation[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 1997, 21(5): 94-97. [2] 公言杰, 柳少波, 姜林, 等. 油气二次运移可视化物理模拟实验技术研究进展[J]. 断块油气田, 2014, 21(4): 458-462.GONG Yanjie, LIU Shaobo, JIANG Lin, et al. Research progress in visual physical simulation experiment technology of secondary hydrocarbon migration[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2014, 21(4): 458-462. [3] MUNN M J. Studies in the application of the anticlinal theory of oil and gas accumulation[J]. Economic Geology, 1909, 4(2): 141-157. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.4.2.141 [4] EMMONS W H. Experiments on accumulation of oil in sands: abstract[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1921, 5(1): 103-104. [5] HUBBERT M K. Entrapment of petroleum under hydrodynamic conditions[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1953, 37(8): 1954-2026. [6] HILL V G. Geochemical prospecting for nickel in the Blue Mountain area, Jamaica, W.I. [J]. Economic Geology, 1961, 56(6): 1025-1032. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.56.6.1025 [7] LENORMAND R, TOUBOUL E, ZARCONE C. Numerical models and experiments on immiscible displacements in porous media[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 189: 165-187. doi: 10.1017/S0022112088000953 [8] SCHOWALTER T T. Mechanics of secondary hydrocarbon migration and entrapment[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1979, 63(5): 723-760. [9] DEMBICKI Jr H, ANDERSON M J. Secondary migration of oil: experiments supporting efficient movement of separate, buoyant oil phase along limited conduits: geologic note[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73(8): 1018-1021. [10] CATALAN L, FU X, CHATZIS I, et al. An experimental study of secondary oil migration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(5): 638-650. [11] TOKUNAGA T, MOGI K, MATSUBARA O, et al. Buoyancy and interfacial force effects on two-phase displacement patterns: an experimental study[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(1): 65-74. [12] THOMAS M M, CLOUSE J A. Scaled physical model of secondary oil migration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1995, 79(1): 19-28. [13] 张发强, 罗晓容, 苗盛, 等. 石油二次运移优势路径形成过程实验及机理分析[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(2): 159-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.02.002ZHANG Faqiang, LUO Xiaorong, MIAO Sheng, et al. Experiments on oil migrating in a limited pathway and the mechanism analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(2): 159-167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.02.002 [14] 张云峰, 王朋岩, 陈章明. 烃源岩之下岩性油藏成藏模拟实验及其机制分析[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(4): 436-443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.00705-2013ZHANG Yunfeng, WANG Pengyan, CHEN Zhangming. A modeling experiment on lithologic reservoir formation underlying source rocks and analysis of the mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2002, 37(4): 436-443. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.00705-2013 [15] 曾溅辉, 王洪玉. 反韵律砂层石油运移模拟实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(4): 592-597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.04.019ZENG Jianhui, WANG Hongyu. Experimental study of oil migration in coarsening upwards sands[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(4): 592-597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.04.019 [16] 姜林, 洪峰, 柳少波, 等. 油气二次运移过程差异物理模拟实验[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(5): 784-788.JlANG Lin, HONG Feng, LIU Shaobo, et al. Physical simulation of oil and natural gas secondary migration[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(5): 784-788. [17] 苗顺德, 曾溅辉, 李秋芬. 复合反"Y"字型构造中油气二次运移与聚集过程物理模拟研究: 以黄骅坳陷港东构造带为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(6): 18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2007.06.004MIAO Shunde, ZENG Jianhui, LI Qiufen. Physical simulation of secondary petroleum migration and accumulation process in complicated reserve Y-type structures by taking Gangdong tectonic belt in Huanghua Depression for example[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2007, 29(6): 18-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2007.06.004 [18] 罗晓容. 油气运聚动力学研究进展及存在问题[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(5): 337-346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.05.002LUO Xiaorong. Review of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation dynamics[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(5): 337-346. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.05.002 [19] 罗群, 王仕琛, 贾春, 等. 断控气藏的动态成藏物理模拟与启示: 以柴达木盆地西北地区典型气藏为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(5): 790-803. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205790LUO Qun, WANG Shichen, JIA Chun, et al. Physical simulation of dynamic accumulation of fault-controlled gas reservoirs and its implications: a case study of typical gas reservoirs in northwestern part of Qaidam Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(5): 790-803. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205790 [20] 韩晓影, 汤良杰, 曹自成, 等. 塔中北坡"复合花状"构造发育特征及成因机制[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(2): 525-537.HAN Xiaoying, TANG Liangjie, CAO Zicheng, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of composite flower structures in northern slope of Tazhong Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(2): 525-537. [21] 汤良杰, 漆立新, 邱海峻, 等. 塔里木盆地断裂构造分期差异活动及其变形机理[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8): 2569-2583.TANG Liangjie, QI Lixin, QIU Haijun, et al. Poly-phase differential fault movement and hydrocarbon accumulation of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2569-2583. [22] 刘雨晴, 邓尚, 张继标, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区走滑断裂体系差异发育特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 95-109.LIU Yuqing, DENG Shang, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the strike-slip fault networks in the Shunbei area and the surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 95-109. [23] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888.DENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. [24] 邓尚, 刘雨晴, 刘军, 等. 克拉通盆地内部走滑断裂发育、演化特征及其石油地质意义: 以塔里木盆地顺北地区为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(6): 1111-1126.DENG Shang, LIU Yuqing, LIU Jun, et al. Structural styles and evolution models of intracratonic strike-slip faults and the implications for reservoir exploration and appraisal: a case study of the Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 45(6): 1111-1126. [25] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 韩俊, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断裂中段活动特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(5): 990-998.DENG Shang, LI Huili, HAN Jun, et al. Characteristics of the central segment of Shunbei 5 strike-slip fault zone in Tarim Basin and its geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(5): 990-998. [26] 林波, 张旭, 况安鹏, 等. 塔里木盆地走滑断裂构造变形特征及油气意义: 以顺北地区1号和5号断裂为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 906-923.LIN Bo, ZHANG Xu, KUANG Anpeng, et al. Structural deformation characteristics of strike-slip faults in Tarim Basin and their hydrocarbon significance: a case study of No. 1 fault and No. 5 fault in Shunbei area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 906-923. [27] 云露, 朱秀香. 一种新型圈闭: 断控缝洞型圈闭[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 34-42.YUN Lu, ZHU Xiuxiang. A new trap type: fault-controlled fracture-vuggy trap[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 34-42. [28] 漆立新. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒隆起奥陶系碳酸盐岩超深层油气突破及其意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(3): 38-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.03.004QI Lixin. Oil and gas breakthrough in ultra-deep Ordovician carbonate formations in Shuntuoguole Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(3): 38-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2016.03.004 [29] 焦方正. 塔里木盆地顺北特深碳酸盐岩断溶体油气藏发现意义与前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 207-216.JIAO Fangzheng. Significance and prospect of ultra-deep carbonate fault-karst reservoirs in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 207-216. [30] 刘宝增. 塔里木盆地顺北地区油气差异聚集主控因素分析: 以顺北1号、顺北5号走滑断裂带为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(3): 83-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.008LIU Baozeng. Analysis of main controlling factors of oil and gas differential accumulation in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin: taking Shunbei No. 1 and No. 5 strike slip fault zones as examples[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(3): 83-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.008 [31] 漆立新. 塔里木盆地顺北超深断溶体油藏特征与启示[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 102-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.010QI Lixin. Characteristics and inspiration of ultra-deep fault-karst reservoir in the Shunbei area of the Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 102-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.010 [32] 漆立新, 云露, 曹自成, 等. 顺北油气田地质储量评估与油气勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 127-135.QI Lixin, YUN Lu, CAO Zicheng, et al. Geological reserves assessment and petroleum exploration targets in Shunbei oil & gas field[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 127-135. [33] 云露, 邓尚. 塔里木盆地深层走滑断裂差异变形与控储控藏特征: 以顺北油气田为例[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(6): 770-787.YUN Lu, DENG Shang. Structural styles of deep strike-slip faults in Tarim Basin and the characteristics of their control on reservoir formation and hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Shunbei oil and gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(6): 770-787. [34] 林波, 云露, 李海英, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断层空间结构及其油气关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(6): 1344-1353.LIN Bo, YUN Lu, LI Haiying, et al. Spatial structure of Shunbei No. 5 strike-slip fault and its relationship with oil and gas reservoirs in the Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(6): 1344-1353. [35] 鲍典, 曹飞, 张娟, 等. 超深层走滑断裂带应力场模拟及其开发意义: 以顺北5号断裂带南段为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(31): 13254-13264. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.31.13254BAO Dian, CAO Fei, ZHANG Juan, et al. Simulation of stress field in ultra deep strike slip fault zone and its development significance: a case study of the southern section of Shunbei No. 5 fault zone[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(31): 13254-13264. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.23.31.13254 [36] 李映涛, 邓尚, 张继标, 等. 深层致密碳酸盐岩走滑断裂带核带结构与断控储集体簇状发育模式: 以塔里木盆地顺北4号断裂带为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 80-94.LI Yingtao, DENG Shang, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Fault zone architecture of strike-slip faults in deep, tight carbonates and development of reservoir clusters under fault control: a case study in Shunbei, Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 80-94. [37] 郭铮. 埕岛地区新近系石油运移与聚集物理模拟实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.GUO Zheng. Physical simulation experiment study of Neogene petroleum migration and accumulation in Chengdao area[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018. [38] 曾溅辉, 王洪玉. 输导层和岩性圈闭中石油运移和聚集模拟实验研究[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 1999, 24(2): 193-196.ZENG Jianhui, WANG Hongyu, An experimental study of petroleum migration and accumulation in carrier bed and lithological trap[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 1999, 24(2): 193-196. [39] 曾溅辉, 王捷等. 油气运移机理及物理模拟实验[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003: 1-2.ZENG Jianhui, WANG Jie, et al. Mechanisms and physical simulation of hydrocarbon migration[M]Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 1-2. [40] 陈章明, 张云峰, 韩有信, 等. 凸镜状砂体聚油模拟实验及其机理分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 1998, 20(2): 166-170. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199802166CHEN Zhangming, ZHANG Yunfeng, HAN Youxin, et al. A modelling experiment and mechanism analysis of oil accumulation in pod-like sand-body[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1998, 20(2): 166-170. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199802166 -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号