Overpressure formation mechanism in deep and ultra-deep layers in middle section of southern margin of Junggar Basin and its relationship with reservoir formation: a case study of Hutan 1 gas reservoir
-
摘要: 近年来,准噶尔盆地南缘深层—超深层油气勘探不断取得突破,该地区深层—超深层普遍发育超压,明确超压成因机制及其与油气富集关系,对深层—超深层的油气勘探具有指导意义。利用DST实测压力资料分析了南缘深层—超深层压力分布特征,通过综合泥岩压实曲线、VES-VP交会图版、DEN-VP交会图版综合判识了HT1气藏复杂超压成因,并结合声发射实验及应力场模拟等技术方法,分析讨论了HT1气藏超压与油气成藏的关系。分析认为:(1)南缘深层—超深层除山前第一排冲断带外,普遍发育压力系数达2.0以上的极强超压。垂向上超压分布在吐谷鲁群厚层泥岩及其之下地层中,平面上强超压主要发育在南缘中段山前第二、三排构造带及西段四棵树凹陷内;(2)综合识别出HT1气藏发育欠压实成因及构造挤压成因超压,其中区域性厚层泥岩快速沉积造成欠压实超压产生,而喜马拉雅运动晚期天山隆起对南缘形成的N-S向强挤压应力是深层—超深层构造挤压超压形成的原因;(3)深层流体超压的形成,一方面促进了HT1气藏清水河组背斜圈闭的褶皱变形,形成油气优势汇聚部位,另一方面改变了呼西背斜周缘的流体动力场格局,使得气势梯度增加,增强了天然气运移动力,为油气在呼西背斜的富集提供了良好的动力条件。Abstract: In recent years, breakthroughs have been continuously made in deep and ultra-deep oil and gas exploration in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin. Overpressure is commonly developed in the deep and ultra-deep layers of this area. Clarifying the overpressure formation mechanism and its relationship with oil and gas enrichment is of great significance for guiding oil and gas exploration in these areas. In this study, the pressure distribution characteristics in the deep and ultra-deep layers of the southern margin were analyzed using drill stem test (DST)-measured pressure data. The complex overpressure formation mechanism in Hutan 1 (HT1) gas reservoir was identified through comprehensive analysis of mudstone compaction curves, VES-VP cross-plots, and DEN-VP cross-plots. Based on the acoustic emission experiments and stress field simulations, the relationship between overpressure and oil and gas accumulation in HT1 gas reservoir was analyzed and discussed. The analysis showed that: (1) Except for the first row of thrust belts at the mountain front, extremely strong overpressure with a pressure coefficient greater than 2.0 was widely developed in the deep and ultra-deep layers of the southern margin. Vertically, overpressure was distributed in the thick mudstone of the Tugulu Group and its underlying strata. Horizontally, strong overpressure mainly developed in the second and third rows of structural belts at the mountain front in the middle section of the southern margin and in the Sikeshu Sag in the western section. (2) Comprehensive analysis identified that the overpressure in HT1 gas reservoir was caused by undercompaction and structural compression. Regional rapid deposition of thick mudstone caused undercompaction-associated overpressure, while the strong north-south trending compressive stress exerted by the Tianshan uplift during the late Himalayan Movement onto the southern margin caused structural compression overpressure in the deep and ultra-deep layers. (3) The formation of fluid overpressure in the deep layers promoted the folding deformation of the anticline trap in the Qingshuihe Formation of HT1 gas reservoir, forming an optimal area for oil and gas accumulation. Meanwhile, it changed the fluid dynamic field pattern around the Huxi anticline, increasing the gas potential gradient and enhancing the natural gas migration dynamics, thus providing favorable dynamic conditions for oil and gas enrichment in the Huxi anticline.
-
图 3 准噶尔盆地南缘深层—超深层典型井压力剖面
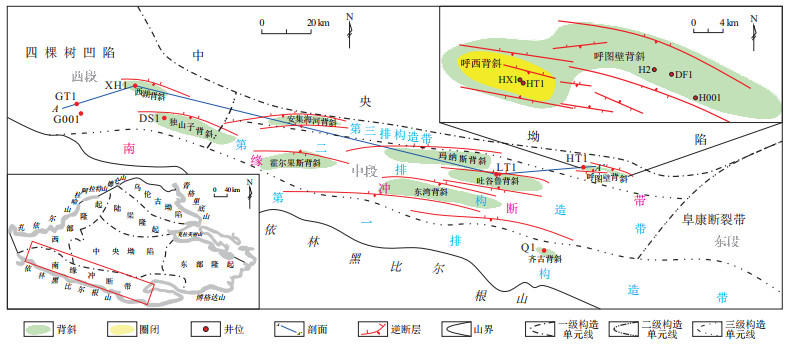
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 3. Pressure profiles of typical wells in deep and ultra-deep layers of southern margin of Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地南缘白垩系清水河组声发射样品测试结果
Table 1. Acoustic emission test results of samples from Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in southern margin of Junggar Basin
地点 水平最大有效应力/MPa 水平最小有效应力/MPa 头屯河剖面 36.62 22.71 清水河剖面 74.83 41.43 清水河鼻状构造剖面 94.79 3.51 G001井 65.63 6.23 -
[1] 李剑, 佘源琦, 高阳, 等. 中国陆上深层—超深层天然气勘探领域及潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(4): 403-417.LI Jian, SHE Yuanqi, GAO Yang, et al. Onshore deep and ultra-deep natural gas exploration fields and potentials in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(4): 403-417. [2] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 黄仁春, 等. 四川盆地深层—超深层天然气勘探进展与展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(5): 1-14.GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, HUANG Renchun, et al. Deep and ultra-deep natural gas exploration in the Sichuan Basin: progress and prospect[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(5): 1-14. [3] ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Theory, technology and practice of unconventional petroleum geology[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2023, 34(4): 951-965. doi: 10.1007/s12583-023-2000-8 [4] 杜金虎, 支东明, 李建忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井重大发现及下组合勘探前景展望[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(2): 205-215.DU Jinhu, ZHI Dongming, LI Jianzhong, et al. Major breakthrough of well Gaotan 1 and exploration prospects of lower assemblage in southern margin of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(2): 205-215. [5] 王招明. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷克拉苏盐下深层大气田形成机制与富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(2): 153-166.WANG Zhaoming. Formation mechanism and enrichment regularities of Kelasu subsalt deep large gas field in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(2): 153-166. [6] 郭旭升, 腾格尔, 魏祥峰, 等. 四川盆地深层海相页岩气赋存机理与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 453-468.GUO Xusheng, BORJIGIN Tenger, WEI Xiangfeng, et al. Occurrence mechanism and exploration potential of deep marine shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. [7] 邱振, 窦立荣, 吴建发, 等. 川北—鄂西地区中二叠统层序岩相古地理演化及页岩气勘探潜力[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(2): 712-748.QIU Zhen, DOU Lirong, WU Jianfa, et al. 2023. Lithofacies palaeogeographic evolution of the Middle Permian sequence stratigraphy and its implications for shale gas exploration in the northern Sichuan and western Hubei provinces[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(2): 712-748. [8] 张向涛, 李军, 向绪洪, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区白云凹陷超压成因机制及其勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(1): 41-57.ZHANG Xiangtao, LI Jun, XIANG Xuhong, et al. Genetic mechanism of overpressure and its significance on petroleum exploration in Baiyun Sag in the deep water zone of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 41-57. [9] 张凤奇, 王震亮, 赵雪娇, 等. 库车坳陷迪那2气田异常高压成因机制及其与油气成藏的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 739-747.ZHANG Fengqi, WANG Zhenliang, ZHAO Xuejiao, et al. Genetic mechanism of overpressure and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in Dina-2 gasfield, Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 739-747. [10] 鲁雪松, 张凤奇, 赵孟军, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井超压成因与盖层封闭能力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 666-675.LU Xuesong, ZHANG Fengqi, ZHAO Mengjun, et al. Genesis of overpressure and sealing ability of caprocks in well Gaotan 1 in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 666-675. [11] 胡东风, 魏志红, 李宇平, 等. 四川盆地东南部地区复杂构造带深层页岩气勘探进展与突破[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8): 35-44. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.004HU Dongfeng, WEI Zhihong, LI Yuping, et al. Deep shale gas exploration in complex structure belt of the southeastern Sichuan Basin: progress and breakthrough[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8): 35-44. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.004 [12] 苏义脑, 路保平, 刘岩生, 等. 中国陆上深井超深井钻完井技术现状及攻关建议[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2020, 42(5): 527-542.SU Yi'nao, LU Baoping, LIU Yansheng, et al. Status and research suggestions on the drilling and completion technologies for onshore deep and ultra deep wells in China[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 42(5): 527-542. [13] 李阳, 薛兆杰, 程喆, 等. 中国深层油气勘探开发进展与发展方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 45-57.LI Yang, XUE Zhaojie, CHENG Zhe, et al. Progress and development directions of deep oil and gas exploration and development in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 45-57. [14] 况军. 准噶尔盆地西南部构造特征及油气聚集分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1991, 18(6): 11-18.KUANG Jun. The structural characteristics and analysis of oil and gas accumulation in the southwestern part of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Expoloration and Development, 1991, 18(6): 11-18. [15] 廖健德, 赵增义, 马万云, 等. 准噶尔盆地呼图壁气田油气成因及成藏分析[J]. 新疆地质, 2011, 29(4): 453-456.LIAO Jiande, ZHAO Zengyi, MA Wanyun, et al. Analysis on oil-gas origin and accumulation hydrocarbons in Hutubi Gas Field, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2011, 29(4): 453-456. [16] 查明, 张卫海, 曲江秀. 准噶尔盆地异常高压特征、成因及勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(2): 31-35.ZHA Ming, Zhang Weihai, Qu Jiangxiu. The character and origin of overpressure and its explorational significance in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(2): 31-35. [17] 宋岩, 夏新宇, 洪峰, 等. 前陆盆地异常压力特征与天然气成藏模式[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(S1): 70-76.SONG Yan, XIA Xinyu, HONG Feng et al. Abnormal overpressure distribution and natural gas accumulation in foreland basins, Western China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(S1): 70-76. [18] 王震亮, 孙明亮, 耿鹏, 等. 准南地区异常地层压力发育特征及形成机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(1): 32-34.WANG Zhenliang, SUN Mingliang, GENG Peng, et al. The development features and formation mechanisms of abnormal high formation pressure in southern Junggar region[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(1): 32-34. [19] 罗晓容, 肖立新, 李学义, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘中段异常压力分布及影响因素[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2004, 29(4): 404-412.LUO Xiaorong, XIAO Lixin, LI Xueyi, et al. Overpressure distribution and affecting factors in southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2004, 29(4): 404-412. [20] 吴孔友, 查明, 钟建华. 准噶尔盆地超压系统分布及其演化[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(4): 636-647.WU Kongyou, ZHA Ming, ZHONG Jianhua. Distribution and evolution of overpressure systems in the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2006, 41(4): 636-647. [21] 刘伟. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合异常高压形成机制及其演化特征[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2019.LIU Wei. Formation mechanism and evolution characteristics of the lower anomaloushigh pressure in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Petroleum, 2019. [22] 张凤奇, 鲁雪松, 卓勤功, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合储层异常高压成因机制及演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 1004-1016.ZHANG Fengqi, LU Xuesong, ZHUO Qingong, et al. Genetic mechanism and evolution characteristics of overpressure in the lower play at the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1004-1016. [23] 鲁雪松, 赵孟军, 张凤奇, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘前陆冲断带超压发育特征、成因及其控藏作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(5): 859-870.LU Xuesong, ZHAO Mengjun, ZHANG Fengqi, et al. Characteristics, origin and controlling effects on hydrocarbon accumulation of overpressure in foreland thrust belt of southern margin of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(5): 859-870. [24] 宋岩, 方世虎, 赵孟军, 等. 前陆盆地冲断带构造分段特征及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 31-38.SONG Yan, FANG Shihu, ZHAO Mengjun, et al. The structural segmentation of foreland thrust belts and its implications for hydrocarbon accumulation in foreland basins in central and western China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 31-38. [25] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 倪云燕, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘天然气成因类型与气源[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3): 461-473.CHEN Jianping, WANG Xulong, NI Yunyan, et al. Genetic type and source of natural gas in the southern margin of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3): 461-473. [26] 马宗晋, 曲国胜, 李涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地盆山构造耦合与分段性[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2008, 29(3): 271-277.MA Zongjin, QU Guosheng, LI Tao, et al. Tectonic coupling and segmentation of marginal structural belt in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2008, 29(3): 271-277. [27] 何登发, 翟光明, 况军, 等. 准噶尔盆地古隆起的分布与基本特征[J]. 地质科学, 2005, 40(2): 248-261.HE Dengfa, ZHAI Guangming, KUANG Jun, et al. Distribution and tectonic features of paleo-uplifts in the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(2): 248-261. [28] 马德龙, 何登发, 袁剑英, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘前陆冲断带深层地质结构及对油气藏的控制作用: 以霍尔果斯—玛纳斯—吐谷鲁褶皱冲断带为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 165-177.MA Delong, HE Dengfa, YUAN Jianying, et al. The deep structures in the south Junggar foreland thrust belt and their control on petroleum accumulation: insights from the Huoerguosi-Manasi- Tugulu fold and thrust belt[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 165-177. [29] 刘刚, 李建忠, 齐雪峰, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段下部成藏组合油气藏形成过程: 以独山子背斜独山1井为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(7): 1009-1021.LIU Gang, LI Jianzhong, QI Xuefeng, et al. Reservoir formation process of the lower accumulation assemblage in the west part of the southern Junggar Basin: case study of well Dushan1 in the Dushanzi anticline[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(7): 1009-1021. [30] 李伟, 陈竹新, 黄平辉, 等. 中国中西部典型前陆盆地超压体系形成机制与大气田关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 536-548.LI Wei, CHEN Zhuxin, HUANG Pinghui, et al. Formation of overpressure system and its relationship with the distribution of large gas fields in typical foreland basins in central and western China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 536-548. [31] BOWERS G L. Pore pressure estimation from velocity data: accounting for overpressure mechanisms besides undercompaction[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 1995, 10(2): 89-95. [32] 赵靖舟, 李军, 徐泽阳. 沉积盆地超压成因研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 33(9): 973-998.ZHAO Jingzhou, LI Jun, XU Zeyang. Advances in the origin of overpressures in sedimentary basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(9): 973-998. [33] TINGAY M R P, MORLEY C K, LAIRD A, et al. Evidence for overpressure generation by kerogen-to-gas maturation in the northern Malay Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(4): 639-672. [34] 张凤奇, 王震亮, 钟红利, 等. 沉积盆地主要超压成因机制识别模式及贡献[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 25(6): 1151-1158.ZHANG Fengqi, WANG Zhenliang, ZHONG Hongli, et al. Recognition model and contribution evaluation of main overpressure formation mechanisms in sedimentary basins[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 25(6): 1151-1158. [35] FAN Changyu, WANG Gang, WANG Zhenliang, et al. Prediction of multiple origin overpressure in deep fold-thrust belt: a case study of Kuqa subbasin, Tarim Basin, northwestern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2021, 105(8): 1511-1533. [36] FAN Changyu, WANG Gang. The significance of a piecemeal geometric model of mudstone compaction: Pinghu Slope, Xihu Depression, Eastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 131: 105138. [37] 王刚, 范昌育, 李子龙, 等. 强挤压型盆地最大埋深期泥岩压实重建及其油气地质意义: 以库车前陆盆地为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(10): 29-38.WANG Gang, FAN Changyu, LI Zilong, et al. Reconstruction of mudstone compaction in the maximum burial depth period of strongly compressional basin and its petroleum geological implications: take the Kuqa Foreland Basin as an example[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(10): 29-38. [38] 韩晓洁, 范昌育, 高潮, 等. 构造抬升区欠压实超压恢复方法: 以鄂尔多斯盆地下寺湾地区延长组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(7): 1163-1172.HAN Xiaojie, FAN Changyu, GAO Chao, et al. Restoration method of disequilibrium compaction overpressure in tectonically uplifted area: a case study of Yanchang Formation in Xiasiwan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(7): 1163-1172. [39] BOWERS G L. Determining an appropriate pore-pressure estimation strategy[C]//Proceedings of Offshore Technology Conference. Houston: OTC, 2001: OTC-13042-MS. [40] 罗晓容. 构造应力超压机制的定量分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(6): 1086-1093.LUO Xiaorong. Quantitative analysis on overpressuring mechanism resulted from tectonic stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(6): 1086-1093. [41] 李铁军. 准噶尔盆地南缘异常高压及其成因机制初探[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(2): 234-244.LI Tiejun. Overpressure and its generation in south edge of the Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(2): 234-244. [42] 张凤奇, 刘伟, 鲁雪松, 等. 喜马拉雅晚期构造应力场及其与油气分布的关系: 以准噶尔盆地南缘为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 433-439.ZHANG Fengqi, LIU Wei, LU Xuesong, et al. Late Himalayan tectonic stress field and its relationship with hydrocarbon distribution: a case study of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. [43] 王刚. 脆性—脆塑性岩石孔隙流体构造挤压增压定量评价及油气运聚意义: 以库车坳陷克拉苏冲断带为例[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021.WANG Gang. Quantitative evaluation of structural compression and pressurize of pore fluid in brittle and brittle-plastic rock and its significance of hydrocarbon migration and accumulation: a case study from Klasu thrust belt in Kuqa Depression[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2021. [44] TERZAGHI K. Theoretical soil mechanics[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1943: 510. [45] TINGAY M R P, HILLIS R R, MORLEY C K, et al. Present-day stress and neotectonics of Brunei: implications for petroleum exploration and production[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(1): 75-100. [46] ALTMANN J B, MVLLER B I R, MVLLER T M, et al. Pore pressure stress coupling in 3D and consequences for reservoir stress states and fault reactivation[J]. Geothermics, 2014, 52: 195-205. [47] HUBBERT M K. Entrapment of petroleum under hydrodynamic conditions[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1953, 37(8): 1954-2026. [48] 张快乐. 准南前陆盆地流体动力的构成、演化及对油气成藏的影响[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2020.ZHANG Kuaile. The formation and evolution of fluid dynamic field and its effect on hydrocarbon accumulation in southern Junggar Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2020. [49] 陈世加, 王绪龙, 阿布力米提, 等. 呼图壁气藏成藏地球化学特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2004(3): 16-18.CHEN Shijia, WANG Xulong, Abulimiti, et al. Geochemical study of forming gas reservoir in Hutubi field in Zhunge'er Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004(3): 16-18. -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号