Slope—sedimentary source rock-type helium enrichment model: a case study of Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地氦气资源丰富,已在伊盟隆起、伊陕斜坡南部等地区发现高含氦、富氦天然气田,这些气田的氦气富集多与断裂发育密切相关。然而,盆地内的构造背景较为复杂,为研究盆地内不同地质背景下氦气的富集特征及控制因素,对鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡东北部开展天然气组分分析测试,并结合研究区基础地质资料及前人研究成果,对鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田上古生界的氦气分布特征及其地质影响因素进行探究。神木气田上古生界氦气含量达0.017%~0.116%,平均氦气含量为0.05%,达到含氦气田标准;氦气含量在平面上呈“西低东高”的整体分布格局,东部部分地区的氦气含量大于0.1%;氦气含量与氮气含量呈明显正相关关系,表明天然气藏中的氦气和氮气在成因和溶解—脱溶机制上可能存在必然联系。神木气田氦气的富集受多种地质因素共同影响:上古生界广泛分布的煤系烃源岩提供了充足的氦气;地壳抬升和构造反转控制了氦气的运移方向,且促进了溶解氦的脱溶和聚集;适量的载体气有助于氦气的富集。结合研究区构造背景和氦气成藏地质因素,提出了一种新的氦气富集模式,即斜坡—沉积源岩型含氦天然气富集模式,这为氦气勘探和开发工作提供了重要的理论支持。Abstract: The Ordos Basin is rich in helium resources, with high helium and helium-rich natural gas fields discovered in areas such as the Yimeng Uplift and the southern Yishan Slope. The enrichment of helium in these gas fields is often closely related to the development of faults. However, the structural background within the basin is complex. To study the characteristics and controlling factors of helium enrichment under different geological backgrounds within the basin, an analysis of natural gas composition was conducted in the northeastern Yishan Slope of the Ordos Basin. Combining basic geological data of the study area and previous research findings, the helium distribution characteristics and geological influencing factors in the Upper Paleozoic of the Shenmu Gas Field in the Ordos Basin were explored. The results showed that the helium content in the Upper Paleozoic of the Shenmu Gas Field ranged from 0.017% to 0.116%, with an average content of 0.05%, meeting the standard of a helium-containing gas field. The helium content showed a spatial distribution pattern of "low in the west and high in the east", with helium content exceeding 0.1% in some eastern areas. There was a significant positive correlation between helium and nitrogen content, indicating a possible inherent connection between the genesis and dissolution-exsolution mechanisms of helium and nitrogen in natural gas reservoirs. The enrichment of helium in the Shenmu Gas Field was influenced by various geological factors: (1) The widely distributed coal-measure source rocks in the Upper Paleozoic provided ample helium; (2) Crustal uplift and tectonic inversion controlled the migration direction of helium and promoted the exsolution and accumulation of dissolved helium; (3) An appropriate amount of carrier gas aided in helium enrichment. Based on the tectonic conditions of the study area and the geological factors controlling helium accumulation, a new helium enrichment model was proposed, the slope-sedimentary source rock-type helium-rich natural gas enrichment model, providing theoretical support for helium exploration and development.
-
Key words:
- tectonic movement /
- slope-sedimentary source rock type /
- helium /
- Upper Paleozoic /
- Shenmu Gas Field /
- Ordos Basin
-
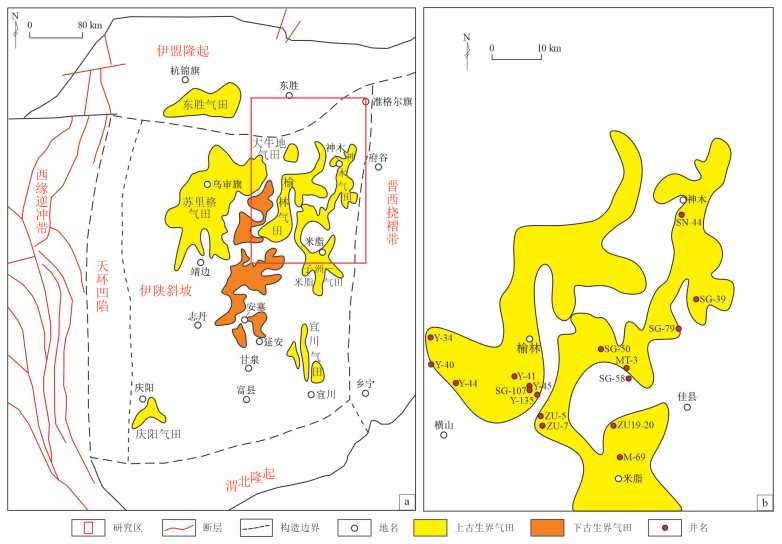
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田及周缘天然气组分特征
Table 1. Characteristics of natural gas composition in Shenmu Gas Field and surrounding areas of Ordos Basin
编号 气田 井代号 烃类气体组分特征 非烃气组分含量 C1/% C2-5/% C2+/C1+ C1/C1-5 CO2/% N2/% He/% H2/% 1 神木气田 SG-39 85.622 6.878 0.07 0.93 2.106 0.120 0.036 2 SG-79 90.204 3.357 0.04 0.96 1.443 0.082 0.014 3 SN-44 82.009 9.304 0.10 0.90 0.030 3.884 0.085 0.013 4 SG-50 88.787 6.474 0.07 0.93 0.584 0.352 0.030 0.028 5 SG-58C4 88.873 5.878 0.06 0.94 1.242 0.206 0.017 0.010 6 SG-50C3 89.296 6.489 0.07 0.93 0.594 0.343 0.029 0.028 7 MT-3 91.940 1.393 0.01 0.99 3.439 0.124 0.018 8 MT-3C6 92.491 1.338 0.01 0.99 3.472 0.109 0.019 9 SG-39C3 85.185 8.299 0.09 0.91 0.036 1.746 0.091 0.060 10 SG-58 90.075 4.161 0.04 0.96 0.881 0.421 0.032 0.012 11 SG-38C1 92.577 1.860 0.02 0.98 1.750 0.233 0.019 12 榆林气田 Y-44 89.806 4.424 0.05 0.95 1.765 0.284 0.028 0.028 13 Y-45 89.658 4.761 0.05 0.95 1.005 0.294 0.025 0.014 14 SG-107 88.317 5.706 0.06 0.94 0.695 0.345 0.026 0.021 15 SG-135 85.112 8.554 0.09 0.91 1.327 0.305 0.017 0.010 16 Y-47C6 87.465 7.096 0.08 0.92 0.925 0.314 0.028 0.032 17 Y-40 90.397 3.705 0.04 0.96 0.812 0.584 0.040 0.026 18 Y-40C8 91.017 2.715 0.03 0.97 1.861 0.346 0.030 0.050 19 Y-41 88.924 5.276 0.06 0.94 1.042 0.318 0.025 0.015 20 Y-34 89.804 3.645 0.04 0.96 0.925 0.662 0.032 0.035 21 Y-29 89.442 3.932 0.04 0.96 1.758 0.267 0.023 0.010 22 子洲—米脂气田 M-69 91.122 4.367 0.05 0.95 0.042 0.507 0.032 0.017 23 M-31 89.732 5.470 0.06 0.94 0.574 0.540 0.035 0.019 24 M-22C2 90.880 3.266 0.03 0.97 1.538 0.305 0.028 0.012 25 ZU-18 92.534 1.236 0.01 0.99 2.055 0.199 0.028 0.036 26 ZU-19 89.512 4.764 0.05 0.95 0.954 0.404 0.037 0.030 27 ZU-5-14 87.646 6.377 0.07 0.93 0.580 0.433 0.032 0.036 28 ZU-5-13 86.571 6.211 0.07 0.93 2.454 0.274 0.023 0.015 29 ZU-7-14 90.477 3.845 0.04 0.96 1.316 0.270 0.024 0.022 -
[1] 何发岐, 王付斌, 王杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜气田氦气分布规律及特大型富氦气田的发现[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201001HE Faqi, WANG Fubin, WANG Jie, et al. Helium distribution of Dongsheng gas field in Ordos Basin and discovery of a super large helium-rich gas field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 1-10. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201001 [2] 何发岐, 王杰, 赵永强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东胜富氦气田成藏特征及其大地构造背景[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(5): 937-950.HE Faqi, WANG Jie, ZHAO Yongqiang, et al. Accumulation characteristics of Dongsheng helium-rich gas field in Ordos Basin and its tectonic background[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2022, 24(5): 937-950. [3] 秦胜飞, 李济远, 梁传国, 等. 中国中西部富氦气藏氦气富集机理: 古老地层水脱氦富集[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(8): 1203-1217.QIN Shengfei, LI Jiyuan, LIANG Chuanguo, et al. Helium enrichment mechanism of helium rich gas reservoirs in central and western China: degassing and accumulation from old formation water[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(8): 1203-1217. [4] 秦胜飞, 李济远. 氦气到底有什么用?[J]. 石油知识, 2021(4): 44-45.QIN Shengfei, LI Jiyuan. What exactly is the use of helium gas?[J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2021(4): 44-45. [5] DANABALAN D, GLUYAS J G, MACPHERSON C G, et al. The principles of helium exploration[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 2022, 28(2): petgeo2021-029. [6] ANDERSON S T. Economics, helium, and the U.S. federal helium reserve: summary and outlook[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2018, 27(4): 455-477. doi: 10.1007/s11053-017-9359-y [7] MASSOL O, RIFAAT O. Phasing out the U.S. federal helium reserve: policy insights from a world helium model[J]. Resource and Energy Economics, 2018, 54: 186-211. doi: 10.1016/j.reseneeco.2018.08.003 [8] HAND E. Massive helium fields found in rift zone of Tanzania[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295): 109-110. doi: 10.1126/science.353.6295.109 [9] 韩元红, 罗厚勇, 薛宇泽, 等. 渭河盆地地热水伴生天然气成因及氦气富集机理[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(2): 277-287.HAN Yuanhong, LUO Houyong, XUE Yuze, et al. Genesis and helium enrichment mechanism of geothermal water-associated gas in Weihe Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(2): 277-287. [10] 张文. 关中和柴北缘地区战略性氦气资源成藏机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2019.ZHANG Wen. Accumulation mechanism of helium, a strategic resource, in Guanzhong and north Qaidam Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2019. [11] 孟伟. 东营凹陷古近系油气运移和聚集的流体和岩石的地球化学响应[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.MENG Wei. Geochemical response of fluids and rocks to hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in Paleogene of Dongying Depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018. [12] 陶成, 刘文汇, 腾格尔, 等. 基于He年代累积效应约束天然成藏时代: 以四川威远气田为例[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(S1): 183-184.TAO Cheng, LIU Wenhui, TENGER, et al. Take Weiyuan gas field in Sichuan Province as an example[J]. Journal of Geology, 2015, 89(S1): 183-184. [13] 张健, 杨威, 易海永, 等. 四川盆地前震旦系勘探高含氦天然气藏的可行性[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(1): 45-52.ZHANG Jian, YANG Wei, YI Haiyong, et al. Feasibility of high- helium natural gas exploration in the Presinian strata of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(1): 45-52. [14] 刘强. 渝东地区氦气资源分布特征及开发利用前景[J]. 江汉石油职工大学学报, 2023, 36(2): 4-6.LIU Qiang. Distribution characteristics and development prospects of helium resources in eastern Chongqing[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum University of Staff and Workers, 2023, 36(2): 4-6. [15] 范立勇, 单长安, 李进步, 等. 基于磁力资料的鄂尔多斯盆地氦气分布规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(10): 1780-1789.FAN Liyong, SHAN Chang'an, LI Jinbu, et al. Distribution of helium resources in Ordos Basin based on magnetic data[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(10): 1780-1789. [16] 柳永刚, 张翔, 刘子锐, 等. 甘肃省首个高品位氦气盆地的发现及勘探前景[J]. 甘肃地质, 2020, 29(S2): 29-36.LIU Yonggang, ZHANG Xiang, LIU Zirui, et al. The first discovery and exploration prospect of high grade helium basin in Gansu Province[J]. Geology of Gansu Province, 2020, 29(S2): 29-36. [17] 陶小晚, 李建忠, 赵力彬, 等. 我国氦气资源现状及首个特大型富氦储量的发现: 和田河气田[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 44(3): 1024-1041.TAO Xiaowan, LI Jianzhong, ZHAO Libin, et al. Helium resources and discovery of first supergiant Helium reserve in China: Hetianhe gas field[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 1024-1041. [18] 余琪祥, 史政, 王登高, 等. 塔里木盆地西北部氦气富集特征与成藏条件分析[J]. 西北地质, 2013, 46(4): 215-222.YU Qixiang, SHI Zheng, WANG Denggao, et al. Analysis on helium enrichment characteristics and reservoir forming conditions in northwest Tarim Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(4): 215-222. [19] 薛华锋, 朱兴国, 王润三, 等. 西安地热田伴生富氦天然气资源的发现及意义[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 34(6): 751-754.XUE Huafeng, ZHU Xingguo, WANG Runsan, et al. The discovery and significance of rich helium natural gas resource in Xi'an geothermic field[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2004, 34(6): 751-754. [20] 冯子辉, 霍秋立, 王雪. 松辽盆地北部氦气成藏特征研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2001, 21(5): 27-30.FENG Zihui, HUO Qiuli, WANG Xue. A study of helium reservoir formation characteristic in the north part of Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2001, 21(5): 27-30. [21] 常兴浩, 宋凯. 巴什托构造石炭系小海子组高氦气藏成藏机理浅析[J]. 天然气工业, 1997, 17(2): 30-32.CHANG Xinghao, SONG Kai. Analysis of reservoir forming mechanism of high He pool in the Carboniferious of Xiaohaizi Formation of Bashitou structure[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1997, 17(2): 30-32. [22] 高卓林. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部上古生界山西组山1、山2段气藏地质特征[J]. 云南化工, 2018, 45(10): 220-221.GAO Zhuolin. Geological characteristics of the first and second sections of Shanxi Formation gas reservoir in the eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2018, 45(10): 220-221. [23] 李明, 高建荣. 鄂尔多斯盆地基底断裂与火山岩的分布[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010, 40(8): 1005-1013.LI Ming, GAO Jianrong. Basement faults and volcanic rock distributions in the Ordos Basin[J]. Science China Earth: Sciences, 2010, 53(11): 1625-1633. [24] 米敬奎. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界天然气藏的运聚特征[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所地球化学, 2003.MI Jingkui. The migration and accumulation characters of the Upper Paleozoic gas reservoir in Ordos Basin[D]. Guangzhou: Geochemistry, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003. [25] 姜福杰, 贾承造, 庞雄奇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界全油气系统成藏特征与天然气富集地质模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(2): 250-261.JIANG Fujie, JIA Chengzao, PANG Xiongqi, et al. Upper Paleozoic total petroleum system and geological model of natural gas enrichment in Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(2): 250-261. [26] SHAO Xinhe, PANG Xiongqi, JIANG Fujie, et al. Genesis and accumulation of natural gas in the Upper Palaeozoic strata of north-eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2019, 54(6): 3212-3225. doi: 10.1002/gj.3321 [27] XI Shenglia, LIU Xinshe, MENG Peilong. Exploration practices and prospect of Upper Paleozoic giant gas fields in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2015, 2(5): 430-439. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2015.09.019 [28] 蒙炳坤, 周世新, 李靖, 等. 上扬子地区不同类型岩石生氦潜力评价及泥页岩氦气开采条件理论计算[J]. 矿物岩石, 2021, 41(4): 102-113.MENG Bingkun, ZHOU Shixin, LI Jing, et al. Helium potential evaluation of different types of rocks in the Upper Yangtze region and theoretical calculation of helium recovery conditions for shale in Upper Yangtze region[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2021, 41(4): 102-113. [29] 何衍鑫, 田伟, 王磊, 等. 基于自然伽马能谱测井的氦气资源评价方法: 以塔里木盆地古城地区为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 719-733.HE Yanxin, TIAN Wei, WANG Lei, et al. Quantifying the helium generation based on natural gamma-ray spectrometry data: Gucheng area, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 719-733. [30] CHENG Anran, SHERWOOD LOLLAR B, GLUYAS J G, et al. Primary N2-He gas field formation in intracratonic sedimentary basins[J]. Nature, 2023, 615(7950): 94-99. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05659-0 [31] PADRÓN E, PÉREZ N M, HERNÁNDEZ P A, et al. Diffusive helium emissions as a precursory sign of volcanic unrest[J]. Geology, 2013, 41(5): 539-542. doi: 10.1130/G34027.1 [32] 刘雨桐, 段堃, 张晓宝, 等. 基岩型富氦气藏形成条件: 以柴达木盆地东坪气田和美国中部潘汉德—胡果顿气田为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 618-627.LIU Yutong, DUAN Kun, ZHANG Xiaobao, et al. Formation conditions of helium-rich gas in bedrock reservoirs: taking Dongping Gas Field in Qaidam Basin and Panhandle-Hugoton Gas Field in central United States as examples[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 618-627. [33] BALLENTINE C J, BURGESS R, MARTY B. Tracing fluid origin, transport and interaction in the crust[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002, 47(1): 539-614. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.47.13 [34] IDLEMANA B D, ZEITLERA P K, MCDANNELL K T. Characterization of helium release from apatite by continuous ramped heating[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 481: 165. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.02.006 [35] SATHAYE K J, LARSON T E, HESSE M A. Noble gas fractionation during subsurface gas migration[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 450: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.05.034 [36] 李平, 马向贤, 张明震, 等. 矿物中氦的扩散过程及控制因素研究进展[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(4): 697-706.LI Ping, MA Xiangxian, ZHANG Mingzhen, et al. Research progress on diffusion process and controlling factors of helium in minerals[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(4): 697-706. [37] ZHANG Wen, LI Yuhong, ZHAO Fenghua, et al. Granite is an effective helium source rock: insights from the helium generation and release characteristics in granites from the north Qinling Orogen, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica—English Edition, 2020, 94(1): 114-125. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14397 [38] 张涛, 巩肖可, 黄朝, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组低品质气藏储层微观特征及形成机理[J]. 石油实验地质, 2024, 46(1): 32-45. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401032ZHANG Tao, GONG Xiaoke, HUANG Chao, et al. Micro characteristics and formation mechanism of low-quality gas reservoirs in Taiyuan Formation of Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2024, 46(1): 32-45. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202401032 [39] BROWN A A. Formation of high helium gases: a guide for explorationists[R]. W. Searchanddiscovery. Com, 2010. [40] 邓伟, 谭秀成, 张道锋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部奥陶系马家沟组马五6亚段硬石膏产状类型与成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(2): 226-244.DENG Wei, TAN Xiucheng, ZHANG Daofeng, et al. Occurrence types and genesis of anhydrite from the Ma56 submember of Ordovician Majiagou Formation in central and eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2022, 24(2): 226-244. [41] XU Wanglin, LI Jianzhong, LIU Xinshe, et al. Accumulation conditions and exploration directions of Ordovician lower assemblage natural gas, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 641-654. [42] 杨帅, 陈安清, 陈洪德, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部马家沟组含钾蒸发岩系沉积机制及保存条件[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(6): 2192-2201.YANG Shuai, CHEN Anqing, CHEN Hongde, et al. The sedimentation mechanism and preservation condition of the potassium evaporate series in the Majiagou Formation, east of Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(6): 2192-2201. [43] 马东烨, 陈宇航, 王应斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部上古生界盖层封闭性能评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(11): 1673-1684.MA Dongye, CHEN Yuhang, WANG Yingbin, et al. Sealing capability evaluation of the Upper Paleozoic cap rock in the eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32 (11): 1673-1684. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号