In-situ stress orientation and main controlling factors of deep shale reservoirs in the second member of Paleogene Funing Formation in Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
-
摘要: 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜宁组二段页岩油资源量超7亿吨,但该区构造、应力双复杂的地质条件对页岩油勘探开发造成较大影响,尤其是现今地应力方向的认识不清,制约了水平井井组方案的部署和压裂方案的设计与优化。基于区域震源机制解、特殊测井和水平井压裂微地震监测等资料,结合波速各向异性、古地磁等实验测试分析资料,开展了各类地应力方向解释方法在深层页岩储层中的适用性研究,查明了花庄地区现今地应力的分布特征,并对其影响因素进行了分析。高邮凹陷阜二段现今水平最大主应力方向主要分布在40°—55°,平均方位角为45°,即现今水平最大主应力方向为NE向。平面上,研究区地应力方向与大区域上应力方向具有较小的应力偏转,主要受构造格局的影响;此外,断层附近存在应力扰动带,扰动带内应力偏转较为明显,扰动带的宽度与断层的断距和延伸长度成正相关。通过对比分析,认为微地震监测、诱导裂缝/井壁崩落、岩心实测、阵列声波各向异性的适用性逐级降低,阵列声波测井中的波速各向异性受平面上岩相相变的影响较大。结合地应力方向解释结果、天然裂缝优势走向,建议该区水平井的部署方位为SE155°—SSE170°。Abstract: The shale oil resources in the second member of the Paleogene Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin exceed 700 million tons. However, the complex geological conditions of both its structure and stress significantly impact the shale oil exploration and development in this area. In particular, the lack of clarity regarding the present-day in-situ stress orientations constrains the deployment of horizontal well groups and the design and optimization of fracturing projects. In this study, the applicability of various methods for interpreting in-situ stress orientations in deep shale reservoirs was investigated based on data from regional focal mechanism solutions, specialized logging, and microseismic monitoring of horizontal well fracturing, as well as the experimental analysis such as velocity anisotropy and paleomagnetic tests. The distribution characteristics of the present-day in-situ stress in the Huazhuang area were identified, and their influencing factors were analyzed. The results indicated that the present-day maximum horizontal principal stress direction in the second member of the Funing Formation mainly ranged from 40° to 55°, with an average azimuth of 45°, indicating a northeastward orientation. In the planar view, the in-situ stress orientation in the study area exhibited minor stress deviations on a larger regional scale, mainly influenced by the structural patterns. Furthermore, stress perturbation zones were found near faults, where stress deviations were more pronounced, and the width of these perturbation zones was positively correlated with fault displacement and extension length. Comparative analysis suggested a decreasing applicability of microseismic monitoring, induced fractures/wellbore collapses, core measurements, and array acoustic anisotropy. Specifically, the velocity anisotropy in array acoustic logging was significantly influenced by lithological phase transitions on a planar scale. Based on the interpretation of stress orientations and the dominant trends of natural fractures, the recommended horizontal well deployment azimuth for this area is SE155° to SSE170°.
-
Key words:
- shale reservoir /
- in-situ stress orientation /
- Funing Formation /
- Paleogene /
- Gaoyou Sag /
- Subei Basin
-
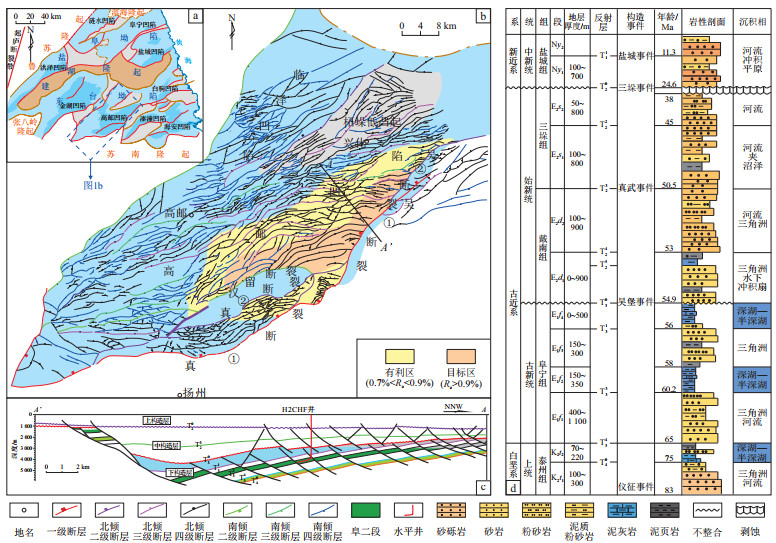
图 1 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜宁组二段断裂特征
据方志雄等[21]修改。
a.苏北盆地构造单元划分;b.高邮凹陷阜二段断裂体;c.高邮凹陷NNW—SSE向剖面;d.高邮凹陷地层综合柱状图。Figure 1. Fault characteristics of the second member of Funing Formation in Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
图 2 郯庐断裂带南段及其邻区水平最大主应力轴分布
据宋尚武等[12]修改。
Figure 2. Distribution of maximum horizontal principal stress axes in southern section of Tanlu Fault and surrounding areas
图 9 苏北盆地高邮凹陷花庄地区阜宁组二段断层附近应力扰动带宽度变化规律
底图据翁剑桥等[31]修改。
Figure 9. Width variations in stress perturbation zones near faults in the second member of Funing Formation, Huazhuang area, Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
表 1 苏北盆地高邮凹陷阜宁组二段岩心实测地应力方向统计
Table 1. Statistics of measured in-situ stress orientations in core samples from the second member of Funing Formation in Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
井号 层位 深度/m 标志线古地磁定向方向 水平最大主应力与标志线夹角 测试方法 水平最大主应力方向 HY1井 阜二段页Ⅴ亚段 3 586.02 212.3° 191.5° 波速各向异性 NE43.8° HY7井 阜二段页Ⅳ亚段 4 080.40 122.0° 135.0° 波速各向异性 NEE77.0° 表 2 苏北盆地高邮凹陷不同方法分析水平最大主应力方向结果对比分析
Table 2. Comparative analysis of maximum horizontal principal stress orientations interpreted by different methods in Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
分析方法 水平最大主应力方向 HY1井 H2C井 HY3井 HY7井 岩心实测 43.6° 77.0° 测井波速各向异性 65°—75°(*) 90°—100°(*) 65°—75° 成像测井诱导裂缝 35°—50° 70°—80° 65°—75° 70°—80° 成像测井井壁崩落 65°—75° 70°—80° 与区域应力方向一致性 是 否 否 否 注:“*”表示判定为不准确。 -
[1] 金之钧, 王冠平, 刘光祥, 等. 中国陆相页岩油研究进展与关键科学问题[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 821-835.JIN Zhijun, WANG Guanping, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Research progress and key scientific issues of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 821-835. [2] US Energy Information Administration. Annual energy outlook 2019 with projections to 2050[R]. Washington: US Energy Information Administration, 2021. [3] 何文渊, 蒙启安, 冯子辉, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩油原位成藏理论认识及勘探开发实践[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(1): 1-14.HE Wenyuan, MENG Qian, FENG Zihui, et al. In-situ accumulation theory and exploration & development practice of Gulong shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 1-14. [4] 刘惠民. 济阳坳陷页岩油勘探实践与前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1): 73-87.LIU Huimin. Exploration practice and prospect of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1): 73-87. [5] 赵贤正, 蒲秀刚, 周立宏, 等. 深盆湖相区页岩油富集理论、勘探技术及前景: 以渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷古近系为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(2): 143-162.ZHAO Xianzheng, PU Xiugang, ZHOU Lihong, et al. Enrichment theory, exploration technology and prospects of shale oil in lacustrine facies zone of deep basin: a case study of the Paleogene in Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 143-162. [6] 包友书. 陆相泥页岩在水平地应力作用下裂缝的多样性: 以济阳坳陷古近系泥页岩为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(7): 777-785.BAO Youshu. Fracture diversity of continental shale under horizontal geostress: a case study of the Paleogene shale in Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(7): 777-785. [7] 张皓宇, 陈军斌, 王涛, 等. "井工厂"不同压裂模式下裂缝扩展规律数值模拟研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(9): 3561-3574.ZHANG Haoyu, CHEN Junbin, WANG Tao, et al. Numerical simulation of fracture propagation in different fracturing modes of "well factory"[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(9): 3561-3574. [8] 赵金洲, 赵金, 胡永全, 等. 水力压裂裂缝应力场变化规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(12): 1677-1683.ZHAO Jinzhou, ZHAO Jin, HU Yongquan, et al. Study on stress field distribution of hydraulic fracturing[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(12): 1677-1683. [9] GALE J F W, LAUBACH S E, OLSON J E, et al. Natural Fractures in shale: a review and new observations[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2014, 98(11): 2165-2216. doi: 10.1306/08121413151 [10] DAHI-TALEGHANI A, OLSIN J E. Numerical modeling of multistranded-hydraulic-fracture propagation: accounting for the interaction between induced and natural fractures[J]. SPE Journal, 2011, 16(3): 575-581. doi: 10.2118/124884-PA [11] 蒋廷学, 卞晓冰, 王海涛, 等. 深层页岩气水平井体积压裂技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(1): 90-96.JIANG Tingxue, BIAN Xiaobing, WANG Haitao, et al. Volume fracturing of deep shale gas horizontal wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(1): 90-96. [12] 宋尚武, 王庆良, 张佩, 等. 郯庐断裂带南段及其周边地区应力场分区与反演[J]. 地震研究, 2018, 41(3): 457-463.SONG Shangwu, WANG Qingliang, ZHANG Pei, et al. The stress field inversion and stress field partition of the southern Tanlu fault and surrounding areas[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2018, 41(3): 457-463. [13] 孙业君, 黄耘, 刘泽民, 等. 郯庐断裂带鲁苏皖段及邻区构造应力场特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1188-1207.SUN Yejun, HUANG Yun, LIU Zemin, et al. 2021. Characteristics of tectonic stress field and dynamic significance in the Shandong- Jiangsu-Anhui segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone and its adjacent areas[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(5): 1188-1207. [14] 曹峰, 何建华, 王园园, 等. 合川地区须二段低各向异性储层现今地应力方向评价方法[J]. 地球科学进展. 2022, 37(7): 742-755.CAO Feng, HE Jianhua, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. Methods to evaluate present-day in-situ stress direction for low anisotropic reservoirs in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in Hechuan area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(7): 742-755. [15] HAN Yannong, FENG Yongcun, LI Xiaorong, et al. Evaluation of in-situ stress orientation: a laboratory approach combining paleomagnetic test and acoustic anisotropy test[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107870. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107870 [16] SHEN L W, SCHMITT D R, HAUG K. Quantitative constraints to the complete state of stress from the combined borehole and focal mechanism inversions: Fox Creek, Alberta[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019, 764: 110-123. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2019.04.023 [17] LEE H, CHANG Chandong, ONG S H, et al. Effect of anisotropic borehole wall failures when estimating in situ stresses: a case study in the Nankai accretionary wedge[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48: 411-422. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.09.004 [18] 尹帅, 刘翰林, 何建华, 等. 动静态地质力学方法约束的致密油砂岩地应力综合评估[J]. 地球科学进展, 2023, 38(12): 1285-1296.YIN Shuai, LIU Hanlin, HE Jianhua, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of geo-stress in tight oil sandstone under constraints of dynamic-static geomechanical methods[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2023, 38(12): 1285-1296. [19] MAXWELL S C, URBANCIC T I, STEINSBERGER N, et al. Microseismic imaging of hydraulic fracture complexity in the Barnett shale[C]//Paper Presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. San Antonio: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2002: 2-8. [20] 朱相羽, 段宏亮, 孙雅雄. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷古近系陆相页岩油勘探突破及意义[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(8): 1206-1221.ZHU Xiangyu, DUAN Hongliang, SUN Yaxiong. Breakthrough and significance of Paleogene continental shale oil exploration in Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(8): 1206-1221. [21] 方志雄, 肖秋生, 张殿伟, 等. 苏北盆地陆相"断块型"页岩油地质特征及勘探实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6): 1468-1478.FANG Zhixiong, XIAO Qiusheng, ZHANG Dianwei, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration of continental fault-block shale oil reservoirs in the Subei Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6): 1468-1478. [22] 云露, 何希鹏, 花彩霞, 等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷古近系陆相页岩油成藏地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(1): 176-187.YUN Lu, HE Xipeng, HUA Caixia, et al. Accumulation characteristics and resource potential of Paleogene continental shale oil in Qintong Sag of Subei Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(1): 176-187. [23] 舒良树, 王博, 王良书, 等. 苏北盆地晚白垩世—新近纪原型盆地分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(4): 534-543.SHU Liangshu, WANG Bo, WANG Liangshu, et al. Analysis of northern Jiangsu prototype basin from late Cretaceous to Neogene[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(4): 534-543. [24] 邱海峻, 许志琴, 乔德武. 苏北盆地构造演化研究进展[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(9): 1117-1120.QIU Haijun, XU Zhiqin, QIAO Dewu. Progress in the study of the tectonic evolution of the Subei Basin, Jiangsu, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(9): 1117-1120. [25] 陈安定. 苏北盆地构造特征及箕状断陷形成机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(2): 140-150.CHEN Anding. Tectonic features of the Subei Basin and the forming mechanism of its dustpan-shaped fault depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(2): 140-150. [26] 唐旭. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷断裂演化及砂箱物理模拟[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2019.TANG Xu. Fault evolution and analogue modelling of Gaoyou Sag in Subei Basin[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2019. [27] 齐晴. 地应力预测技术在页岩气水平井开发中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(3): 1117-1122.QI Qing. Application of in-suit stress prediction technology in shale gas horizontal wells development[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(3): 1117-1122. [28] 雪宇超. 井旁地应力对全波列声波测井影响的正反演研究及应用[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2021.XUE Yuchao. Research and application of forward and inverse analysis of the influence of borehole in-situ stress on the full-wave sonic logging[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2021. [29] 马晓鸣. 高邮凹陷构造特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2009.MA Xiaoming. Research of structural characteristics of Gaoyou Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2009. [30] 邱旭明, 陈伟, 李鹤永, 等. 苏北盆地走滑构造与复杂断块油气成藏[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 393-401. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303393 QIU Xuming, CHEN Wei, LI Heyong, et al. Strike-slip structures and hydrocarbon accumulation in complex fault blocks in Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 393-401. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303393 [31] 翁剑桥, 曾联波, 吕文雅, 等. 断层附近地应力扰动带宽度及其影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(1): 39-47.WENG Jianqiao, ZENG Lianbo, LYU Wenya, et al. Width of stress disturbed zone near fault and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(1): 39-47. [32] FOSSEN H, HESTHAMMER J. Possible absence of small faults in the Gullfaks Field, northern North Sea: implications for downscaling of faults in some porous sandstones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2000, 22(7): 851-863. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(00)00013-4 [33] CHILDS C, MANZOCCHI T, WALSH J J, et al. A geometric model of fault zone and fault rock thickness variations[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2009, 31(2): 117-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2008.08.009 [34] FOSSEN H, SCHULTZ R A, SHIPTON Z K, et al. Deformation bands in sandstone: a review[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(4): 755-769. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-036 [35] 沈海超, 程远方, 王京印, 等. 断层对地应力场影响的有限元研究[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2007, 26(2): 34-37.SHEN Haichao, CHENG Yuanfang, WANG Jingyin, et al. Study of finite element on effects of faults on ground stress field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2007, 26(2): 34-37. [36] 刘中春, 吕心瑞, 李玉坤, 等. 断层对地应力场方向的影响机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(3): 387-393.LIU Zhongchun, LYU Xinrui, LI Yukun, et al. Mechanism of faults acting on in-situ stress field direction[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(3): 387-393. [37] 刘振. 复杂断层构造区地应力分布规律及影响因素研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.LIU Zhen. Research on the distribution and influence factors of in-situ stress in complex fault tectonic region[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2009. [38] 刘向君, 丁乙, 罗平亚, 等. 天然裂缝对水力裂缝延伸的影响研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(2): 148-153.LIU Xiangjun, DING Yi, LUO Pingya, et al. Influence of natural fracture on hydraulic fracture propagation[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(2): 148-153. [39] 李建红, 王延斌. 临兴地区盒八段砂岩裂缝发育特征及其对压裂效果的影响[J]. 矿业科学学报, 2021, 6(4): 379-388.LI Jianhong, WANG Yanbin. Fracture characteristics of the 8th member of Shihezi Formation in Linxing area and its influence on fracturing effect[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2021, 6(4): 379-388. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号