Prediction and zoning evaluation of in-situ stress field in deep tight sandstone reservoirs of Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin: a case study of the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang and Fenggu area
-
摘要: 四川盆地川西坳陷新场构造带三叠系须家河组二段致密气藏资源潜力巨大,但地质构造复杂,勘探开发面临巨大挑战。尤其是对现今地应力状态和展布规律的认识尚不清晰,严重制约了工程甜点选取、井眼轨迹优化以及储层压裂改造工作的开展。为明确研究区须二段致密气藏现今地应力的分布特征,从岩心试验、矿场测试和测井解释等多个角度切入,明确单井地应力特征;充分考虑构造变形和断裂对地应力的扰动特征,采用Rhinoceros和FLAC3D软件,对须二段进行了精细的三维应力场建模与预测;基于地应力分布预测结果,选取对压裂和产量影响较大的最小主应力和应力差作为评价指标,对应力场特征进行了分区评价,并对不同应力区井位部署、井轨迹及压裂改造设计给出了初步建议。新场构造带须二段的现今最大水平主应力方向多在N85°—108°E之间,整体随埋深增加逆时针偏转;现今地应力属于走滑应力机制,中部合兴场三向应力明显高于新场和丰谷地区,构造变形和断裂对局部应力场存在扰动。应力分区结果显示,有利于压裂改造的低应力差—低地应力区主要发育在新场和合兴场的三级东西向断裂和四级南北、北东向断裂带附近,以及丰谷地区的构造张性扰动区域。Abstract: The second member of the Triassic Xujiahe Formation (Xu 2 Member) in the Xinchang structural belt of the Western Sichuan Depression in the Sichuan Basin contains tight gas reservoirs with enormous resource potential. However, the geological structure is complex, presenting significant challenges for exploration and development. In particular, the current understanding of its in-situ stress state and distribution patterns is insufficient, severely restricting the selection of sweet spots for engineering, wellbore trajectory optimization, and reservoir fracturing modification. To clarify the current in-situ stress distribution characteristics in the tight gas reservoirs of the Xu 2 Member, the paper analyzed data from core tests, field tests, and well logging interpretation to determine the stress characteristics at individual wells. Considering the disturbances to the stress field caused by tectonic deformation and faults, Rhinoceros and FLAC3D software were used to precisely model and predict the three-dimensional in-situ stress field of the Xu 2 Member. Based on the stress distribution predictions, the minimum principal stress and stress differential, which significantly impacted fracturing and production, were selected as evaluation indicators. The stress field characteristics were zoned and evaluated, and preliminary suggestions were provided for well location deployment, well trajectory, and fracturing modification design in different in-situ stress zones. The results show that the current maximum horizontal principal stress direction in the Xu 2 Member of the Xinchang structural belt mostly ranges from N85° to 108°E, with an overall counterclockwise rotation as burial depth increases. The current in-situ stress regime corresponds to a strike-slip stress mechanism, with the central Hexingchang area showing significantly higher triaxial stress than the Xinchang and Fenggu areas. Moreover, local in-situ stress fields are disturbed by tectonic deformation and faults. The stress zoning results show that the low stress differential and low in-situ stress zones, which are favorable for fracturing modification, mainly develop near the third-order east-west-trending faults and the fourth-order north-south and northeast-trending faults in the Xinchang and Hexingchang areas, as well as in the extensional disturbance areas in the Fenggu area.
-
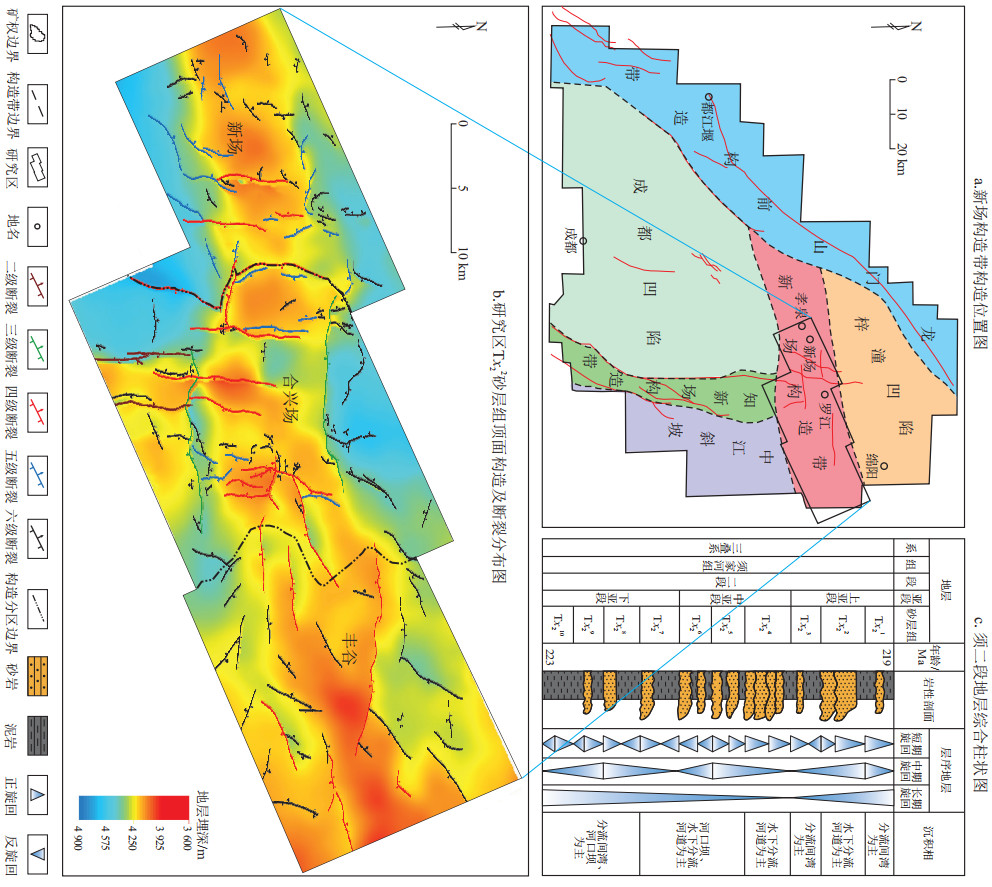
图 1 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段气藏地理位置、区域构造特征
据参考文献[26]修改。
Figure 1. Geographic location and regional structural characteristics of gas reservoirs in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
表 1 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段岩心古地磁和波速各向异性实验测试结果
Table 1. Experimental results of paleomagnetism and wave velocity anisotropy on core samples from the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
井号 深度/m 层位 古地磁定向角度β 最大水平主应力与标志线夹角α 最大水平主应力方向θ W51 4 488.00 Tx21 N77.8°E 30° N107.8°E W38 4 623.81 Tx22 N173.2°E 100° N93.2°E W45 4 887.16 Tx23 N290.2°E 170° N100.2°E W12 5 080.72 Tx26 N338.2°E 120° N98.2°E W30 5 270.30 Tx26 N209.8°E 80° N109.8°E 表 2 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段现今地应力方向评价方法汇总[37-40]
Table 2. Summary of evaluation methods for current in-situ stress direction in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
现今地应力方向解释方法 原理 单井解释实例与地应力方向玫瑰花图 诱导缝和井壁崩落影像分析 

多井径测井分析 

偶极横波各向异性分析 

广域电磁监测 

注: σH和σh, 分别为最大水平主应力和最小水平主应力。 表 3 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段岩石声发射实验测试结果[29]
Table 3. Experimental results of acoustic emission testing on rock samples from the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
井号 井深/m 层位 最大水平主应力/MPa 最小水平主应力/MPa 垂向主应力/MPa W51 4 487.00 Tx21 118.76 90.04 110.71 W5 4 762.24 Tx22 135.26 100.68 129.56 W54 4 943.80 Tx24 132.71 98.07 120.12 W63 4 766.83 Tx24 133.13 105.09 124.14 W30 5 270.70 Tx26 144.01 109.79 128.87 表 4 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段差应变实验测试结果[44]
Table 4. Experimental results of differential strain testing in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
井号 深度/m 层位 最大水平主应力/MPa 最小水平主应力/MPa 垂向主应力/MPa W38 4 566.14 Tx21 135.09 100.65 111.87 W25 4 810.97 Tx22 141.00 102.00 125.00 W38 4 639.29 Tx22 137.60 104.72 113.66 W4 4 882.06 Tx24 148.86 107.93 119.61 W4 4 884.04 Tx24 140.75 104.76 119.66 表 5 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段现今地应力大小评价方法汇总[29, 46-49]
Table 5. Summary of evaluation methods for current in-situ stress magnitude in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
现今地应力大小解释方法 原理 单井解释实例 水力压裂资料 

诱导缝影像反演 

井壁崩落反演 

测井资料 基于连续采集的密度测井资料,对上覆岩层进行密度积分可求得垂向主应力。利用横波测井和三孔隙度测井数据,可计算出泊松比、弹性模量等岩石力学参数,并通过对应的地应力模型可计算出水平主应力,并构建连续的地应力剖面。 
注: H为岩心长度; d为岩心直径; dmax为岩心椭圆端面长轴直径; dmin为岩心椭圆端面短轴直径; μ为断层滑动摩擦系数; B0为井壁崩落宽度; EUCS为有效单轴抗压强度; NF为正断层状态; SS为走滑断层状态; RF为逆断层状态。 表 6 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段不同小层岩石力学参数相关性分析汇总
Table 6. Summary of correlation analysis of rock mechanical parameters for different sublayers in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
相应参数 须家河组二段各小层 Tx21 Tx22 Tx23 Tx24 Tx25和Tx26 弹性模量 y=0.203 5x+33.146 y=0.161 9x+36.485 y=0.153 1x+36.923 y=0.051 4x+43.191 y=0.184 8x+35.234 泊松比 y=-0.000 2x+0.188 2 y=-0.002 1x+0.344 7 y=-0.001x+0.258 7 y=-0.001 5x+0.303 5 y=-0.001 6x+0.313 2 内摩擦力 y=-279.1x+115.62 内摩擦角 y=-122.45x+60.04 抗拉强度 y=22.329x+1.558 3 注:参数弹性模量和泊松比公式中的x表示砂地比;内摩擦力、内摩擦角、抗拉强度公式中的x表示泊松比。 表 7 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段断裂附近岩石力学参数分析汇总
Table 7. Summary of rock mechanical parameter analysis near faults in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
参数 三、四级断裂 五级断裂 SN向 NE向 EW向 SN向 NE向 EW向 断裂扰动范围/m 500 400 300 400 300 200 弹性模量/GPa(从断裂核部到平稳区过渡) 20~50 25~50 40~50 25~50 30~50 45~50 泊松比(从断裂核部到平稳区过渡) 0.4~0.2 0.35~0.20 0.25~0.20 0.35~0.20 0.3~0.20 0.25~0.20 表 8 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段应力分级评价标准
Table 8. Evaluation criteria of in-situ stress classification for the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
分级标准 应力分级评价 水平两向应力差/MPa 最小水平主应力/MPa Ⅰ类(低应力差—低地应力) < 44 < 95 Ⅱ类(高应力差—低地应力) >44 < 95 Ⅲ类(低应力差—高地应力) < 44 >95 不利区(高应力差—高地应力) >44 >95 表 9 四川盆地新场构造带须家河组二段工程改造建议
Table 9. Engineering modification suggestions for the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin
项目 I类有利区 Ⅱ类有利区 Ⅲ类有利区 分布位置 SN向四级断褶或NE向三级断褶内 SN向四级断裂、NE向三级断裂、EW向三级断裂及其复合 NE向褶皱与SN或EW向褶皱复合区 五级以下SN向断缝体、四级以下NE和EW向断缝体 地应力特征 断裂应力释放带和张性扰动区应力规模较小,应力差较小 地应力方向近EW向,断裂应力释放带内应力规模较小,应力差系数较小 须二段2小层以上主要为张性扰动区,应力规模较小,地应力以N80°E为主 地应力受河道方向影响弱偏转,以NEE向为主,应力规模相对较大 井型与井位轨迹建议示意图 



压裂改造方式 提高有效裂缝与应力释放带钻遇率,采用少段少簇、大液量、中砂量等改造方式 提高有效裂缝与应力释放带钻遇率,采用少段少簇、大液量、中砂量等改造方式 提高有效裂缝与张性扰动区钻遇率,中高黏液体压裂,以垂向射孔方式完井,采用多段多簇、大液量、中-大砂量进行压裂 提高有效裂缝与优势砂体的钻遇率,高黏-交联液体压裂,以垂向射孔方式完井,采用多段少簇、中液量、大砂量进行压裂 -
[1] 窦立荣, 李大伟, 温志新, 等. 全球油气资源评价历程及展望[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(8): 1035-1048.DOU Lirong, LI Dawei, WEN Zhixin, et al. History and outlook of global oil and gas resources evaluation[J]. Acta Petrolei sinica, 2022, 43(8): 1035-1048. [2] 贾爱林, 位云生, 郭智, 等. 中国致密砂岩气开发现状与前景展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(1): 83-92.JIA Ailin, WEI Yunsheng, GUO Zhi, et al. Development status and prospect of tight sandstone gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(1): 83-92. [3] 郑和荣, 刘忠群, 徐士林, 等. 四川盆地中国石化探区须家河组致密砂岩气勘探开发进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4): 765-783.ZHENG Herong, LIU Zhongqun, XU Shilin, et al. Progress and key research directions of tight gas exploration and development in Xujiahe Formation, SINOPEC exploration areas, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 765-783. [4] 张金才, 范鑫, 黄志文, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组储层各向异性地应力评价方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4): 963-972.ZHANG Jincai, FAN Xin, HUANG Zhiwen, et al. Assessment of anisotropic in-situ stresses in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation reservoirs in western Sichuan Depression of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 963-972. [5] 朱化蜀, 刘林, 黄志文, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷新场气田须家河组储层工程地质特征及增产实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4): 1002-1010.ZHU Huashu, LIU Lin, HUANG Zhiwen, et al. Reservoir engineering geological characteristics and stimulation in Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang gas field, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 1002-1010. [6] 康红普, 林健, 张晓. 深部矿井地应力测量方法研究与应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(5): 929-933.KANG Hongpu, LIN Jian, ZHANG Xiao. Research and application of in-situ stress measurement in deep mines[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(5): 929-933. [7] 解东亮. 地应力测量方法综述[J]. 科技资讯, 2013(6): 150-153.JIE Dongliang. Review of in-situ stress measurement methods[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2013, (6): 150-153. [8] ZHAO Jian, HEFNY A M, ZHOU Yingxin. Hydrofracturing in-situ stress measurements in Singapore granite[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2005, 42(4): 577-583. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.02.002 [9] 高会春, 杨胜利, 刘新杰, 等. 空心包体地应力测试方法与工程应用[J]. 煤炭工程, 2015, 47(4): 83-85.GAO Huichun, YANG Shengli, LIU Xinjie, et al. Hollow inclusion in-situ stress test method and engineering application[J]. Coal Engineering, 2015, 47(4): 83-85. [10] 陈文婷, 郑质彬, 彭岩岩. 水力压裂法在地应力测量中的应用[J]. 煤炭技术, 2020, 39(2): 66-68.CHEN Wenting, ZHENG Zhibin, PENG Yanyan. Application of hydraulic fracturing method in in-situ stress measurement[J]. Coal Technology, 2020, 39(2): 66-68. [11] LEHTONEN A, COSGROVE J W, HUDSON J A, et al. An examination of in situ rock stress estimation using the Kaiser effect[J]. Engineering Geology, 2012, 124: 24-37. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.09.012 [12] ITO T, SAWAKAMI K, ISHIKAWA S, et al. Progression of paralysis is the most useful factor for differentiating malignant from benign intramedullary tumors[J]. Spinal Cord, 2013, 51(4): 319-321. doi: 10.1038/sc.2012.152 [13] 邓虎成, 周文, 姜昊罡, 等. 构造变形对现今地应力方向的影响[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2009, 31(4): 57-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2009.04.014DENG Hucheng, ZHOU Wen, JIANG Haogang, et al. Effect of tectonic deformation on current geo-stress orientation[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 31(4): 57-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2009.04.014 [14] MITSAKAKI C, SAKELLARIOU M G, TSINAS D. A study of the crust stress field for the Aegean region (Greece)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 597-598;50-72. [15] HAN Hongxue, VAN DER BAAN M. Constraint strategies for estimating in-situ stress from borehole measurements[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 2024, 37: 100518. doi: 10.1016/j.gete.2023.100518 [16] 尹帅, 刘翰林, 何建华, 等. 动静态地质力学方法约束的致密油砂岩地应力综合评估[J]. 地球科学进展, 2023, 38(12): 1285-1296.YIN Shuai, LIU Hanlin, HE Jianhua, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of geo-stress in tight oil sandstone under constraints of dynamic-static geomechanical methods[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2023, 38(12): 1285-1296. [17] YIN Shuai, DING Wenlong, ZHOU Wen, et al. In situ stress field evaluation of deep marine tight sandstone oil reservoir: a case study of Silurian strata in northern Tazhong area, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 80: 49-69. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.11.021 [18] JU Wei, NIU Xiaobing, FENG Shengbin, et al. Present-day in-situ stress field within the Yanchang Formation tight oil reservoir of Ordos Basin, central China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106809. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106809 [19] 张小菊, 何建华, 徐庆龙, 等. 合川地区须二段现今地应力场分布特征与扰动机制研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2022, 42(4): 71-82.ZHANG Xiaoju, HE Jianhua, XU Qinglong, et al. Distribution characteristics and disturbance mechanism of present in-situ stress field in the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Hechuan area[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2022, 42(4): 71-82. [20] LIU Jingshou, DING Wenlong, YANG Haimeng, et al. 3D geomechanical modeling and numerical simulation of in-situ stress fields in shale reservoirs: a case study of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in the Cen'gong block, South China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2017, 712-713;663-683. [21] SINGHA D K, CHATTERJEE R. Geomechanical modeling using finite element method for prediction of in-situ stress in Krishna-Godavari Basin, India[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 73: 15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.10.003 [22] 徐珂, 戴俊生, 冯建伟, 等. 南堡凹陷高深北区三维非均质应力场精细预测[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(6): 1276-1286.XU Ke, DAI Junsheng, FENG Jianwei, et al. Prediction of 3D heterogeneous in-situ stress field of northern area in Gaoshen, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(6): 1276-1286. [23] FAN Hongzhuo, LI Sanbai, FENG Xiating, et al. A high-efficiency 3D boundary element method for estimating the stress/displacement field induced by complex fracture networks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106815. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106815 [24] 王胜宇, 鞠玮, 杨兆彪, 等. 滇东北新庄地区煤层现今地应力分布预测与分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2021, 33(8): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.08.01WANG Shengyu, JU Wei, YANG Zhaobiao, et al. Prediction and analysis of present-day in-situ stress distribution within coal reservoirs of Xinzhuang area, northeastern Yunnan region[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2021, 33(8): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.08.01 [25] 商晓飞, 赵磊, 易杰, 等. 川西新场地区须家河组二段砂体沉积充填特征及定量地质建模[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(4): 144-155. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.04.013SHANG Xiaofei, ZHAO Lei, YI Jie, et al. Sedimentary filling characteristics and quantitative geological modeling of sand bodies in Xu2 Member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, western Sichuan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(4): 144-155. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2022.04.013 [26] 邓文龙, 叶泰然, 纪友亮, 等. 川西新场构造带须二段浅水三角洲砂体结构特征及控制因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2024, 26(3): 545-566.DENG Wenlong, YE Tairan, JI Youliang, et al. Sand body architecture and controlling factors of shallow water delta in the member 2 of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang structural belt, western Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2024, 26(3): 545-566. [27] 刘忠群, 徐士林, 刘君龙, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷深层致密砂岩气藏富集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(2): 31-40.LIU Zhongqun, XU Shilin, LIU Junlong, et al. Enrichment laws of deep tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(2): 31-40. [28] 刘君龙, 刘忠群, 刘振峰, 等. 四川盆地新场构造带深层须二段致密砂岩断褶裂缝体特征和地质模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(3): 530-540.LIU Junlong, LIU Zhongqun, LIU Zhenfeng, et al. Geological characteristics and models of fault-fold-fracture body in deep tight sandstone of the second member of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang structural belt of Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(3): 530-540. [29] 黄滔, 刘岩, 何建华, 等. 川西孝泉—丰谷地区须二段深层致密砂岩储层地应力大小评价方法及其工程应用[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(1): 89-104.HUANG Tao, LIU Yan, HE Jianhua, et al. Evaluation method and engineering application of in-situ stress of deep tight sandstone reservoir in the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Xiaoquan-Fenggu area, western Sichuan[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(1): 89-104. [30] 刘君龙, 刘忠群, 肖开华, 等. 四川盆地新场地区三叠系须家河组二段致密砂岩有利岩石相表征及油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1111-1121.LIU Junlong, LIU Zhongqun, XIAO Kaihua, et al. Characterization of favorable lithofacies in tight sandstone reservoirs and its significance for gas exploration and exploitation: a case study of the 2nd member of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1111-1121. [31] 苏加亮, 林良彪, 余瑜, 等. 川西新场地区上三叠统须家河组二四段物源及储层特征差异对比研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2023, 41(5): 1451-1467.SU Jialiang, LIN Liangbiao, YU Yu, et al. Comparative study on the provenance and reservoir characteristics of the second and fourth members of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area, western Sichuan, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2023, 41(5): 1451-1467. [32] 田军, 张世华, 叶素娟, 等. 川西拗陷新场构造带须二段气藏类型划分及成藏主控因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(6): 659-667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2017.06.03TIAN Jun, ZHANG Shihua, YE Sujuan, et al. Classification of gas accumulation types and main controlling factors of gas accumulation of the Xu-2 member in Xinchang structural zone, Western Sichuan Depression, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2017, 44(6): 659-667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2017.06.03 [33] 邓虎成, 周文, 姜浩罡, 等. 川西坳陷盐井沟构造沙溪庙组现今地应力方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(6): 720-725. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.06.008DENG Hucheng, ZHOU Wen, JIANG Haogang, et al. Current terrestrial stress direction of the Shaximiao Formation in the Yanjinggou structure of the West Sichuan Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(6): 720-725. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.06.008 [34] 闵建, 马辉运, 彭钧亮, 等. 波速各向异性结合古地磁测试地应力方向研究[J]. 钻采工艺, 2020, 43(S1): 17-19.MIN Jian, MA Huiyun, PENG Junliang, et al. Study on determination of in-situ stress direction using wave velocity anisotropy method combined with paleomagnetism method[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2020, 43(S1): 17-19. [35] 曹峰, 何建华, 王园园, 等. 合川地区须二段低各向异性储层现今地应力方向评价方法[J]. 地球科学进展, 2022, 37(7): 742-755.CAO Feng, HE Jianhua, WANG Yuanyuan, et al. Methods to evaluate present-day in-situ stress direction for low anisotropic reservoirs in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in Hechuan area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2022, 37(7): 742-755. [36] 佟恺林, 蔡鸿燕, 李金玺, 等. 四川LZ页岩储层现今地应力方向及主控因素: 以龙一段为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(8): 3224-3236.TONG Kailin, CAI Hongyan, LI Jinxi, et al. Present stress orientations and controlling factors of shale reservoirs in LZ region, Sichuan Basin: example of the first member of Longmaxi Formation[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(8): 3224-3236. [37] 赖锦, 白天宇, 肖露, 等. 地应力测井评价方法及其地质与工程意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4): 1033-1043.LAI Jin, BAI Tianyu, XIAO Lu, et al. Well-logging evaluation of in-situ stress fields and its geological and engineering significances[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4): 1033-1043. [38] 赵军, 秦伟强, 张莉, 等. 偶极横波各向异性特征及其在地应力评价中的应用[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(4): 54-57.ZHAO Jun, QIN Weiqiang, ZHANG Li, et al. Anisotropy of dipole shear wave and its application to ground stress evaluation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(4): 54-57. [39] 张乔勋, 李帝铨, 田茂军. 广域电磁法在赣南某盆地油气勘探中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2017, 52(5): 1085-1092.ZHANG Qiaoxun, LI Diquan, TIAN Maojun. Application of wide field electromagnetic method to the hydrocarbon exploration in a basin of South Jiangxi[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2017, 52(5): 1085-1092. [40] 胡东风, 魏志红, 李宇平, 等. 四川盆地东南部地区复杂构造带深层页岩气勘探进展与突破[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8): 35-44. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.004HU Dongfeng, WEI Zhihong, LI Yuping, et al. Deep shale gas exploration in complex structure belt of the southeastern Sichuan Basin: progress and breakthrough. [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8): 35-44. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.004 [41] 张昕, 付小敏, 沈忠, 等. 利用岩石声发射Kaiser效应测试地应力的方法研究[J]. 中国测试, 2017, 43(10): 18-23. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2017.10.004ZHANG Xin, FU Xiaomin, SHEN Zhong, et al. Study on the method of in-situ stress measurement with Kaiser effect of rock acoustic emission[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2017, 43(10): 18-23. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2017.10.004 [42] 何建华, 曹峰, 邓虎成, 等. 四川盆地HC地区须二段致密砂岩储层地应力评价及其在致密气开发中的应用[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(4): 1107-1121.HE Jianhua, CAO Feng, DENG Hucheng, et al. Evaluation of in-situ stress in dense sandstone reservoirs in the second member of Xujiahe Formation of the HC area of the Sichuan Basin and its application to dense sandstone gas development[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(4): 1107-1121. [43] 白金朋, 彭华, 郑哲夏, 等. 屯1井差应变分析法地应力测量[J]. 地质力学学报, 2013, 19(02): 117-124.BAI Jinpeng, PENG Hua, ZHENG Zhexia, et al. In-situ stress measurement by differential strain analysis method in the well Tun-1[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2013, 19(2): 117-124. [44] 刘向君. 川西地区工程地质特征研究[R]. 四川: 中石化西南油气分公司工程技术研究院, 2008.LIU Xiangjun. Research on engineering geological characteristics in western Sichuan[R]. Sichuan: Engineering Technology Research Institute of Southwest Oil and Gas Branch of Sinopec, 2008. [45] 黄荣樽, 庄锦江. 一种新的地层破裂压力预测方法[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 1986(3): 1-14.HUANG Rongzun, ZHUANG Jinjiang. A new prediction method of formation fracture pressure[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 1986(3): 1-14. [46] 王成虎, 高桂云, 王洪, 等. 利用室内和现场水压致裂试验联合确定地应力与岩石抗拉强度[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(2): 167-174.WANG Chenghu, GAO Guiyun, WANG Hong, et al. Integrated determination of principal stress and tensile strength of rock based on the laboratory and field hydraulic fracturing tests[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(2): 167-174. [47] ZOBACK M D, BARTON C A, BRUDY M, et al. Determination of stress orientation and magnitude in deep wells[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7/8): 1049-1076. [48] 王璞, 王成虎, 杨汝华, 等. 基于应力多边形与震源机制解的深部岩体应力状态预测方法初探[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(11): 4486-4496.WANG Pu, WANG Chenhu, YANG Ruhua, et al. Preliminary investigation on the deep rock stresses prediction method based on stress polygon and focal mechanism solution[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(11): 4486-4496. [49] ZIEGLER M, VALLEY B. Evaluation of the diametrical core deformation and discing analyses for in-situ stress estimation and application to the 4.9 km deep rock core from the Basel geothermal borehole, Switzerland[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2021, 54(12): 6511-6532. [50] 周文. 川西致密储层现今地应力场特征及石油工程地质应用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2006.ZHOU Wen. The characteristics of in-situ earth stress and its application research in engineering geology of petroleum on compact reservoir in Western Sichuan Depression[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2006. -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号