Genesis and source of Permian natural gas in well Qiatan-1 of piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
-
摘要: 近期,塔里木盆地西南山前坳陷恰探1井在西天山冲断带二叠系碳酸盐岩地层取得了天然气勘探的重大突破,标志着塔西南山前地区一个全新勘探层系的发现。然而,该区存在多套烃源岩,且具有异常复杂的沉积和构造特征,对于恰探1井天然气成因及来源的研究十分薄弱,制约了其下一步天然气的勘探部署。为此,基于区域地质背景、天然气地球化学特征、潜在烃源岩特征等系统开展了恰探1井天然气成因及其来源研究。实测结果表明,恰探1井天然气以甲烷为主(83.53%),气体干燥系数(C1/C1-5)为0.992,具有较高含量的N2(8.36%)、CO2(7.28%)和He(0.110%)。天然气中甲烷、乙烷、丙烷和CO2的碳同位素值分别为-27.8‰、-20.2‰、-18.4‰、1.7‰。基于天然气组分、烷烃碳/氢同位素组成等综合判识认为,恰探1井天然气为高—过成熟阶段的煤型气。结合潜在烃源岩的分布、有机质丰度、类型、热成熟度特征认为,该井天然气主要来源于二叠系棋盘组烃源岩,可能还混入了少量碳同位素组成更重的无机烃类气体。另外,N2、CO2等非烃气体及He同位素证据均表明恰探1井天然气有一定比例的无机气体混入,幔源氦比例约占14.6%,其氦含量已达到富氦天然气(He≥0.100%)标准。Abstract: Recently, a significant breakthrough in natural gas exploration was achieved in well Qiatan-1 in the Permian carbonate strata of the Western Tianshan thrust belt in the piedmont depression of southwestern Tarim Basin, marking the discovery of a new exploration layer in the area. However, this region is characterized by multiple sets of source rocks and extremely complex sedimentary and structural features. Research on the genesis and source of the natural gas in well Qiatan-1 is insufficient, restricting its further natural gas exploration. Therefore, the study systematically investigated the genesis and source of the natural gas in well Qiatan-1 based on regional geological background, geochemical characteristics of the gas, and potential source rock features. The measured results showed that the natural gas in well Qiatan-1 was mainly composed of methane (83.53%), with a gas dryness coefficient (C1/C1-5) of 0.992, and contained relatively high levels of N2 (8.36%), CO2 (7.28%), and He (0.110%). The carbon isotope values of methane, ethane, propane, and CO2 in the gas were -27.8‰, -20.2‰, -18.4‰, and 1.7‰, respectively. Based on the natural gas composition and alkane carbon/hydrogen isotope composition, the natural gas in well Qiatan-1 was determined to be coal-type gas in the high to over-mature stage. Considering the distribution, organic matter abundance, type, thermal maturity of its potential source rocks, the gas in this well was mainly sourced from Permian source rocks in the Permian Qipan Formation, and may also be mixed with a small amount of carbon isotopes, forming heavier inorganic hydrocarbon gases. In addition, the components and isotopic evidence of non-hydrocarbon gases such as N2, CO2, and He showed that a certain proportion of inorganic gas had mixed into the natural gas in well Qiatan-1. The helium isotopic composition suggested that the proportion of mantle-derived helium was about 14.6%, and the He content had reached the standard for helium-rich natural gas (He ≥ 0.100%).
-
Key words:
- natural gas /
- carbon isotope /
- hydrogen isotope /
- inorganic genetic gas /
- coal-type gas /
- Permian /
- southwestern Tarim Basin
-
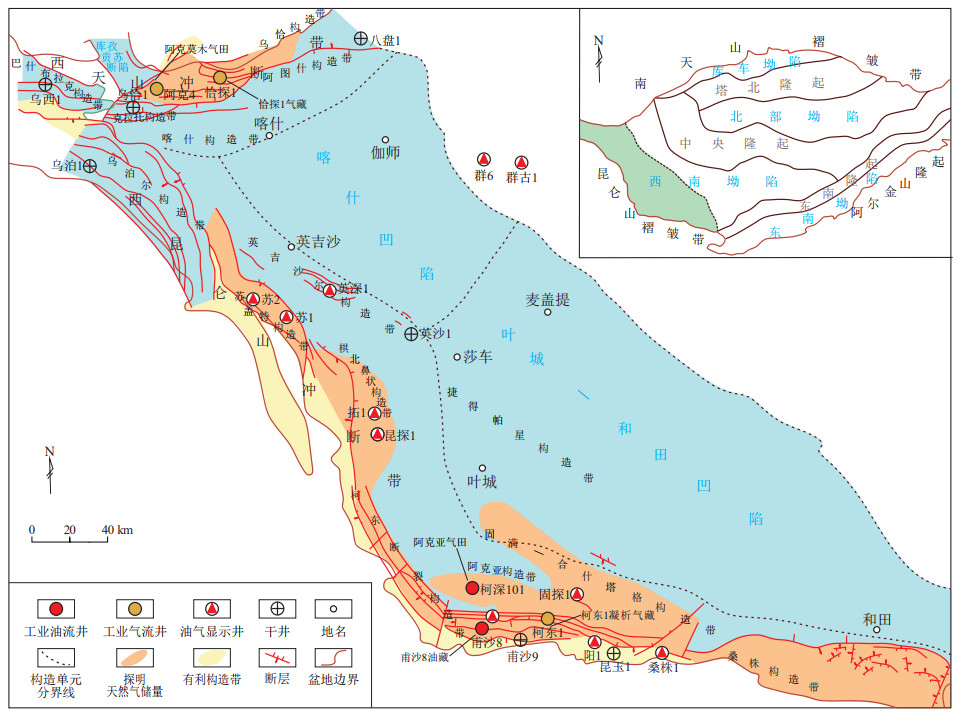
图 1 塔里木盆地西南山前坳陷恰探1井气藏构造位置
据参考文献[7]修改。
Figure 1. Structural location of gas reservoir in well Qiatan-1 of piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
图 4 塔西南山前坳陷天然气甲烷碳同位素组成与C1/C2+3关系
Figure 4. Relationship between methane carbon isotope composition and C1/C2+3 in natural gas from piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim BasinRelationship between methane carbon isotope composition and C1/C2+3 in natural gas from piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
图 5 塔西南山前坳陷天然气甲烷碳、氢同位素(a),甲烷氢同位素和乙烷碳同位素(b)组成特征
图版参考自文献[43]。
Figure 5. Compositional characteristics of methane carbon and hydrogen isotopes (a), methane hydrogen and ethane carbon isotopes (b) in natural gas from piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
表 1 塔里木盆地西南山前坳陷天然气地球化学特征
Table 1. Geochemical characteristics of natural gas in piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
区域 井号 深度/m 层位 气体组分/% δ13CVPDB/‰ δDVSMOW/‰ CH4 C2H6 C3H8 iC4H10 nC4H10 iC5H12 nC5H12 N2 CO2 CH4 CO2 C2H6 C3H8 iC4H10 nC4H10 CH4 C2H6 C3H8 乌恰 恰探11 5 702~5 760 P1t 79.76 0.57 0.07 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 8.26 11.17 -27.2 2.7 -19.8 -17.8 -16.7 -17.3 -145 恰探12 5 702~5 760 P1t 81.08 0.57 0.07 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 8.45 9.66 -28.2 1.9 -20.2 -18.5 -15.9 -18.0 -142 恰探13 5 702~5 760 P1t 85.87 0.61 0.07 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 8.52 4.74 -27.6 2.0 -20.2 -18.2 -16.4 -18.0 -142 恰探14 5 702~5 760 P1t 87.40 0.61 0.07 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 8.21 3.54 -28.1 0.2 -20.5 -19.2 -18.2 -19.0 -143 恰探1 5 237~5 241 P1q 2.55 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 97.09 0.34 -31.6 -18.5 -24.0 -145 恰探1 5 252~5 257 P1q 6.57 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.08 0.32 -31.5 -17.9 -22.5 -142 恰探1 5 301~5 309 P1q 5.71 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 93.94 0.31 -32.4 -17.6 -22.4 -142 -85 阿克莫木 阿克101 K2 74.54 0.30 0.03 0.03 7.96 17.01 -25.8 -3.2 -22.8 -137 -67 阿克401 K2 75.49 0.39 0.05 0.05 7.43 16.45 -26.0 -2.6 -22.4 -146 -190 -168 康苏 康苏6 6 203.32 59.71 13.59 10.05 1.56 2.75 0.65 0.54 10.40 0.74 -47.9 -24.4 -31.7 -29.2 -30.4 -28.1 -225 -191 -168 康苏6 6 212.32 59.32 14.86 10.05 1.49 2.72 0.65 0.53 10.36 0.01 -48.1 -31.8 -29.1 -30.2 -28.3 -225 棋北 昆探1 7 046.5~7 054.5 C2t 17.25 0.15 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.09 0.05 0.16 82.35 -29.5 0.9 -22.1 -19.9 -20.1 -19.3 昆探1 7 046.5~7 054.5 C2t 11.50 0.01 88.23 -28.4 2.0 甫沙 甫沙8 3 859.5~3 877.5 J1s 63.95 16.26 7.39 0.78 2.16 0.25 0.53 8.60 0.08 -42.2 -31.3 -29.6 -30.0 -29.6 甫沙8 3 859.5~3 877.5 J1s 63.38 15.29 6.56 0.65 1.70 0.18 0.35 11.85 0.04 -42.7 -31.1 -29.6 -29.3 -29.4 柯克亚 柯300 N1x 79.91 7.48 2.21 0.44 1.22 0.43 1.00 6.04 0.32 -38.8 -26.3 -24.7 -25.6 -25.7 -168 -137 -118 柯516 N1x 79.39 8.45 2.07 0.42 1.17 0.49 1.10 6.33 0.35 -38.8 -26.3 -24.9 -26.0 -25.9 -168 -140 -116 柯7102 N1x 83.59 7.15 2.30 0.40 0.91 0.19 0.38 4.36 0.42 -37.6 -25.9 -24.4 -26.3 -25.4 -166 -137 -121 柯412 N1x 82.95 7.47 2.27 0.35 0.72 0.13 0.28 5.13 0.30 -37.9 -26.1 -24.5 -26.3 -25.8 -166 -139 -119 柯301 N1x 87.20 7.32 1.04 0.04 0.09 0.02 0.06 3.89 0.21 -37.1 -26.0 -24.0 -26.4 -166 -138 -94 柯7102 N1x 83.36 7.05 2.47 0.48 1.13 0.24 0.52 3.61 0.62 -37.6 -25.9 -24.4 -26.3 -25.4 -166 -138 -118 柯7010 N1x 85.57 7.11 1.69 0.24 0.51 0.10 0.20 4.04 0.29 -37.4 -26.0 -24.2 -26.3 -25.4 -166 -138 -113 柯233 N1x 80.10 8.31 2.68 0.44 0.96 0.19 0.37 6.27 0.27 -38.8 -26.4 -24.6 -26.1 -26.3 -168 -155 -121 柯深 柯深101 6 354~6 363 E2k 88.97 5.60 1.50 1.02 2.38 0.52 -35.6 -9.6 -24.2 -25.3 柯深102 6 277~6 328 E2k 88.84 5.88 1.80 0.96 1.89 0.00 -35.0 -27.7 -24.7 -154 -125 -111 柯深101 6 807~6 835 K1kz 80.65 1.46 0.07 0.03 17.66 0.12 -38.4 -24.9 注:1为2023年2月26日08:30时取样;2为2023年2月26日16:30时取样;3为2023年3月1日08:30时取样;4为2023年3月1日16:30时取样。C2t为石炭系塔哈奇组;E2k为古近系卡拉塔尔组。 表 2 塔里木盆地西南山前坳陷天然气中的稀有气体地球化学特征
Table 2. Geochemical characteristics of rare gases in natural gas from piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
井名/地区 层位 深度/m He/% Ar/% 3He/4He/10-8 R/Ra 幔源He/% 恰探1井 P1t 5 702~2 760 0.110 0.036 170 1.214 14.60 阿克1井 K2 3 225~3 341 0.134 83.4 0.596 6.80 柯深101井 E2k 6 354~6 363 13.7 0.098 1.20 柯克亚地区 N1 0.010 6.1~8.6 0.050~0.075 0.65 大北2井 K 5 658~5 670 5.32 0.038 0.43 迪那2井 N1 4 598 2.48 0.018 0.15 DW105-25井 N1 367~396 5.67 0.041 0.45 YH23-1井 N1 4 946~4 988 3.46 0.025 0.25 YH1井 E 5 451~5 466 3.81 0.027 0.28 却勒1井 K 5 761~5 764 5.36 0.038 0.44 表 3 塔里木盆地西南山前坳陷天然气的烷烃碳同位素组成(平均)及其烃源岩镜质体反射率
Table 3. Average alkane carbon isotope composition of natural gas and calculated vitrinite reflectance of source rocks in piedmont depression, southwestern Tarim Basin
地区/井号 δ13C/‰ 煤型气Ro/% CH4 C2H6 C3H8 Ro① Ro② Ro③ Ro④ Ro⑤ Ro⑥ Ro⑦ 克拉2 -27.0 -18.6 -19.7 1.18 1.31 3.34 4.69 1.49 2.23 2.63 大北 -29.6 -20.5 -20.6 0.77 0.65 2.18 2.35 1.28 1.71 2.07 阿克1 -24.9 -21.7 -20.3 1.67 2.29 4.70 8.21 1.68 2.76 3.19 甫沙8 -42.5 -31.2 -29.6 0.09 0.02 0.27 0.08 0.62 0.45 0.63 柯东1 -36.0 -24.7 -23.4 0.27 0.12 0.77 0.43 0.89 0.88 1.15 柯克亚 -38.6 -26.0 -25.5 0.17 0.06 0.50 0.21 0.77 0.68 0.90 恰探1 -27.8 -20.2 -18.4 1.03 1.06 2.93 3.79 1.42 2.05 2.44 注:Ro①~ Ro⑦分别据STAHL[34]、SCHOELL[35]、戴金星等[29]、沈平等[36]、徐永昌等[30]、刘文汇等[37]、陈建平等[38]。 -
[1] 何登发, 李洪辉. 塔西南拗陷油气勘探历程与对策[J]. 勘探家, 1998, 3(1): 37-42.HE Dengfa, LI Honghui. History and counter measures of petroleum exploration in Tarim South-west Depression[J]. Petroleum Explorationist, 1998, 3(1): 37-42. [2] 金之钧, 吕修祥. 塔西南前陆盆地油气资源与勘探对策[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(2): 110-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2000.02.004JIN Zhijun, LÜ Xiuxiang. Hydrocarbon resources and exploration strategy of foreland basins in southwest Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2000, 21(2): 110-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2000.02.004 [3] 胡剑风, 郑多明, 胡轩, 等. 塔西南前陆盆地战略接替区天然气勘探的突破[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2002, 7(1): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2002.01.008HU Jianfeng, ZHENG Duoming, HU Xuan, et al. Breakthrough of gas exploration in Southwest Tarim Foreland Basin: the strategic replacement area of CNPC and TOC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2002, 7(1): 74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2002.01.008 [4] 何登发, 李德生, 何金有, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷和西南坳陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 201-218.HE Dengfa, LI Desheng, HE Jinyou, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Kuqa Depression and Southwest Depression in Tarim Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 201-218. [5] 王招明, 赵孟军, 张水昌, 等. 塔里木盆地西部阿克莫木气田形成初探[J]. 地质科学, 2005, 40(2): 237-247. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.02.008WANG Zhaoming, ZHAO Mengjun, ZHANG Shuichang, et al. A preliminary study on formation of Akemo Gas field in the Kashi Sag, Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(2): 237-247. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2005.02.008 [6] 莫午零, 林潼, 张英, 等. 西昆仑山前柯东—柯克亚构造带油气来源及成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(4): 364-371. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201304364MO Wuling, LIN Tong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Hydrocarbon origin and accumulation model of Kedong-Kekeya tectonic belt in piedmont of West Kunlun Mountain[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(4): 364-371. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201304364 [7] 王清华, 杨海军, 李勇, 等. 塔西南山前地区恰探1井石炭系—二叠系重大突破与勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2023, 28(4): 34-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.04.004WANG Qinghua, YANG Haijun, LI Yong, et al. Major breakthrough in the Carboniferous-Permian in well Qiatan 1 and exploration prospect in the piedmont southwestern Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2023, 28(4): 34-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.04.004 [8] 赵孟军, 张水昌. 塔里木盆地天然气成因类型及成藏条件[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2001, 6(2): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2001.02.006ZHAO Mengjun, ZHANG Shuichang. Genetic classification of natural gas and conditions of gas reservoir formation in Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2001, 6(2): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2001.02.006 [9] 张秋茶, 王福焕, 肖中尧, 等. 阿克1井天然气气源探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(6): 484-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.06.012ZHANG Qiucha, WANG Fuhuan, XIAO Zhongyao, et al. The discussion of natural gas source in well Ake 1[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(6): 484-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.06.012 [10] 王东良, 李勇, 敬兵, 等. 柯克亚原油、天然气差异与成因分析[C]//中国地球物理学会第22届年会论文集. 成都: 中国地球物理学会, 2006: 453.WANG Dongliang, LI Yong, JING Bing, et al. Analysis of differences and causes of Kekeya crude oil and natural gas[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Meeting of the Chinese Geophysical Society. Chengdu: Chinese Geophysical Society, 2006: 453. [11] WU Xiaoqi, TAO Xiaowan, HU Guoyi. Geochemical characteristics and source of natural gases from Southwest Depression of the Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2014, 74: 106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.02.002 [12] 韩文学, 陶士振, 胡国艺, 等. 塔西南坳陷山前带天然气地球化学特征和成因[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(1): 121-130.HAN Wenxue, TAO Shizhen, HU Guoyi, et al. Geochemical characteristics of natural gas and its genesis in piedmont zone of southwest Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(1): 121-130. [13] 刘伟, 杨飞, 吴金才, 等. 喀什凹陷北缘阿克莫木气田气源探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(3): 486-494.LIU Wei, YANG Fei, WU Jincai, et al. The discussion on natural gas source in Akmomu Gasfield, northern margin of Kashi Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(3): 486-494. [14] 戴金星, 宋岩, 张厚福. 中国大中型气田形成的主要控制因素[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 1996, 26(6): 481-487.DAI Jinxing, SONG Yan, ZHANG Houfu. Main factors controlling the foundation of medium-giant gas fields in China[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 1997, 40(1): 1-10. [15] 戴金星, 于聪, 黄士鹏, 等. 中国大气田的地质和地球化学若干特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1): 1-13.DAI Jinxing, YU Cong, HUANG Shipeng, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics of large gas fields in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1): 1-13. [16] 龚德瑜, 房忱琛, 肖中尧. 柯克亚凝析气田油气来源再认识: 一个复杂地球化学过程下的油气源对比实例[C]//2015学术年会论文摘要汇编(中册). 西安: 中国地质学会, 2015: 369-370.GONG Deyu, FANG Chenchen, XIAO Zhongyao. Restudy on the oil and gas origins in the Kekeya gas condensates field, Northwest China: a case study of hydrocarbon source correlation under sophisticated geochemical processes[C]//Abstract compilation of papers at the 2015 Annual Meeting of the Geological Society of China (Volume 2). Xi'an: Chinese Geological Society, 2015: 369-370. [17] 刘得光, 王绪龙. 塔里木盆地西南坳陷油气源研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(2): 35-39.LIU Deguang, WANG Xulong. Oil and gas source study in the southwest depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(2): 35-39. [18] 侯读杰, 肖中尧, 唐友军, 等. 柯克亚油气田混合来源天然气的地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(6): 474-479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.06.010HOU Dujie, XIAO Zhongyao, TANG Youjun, et al. Geochemical characterization of mixing natural gas in Kekeya Field, Tarim Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(6): 474-479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1926.2003.06.010 [19] 唐友军, 侯读杰, 肖中尧, 等. 柯克亚地区天然气的成因[J]. 海洋石油, 2006, 26(2): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2006.02.004TANG Youjun, HOU Dujie, XIAO Zhongyao, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of gas in Kekeya field[J]. Offshore Oil, 2006, 26(2): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2006.02.004 [20] 程晓敢, 黄智斌, 陈汉林, 等. 西昆仑山前冲断带断裂特征及构造单元划分[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(2): 2591-2601.CHENG Xiaogan, HUANG Zhibin, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Fault characteristics and division of tectonic units of the thrust belt in the front of the West Kunlun mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8): 2591-2601. [21] 曲国胜, 李亦纲, 李岩峰, 等. 塔里木盆地西南前陆构造分段及其成因[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2005, 35(3): 193-202.QU Guosheng, LI Yigang, LI Yanfeng, et al. Segmentations of foreland belts and their tectonic mechanism in the southwest Tarim Basin[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 2005, 48(10): 1585-1598. [22] 贾承造. 中国中西部前陆冲断带构造特征与天然气富集规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4): 9-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.002JIA Chengzao. Foreland thrust fold belt features and gas accumulation in Midwest China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 9-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.002 [23] 赵文智, 张光亚. 被动大陆边缘演化与油气地质: 以塔里木盆地西南地区为例[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2007: 1-155.ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHANG Guangya. Petroleum geology and evolution of passive continental margin: example of southwest Tarim Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2007: 1-155. [24] 杨威, 王清华, 王媛, 等. 塔里木盆地玛扎塔格构造带石炭系层序地层和储集层特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1999, 20(3): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.1999.03.014YANG Wei, WANG Qinghua, WANG Yuan, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and reservoir characteristics of Carboniferous in Mazartag structural belt, Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1999, 20(3): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.1999.03.014 [25] 赵孟军, 王招明, 宋岩, 等. 塔里木盆地喀什凹陷油气来源及其成藏过程[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(2): 50-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.02.012ZHAO Mengjun, WANG Zhaoming, SONG Yan, et al. Source and accumulation of oil and gas in Kashi Sag, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(2): 50-54. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.02.012 [26] 孟强, 史江龙, 赵恒, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部奥陶系马家沟组米探1井天然气成因与来源[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(10): 1696-1709.MENG Qiang, SHI Jianglong, ZHAO Heng, et al. Genesis and source of natural gas in well Mitan-1 of Ordovician Majiagou Formation, middle-eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(10): 1696-1709. [27] 刘全有, 金之钧, 王毅, 等. 塔里木盆地天然气成因类型与分布规律[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(1): 46-50.LIU Quanyou, JIN Zhijun, WANG Yi, et al. Genetic type and distribution of natural gas in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(1): 46-50. [28] LIU Quanyou, WU Xiaoqi, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. Carbon and hydrogen isotopes of methane, ethane, and propane: a review of genetic identification of natural gas[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 190: 247-272. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.11.017 [29] 戴金星, 戚厚发, 郝石生. 天然气地质学概论[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1989.DAI Jinxing, QI Houfa, HAO Shisheng. Introduction to natural gas geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1989. [30] 徐永昌. 天然气成因理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 1-414.XU Yongchang. Genetic theory of natural gases and its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 1-414. [31] 王先彬, 李春园, 陈践发, 等. 论非生物成因天然气[J]. 科学通报, 1997, 42(12): 1233-1241.WANG Xianbin, LI Chunyuan, CHEN Jianfa, et al. Mantle-derived methane homologue and helium in natural gas from Songliao Basin, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(1): 142. [32] CHUNG H M, GORMLY J R, SQUIRES R M. Origin of gaseous hydrocarbons in subsurface environments: theoretical considerations of carbon isotope distribution[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 71(1/3): 97-104. [33] WHITICAR M J. Stable isotope geochemistry of coals, humic kerogens and related natural gases[J]. International Journal of Coal geology, 1996, 32(1/4): 191-215. [34] STAHL W J. Carbon and nitrogen isotopes in hydrocarbon research and exploration[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 121-149. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90041-9 [35] SCHOELL M. The hydrogen and carbon isotopic composition of methane from natural gases of various origins[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(5): 649-661. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90155-6 [36] 沈平, 申歧样, 王先彬, 等. 气态烃同位素组成特征及煤型气判识[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1987, 17(6): 647-656.SHEN Ping, SHEN Qixiang, WANG Xianbin, et al. Characteristics of isotope composition of gaseous hydrocarbons and identification of coal-type gas[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1988, 31(6): 734-747. [37] 刘文汇, 徐永昌. 煤型气碳同位素演化二阶段分馏模式及机理[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(4): 359-366. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.04.006LIU Wenhui, XU Yongchang. A two-stage model of carbon isotopic fractionation in coal-gas[J]. Geochimica, 1999, 28(4): 359-366. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.04.006 [38] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 陈践发, 等. 甲烷碳同位素判识天然气及其源岩成熟度新公式[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51(4): 560-581.CHEN Jianping, WANG Xulong, CHEN Jianfa, et al. New equation to decipher the relationship between carbon isotopic composition of methane and maturity of gas source rocks[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(3): 470-493. [39] JENDEN P D, DRAZAN D J, KAPLAN I R. Mixing of thermogenic natural gases in northern Appalachian Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(6): 980-998. [40] ROONEY M A, CLAYPOOL G E, CHUNG H M. Modeling thermogenic gas generation using carbon isotope ratios of natural gas hydrocarbons[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 126(3/4): 219-232. [41] MENG Qiang, WANG Xiaofeng, SHI Baoguang, et al. The 13C-depleted methane in terrigenous shale gas: a case study in the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 141: 105688. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105688 [42] WHITICAR M J. Correlation of natural gases with their sources[M]//MAGOON L B, DOW W G. The petroleum system: from source to trap. Tulsa: AAPG, 1994: 261-284. [43] WANG Xiaofeng, LIU Wenhui, SHI Baoguang, et al. Hydrogen isotope characteristics of thermogenic methane in Chinese sedimentary basins[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2015, (83/84): 178-189. [44] 徐永昌, 沈平, 刘文汇, 等. 天然气中稀有气体地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 1-227.XU Yongchang, SHEN Ping, LIU Wenhui, et al. Geochemistry of rare gas in natural gas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998: 1-227. [45] 陈践发, 朱岳年. 天然气中氮的来源及塔里木盆地东部天然气中氮地球化学特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2003, 14(3): 172-176.CHEN Jianfa, ZHU Yuenian. The origin of molecular nitrogen in natural gas and geochemical characters of molecular nitrogen in natural gas from east part of Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2003, 14(3): 172-176. [46] 李谨, 李志生, 王东良, 等. 塔里木盆地含氮天然气地球化学特征及氮气来源[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(S1): 102-111.LI Jin, LI Zhisheng, WANG Dongliang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and N2 source of nitrogen riched natural gas in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(S1): 102-111. [47] 陈践发, 刘凯旋, 董勍伟, 等. 天然气中氦资源研究现状及我国氦资源前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(10): 1436-1449.CHEN Jianfa, LIU Kaixuan, DONG Qingwei, et al. Research status of helium resources in natural gas and prospects of helium resources in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(10): 1436-1449. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号