A physics and data dual-driven method for real-time fracturing pressure prediction
-
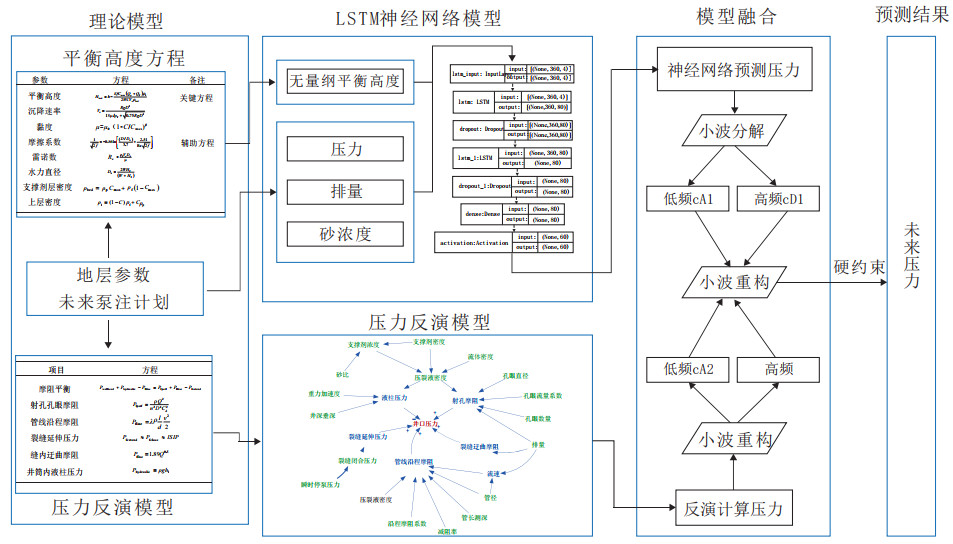
摘要: 井口压力预测存在压力波动剧烈、干扰因素多以及影响机理复杂等问题。现阶段研究中,由于对复杂的地层条件、裂缝特征及流体动力学过程的过度简化,传统物理模型难以捕捉多重非线性变化和突发波动,导致在真实施工环境下的预测精度和实时响应能力受到局限。而人工智能模型尽管具有较强的非线性拟合能力,但往往缺乏对压力波动的物理机理的深入理解,对地层和施工参数的敏感性不足,导致在极端或动态变化的条件下稳定性较差、解释性不足。针对这一难题,提出了一种物理—数据双驱动的压力曲线的预测方法对未来压力趋势进行预测。首先,构建了基于长短期记忆(LSTM)神经网络的智能模型,融合缝内支撑剂床平衡高度计算结果与井场实时泵注数据作为模型输入,预测了未来60 s的压力数据;其次,结合传统井口压力反演方法,使用小波变换分解智能模型与传统模型预测结果,利用LSTM模型整体趋势与压力反演计算方法(IPC)模型中突变点特征,重构了兼顾整体趋势和局部波动的井口压力预测曲线。结果表明,相比LSTM模型,IPC和LSTM的小波融合模型未来60 s井口压力预测的均方根误差(RMSE)和均方绝对误差(MAE)分别下降了37.87%和15.29%,预测结果能够精准捕捉现场施工的压裂压力变化,为现场施工提供更为可靠的指导和决策依据。Abstract: Wellhead pressure prediction is challenging due to problems such as drastic pressure fluctuations, numerous disturbing factors, and complex influencing mechanisms. Current research often adopts traditional physical models which find it difficult to capture multiple nonlinear changes and sudden fluctuations due to the oversimplification of complex formation conditions, fracture characteristics, and fluid dynamics processes, limiting their prediction accuracy and real-time responsiveness in actual operations. Artificial intelligence (AI) models, despite their strong nonlinear fitting capabilities, often lack an in-depth understanding of the physical mechanisms underlying pressure fluctuations and are less sensitive to formation and operational parameters, resulting in poor stability and insufficient interpretability under extreme or dynamically changing conditions. To address these challenges, a physics and data dual-driven prediction method was proposed to predict future pressure trends. An intelligent model based on a long and short-term memory (LSTM) neural network was constructed, integrating the equilibrium height calculations of the proppant bed within the fracture and real-time pumping data at the wellsite as model inputs to predict pressure for the next 60 seconds. Then, combined with traditional wellhead pressure inversion method, wavelet transform was used to decompose predictions from both the intelligent and traditional models. The overall trend of the LSTM model and the characteristics of mutation point in the inverse pressure calculation (IPC) model were utilized to reconstruct the wellhead pressure prediction curves that could balance the overall trend and local fluctuations. Results showed that compared to pure LSTM model, the wavelet fusion model of IPC and LSTM reduced the root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) by 37.87% and 15.29%, respectively, in wellhead pressure prediction for the next 60 seconds. The fusion model can accurately capture fracturing pressure changes during field operations, providing more reliable guidance and decision support for field operations.
-
Key words:
- fracturing pressure prediction /
- physics and data dual driven /
- LSTM /
- IPC /
- wavelet transform /
- fusion model
-
表 1 LSTM模型加入DEH前后预测评价指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of predictive evaluation indicators before and after adding DEH to LSTM model
Params RMSE MSE MAE MAPE 仅压力排量砂浓度 0.787407 0.589 978 0.838 024 加入DEH 0.577 155 0.333 108 0.384 967 0.543 502 表 2 各种压力预测模型预测评价指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of prediction evaluation indicators for various pressure prediction models
模型 RMSE MSE MAE MAPE IPC >10 >10 LSTM 0.583 829 0.340 857 0.412 863 0.557 477 LSTM+IPC+WAVEREC 0.460 177 0.211 763 0.349 780 0.472 104 -
[1] 何玉荣, 宋志超, 张燕明, 等. 机器学习在水力压裂作业中的应用综述[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45, (6): 127-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.06.015HE Yurong, SONG Zhichao, ZHANG Yanming, et al. Review on application of machine learning in hydraulic fracturing[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2021, 45(6): 127-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2021.06.015 [2] 魏海峰. 非均质性页岩水力压裂裂缝扩展形态研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(4): 156-166.WEI Haifeng. Research progress on fracture propagation patterns of hydraulic fracturing in heterogeneous shale[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(4): 156-166. [3] 李鹏飞. 四川盆地页岩气立体开发缝控压裂技术应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(2): 168-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.02.024LI Pengfei. Application of fracture-controlled fracturing technology in tridimensional development of shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(2): 168-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.02.024 [4] 王强, 赵金洲, 胡永全, 等. 页岩水力裂缝网络形态及激活机制研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 44(6): 71-86.WANG Qiang, ZHAO Jinzhou, HU Yongquan, et al. Investigation on the morphology and activation mechanism of hydraulic fracture network in shale[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2022, 44(6): 71-86. [5] 刘建峰. 水平井分段压裂生产剖面测试技术进展与展望[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(5): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.05.001LIU Jianfeng. Progress and prospect of production profile testing technology for staged fracturing in horizontal wells[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(5): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.05.001 [6] 蒲草, 王玲, 熊荣园, 等. 水力压裂施工曲线的应用研究: 以Z油田压裂施工为例[J]. 广州化工, 2023, 51(2): 211-213.PU Cao, WANG Ling, XIONG Rongyuan, et al. Applied study on hydraulic fracturing construction curves: taking fracturing construction in Z oilfield as an example[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2023, 51(2): 211-213. [7] 李春雷, 曹小朋, 张林凤, 等. 基于机器学习算法的水驱储层相渗曲线仿真预测[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(6): 138-142.LI Chunlei, CAO Xiaopeng, ZHANG Linfeng, et al. Simulation and prediction of water-flooding reservoir relative permeability curve based on machine learning[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(6): 138-142. [8] 贾蕊, 袁泉, 汤欣, 等. 广义气水混驱特征曲线的建立及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(5): 562-571.JIA Rui, YUAN Quan, TANG Xin, et al. Establishment and application of generalized characteristic curves of gas-water miscible flooding[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(5): 562-571. [9] 陈元千, 徐良. Arps双曲线递减模型的多解性和不确定性[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(3): 80-84.CHEN Yuanqian, XU Liang. Multi-solution and uncertainty of Arps'hyperbolic exponential decline model[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(3): 80-84. [10] EL SGHER M, AMINIAN K, AMERI S. Evaluation of hydraulic fracturing treatment with microseismic data analysis in a marcellus shale horizontal well[C]//SPE Western Regional Meeting. [s. l. ]: SPE, 2021. [11] 郭建春, 路千里, 何佑伟. 页岩气压裂的几个关键问题与探索[J]. 天然气工业2022, 42(8): 148-161. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.012GUO Jianchun, LU Qianli, HE Youwei. Key issues and explorations in shale gas fracturing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8): 148-161. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.08.012 [12] 赵金洲, 付永强, 王振华, 等页岩气水平井缝网压裂施工压力曲线的诊断识别方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(2): 11-19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.002ZHAO Jinzhou, FU Yongqiang, WANG Zhenhua, et al. Study on diagnosis model of shale gas fracture network fracturing operation pressure curves[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(2): 11-19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.002 [13] 汪海阁, 高博, 郑有成, 等. 机器学习在钻柱振动识别与预测中的研究进展[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(1): 149-158. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.01.014WANG Haige, GAO Bo, ZHEN Youcheng, et al. Research progress of machine learning in drill string vibration recognition and prediction[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(1): 149-158. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2024.01.014 [14] 巫芙蓉, 闫媛媛, 尹陈. 页岩气微地震压裂实时监测技术: 以四川盆地蜀南地区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(11): 46-50. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.11.006WU Furong, YAN Yuanyuan, YIN Chen. Real-time microseismic monitoring technology for hydraulic fracturing in shale gas reservoirs: a case study from the southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(11): 46-50. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.11.006 [15] PIRAYESH E, SOLIMAN M Y, RAFIEE M, et al. A new method to interpret fracturing pressure: application to frac pack[J]. SPE Journal, 2015, 20(3): 508-517. doi: 10.2118/166132-PA [16] 叶燊, 乔江美, 李同春. 注水压力和溶洞内压对水力裂缝扩展影响模拟研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(2): 382-390.YE Shen, QIAO Jiangmei, LI Tongchun. Numerical simulation of influence of water injection pressure and cave internal pressure on fracture propagation[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(2): 382-390. [17] 刘向君, 王小军, 赵保伟, 等. 砂砾岩储集层水力压裂裂缝扩展规律与可压性评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(2): 169-177.LIU Xiangjun, WANG Xiaojun, ZHAO Baowei, et al. Propagation of hydraulic fractures and fracability evaluation of sandy conglomerate reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(2): 169-177. [18] 闵超, 张馨慧, 杨兆中, 等. 基于CBFS-CV算法的煤层气井压裂效果主控因素识别[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(1): 168-174.MIN Chao, ZHANG Xinhui, YANG Zhaozhong, et al. Identification of main controlling factors of fracturing performance in coalbed methane wells based on CBFS-CV algorithm[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(1): 168-174. [19] 刘红磊, 徐胜强, 朱碧蔚, 等. 盐间页岩油体积压裂技术研究与实践[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(2): 149-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.02.022LIU Honglei, XU Shengqiang, ZHU Biwei, et al. Research and practice of SRV fracturing technology for inter-salt shale oil[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(2): 149-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.02.022 [20] 刘子军. 基于Pearson相关系数的低渗透砂岩油藏重复压裂井优选方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(2): 140-144.LIU Zijun. Method for selecting repeated fracturing wells in low-permeability sandstone reservoirs based on Pearson correlation coefficient[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(2): 140-144. [21] 刘合, 张广明, 张劲, 等. 油井水力压裂摩阻计算和井口压力预测[C]//第十一次全国岩石力学与工程学术大会. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 7.LIU He, ZHANG Guangming, ZHANG Jin, et al. Friction loss calculation and surface pressure prediction in oil well hydraulic fracturing[C]//The 11th National Conference on Rock Mechanics and Engineering. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 7. [22] 刘依达. 裸眼水平井分段压裂施工中井口压力预测[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2014, 11(8): 98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409.2014.08.048LIU Yida. Prediction of wellhead pressure in staged fracturing of open hole horizontal wells[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Nature Science Edition), 2014, 11(8): 98-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409.2014.08.048 [23] LIANG Haibo, ZOU Jialing, KHAN M J, et al. An sand plug of fracturing intelligent early warning model embedded in remote monitoring system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 47944-47954. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909647 [24] BEN Yuxing, PERROTTE M, EZZATABADIPOUR M, et al. Real-time hydraulic fracturing pressure prediction with machine learning[C]//SPE Hydraulic Fracturing Technology Conference and Exhibition. The Woodlands: SPE, 2020. [25] 胡瑾秋, 张尚尚, 曾然, 等. 基于深度学习的页岩气压裂砂堵事故预警方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(9): 108-114.HU Jinqiu, ZHANG Shangshang, ZENG Ran, et al. Early warning method for sand plugging accidents in shale gas fracturing based on deep leaning[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(9): 108-114. [26] ZHANG Chengkai, ZHANG Rui, ZHU Zhaopeng, et al. Bottom hole pressure prediction based on hybrid neural networks and Bayesian optimization[J]. Petroleum Science, 2023, 20(6): 3712-3722. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2023.07.009 [27] YUAN Bin, ZHAO Mingze, MENG Siwei, et al. Intelligent identification and real-time warning method of diverse complex events in horizontal well fracturing[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(6): 1487-1496. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(24)60482-9 [28] HU X, WU K, SONG X, et al. Development of a new mathematical model to quantitatively evaluate equilibrium height of proppant bed in hydraulic fractures for slickwater treatment[J]. SPE Journal, 2018, 23(6): 2158-2174. doi: 10.2118/191360-PA [29] 曾庆田, 吕珍珍, 石永奎, 等. 基于Prophet+LSTM模型的煤矿井下工作面矿压预测研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(7): 16-23.ZENG Qingtian, LÜ Zhenzhen, SHI Yongkui, et al. Research on mine pressure prediction of coal mine underground face based on prophet and LSTM model[J]. Coal science and technology, 2021, 49(7): 16-23. [30] 刘庆. 水平井体积压裂井底净压力计算及分析[D]. 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.LIU Qing. Calculation and analysis of net bottomhole pressure in horizontal well volumetric fracturing[D]. China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. [31] ECONOMIDES M J, NOLTE K G. Reservoir Stimulation[M]. New York: Wiley, 2000. [32] 李晓瑜. 基于小波分析的扫描电镜图像处理[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2022, 41(5): 26-29.LI Xiaoyu. Scanning electron microscope image processing based on wavelet analysis[J]. Laboratory research and exploration, 2022, 41(5): 26-29. [33] PAN W, ZHANG N, ZENG F, et al. Time-frequency domain characteristics on the dynamic response of a moored floater under a freak wave by wavelet analysis[J]. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engineering, 2021, 31(2): 160. doi: 10.17736/ijope.2021.mk72 [34] REN Q, ZHANG H, AZEVEDO L, et al. Reconstruction of missing well-logs using facies-informed discrete wavelet transform and time series regression[J]. SPE Journal, 2023, 28(6): 2946-2963. doi: 10.2118/217425-PA -





 下载:
下载:












 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号