Intelligent identification of Cenozoic spore and pollen fossils in Bohai Sea area
-
摘要: 通过鉴定古生物化石类别信息和分布情况,可以为地质年代、古沉积环境及油气勘探工作提供重要信息。但传统古生物化石鉴定工作耗时耗力,人工依赖性高,难以满足当前快速勘探评价的需要。鉴于孢粉化石图像数量有限、属种分类多、具有科、属、种的特定分类逻辑等特点,围绕孢粉化石图像处理、化石图像筛选、化石目标检测、化石分类识别等方面,通过利用目标检测深度学习、标签松弛等技术,改进了有效化石筛选和孢粉化石分类识别的智能化水平。以渤海海域浅层新生代孢粉化石鉴定为例,采用YOLOv5和DenseNet等神经网络开发了一套孢粉化石智能识别方法,其平均识别准确率达94%,基本满足了孢粉化石鉴定实际生产准确性要求,可以辅助人工开展古生物化石鉴定工作。该方法将各种深度学习技术与古生物领域专业知识有效结合,并从数据和模型2个角度相结合,提高了识别模型的泛化能力与识别精度,并得以实际应用,使得能够在减少时间人力成本的前提下提供准确的鉴定结果,证实了人工智能技术在传统古生物鉴定领域的可行性。Abstract: The identification of paleontological fossil types and their distribution provides important information for geochronological, paleoenvironmental studies, and oil and gas exploration. However, traditional fossil identification methods are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and highly dependent on manual efforts, making it difficult to meet the current demand for rapid exploration and evaluation. Given the limited number of spore and pollen fossil images, the complex classification of taxa, and the specific taxonomy of family, genus, and species, this research focused on improving the automation for fossil image processing, image screening, object detection, and classification. By utilizing techniques such as deep learning for object detection and label smoothing, the efficiency of fossil screening and spore and pollen fossil classification was significantly enhanced. Taking the identification of the Cenozoic spore and pollen fossils from the Bohai Sea shallow area as a case study, a set of intelligent identification methods was developed using neural networks such as YOLOv5 and DenseNet, with an average identification accuracy of 94%, basically meeting the practical accuracy requirements for fossil identification in production. The system could assist in the manual identification of paleontological fossils. By effectively combining various deep learning techniques with specialized knowledge in paleontology, the generalization ability and recognition accuracy of the identification model were improved from both data and model perspectives. Its successful application demonstrates the feasibility of artificial intelligence in the traditional field of paleontological fossil identification, reducing time and labor costs while providing accurate results.
-
表 1 孢粉类化石图像智能识别实验准确率结果
Table 1. Experimental accuracy for intelligent identification of spore and pollen fossil images
网络模型 智能识别实验准确率/% 种 Top1 属 Top1 科 Top1 种 Top5 属 Top5 科 Top5 MobileNetV1 52.03 67.15 80.91 78.95 88.70 95.16 MobileNetV2 54.75 66.22 85.69 86.17 90.60 96.79 NASNet-Mob 59.40 73.17 85.69 86.17 90.60 96.79 ResNet50-V1 59.52 75.08 85.27 86.42 90.70 96.97 ResNet50-V2 61.84 75.38 87.67 88.72 92.07 96.97 ResNet101V1 61.26 77.61 88.15 89.08 92.59 98.00 ResNet101-V2 60.26 73.30 84.56 86.71 90.92 95.84 GoogLeNet 67.59 80.23 89.04 91.33 92.27 96.70 Xception 72.02 80.45 90.58 91.04 94.81 98.95 DenseNet121 64.15 78.49 89.82 89.04 93.56 97.90 DenseNet201 75.21 82.01 91.60 94.95 95.87 98.43 表 2 渤海海域新生代主要化石类型及地层分布识别率统计
Table 2. Statistics of identification rate of major fossil types and stratigraphic distribution in Cenozoic of Bohai Sea area
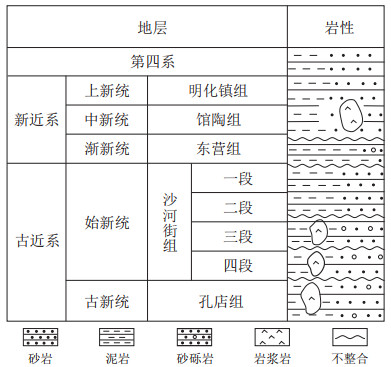
化石类别 地层 识别准确率/% 蓼粉属Persicarioipollis 明化镇组上段为主 85.1 禾本粉属Graminidites 明化镇组上段为主 86.0 粗肋孢属Magnastriatites 明化镇组下段为主 93.0 枫香粉属Liquidambarpollenites 明化镇组下段为主 87.8 伏平粉属Fupingopollenites 明化镇组下段为主 85.6 小菱粉Sporotrapoidites minor 馆陶组 83.0 光面球藻属Leiosphaeridia 东营组、沙河街组 86.5 刺球藻属Baltisphaeridium 东营组、沙河街组 91.0 粒面球藻属Granodiscus 东营组、沙河街组 87.3 细网面球藻Dictyotidium microreticulatum 东营组、沙河街组 88.6 网面球藻属Dictyotidium 东营组、沙河街组 82.3 小亨氏栎粉Quercoidites microhenrici 沙河街组为主 91.0 多刺甲藻属Sentusidinium 沙河街组一段 83.0 小繁棒藻Cleistosphaeridium minor 沙河街组一段 91.0 极管藻属Bipolaribucina 沙河街组三段 81.6 膜突藻属Membranilarnacia 沙河街组三段 83.0 渤海藻属Bohaidina 沙河街组三段 86.5 麻黄粉属Ephedripites 沙河街组为主 87.3 -
[1] 温宏雷, 杨海风, 杨波, 等. 渤海海域莱北低凸起新近系岩性油藏成藏模式及勘探实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 102-111. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201102WEN Honglei, YANG Haifeng, YANG Bo, et al. Exploration advances and accumulation model for Neocene lithological reservoirs in Laibei Low Uplift, Bohai Sea area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 102-111. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201102 [2] 健庄. 微体古生物的自动识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1989, 16(1): 17-25.LIU Jianzhuang. Automatic recognition of microfossils[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1989, 16(1): 17-25. [3] 王益锋, 张逸昆. 人工智能原理在古生物化石归类中的应用[J]. 古生物学报, 1988, 27(4): 521-524.WANG Yifeng, ZHANG Yikun. Application of artificial intelligence principle to paleontologic taxonomy[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 1988, 27(4): 521-524. [4] 赵贤淑, 张俊岭, 陈德岭. 多元统计分析在古生物化石分类鉴定中的应用[J]. 西安矿业学院学报, 1996, 16(2): 183-185.ZHAO Xianshu, ZHANG Junling, CHEN Deling. Application of multivate statistics analysis to classification and identification of paleontologic fossils[J]. Journal of Xi'an Mining Institute, 1996, 16(2): 183-185. [5] RODRIGUEZ-DAMIAN M, CERNADAS E, FORMELLA A, et al. Automatic detection and classification of grains of pollen based on shape and texture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2006, 36(4): 531-542. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2005.855426 [6] TRAVIESO C M, BRICEÑO J C, TICAY-RIVAS J R, et al. Pollen classification based on contour features[C]//201115th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems. Poprad, Slovakia: IEEE, 2011: 17-21. [7] CHEN Ying, HUANG Yiqi, ZHANG Zizhao, et al. Plant image recognition with deep learning: a review[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2023, 212: 108072. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2023.108072 [8] 杨勇. 胜利油田勘探开发大数据及人工智能技术应用进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(1): 1-10.YANG Yong. Application progress of big data & AI technologies in exploration and development of Shengli Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(1): 1-10. [9] 李佳航, 李讳, 刘向君, 等. 基于岩石薄片图像的海陆过渡相页岩纹层识别方法及应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(4): 44-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.04.006LI Jiahang, LI Wei, LIU Xiangjun, et al. Identification method and application of marine-continental transitional shale laminae based on rock thin section image. [J]. Special Oil &Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(4): 44-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.04.006 [10] 孙龙祥, 韩宏伟, 冯德永, 等. 基于人工智能的测井地层划分方法研究现状与展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(3): 49-58.SUN Longxiang, HAN Hongwei, FENG Deyong, et al. Research status and outlook of logging stratigraphic division methods based on artificial intelligence[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(3): 49-58. [11] 安玉钏, 陈雁, 黄玉楠, 等. 基于深度学习的介形类化石层次化识别[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(2): 673-684.AN Yuchuan, CHEN Yan, HUANG Yulan, et al. Hierarchical recognition of ostracod fossils based on deep learning[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(2): 673-684. [12] 徐卉清, 樊隽轩, 杨娇, 等. 应用卷积神经网络进行化石图像分类[C]//中国古生物学会第十二次全国会员代表大会暨第29届学术年会论文摘要集. 郑州: 中国古生物学会, 2018.XU Huiqing, FAN Junxuan, YANG Jiao, et al. Application of convolution neural network in fossils image classification[C]//Abstracts of Papers of the Twelfth National Congress of the Chinese Society of Paleontology and the 29th Annual Academic Conference. Zhengzhou: Palaeontological Society of China, 2018. [13] 张涛, 雷丹博, 王宾, 等. 陕南寒武系底部宽川铺组微体化石人工智能识别[J]. 古生物学报, 2019, 58(2): 141-151.ZHANG Tao, LEI Danbo, WANG Bin, et al. Artificial intelligence identification of microfossils from the Lower Cambrian Kuchuanpu Formation in southern Shaanxi, China[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2019, 58(2): 141-151. [14] KONG Shu, PUNYASENA S, FOWLKES C. Spatially aware dictionary learning and coding for fossil pollen identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016: 1-10. [15] 谢永华, 赵贤国, 王琢. 基于突变点几何约束直方图的花粉图像识别[J]. 计算机仿真, 2018, 35(12): 411-415.XIE Yonghua, ZHAO Xianguo, WANG Zhuo. Pollen image recognition based on geometric constraint histogram of mutation points[J]. Computer Simulation, 2018, 35(12): 411-415. [16] OLSSON O, KARLSSON M, PERSSON A S, et al. Efficient, automated and robust pollen analysis using deep learning[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2021, 12(5): 850-862. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.13575 [17] THEUERKAUF M, SIRADZE N, GILLERT A. A trainable object finder, selector and identifier for pollen, spores and other things: a step towards automated pollen recognition in lake sediments[J]. The Holocene, 2024, 34(3): 297-305. doi: 10.1177/09596836231211876 [18] 乔小燕. 赤潮藻显微图像自动识别方法[J]. 山东大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 1-6.QIAO Xiaoyan. Automatic recognition method of microscopic image of harmful algae[J]. Journal of Shandong University(Engineering Science), 2016, 46(3): 1-6. [19] 乔小燕. 基于自适应形态学的甲藻显微图像顶刺提取[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2013, 43(4): 117-122.QIAO Xiaoyan. Pyrrophyta spine extraction based on adaptive morphology[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(4): 117-122. [20] 夏菁, 白志强, 王宝鹏, 等. 牙形石数字图像采集与图像增强方法研究[J]. 古生物学报, 2014, 53(3): 392-399.XIA Jing, BAI Zhiqiang, WANG Baopeng, et al. Conodont digital image acquisition and the method of image enhancement[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2014, 53(3): 392-399. [21] 杨寿勇, 张海阳, 李成, 等. 基于卷积神经网络模型的微藻种类识别[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(S2): 158-164.YANG Shouyong, ZHANG Haiyang, LI Cheng, et al. Recognition of microalgae species based on convolutional neural network model[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(S2): 158-164. [22] 徐长贵. 渤海湾盆地天然气勘探新进展、未来方向与挑战[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(1): 72-85.XU Changgui. Progress, future direction, and challenges of natural gas exploration in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(1): 72-85. [23] GONZALEZ R C, WOODS R E. 数字图像处理[M]. 2版. 阮秋琦, 阮宇智, 译. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007.GONZALEZ R C, WOODS R E. Digital image processing[M]. 2nd ed. RUAN Qiuqi, RUAN Yuzhi, trans. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2007. [24] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. [25] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 6517-6525. [26] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [27] 余晓露, 叶恺, 杜崇娇, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的碳酸盐岩生物化石显微图像识别[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 880-885. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105880YU Xiaolu, YE Kai, DU Chongjiao, et al. Microscopic recognition of micro fossils in carbonate rocks based on convolutional neural network[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 880-885. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105880 [28] 奚园园, 王永茂, 芦碧波, 等. 基于深度学习单阶段算法的虫筳类化石检测[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2024, 49(3): 1154-1164.XI Yuanyuan, WANG Yongmao, LU Bibo, et al. Fusulinid detection based on deep learning single-stage algorithm[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2024, 49(3): 1154-1164. [29] 余晓露, 李龙龙, 蒋宏, 等. 融合图像处理与深度学习的亮晶颗粒灰岩岩相学分析应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 1026-1038. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023051026YU Xiaolu, LI Longlong, JIANG Hong, et al. Application of sparry grain limestone petrographic analysis combining image processing and deep learning[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 1026-1038. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023051026 [30] 李少华, 史敬华, 于金彪, 等. 基于单一图像生成对抗神经网络方法在沉积相建模中的应用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(1): 37-45.LI Shaohua, SHI Jinghua, YU JinBiao, et al. Application of SinGAN method in sedimentary facies modeling[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(1): 37-45. [31] YANG Guanhao, FENG Wei, JIN Jintao, et al. Face mask recognition system with YOLOV5 based on image recognition[C]//2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications. Chengdu, China: IEEE, 2020. [32] ZHU Yi, SAPRA K, REDA F A, et al. Improving semantic segmentation via video propagation and label relaxation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019: 8856-8865. [33] 韩肖, 马祥. 基于二进制标签松弛模型的遮挡人脸识别[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2022, 32(1): 1-6.HAN Xiao, MA Xiang. Occlusion face recognition based on binary label relaxation[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2022, 32(1): 1-6. [34] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017: 4700-4708. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号